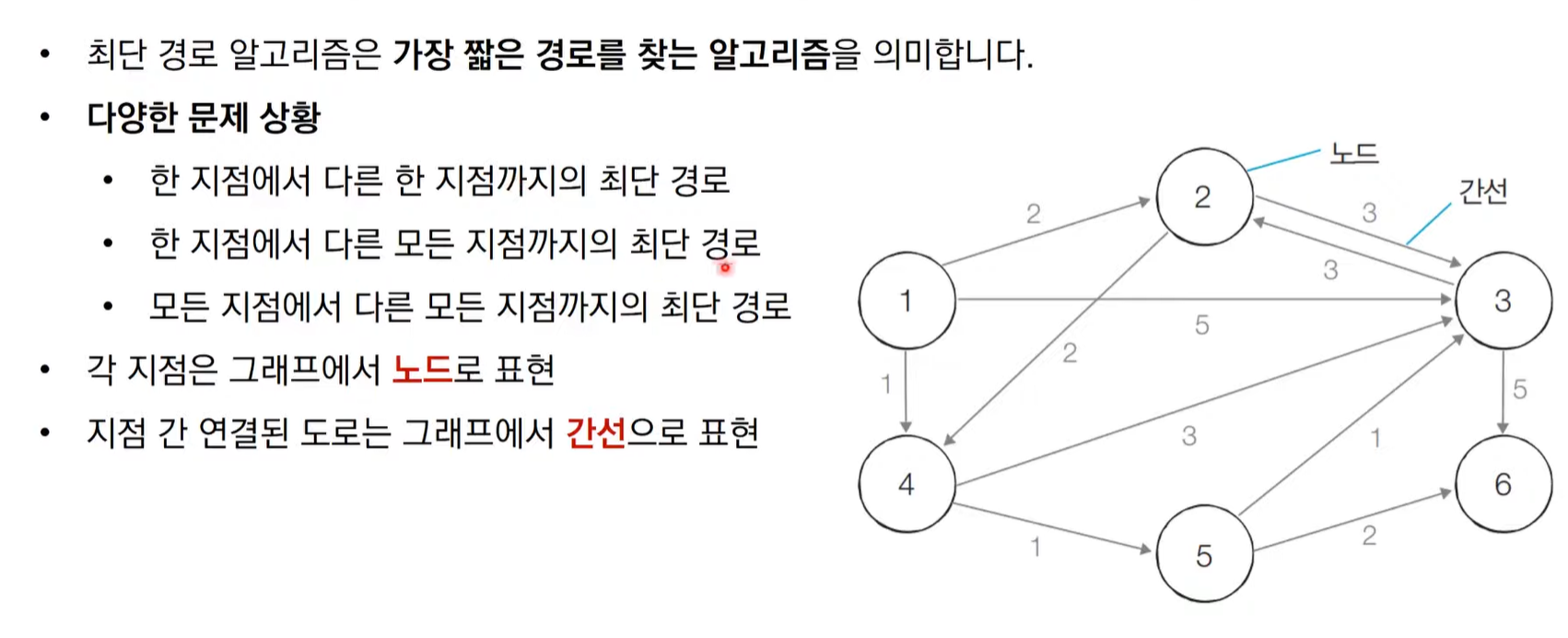
최단 경로 문제
- 가장 짧은 경로를 찾는 알고리즘
- 각 지점은 그래프에서 노드로 표현
- 지점 간 연결된 도로는 그래프에서 간선으로 표현
다익스트라 알고리즘

- 특정한 노드에서 출발하여 다른 모든 노드로 가는 최단 경로 계산
- 음의 간선이 없을 때 정상적으로 작당
- 다익스트라 알고리즘은 그리디 알고리즘으로 분류
- 매 상황에서 가장 비용이 적은 노드를 선택해 임의의 과정을 반복
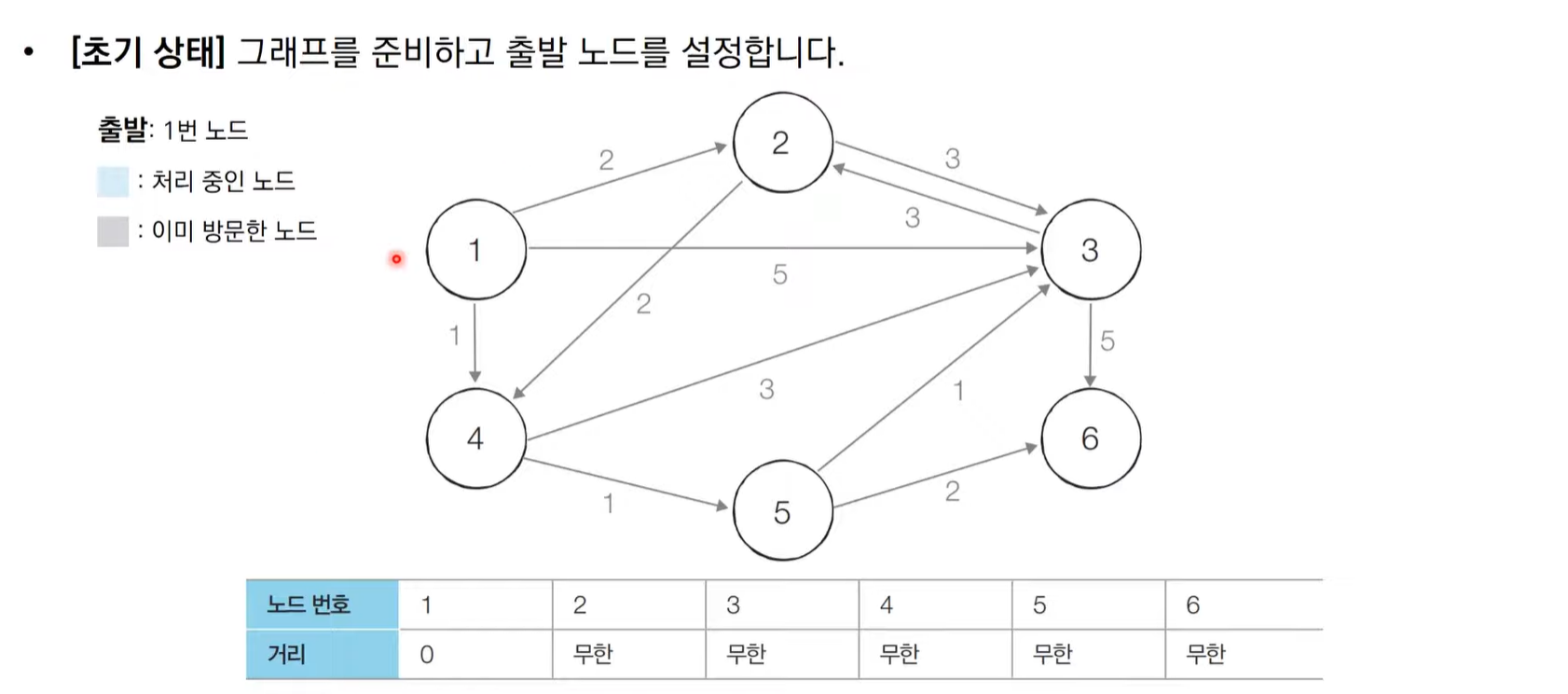
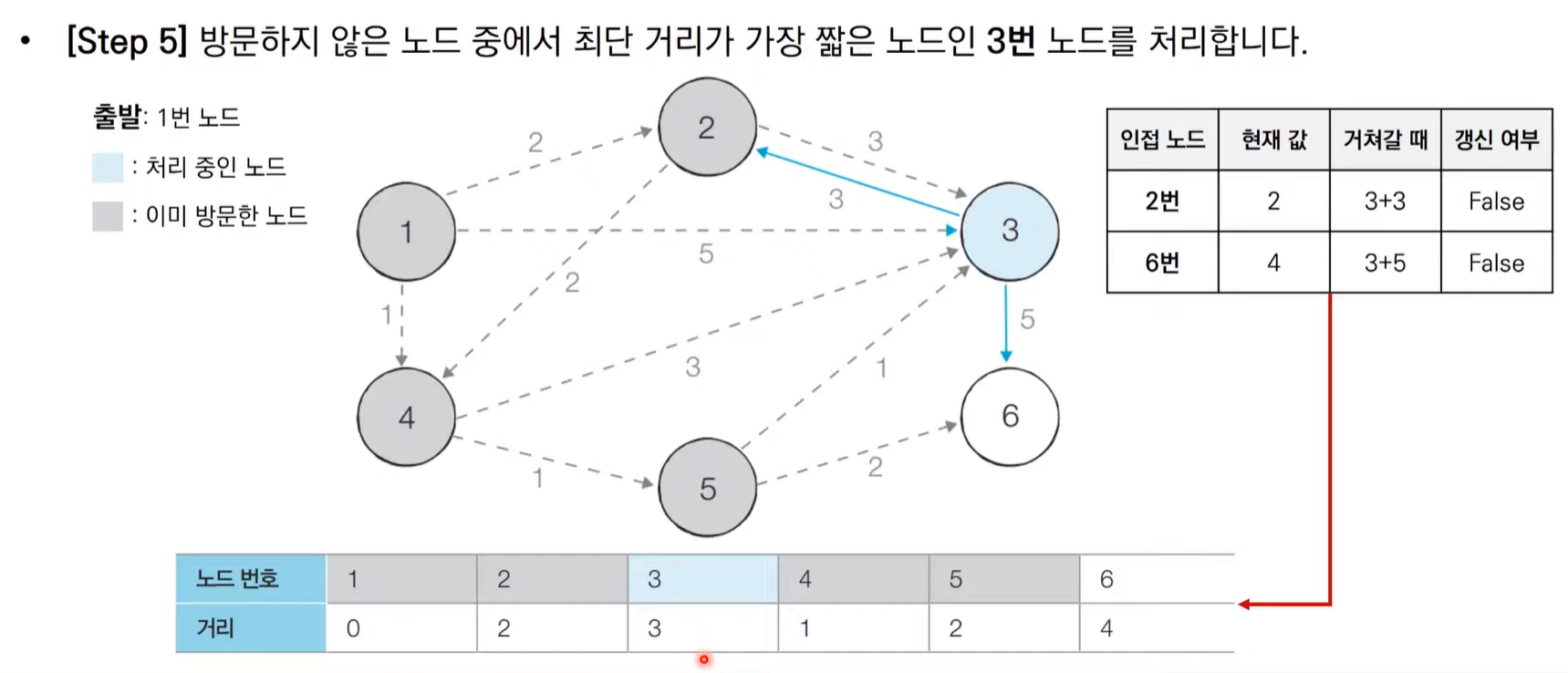
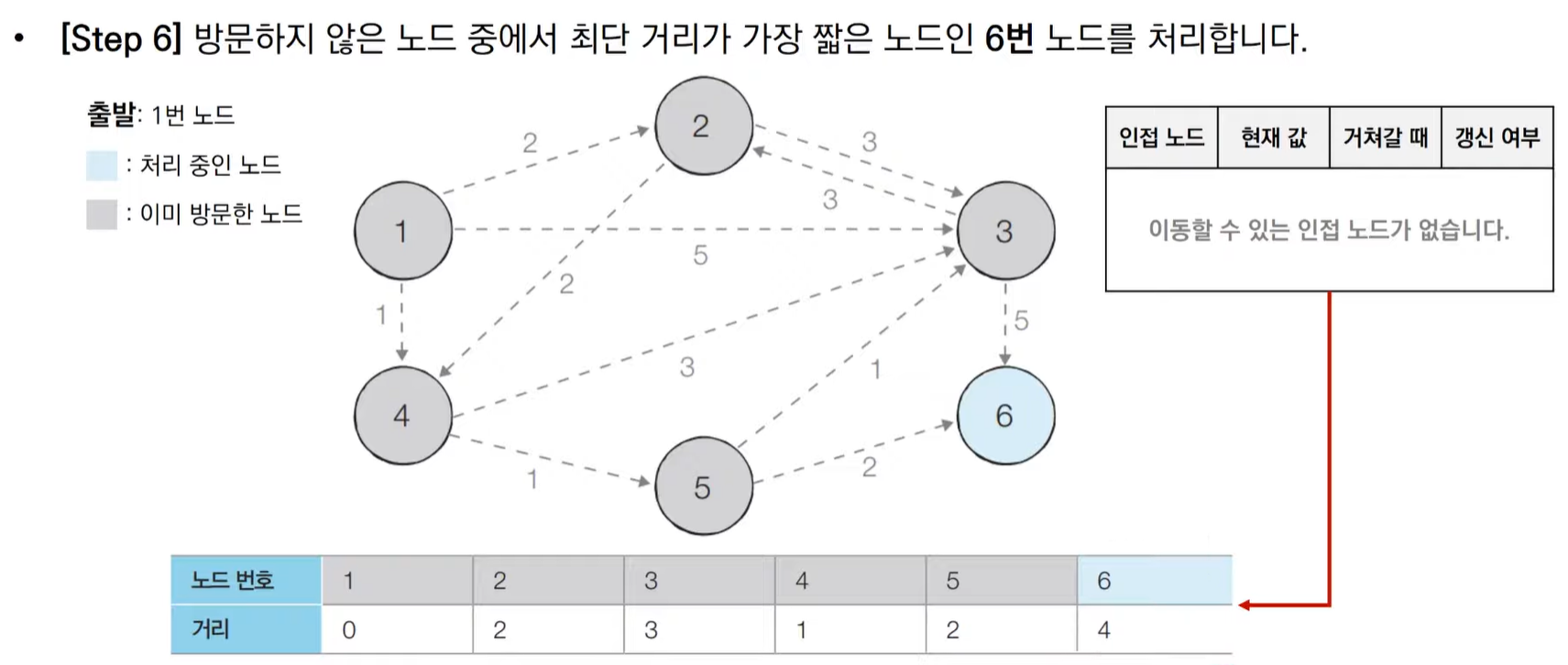
다익스트라 알고리즘 동작 과정

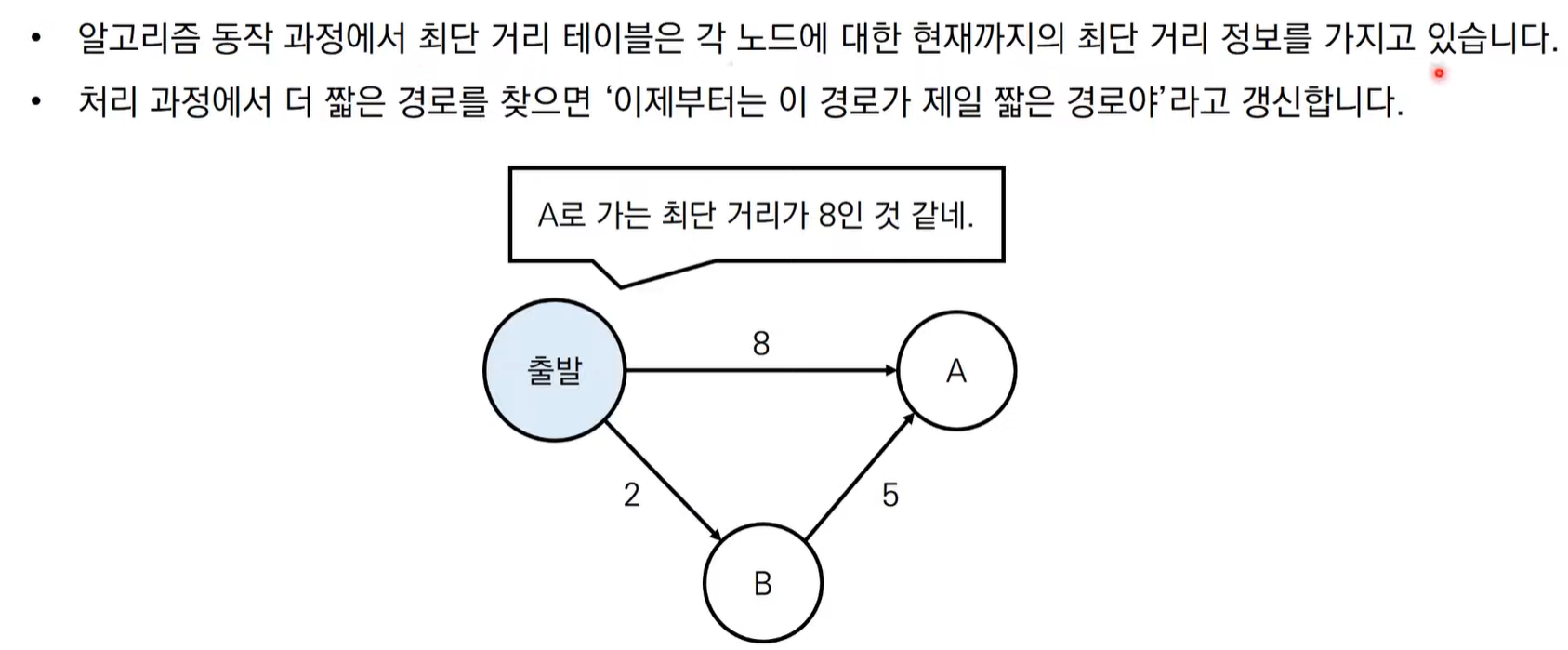
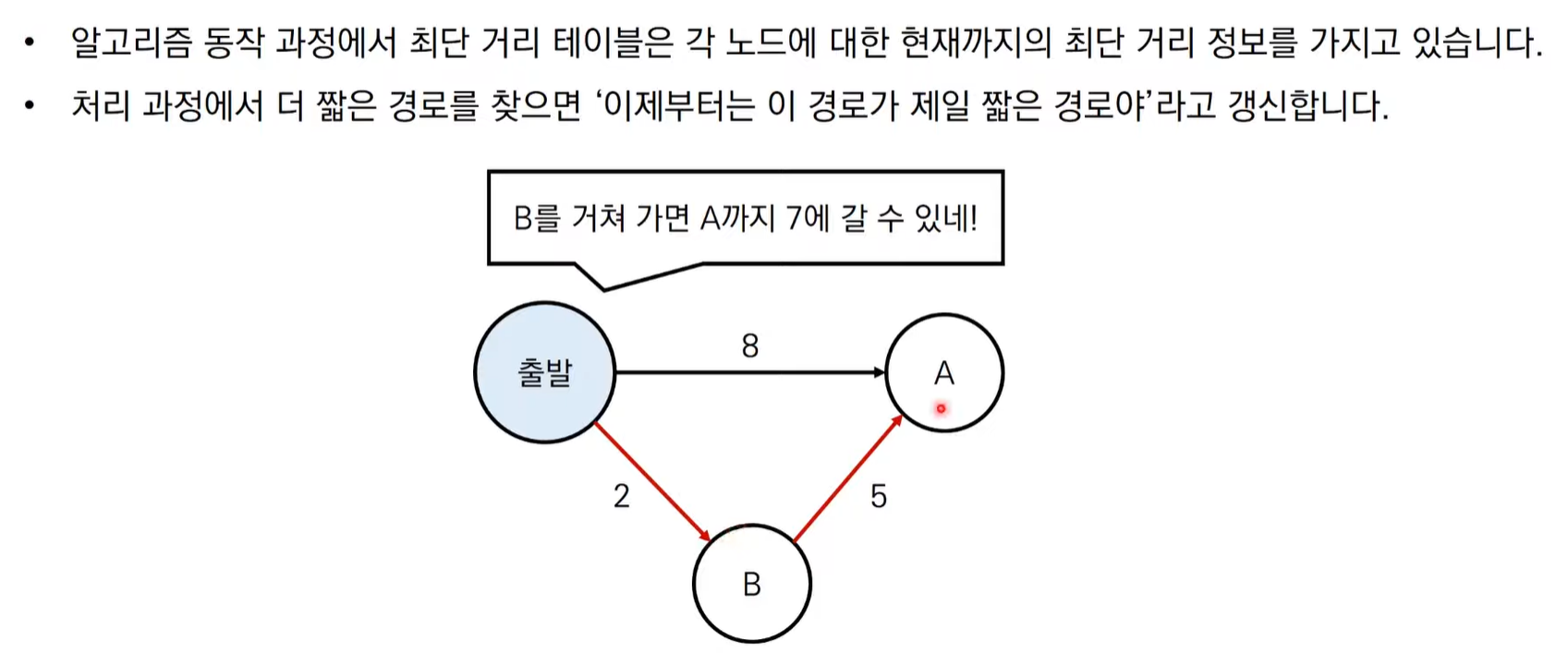
다익스트라 알고리즘 동작 과정 살펴보기
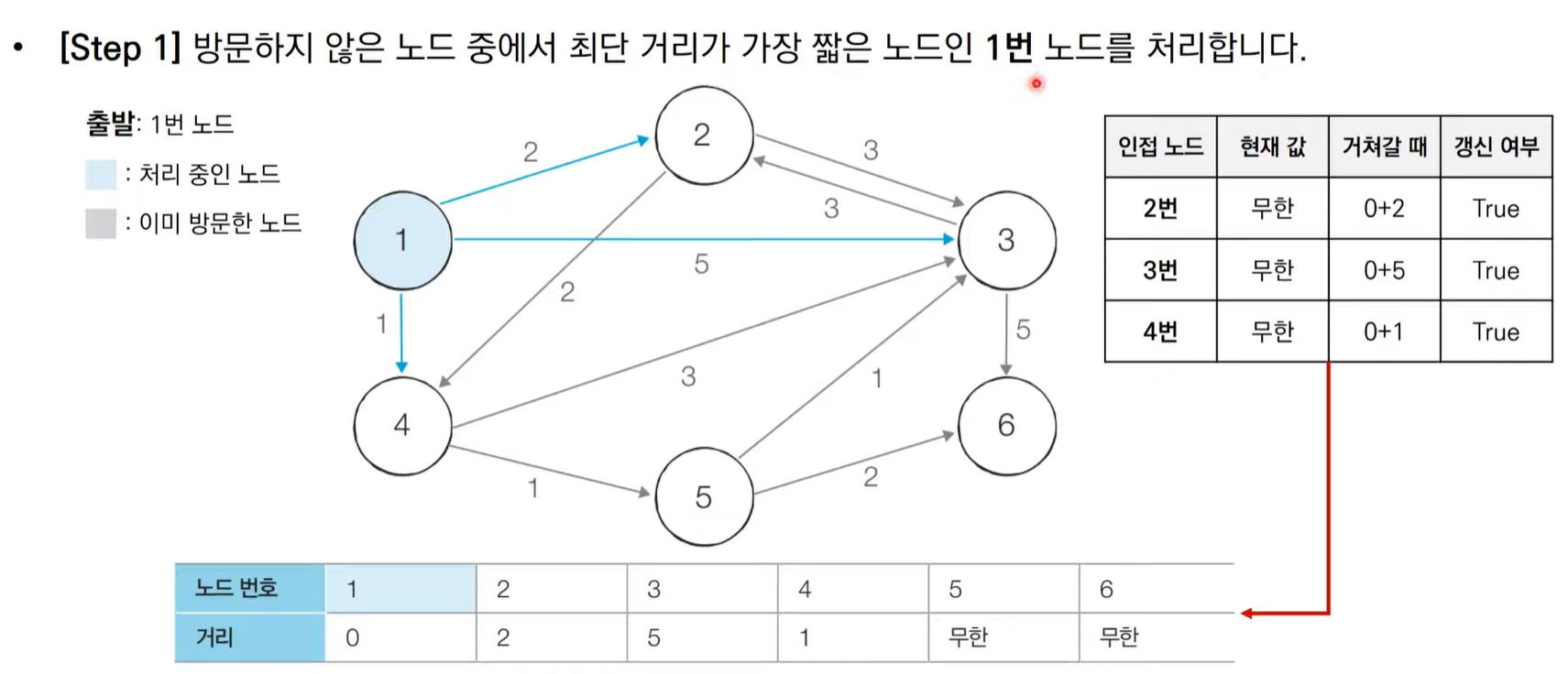
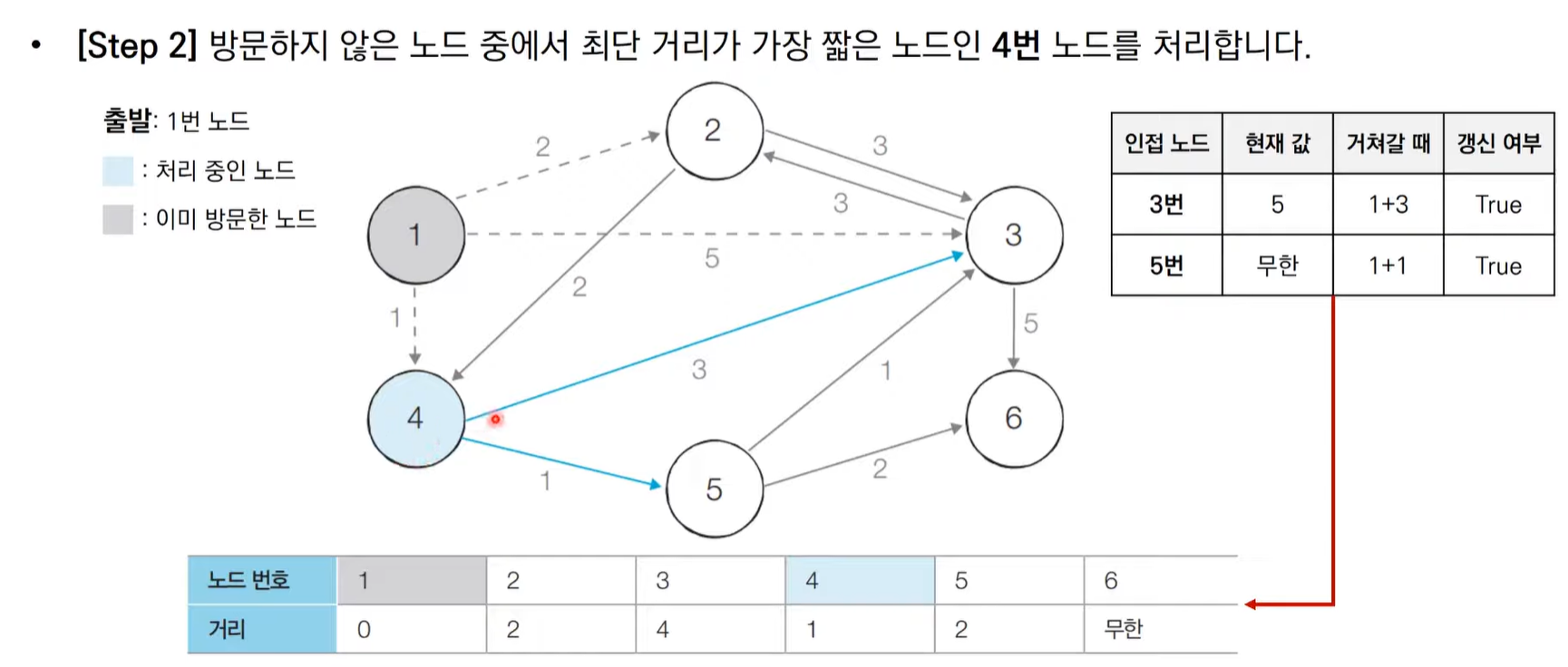
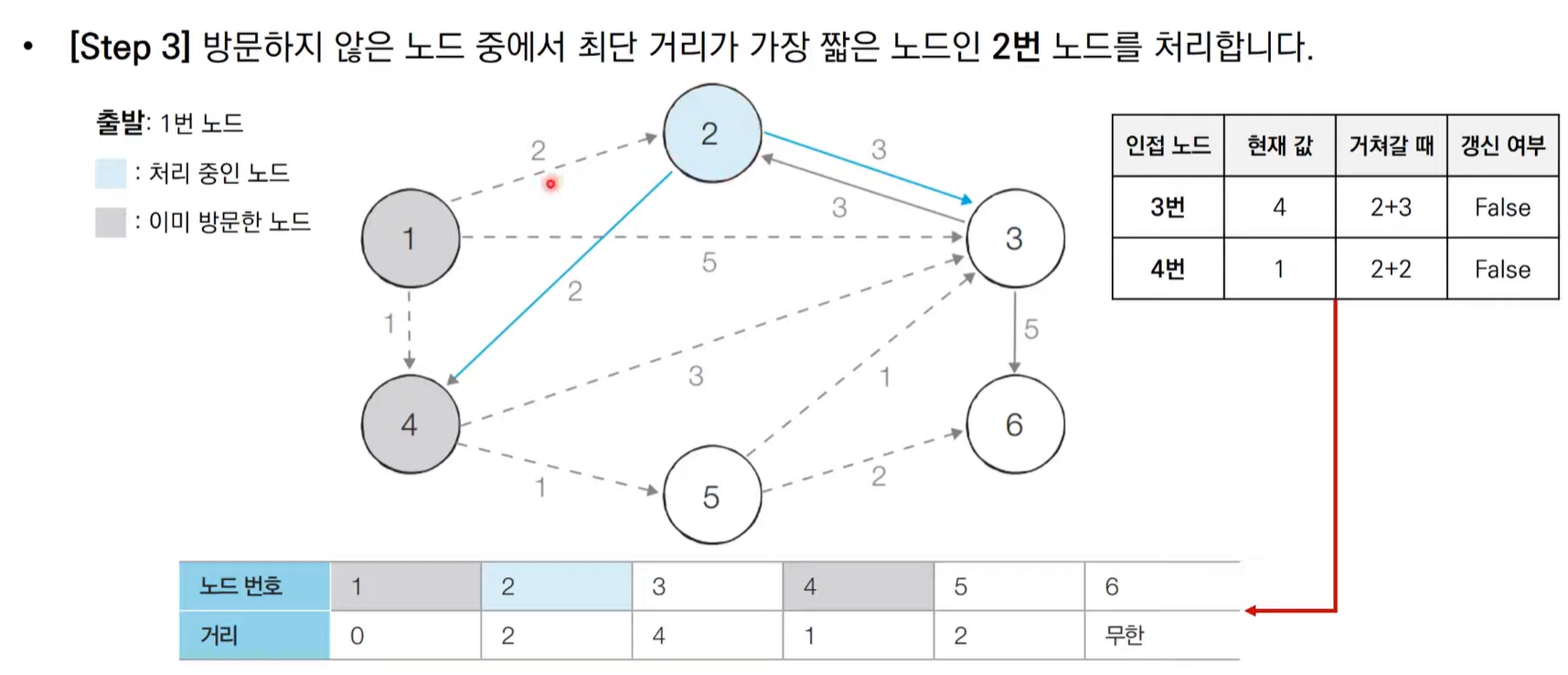
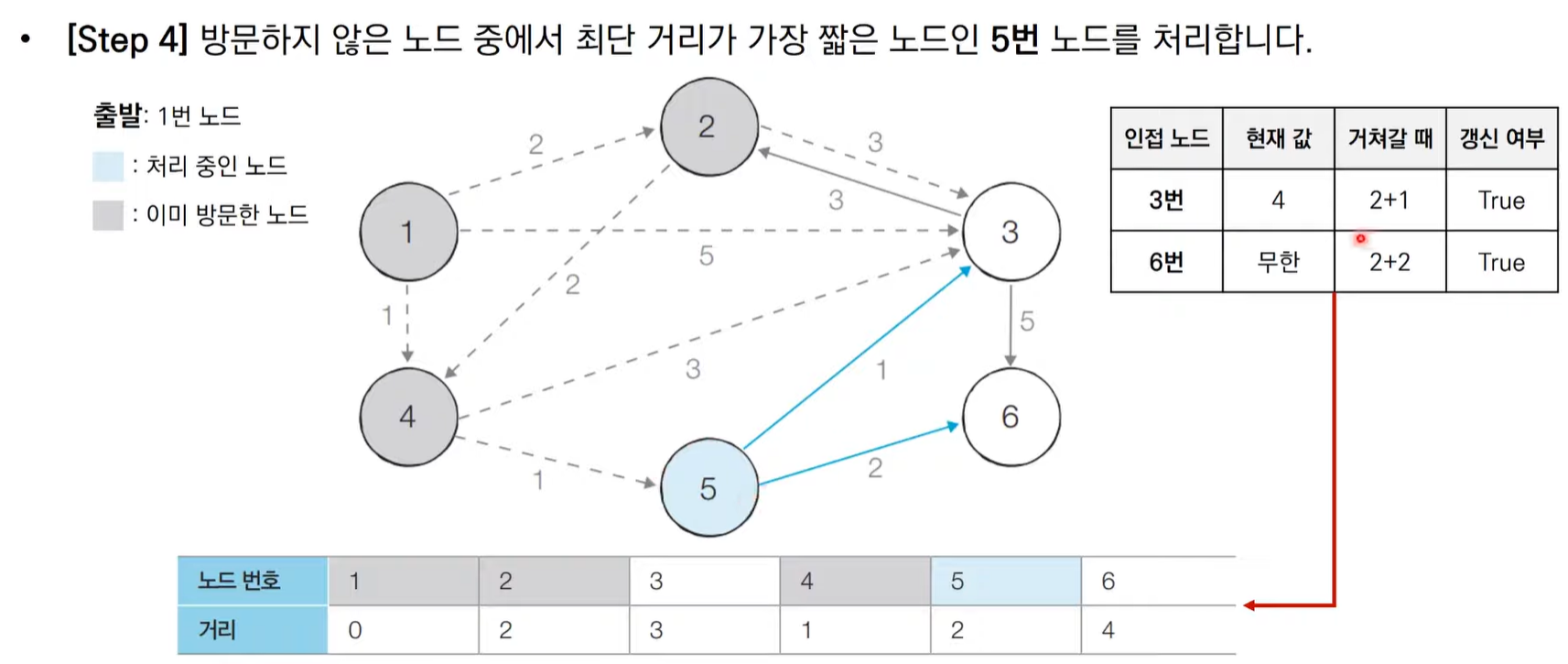
다익스트라 알고리즘 특징
- 그리디 알고리즘: 매 상황에서 방문하지 않은 가장 비용이 적은 노드를 선택
- 단계를 거치며 한 번 처리된 노드의 최단 거리는 고정되어 더 이상 바뀌지 않음
- 한 단계당 하나의 노드에 대한 최단 거리를 확실히 찾는 것으로 이해할 수 있음
- 다익스트라 알고리즘을 수행한 뒤 테이블에 각 노드까지의 최단 거리 정보가 저장
- 완벽한 형태의 최단 경로를 구하려면 소스코드에 추가적인 기능을 더 넣어야 함
다익스트라 알고리즘 간단한 구현 방법
- 단계마다 방문하지 않은 노드 중에서 최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 선택하기 위해 매 단계마다 1차원 테이블의 모든 원소를 확인(순차 탐색)합니다.
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
INF = int(1e9)
n,m = map(int,input().split())
start = int(input())
graph = [[] for i in range(n+1)]
visit = [False] * (n+1)
distance = [INF] * (n+1)
for _ in range(m):
a,b,c = map(int,input().split())
graph[a].append((b,c))
def get_smallest_node():
min_value = INF
idx = 0
for i in range(1,n+1):
if distance[i] < min_value and not visit[i]:
min_value = distance[i]
idx = i
return idx
def dijkstra(start):
distance[start] = 0
visit[start] = True
for j in graph[start]:
distance[j[0]] = j[1]
for i in range(n-1):
now = get_smallest_node
visit[now] = True
for j in graph[now]:
cost = distance[now] + j[i]
if cost < distance[j[0]]:
distance[j[0]] = cost
dijkstra(start)
for i in range(1,n+1):
if distance[i] == INF:
print("INFINITY")
else:
print(distance[i])
다익스트라 알고리즘 성능 분석

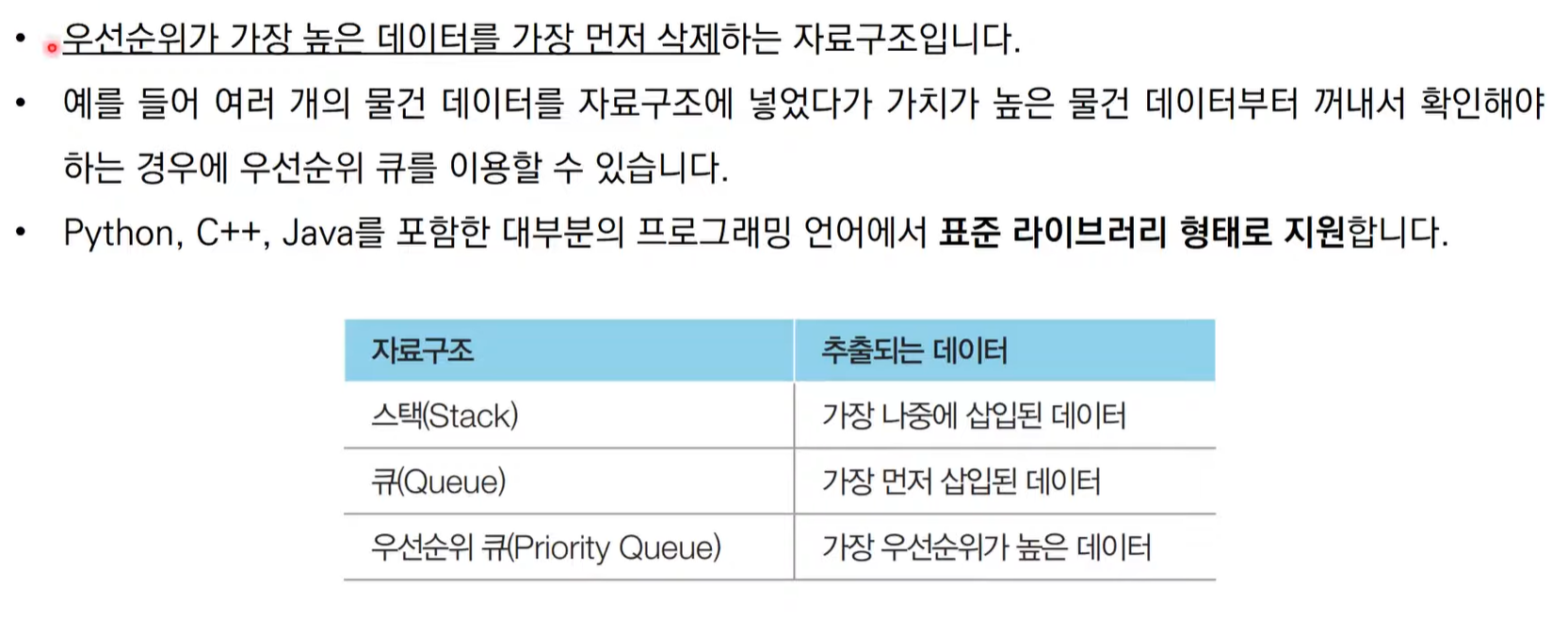
우선순위 큐(Prioriy Queue)
- 우선 순위가 가장 높은 데이터를 가장 먼저 삭제하는 자료구조
- 여러 개의 물건 데이터를 자료구조에 넣었다가 가치가 높은 물건 데이터부터 꺼내서 확인해야 하는 경우에 우선순위 큐를 이용
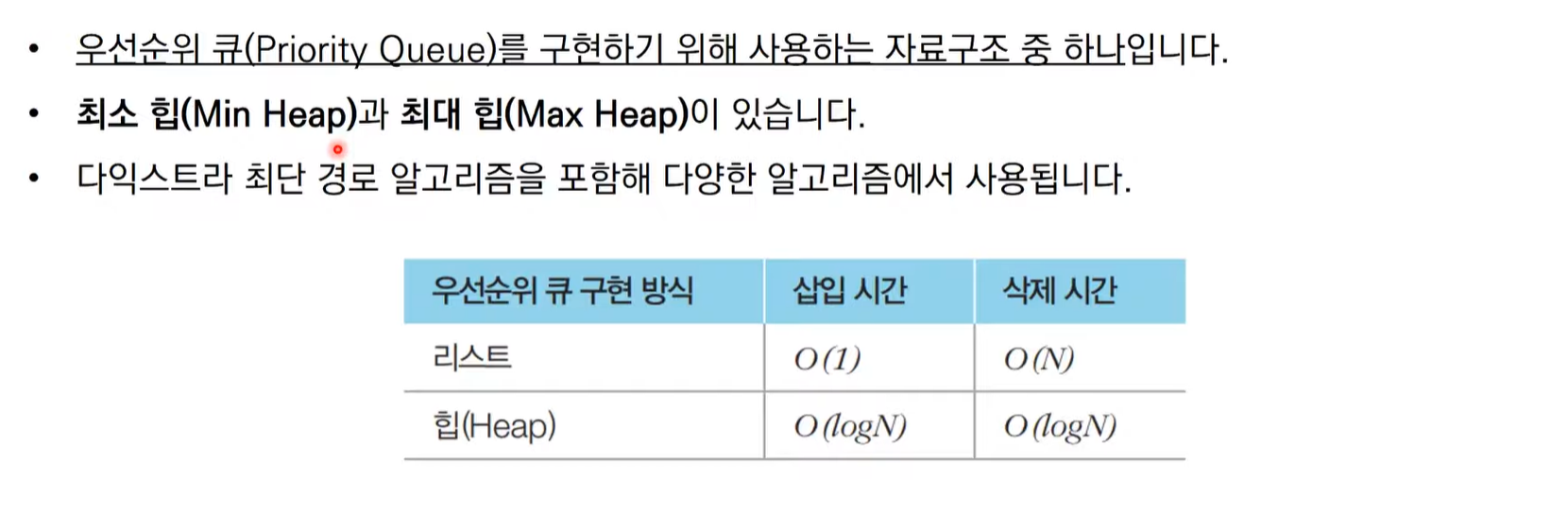
힙(Heap)
- 우선순위 큐를 구현하기 위해 사용하는 자료구조 중 하나
- 최소 힙(Min Heap)과 최대 힙(Max Heap)
- 다익스트라 최단 경로 알고리즘을 포함해 다양한 알고리즘에서 사용
힙 라이브러리 사용 예제: 최소 힙
import heapq
def heapsort(iterable):
h = []
result = []
for value in iterable:
heapq.heappush(h,value)
for i in range(len(h)):
result.append(heapq.heappop(h))
return result
result = heapsort([1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0])
print(result)

힙 라이브러리 사용 예제: 최대 힙
import heapq
def heapsort(iterable):
h = []
result = []
for value in iterable:
heapq.heappush(h,-value)
for i in range(len(h)):
result.append(-heapq.heappop(h))
return result
result = heapsort([1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0])
print(result)

다익스트라 알고리즘 - 개선된 구현 방법
- 단계마다 방문하지 않은 노드 중에서 최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 선택하기 위해 힙(Heap) 자료구조 이용
- 다익스트라 알고리즘이 동작하는 기본 원리는 동일
- 현재 가장 가까운 노드를 저장해 놓기 위해서 힙 자료구조를 추가적으로 이용
- 현재의 최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 선택해야 하므로 최소 힙을 사용
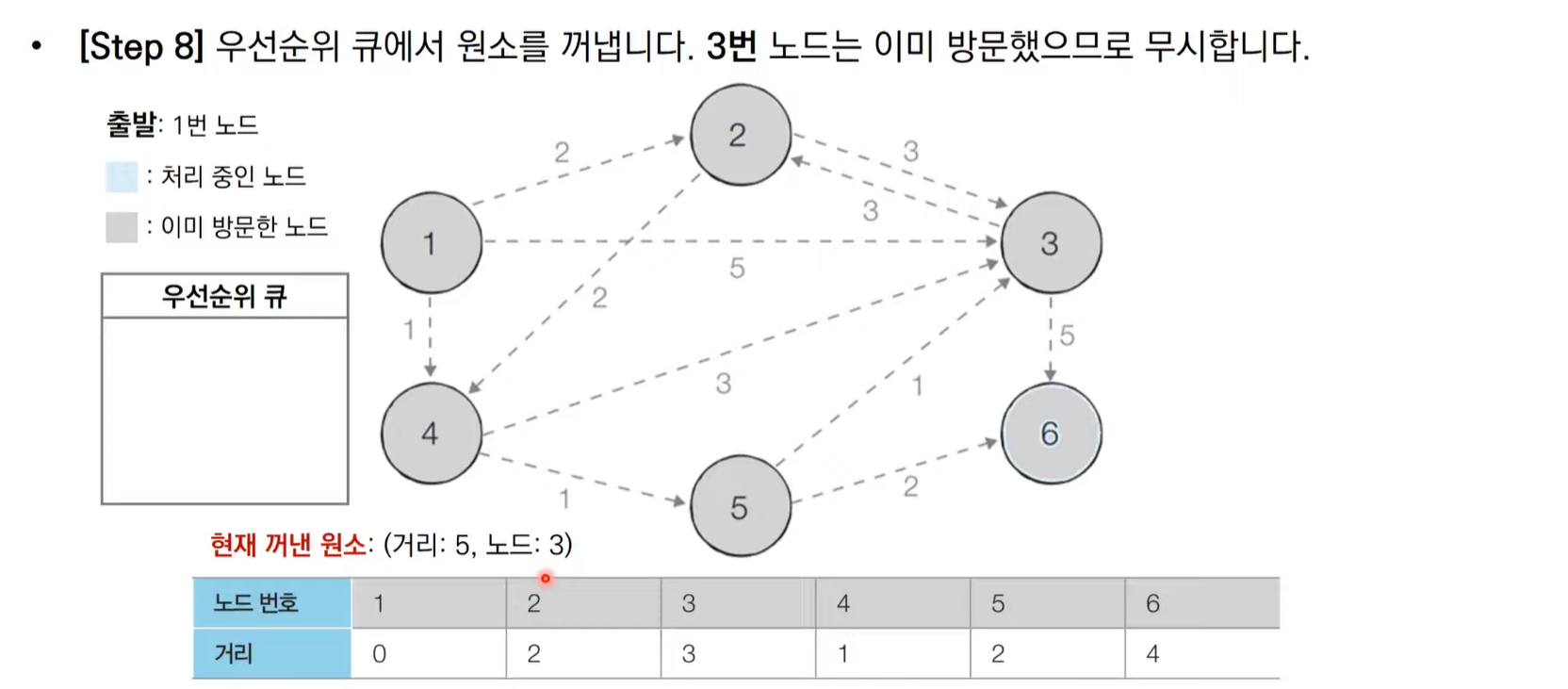
다익스트라 알고리즘 동작 과정 살펴보기(우선순위 큐)
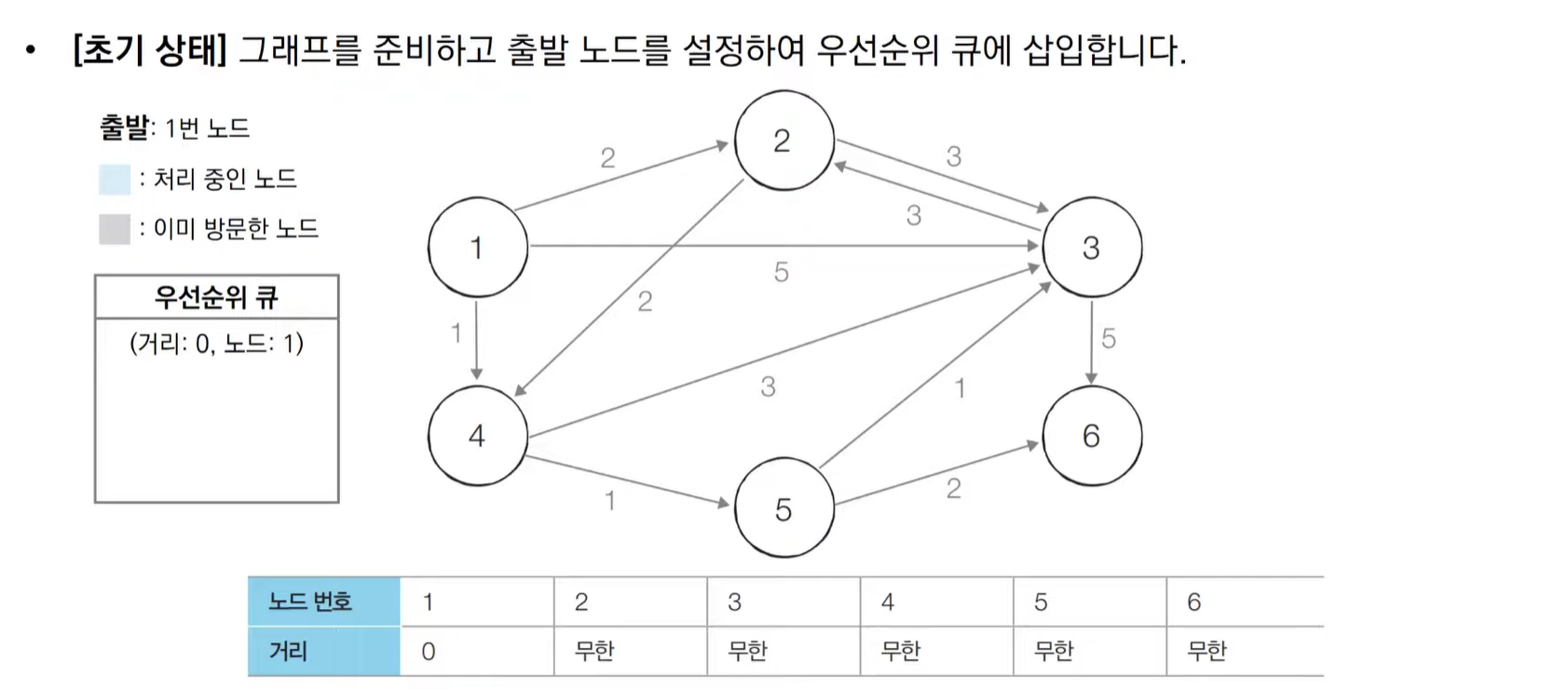
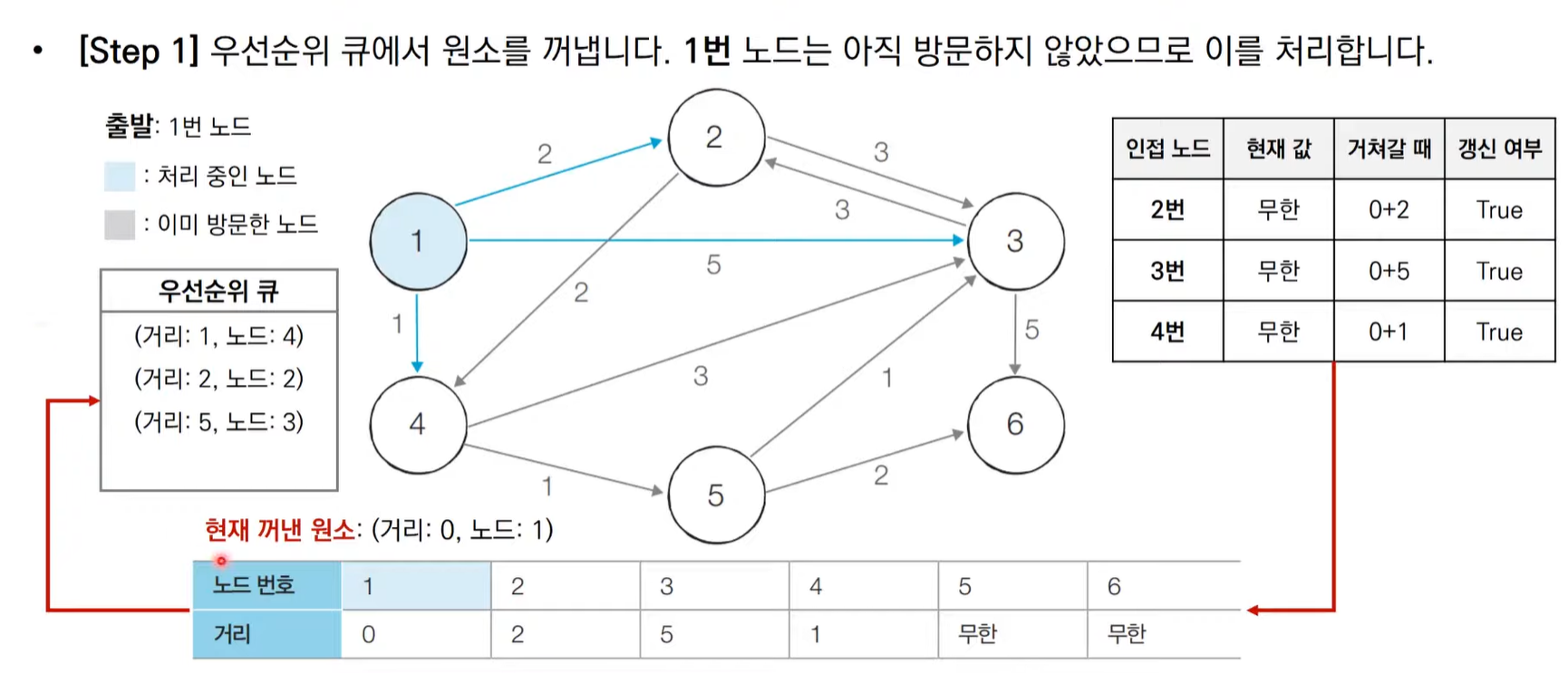
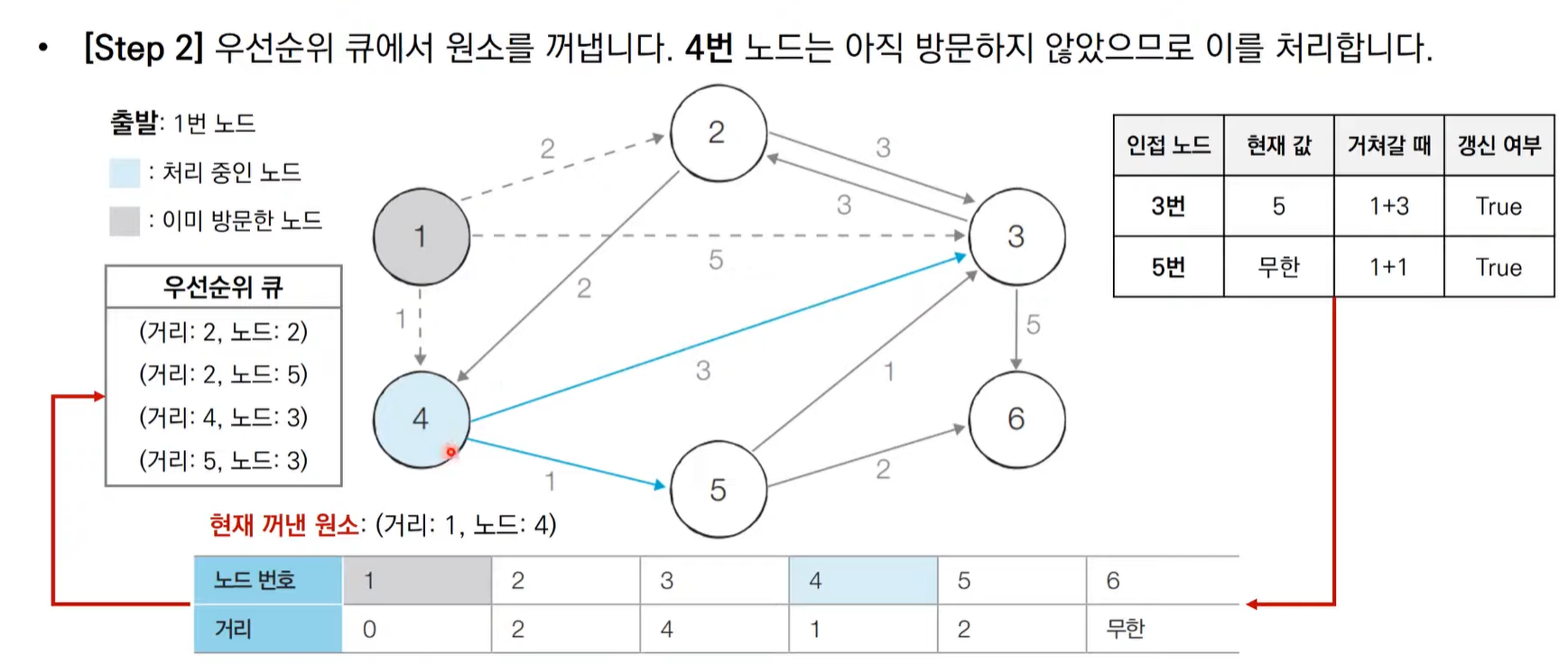
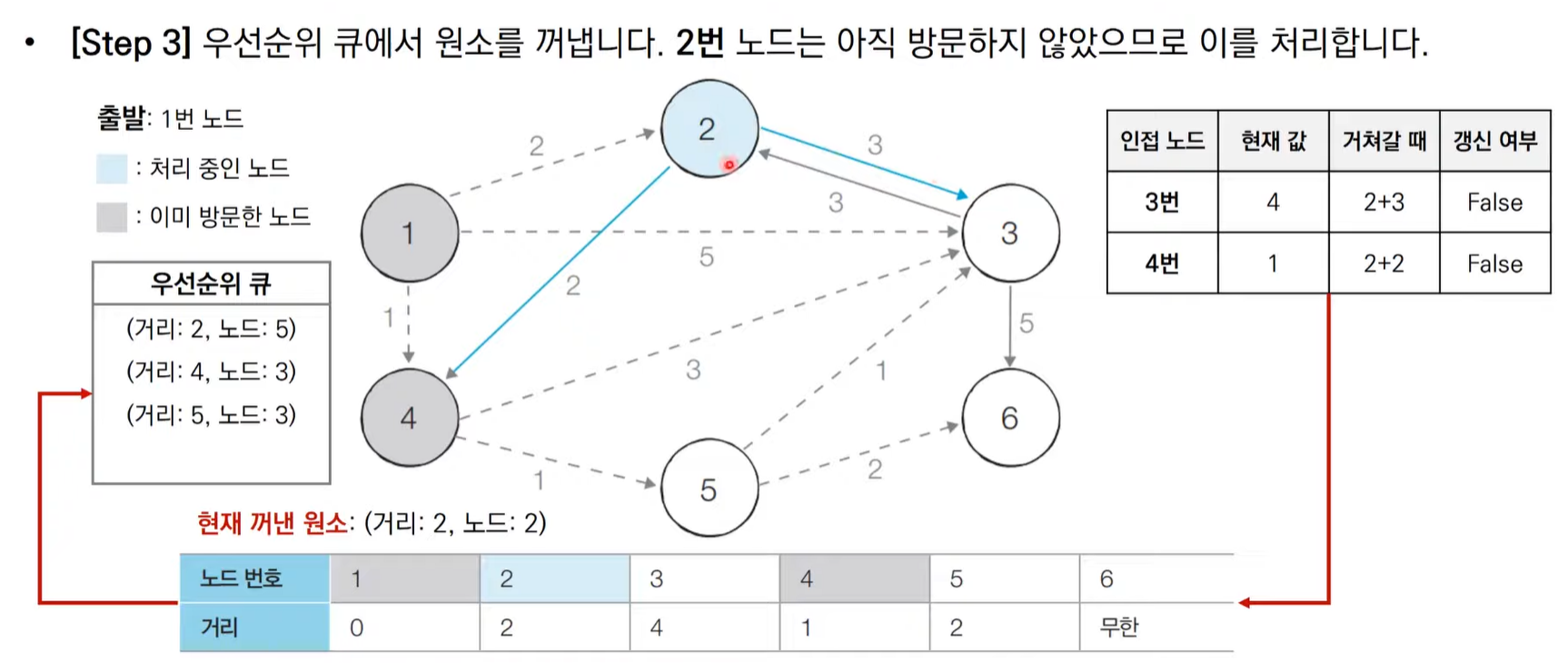
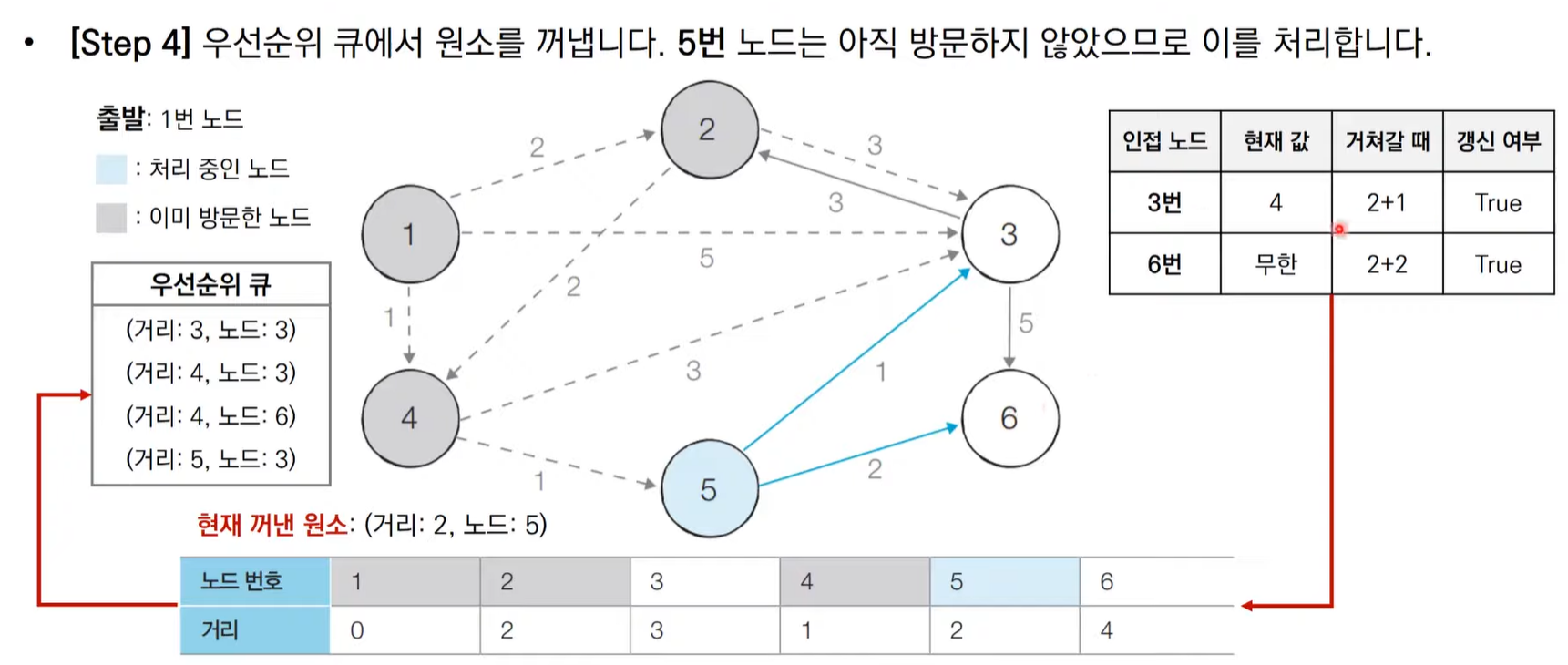
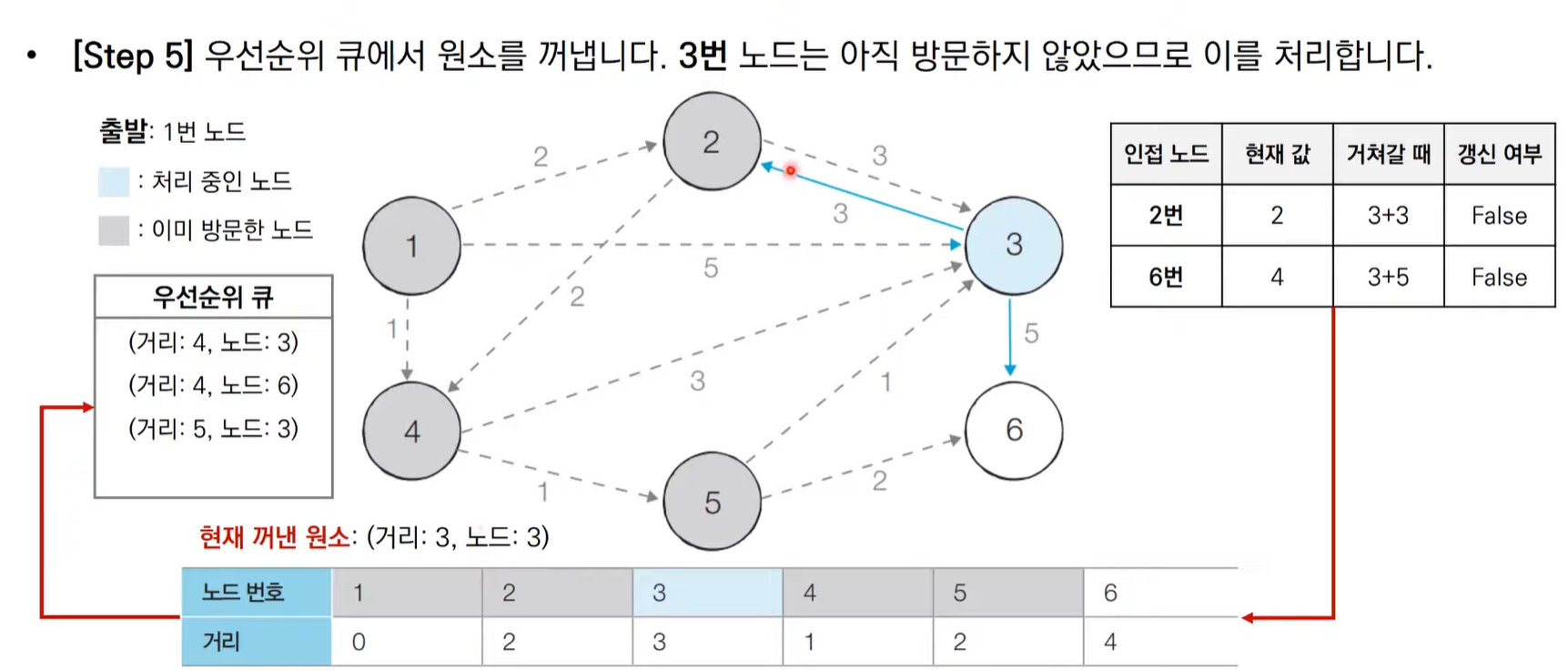
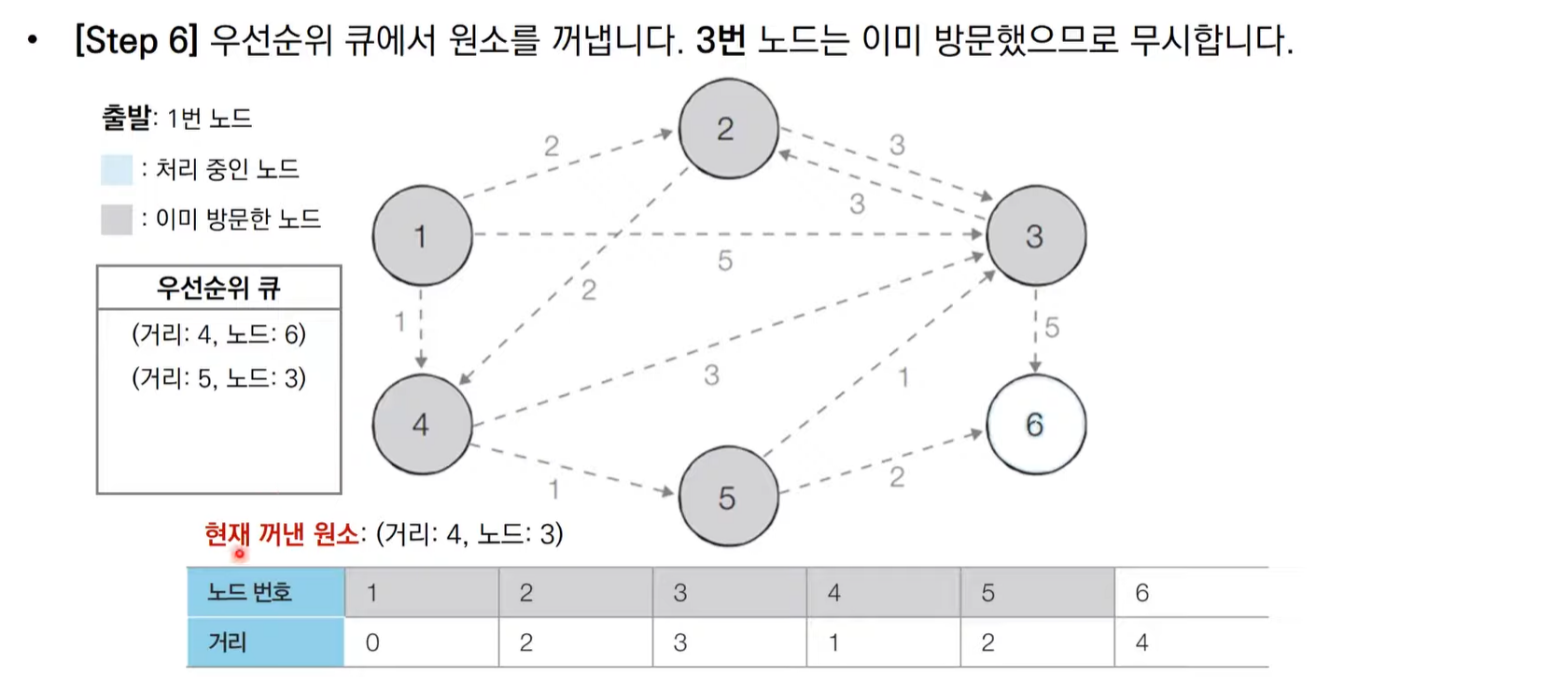
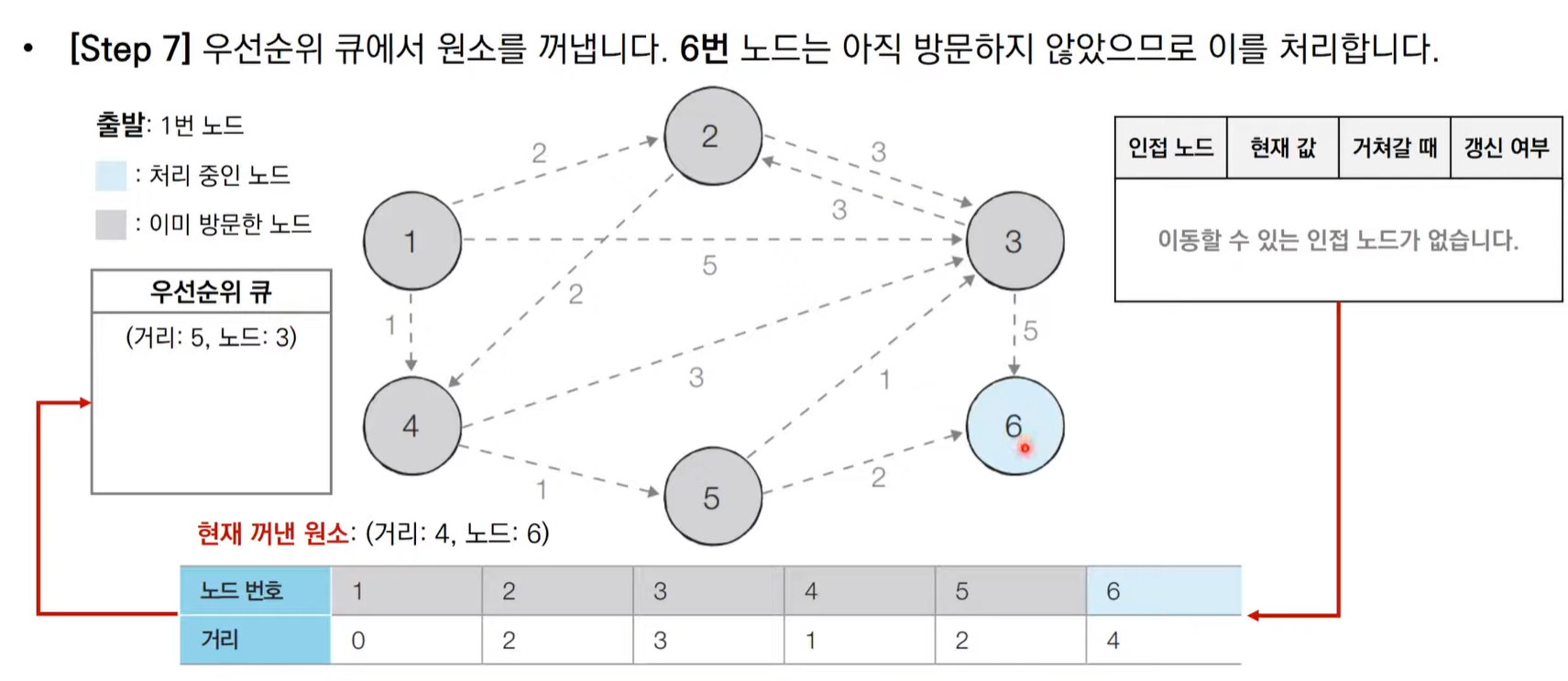
import heapq,sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
INF = int(1e9)
n,m = map(int,input().split())
start = int(input())
graph = [[] for i in range(n+1)]
distance = [INF] * (n+1)
for _ in range(m):
a,b,c = map(int,input().split())
graph[a].append((b,c))
def dijkstra(start):
q = []
heapq.heappush(q,(0,start))
distance[start] = 0
while q:
dist, now = heapq.heappop(q)
if distance[now] < dist:
continue
for i in graph[now]:
cost = dist + i[1]
if cost < distance[i[0]]:
distance[i[0]] = cost
heapq.heappush(q,(cost,i[0]))
dijkstra(start)
for i in range(1,n+1):
if distance[i] == INF:
print("INFINITY")
else:
print(distance[i])
다익스트라 알고리즘(우선순위 큐) 성능 분석

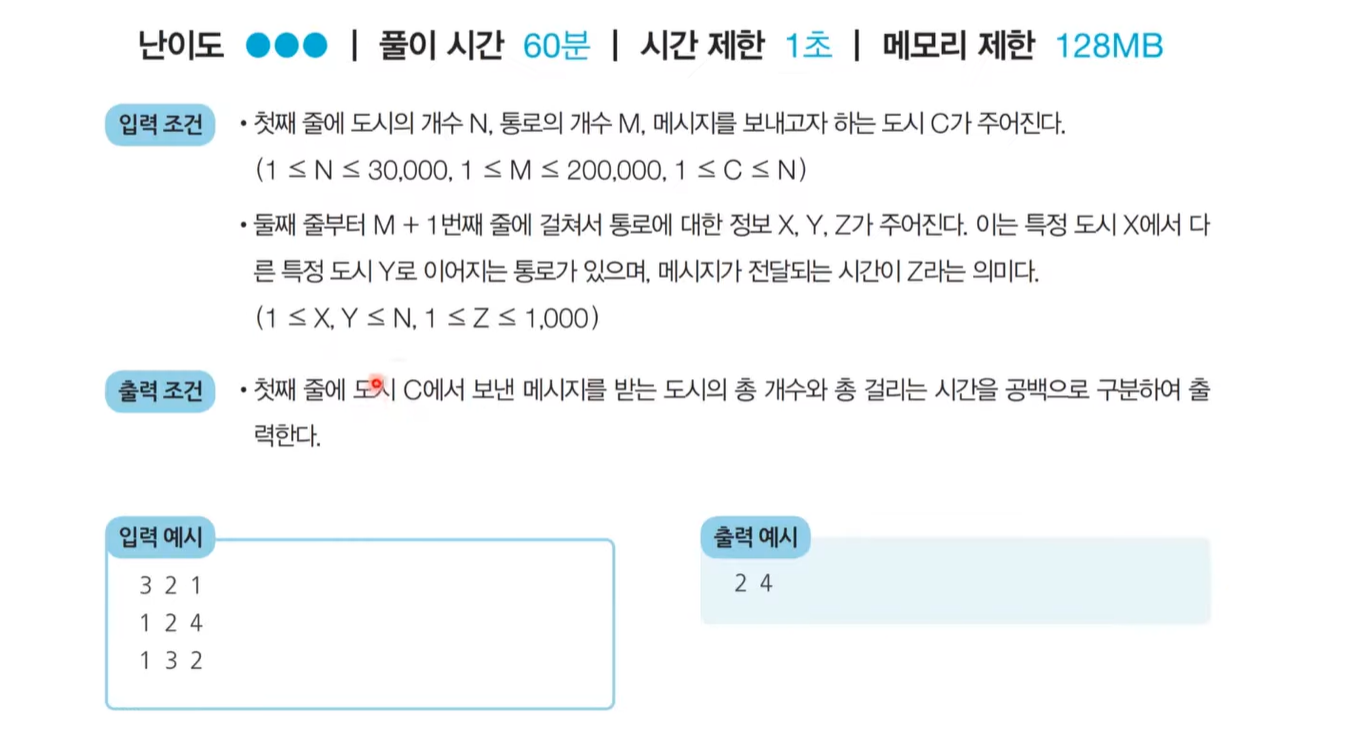
문제 1: 전보


문제 풀이
import heapq,sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
INF = int(1e9)
def dijkstra(start):
q = []
heapq.heappush(q,(0,start))
distance[start] = 0
while q:
dist, now = heapq.heappop(q)
if distance[now] < dist:
continue
for i in graph[now]:
cost = dist + i[1]
if cost < distance[i[0]]:
distance[i[0]] = cost
heapq.heappush(q,(cost,i[0]))
n,m,start = map(int,input().split())
graph = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
distance = [INF] * (n+1)
for _ in range(m):
x,y,z = map(int,input().split())
graph[x].append((y,z))
dijkstra(start)
cnt = 0
max_distance = 0
for d in distance:
if d != 1e9:
cnt += 1
max_distance = max(max_distance,d)
print(cnt - 1,max_distance)































