개요
본 오픈소스 인 NestJS Boilerplate 에서는 헥사고날 아키텍처를 베이스로 되어있다.
Clean Architecture
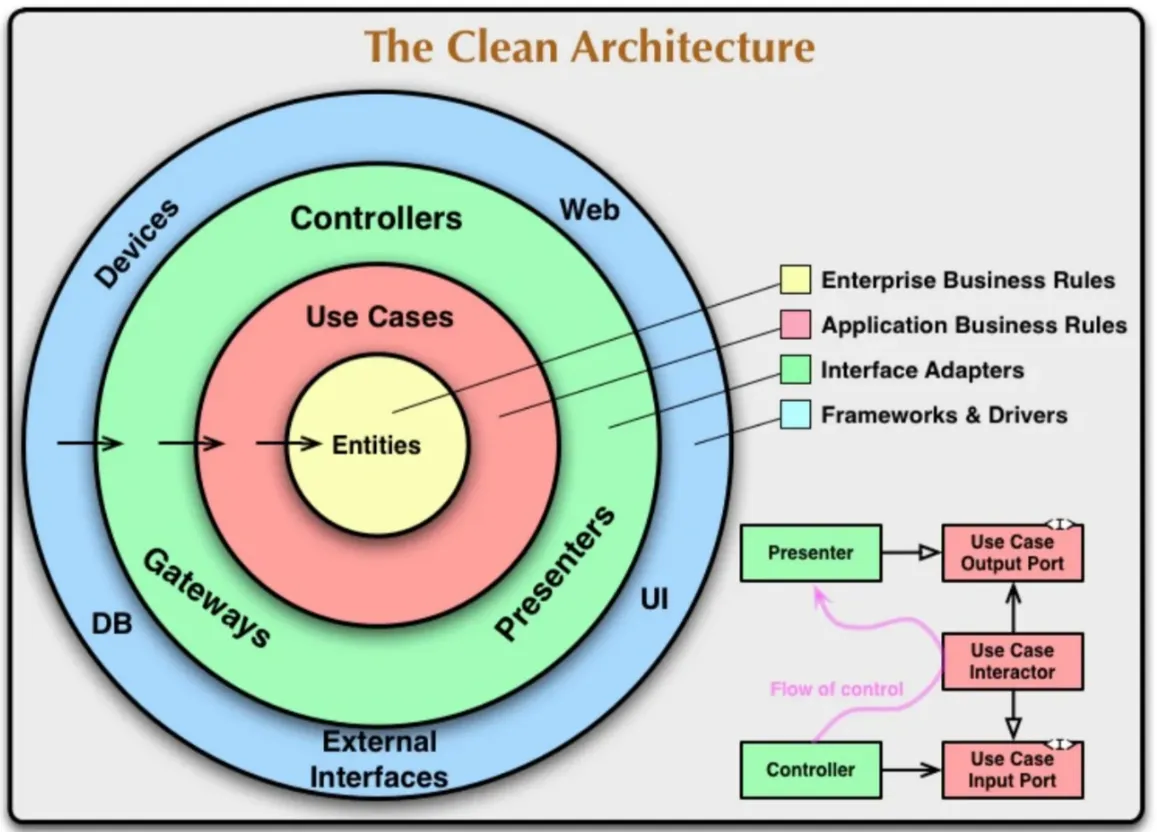
그림. Clean Architecture
헥사고날 아키텍처를 언급하기전에 먼저 베이스가 되는 개념인 클린 아키텍처에 대해서 간단히 살펴보자.
- 의존성이 외부 → 내부로만 흐른다.
- 자연스럽게 entity는 외부에 대해 전혀 몰라도 된다.
- use cases 레이어가 추가되어 전체적으로 흐름을 제어한다.
비즈니스 로직과 외부 사항 간의 결합도를 최소화 하는 것에 목적을 두고있는 패턴이다. 하지만 구현은 어떻게 해야 할까? 실제 구현된 것을 보연 레이어 아키텍처와는 다르지만 그림만 보면 “구현을 어떻게 해야 하지?” 라는 생각을 할때 크게 다를게 없어 보인다.
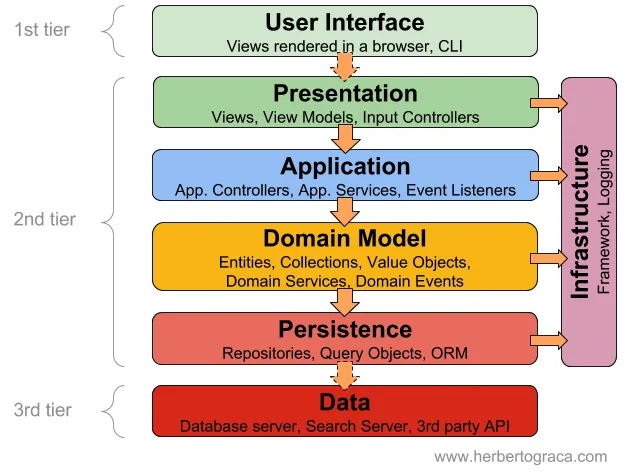
그림. Layered Architecture
이런 구체적으로 clean architecture 를 구현할때 구체적으로 어떻게 구현할지를 제시한게 Hexagonal Architecture 이다.
헥사고날 아키텍처
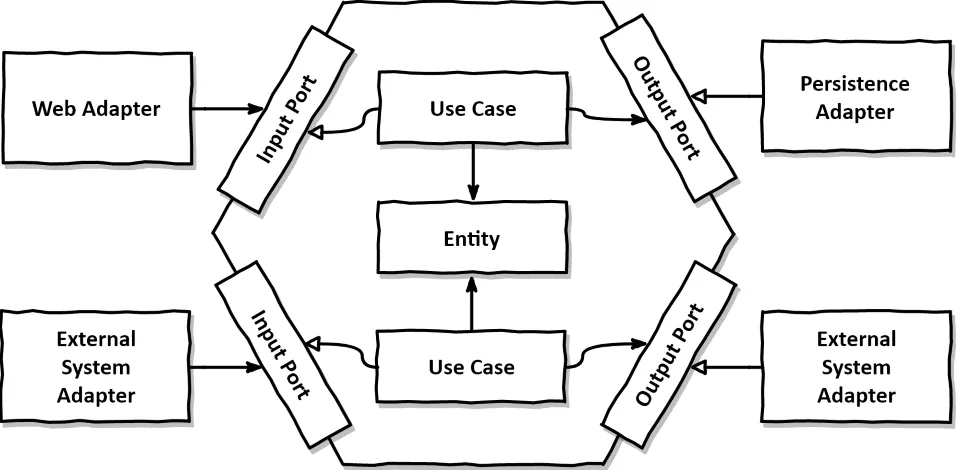
위 그림을 보면 “Adapter” 라는 놈과 “Port” 라는 놈이 등장하게 된다. 용어 정의는 다음과 같다.
Adapter: 외부 시스템간 상호작용을 위한 영역- In Adapter: 외부 시스템에서 애플리케이션을 호출하기 위한 영역 / 수신 영역
- ex. API, MQ, Message Subscribe etc…
- Out Adapter: 애플리케이션에서 외부 시스템을 호출하기 위한 영역 / 송신 영역
- ex. DB, SMS, Messabe Publish etc…
- In Adapter: 외부 시스템에서 애플리케이션을 호출하기 위한 영역 / 수신 영역
Port:Adapter와 애플리케이션을 연결하는 인터페이스 영역- In Port: Use Cases 의 인터페이스
- Out Port: Out Adapter 의 인터페이스
- Use Case
- 도메인 모델에 필요한 준비작업이나 후처리를 담당, 비즈니스 로직을 도메인 모델에게 위임한다.
- 도메인 모델과 어댑터를 적절히 사용하여 애플리케이션의 로직을 조율하고 관리한다.
- Entity
- 애플리케이션의 핵심 비즈니스 로직을 정의하며 도메인 모델로도 불린다.
- 어떠한 의존성도 갖지 않도록 분리하여 외부 사항 간의 결합도를 최대한 낮추어 비즈니스 로직을 처리한다.
NestJS BoilerPlate 의 폴더 구조
.
├── domain
│ └── [DOMAIN_ENTITY].ts
├── dto
│ ├── create.dto.ts
│ ├── find-all.dto.ts
│ └── update.dto.ts
├── infrastructure
│ └── persistence
│ ├── document
│ │ ├── document-persistence.module.ts
│ │ ├── entities
│ │ │ └── [SCHEMA].ts
│ │ ├── mappers
│ │ │ └── [MAPPER].ts
│ │ └── repositories
│ │ └── [ADAPTER].repository.ts
│ ├── relational
│ │ ├── entities
│ │ │ └── [ENTITY].ts
│ │ ├── mappers
│ │ │ └── [MAPPER].ts
│ │ ├── relational-persistence.module.ts
│ │ └── repositories
│ │ └── [ADAPTER].repository.ts
│ └── [PORT].repository.ts
├── controller.ts
├── module.ts
└── service.ts[DOMAIN ENTITY].ts: 비즈니스 로직에서 사용되는 엔티티를 나타낸다. 도메인 엔티티는 데이터베이스나 기타 인프라스트럭처에 대한 의존성이 없다.[SCHEMA].ts: 데이터베이스 구조를 나타낸다. 이는 문서 기반 데이터베이스(MongoDB)에서 사용된다.[ENTITY].ts: 데이터베이스 구조를 나타낸다. 이는 관계형 데이터베이스(PostgreSQL)에서 사용된다.[MAPPER].ts: 데이터베이스 엔티티를 도메인 엔티티로 변환하거나 그 반대로 변환하는 매퍼이다.[PORT].repository.ts: 데이터베이스와 상호작용하기 위한 메서드를 정의하는 레포지토리 포트이다.[ADAPTER].repository.ts:[PORT].repository.ts를 구현한 레포지토리로, 데이터베이스와 상호작용하는 데 사용된다.- infrastructure 폴더: persistence, uploader, senders 등과 같은 모든 인프라스트럭처 관련 구성 요소를 포함한다.
각 구성 요소는 port와 adapters를 가진다.
- Port: 인프라스트럭처와 상호작용하기 위한 메서드를 정의하는 인터페이스입니다.
- Adapters: Port를 구현한 구체적인 어댑터들입니다.
예시
기존 구현되어있는 코드들 중에서 files 를 예시로 살펴보자.
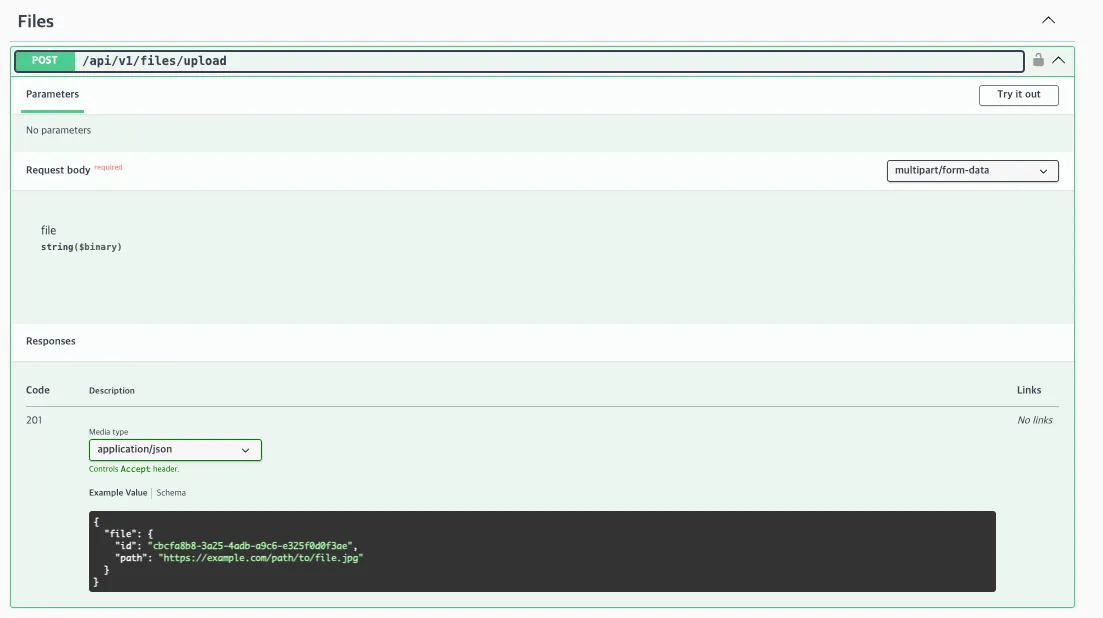
file API 는 POST /api/v1/files/upload API 로 파일을 업로드 하는 API 1개 구현되어있다. 폴더 구조는 다음과 같다.
.
├── config // config 관련 폴더. 아무래도 업로드할 플랫폼의 설정이 필요하니 여기에 별도로 한듯.
│ ├── file-config.type.ts // 파일 업도드할 곳 리스트 정의 및 config 타입 정의
│ └── file.config.ts // 유효성 검사 로직 및 파일 업로드 객체 생성
├── domain // file 도메인에서 사용할 코드
│ └── file.ts // 파일 객체
├── dto // dto 정의
│ └── file.dto.ts // 파일 dto
├── files.module.ts // 파일 도메인 모듈 파일
├── files.service.ts // 파일 도메인 서비스 파일
└── infrastructure
├── persistence // DB 통신하는 부분
│ ├── file.repository.ts
│ └── relational
│ ├── entities
│ │ └── file.entity.ts
│ ├── mappers
│ │ └── file.mapper.ts
│ ├── relational-persistence.module.ts
│ └── repositories
│ └── file.repository.ts
└── uploader // 업로드하는 도메인
├── local // 로컬로 설정한 업로드
│ ├── dto
│ │ └── file-response.dto.ts
│ ├── files.controller.ts
│ ├── files.module.ts
│ └── files.service.ts
├── s3 // s3로 설정한 업로드
│ ├── dto
│ │ └── file-response.dto.ts
│ ├── files.controller.ts
│ ├── files.module.ts
│ └── files.service.ts
└── s3-presigned // s3-presigned 으로 설정한 업로드
├── dto
│ ├── file-response.dto.ts
│ └── file.dto.ts
├── files.controller.ts
├── files.module.ts
└── files.service.tsDB Entity 는 어떻게 구현되어있을까?
DB entity 파일은 ./infrastructure/persistence/relational/entities/file.entity.ts 이다.
import {
// typeorm decorators here
Column,
Entity,
PrimaryGeneratedColumn,
} from 'typeorm';
import { EntityRelationalHelper } from '../../../../../utils/relational-entity-helper';
@Entity({ name: 'file' })
export class FileEntity extends EntityRelationalHelper {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn('uuid')
id: string;
@Column()
path: string;
}코드를 보니 EntityRelationalHelper 라는 놈이 보인다?! 이놈이 뭔지 함 보자.
- 파일 경로:
./src/utils/relational-entity-helper.ts
import { instanceToPlain } from 'class-transformer';
import { AfterLoad, BaseEntity } from 'typeorm';
export class EntityRelationalHelper extends BaseEntity {
__entity?: string;
@AfterLoad()
setEntityName() {
this.__entity = this.constructor.name;
}
toJSON() {
return instanceToPlain(this);
}
}
@AfterLoad: 엔티티가 데이터베이스에서 로드된 후 자동으로 실행- 즉
FileEntity가 DB 에 로드될때 class 이름인 “FileEntity” 값이__entity에 입력된다.
- 즉
toJSON:instanceToPlain함수를 통해서 entity 객체를 json 객체로 변환한다.
DI 구조 파악

POST /api/v1/files/upload 호출 흐름 분석 (Local 설정 흐름)
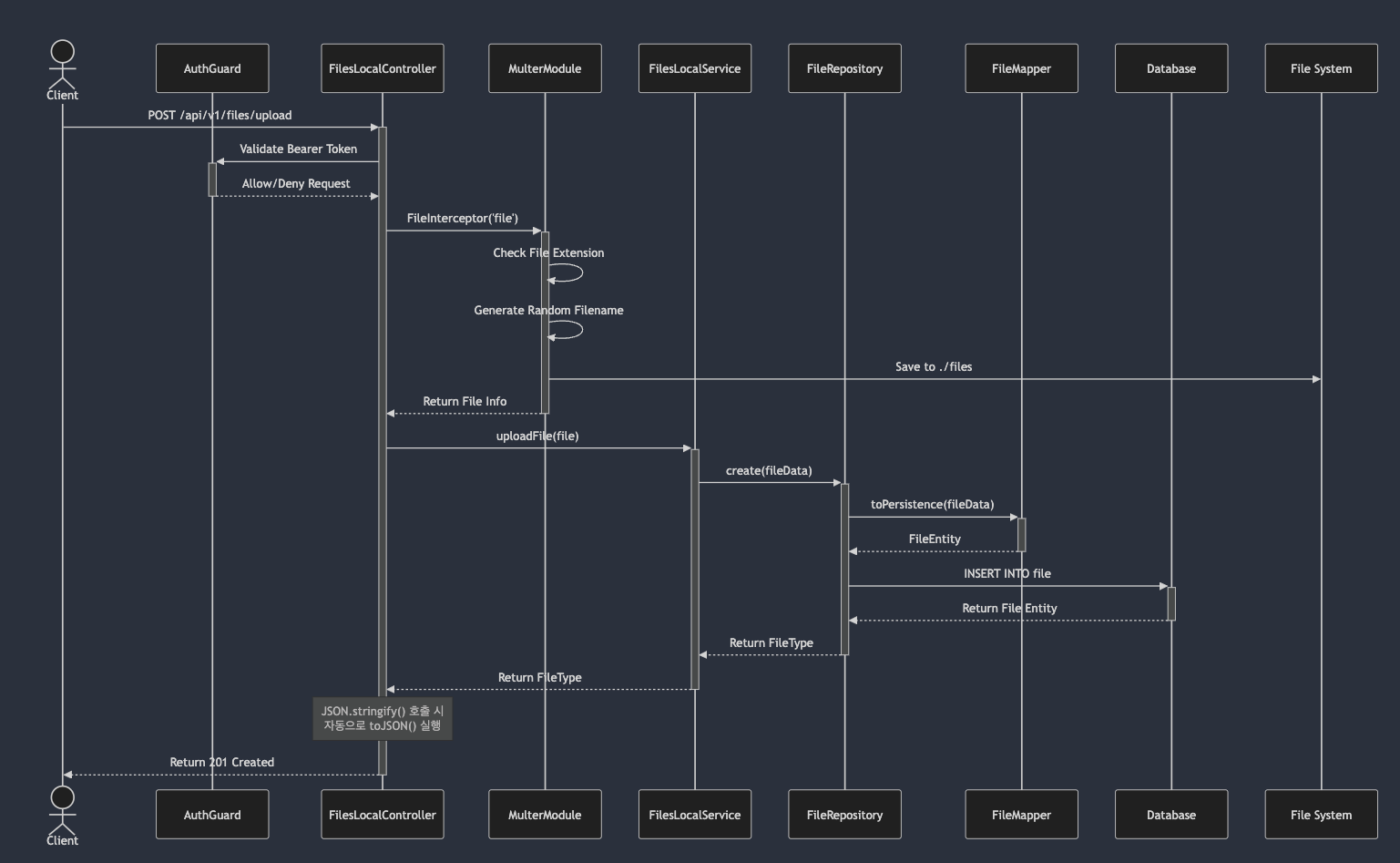
1. files/infrastructure/uploader/local/files/controller.ts 에서 controller 호출
```tsx
@ApiCreatedResponse({
type: FileResponseDto,
})
@ApiBearerAuth()
@UseGuards(AuthGuard('jwt'))
@Post('upload')
@ApiConsumes('multipart/form-data')
@ApiBody({
schema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
file: {
type: 'string',
format: 'binary',
},
},
},
})
@UseInterceptors(FileInterceptor('file'))
async uploadFile(
@UploadedFile() file: Express.Multer.File,
): Promise<FileResponseDto> {
return this.filesService.create(file);
}
```
1-1. JWT 기반 guard 호출
```tsx
// ./src/auth/strategies/jst.strategy.ts
import { ExtractJwt, Strategy } from 'passport-jwt';
import { Injectable, UnauthorizedException } from '@nestjs/common';
import { PassportStrategy } from '@nestjs/passport';
import { ConfigService } from '@nestjs/config';
import { OrNeverType } from '../../utils/types/or-never.type';
import { JwtPayloadType } from './types/jwt-payload.type';
import { AllConfigType } from '../../config/config.type';
@Injectable()
export class JwtStrategy extends PassportStrategy(Strategy, 'jwt') {
constructor(configService: ConfigService<AllConfigType>) {
super({
jwtFromRequest: ExtractJwt.fromAuthHeaderAsBearerToken(),
secretOrKey: configService.get('auth.secret', { infer: true }),
});
}
// Why we don't check if the user exists in the database:
// https://github.com/brocoders/nestjs-boilerplate/blob/main/docs/auth.md#about-jwt-strategy
public validate(payload: JwtPayloadType): OrNeverType<JwtPayloadType> {
if (!payload.id) {
throw new UnauthorizedException();
}
return payload;
}
}
```
2. `FileInterceptor('file')` 호출 ⇒ multer 미들웨어 호출됨
```tsx
// files/infrastructure/uploader/local/files.modules.ts
import {
HttpStatus,
Module,
UnprocessableEntityException,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { FilesLocalController } from './files.controller';
import { MulterModule } from '@nestjs/platform-express';
import { ConfigModule, ConfigService } from '@nestjs/config';
import { diskStorage } from 'multer';
import { randomStringGenerator } from '@nestjs/common/utils/random-string-generator.util';
import { FilesLocalService } from './files.service';
import { RelationalFilePersistenceModule } from '../../persistence/relational/relational-persistence.module';
import { AllConfigType } from '../../../../config/config.type';
const infrastructurePersistenceModule = RelationalFilePersistenceModule;
@Module({
imports: [
infrastructurePersistenceModule,
MulterModule.registerAsync({
imports: [ConfigModule],
inject: [ConfigService],
useFactory: (configService: ConfigService<AllConfigType>) => {
return {
fileFilter: (request, file, callback) => {
if (!file.originalname.match(/\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$/i)) {
return callback(
new UnprocessableEntityException({
status: HttpStatus.UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY,
errors: {
file: `cantUploadFileType`,
},
}),
false,
);
}
callback(null, true);
},
storage: diskStorage({
destination: './files',
filename: (request, file, callback) => {
callback(
null,
`${randomStringGenerator()}.${file.originalname
.split('.')
.pop()
?.toLowerCase()}`,
);
},
}),
limits: {
fileSize: configService.get('file.maxFileSize', { infer: true }),
},
};
},
}),
],
controllers: [FilesLocalController],
providers: [ConfigModule, ConfigService, FilesLocalService],
exports: [FilesLocalService],
})
export class FilesLocalModule {}
```
-
this.filesService.create(file);실행// files/infrastructure/uploader/local/files.service.ts async create(file: Express.Multer.File): Promise<{ file: FileType }> { if (!file) { throw new UnprocessableEntityException({ status: HttpStatus.UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY, errors: { file: 'selectFile', }, }); } return { file: await this.fileRepository.create({ // <-- 이놈은 persistence 도메인에 있는 포트 path: `/${this.configService.get('app.apiPrefix', { infer: true, })}/v1/${file.path}`, }), }; } -
port 인 file.repository.ts 에서 create 선언
- 참고로 port 코드를 보니 추상 클래스로 되어있음. 이를 implements 해서 adapter (
repositories/file.repository.ts) 를 구현한다.
// src/files/infrastructure/persistence/file.repository.ts import { NullableType } from '../../../utils/types/nullable.type'; import { FileType } from '../../domain/file'; export abstract class FileRepository { abstract create(data: Omit<FileType, 'id'>): Promise<FileType>; abstract findById(id: FileType['id']): Promise<NullableType<FileType>>; abstract findByIds(ids: FileType['id'][]): Promise<FileType[]>; } - 참고로 port 코드를 보니 추상 클래스로 되어있음. 이를 implements 해서 adapter (
-
adapter 인 file.repository.ts 의 create 함수 수행
// src/files/infrastructure/persistence/relational/repositories/file.repository.ts import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'; import { InjectRepository } from '@nestjs/typeorm'; import { FileEntity } from '../entities/file.entity'; import { In, Repository } from 'typeorm'; import { FileRepository } from '../../file.repository'; import { FileMapper } from '../mappers/file.mapper'; import { FileType } from '../../../../domain/file'; import { NullableType } from '../../../../../utils/types/nullable.type'; @Injectable() export class FileRelationalRepository implements FileRepository { constructor( @InjectRepository(FileEntity) private readonly fileRepository: Repository<FileEntity>, ) {} async create(data: FileType): Promise<FileType> { // 이 함수 const persistenceModel = FileMapper.toPersistence(data); return this.fileRepository.save( this.fileRepository.create(persistenceModel), ); } async findById(id: FileType['id']): Promise<NullableType<FileType>> { const entity = await this.fileRepository.findOne({ where: { id: id, }, }); return entity ? FileMapper.toDomain(entity) : null; } async findByIds(ids: FileType['id'][]): Promise<FileType[]> { const entities = await this.fileRepository.find({ where: { id: In(ids), }, }); return entities.map((entity) => FileMapper.toDomain(entity)); } }
