
Expo MGF
-
, find MGF, moments
cf. 물리학에서의 관성 모멘트와 분산이 관련이 있음
-
MGF: ,
-
Derivative: , , , ...
-
, (taylor expansion)
-
-
-
, let ,
- so
-
Standard Normal MGF
-
Let , find all its moments.
-
for n odd by symmetry.
-
MGF:
-
Poission MGF
-
-
Let indep. of , Find distribution of .
-
Multiply MGFs:
-
Counterexample) if , dependent:
-
is not Pois. since even
-
, increasing! (is not Pois)
-
-
Joint Distribution (결합 분포)
-
, r.v.s
-
joint CDF
-
joint PMF
-
marginal CDF
is marginal dist. of X.
-
joint PDF(continuous)
such that
-
independence
, indep. if and only if
Equiv. to
(discrete)
all ,
-
-
Getting marginal distribution (주변 분포)
-
discrete
-
-
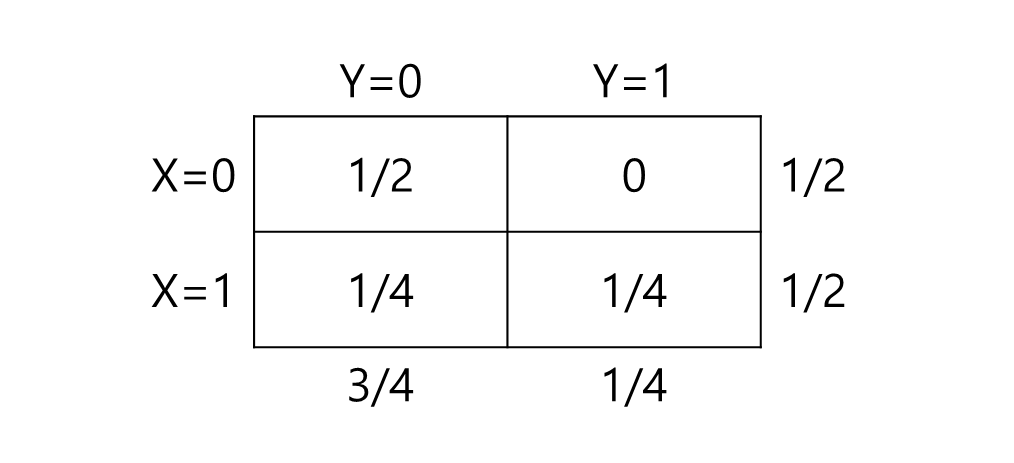
Example
- X, Y Bernulli
Y=0 Y=1 X=0 X=1 ---- ---- ---- ----
-
They are independent.
-
all of * all of
-
-
This one is dependent.
-
all of * all of
-
Examples
-
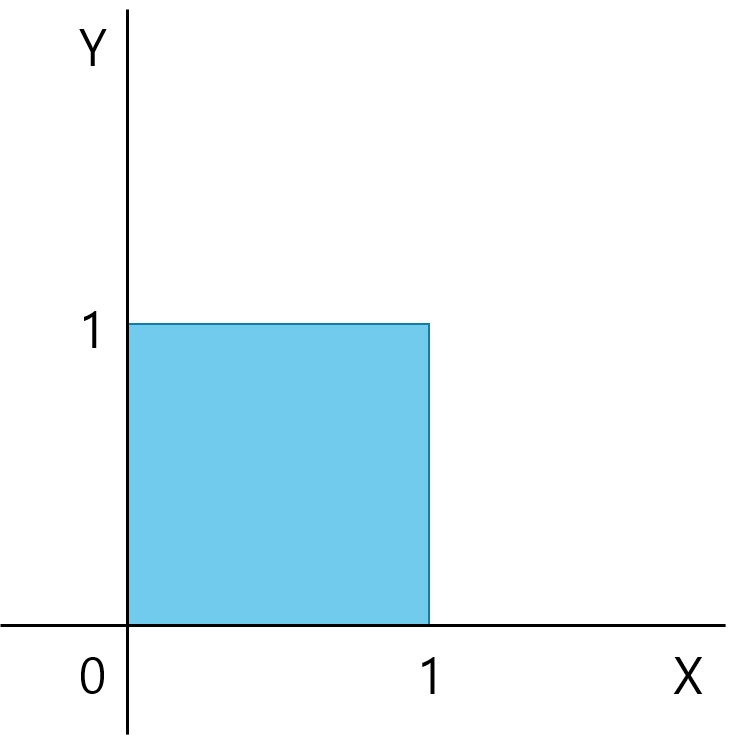
Ex1. Uniform on square
-
joint PDF const. on the square,
-
Integral is area,
- marginal: , are indep. Unif(0, 1)
-
-
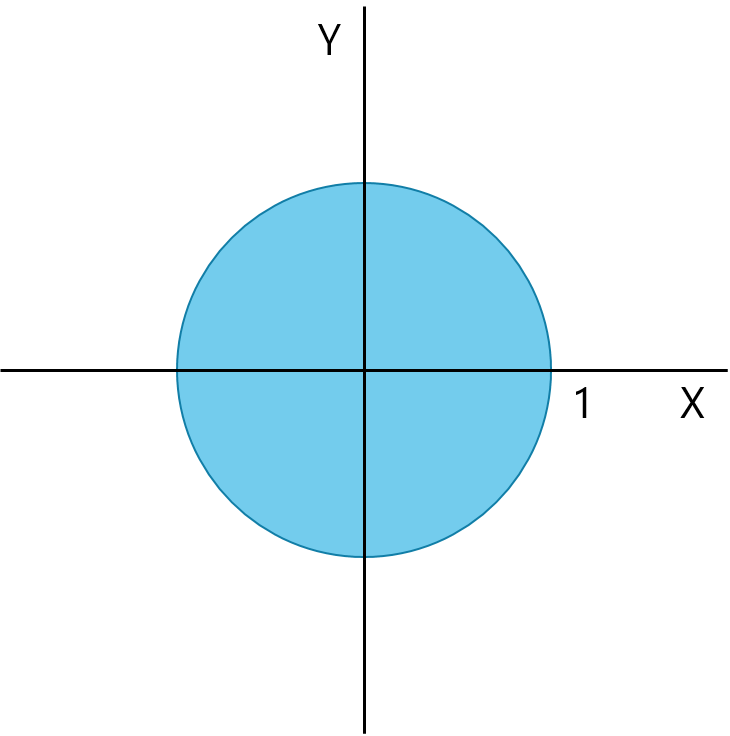
Ex2. Uniform in disc, ← 제약 조건식으로 인해 독립이 아님!
-
joint PDF
-
, Dependent
- Given ,
-
- 출처 : Statistics 110, boostcourse
