Polynomials: 다항식
- 계수: coefficient
- 지수: exponents
- 항: term
Ordered list (linear list):
Operations on ordered list
i. length
ii. reading from right to left(or left to right)
iii. retrieve i-th element, 0<=i<\n
iv. update i-th element's value, 0<=i<\n
v. insertion(i번째 위치, 0<=i<\n)
vi. deletion (i번째 항목, 0<=i<n)
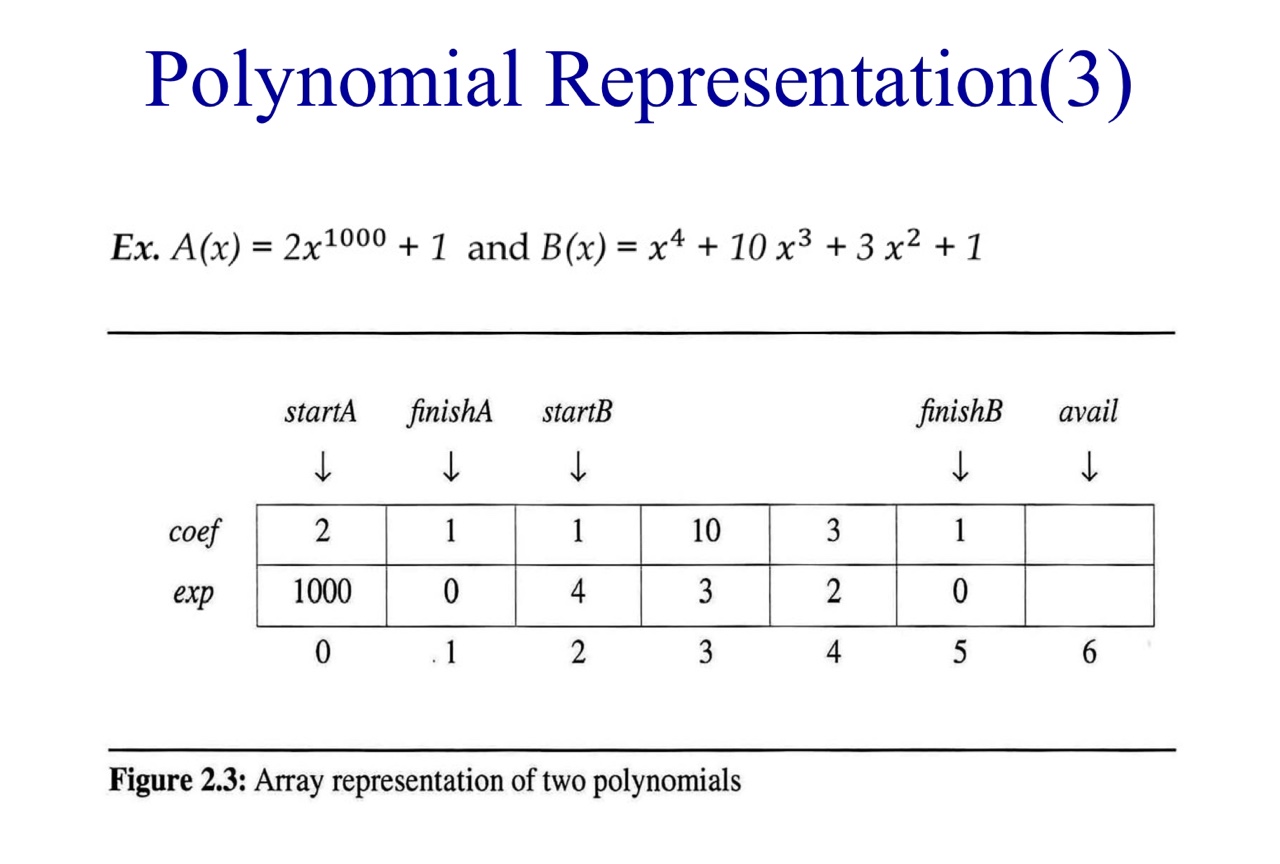
Polynomial Representation
- principle
Unique exponents are arranged in decreasing order
-> 지수가 내림차순으로 중복 되지 않게 나온다.
구현 방법
방법 1. 다항식 담은 두 어레이 각각 순차탐색해서 더한 값 새 어레이에 할당.
단점: sparse한 다항식의 경우(예: 2x^100 + 5x + 3) 메모리 낭비가 심함. 다항식 담은 어레이 처음부터 끝까지 scan 해야됨.
방법 2.
- Store only non-zero terms
- All polynomials are represented in a single array called terms
#define MAX_TERMS 100 //size of terms array typedef struct{ int coef; int expon; } polynomial; polynomial terms[MAX_TERMS]; int avail = 0; int starta, finisha;
avail 부터 결괏값 저장!
#include "string.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#define MAX_TERMS 100
using namespace std;
typedef struct {
int coef;
int expon;
} polynomial;
polynomial terms[MAX_TERMS];
int avail = 0;
int COMPARE(int a, int b) {
if (a > b) return 1; //a>b 이면 1 반환
else if (a < b) return -1; //a<b 이면 -1 반환
else return 0; //a=b 이면 0 반환
}
void attach(int coef, int exp){
if (avail >= MAX_TERMS){
fprintf(stderr, "Too many terms in the polynomial\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
terms[avail].coef = coef;
terms[avail++].expon = exp;
}
void padd(int startA, int finishA, int startB, int finishB, int* startD, int* finishD, polynomial terms[]) {
int coefficient;
*startD = avail;
// avail 인덱스 부터 결괏값 저장, startD는 avail 시작 가리키는 포인터.
while (startA <= finishA && startB <= finishB) {
switch (COMPARE(terms[startA].expon, terms[startB].expon)) {
case -1: // a < b
attach(terms[startB].coef, terms[startB].expon);
startB++;
break;
case 0: // a == b
coefficient = terms[startA].coef + terms[startB].coef;
if (coefficient) {
attach(coefficient, terms[startA].expon);
}
startA++;
startB++;
break;
case 1: // a > b
attach(terms[startA].coef, terms[startA].expon);
startA++;
}
}
for (; startA <= finishA; startA++) {
attach(terms[startA].coef, terms[startA].expon);
}
for (; startB <= finishB; startB++) {
attach(terms[startB].coef, terms[startB].expon);
}
*finishD = avail - 1;
}
int main() {
fstream a("a.txt");
fstream b("b.txt");
int startD, finishD, nA = 0, nB = 0;
a >> nA; b >> nB;
// 2 | 2 100 1 0
// 4 | 1 4 10 3 3 2 -1 0
// nA = 2 nB = 4
for (int i = 0; i < nA; i++) {
a >> terms[i].coef; a >> terms[i].expon;
avail++;
}
for (int i = nA; i < nA + nB; i++) {
b >> terms[i].coef; b >> terms[i].expon;
avail++;
}
padd(0, nA - 1, nA, nA + nB-1, &startD, &finishD, terms);
//padd(int startA, int finishA, int startB,
//int finishB, int* startD, int* finishD, polynomial terms[])
printf("%d ", finishD - startD + 1);
for (int i = startD; i <= finishD; i++) {
printf("%d ", terms[i].coef);
printf("%d ", terms[i].expon);
}
}