
Binomial distribution Bin(n, p)
-
Story: X is # of successes in n independent Bern(p) trials
- Bern(p) p: prob. success
-
Sum of indicator random variables(지시 확률 변수): ,
i.i.d (indep. identically distribution) Bern(p)
-
PMF(Prob. Math Function, 확률 질량 함수): ,
R.V.s (Random Variables)
-
There is a sample space:
- is an event.
-
CDF(Cumulative Distribution Function, 누적 분포 함수)
-
is an event.
-
-
then F is the CDF of X
-
PMF(for discrete r.v.s)
-
Discrete: possible values or
-
PMF: for all j
- ,
-
PMF of Binomial distribution
-
, by Binomial Thm.
-
-
, indep. \Rightarrow
-
Immediate from story: successes of nth and mth trials
-
,
:sum of n+m i.i.d. Bern(p) Bin(n+m, p)
-
→ VanderMonde:
-
Example
-
5 card hand, find distribution(PMF or CDF) of # aces
- Lex
-
Find . This is 0 except if .
-
Assume: Not Binomial
-
for
-
Like(Same as) the elk problem.

-
-
Have b black, w white marbles. Pick simple random sample of size n.
-
Find dist. of (# white marbles in sample)
-
, ,
-
Hypergeometric(초기하 분포): sampling without replacement
→ we do not get a binomial because trials are not indep.(dep!)
-
This is difference between Binomial(복원 추출) and Hypergeometric(비복원 추출)
-
by VanderMonde.
-
CDF
-
Form of distribution
-
Continuous

-
Discrete
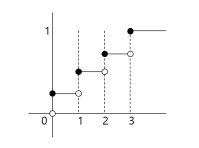
-
-
CDF 참고할 만한 문서 : CDF의 정의
-
CDF 참고할 만한 강의 → CDF의 미분 = PDF(확률 밀도 함수), PDF의 적분 = CDF
-
출처 : Statistics 110, boostcourse
