Heap
SHAPE과 ORDER의 특성을 모두 만족하는 특별한 이진트리
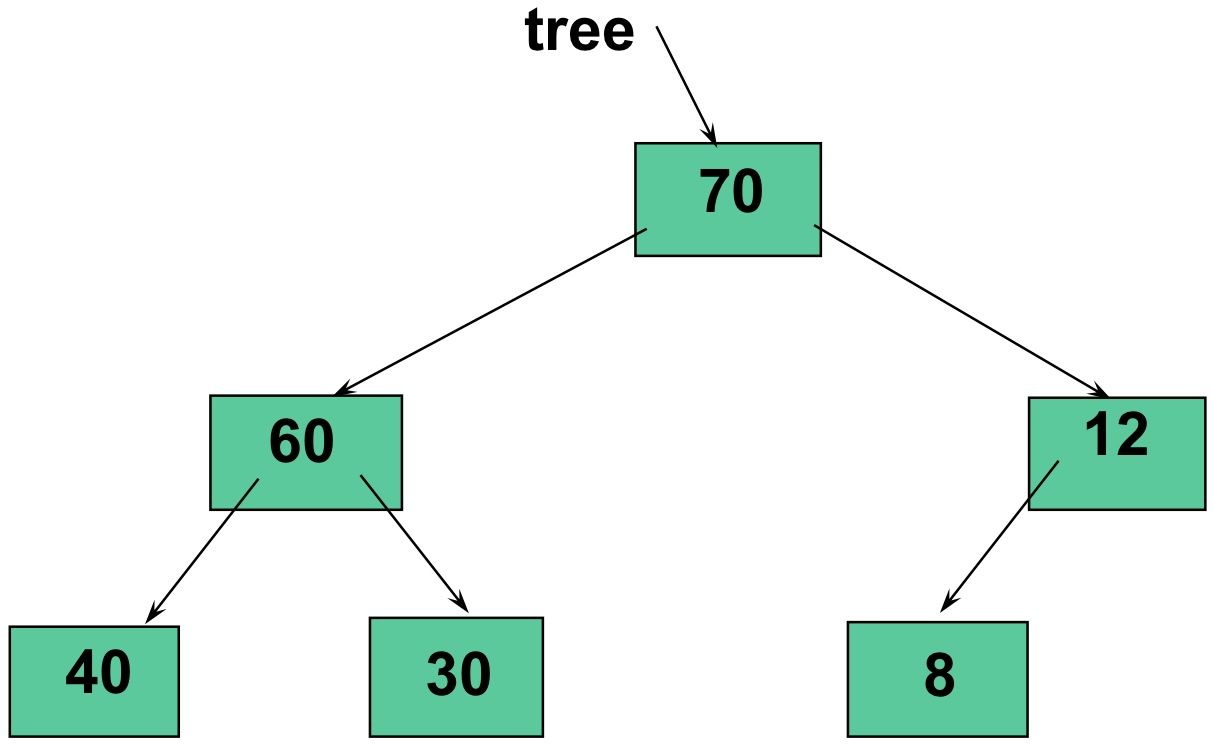
- # SHAPE
Complete binary tree를 만족하며 - # ORDER
모든 부모가 자식노드보다 큰(또는 작은) 값을 가짐
Binary Tree가 그러하듯, Heap 또한 root -> left subtree -> right subtree 순서로 1차원 배열로 나타낼 수 있다.
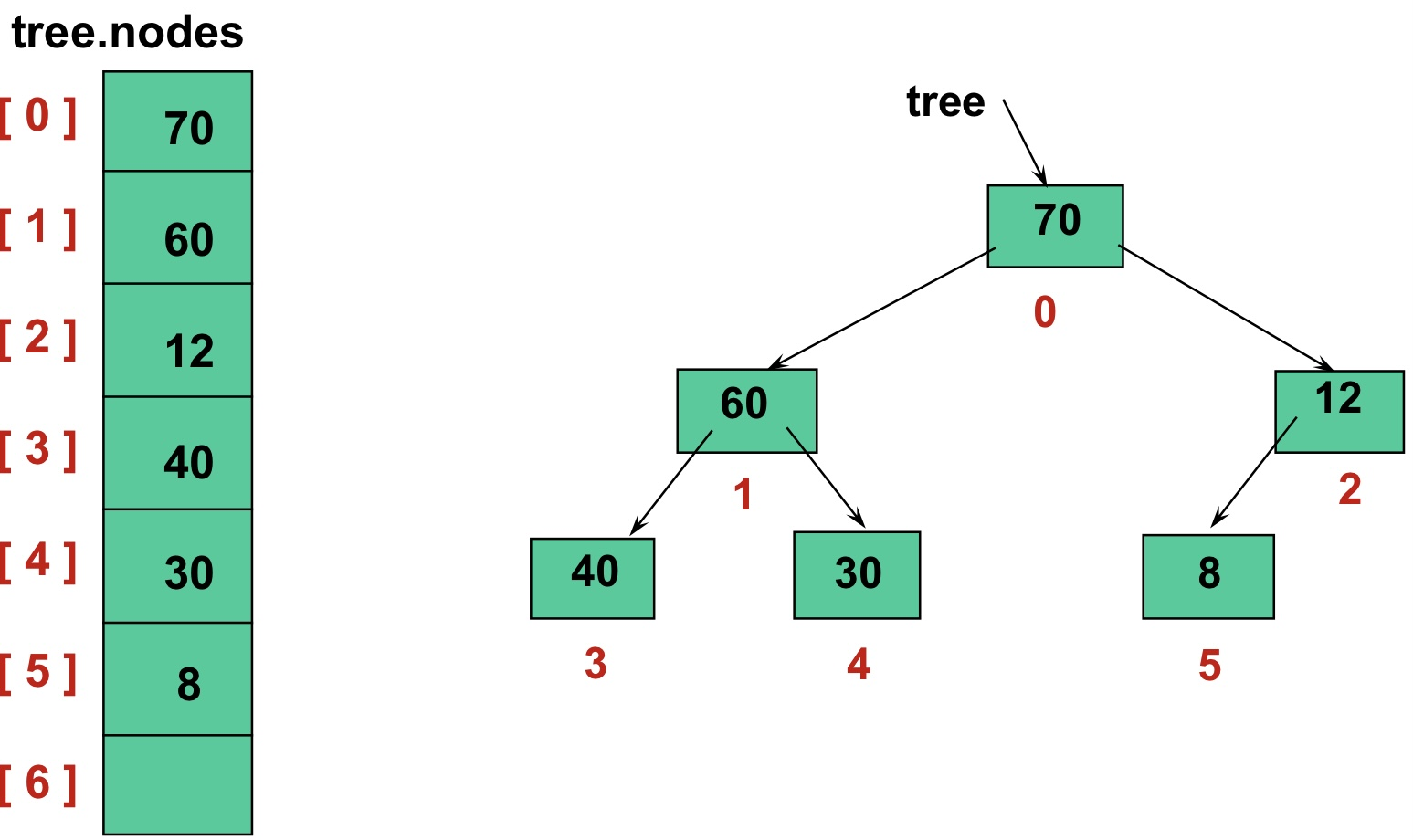
이때 root = n이라고 한다면
left child = 2*n + 1
right child = 2*n + 2
아이템 삭제 - ReheapDown
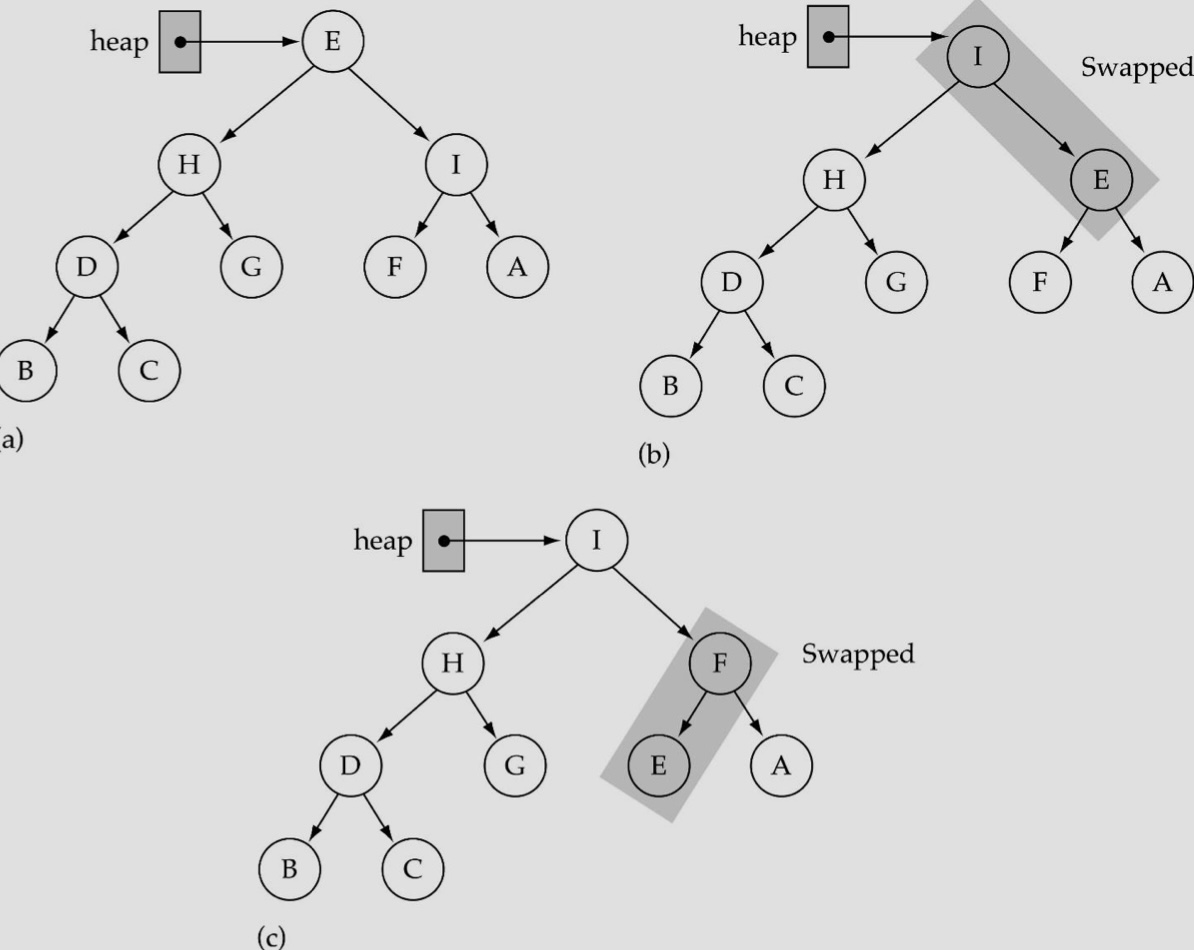
root의 값이 Heap의 특성을 위배하였을 때, 그 하위 레벨로 내려가며 제자리를 찾는 함수
아이템을 삭제할 때 사용된다.
Heap에서 가장 최댓값을 취하고, 다시 Heap의 특성을 회복하는 방법
- Root의 아이템을 사용함.
- 마지막 레벨에서, 가장 오른쪽에 위치한 아이템을 root에 놓음.
- ReheapDown 진행
아이템 추가 - ReheapUp
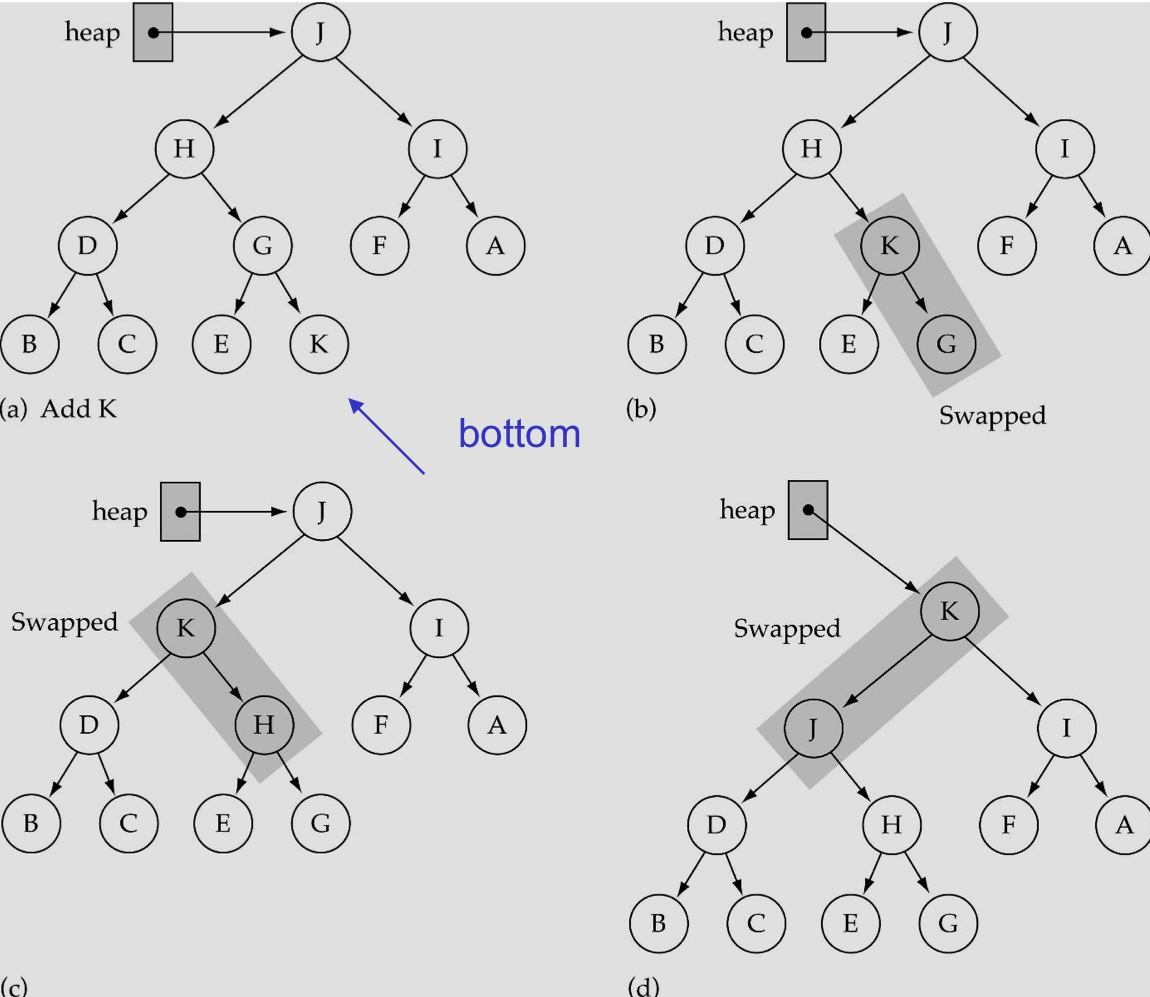
마지막 레벨의 가장 오른쪽 노드가 Heap의 특성을 위배하였을 때 사용하는 함수.
주로 아이템을 추가할 때 사용함
Heap에서 아이템을 추가한 후 다시 Heap의 특성을 회복하는 방법
- Heap의 가장 마지막 레벨에서, 빈 곳 중 가장 왼쪽에 아이템을 추가함.
- ReheapUp 진행.
Priority Queue (우선순위 큐)
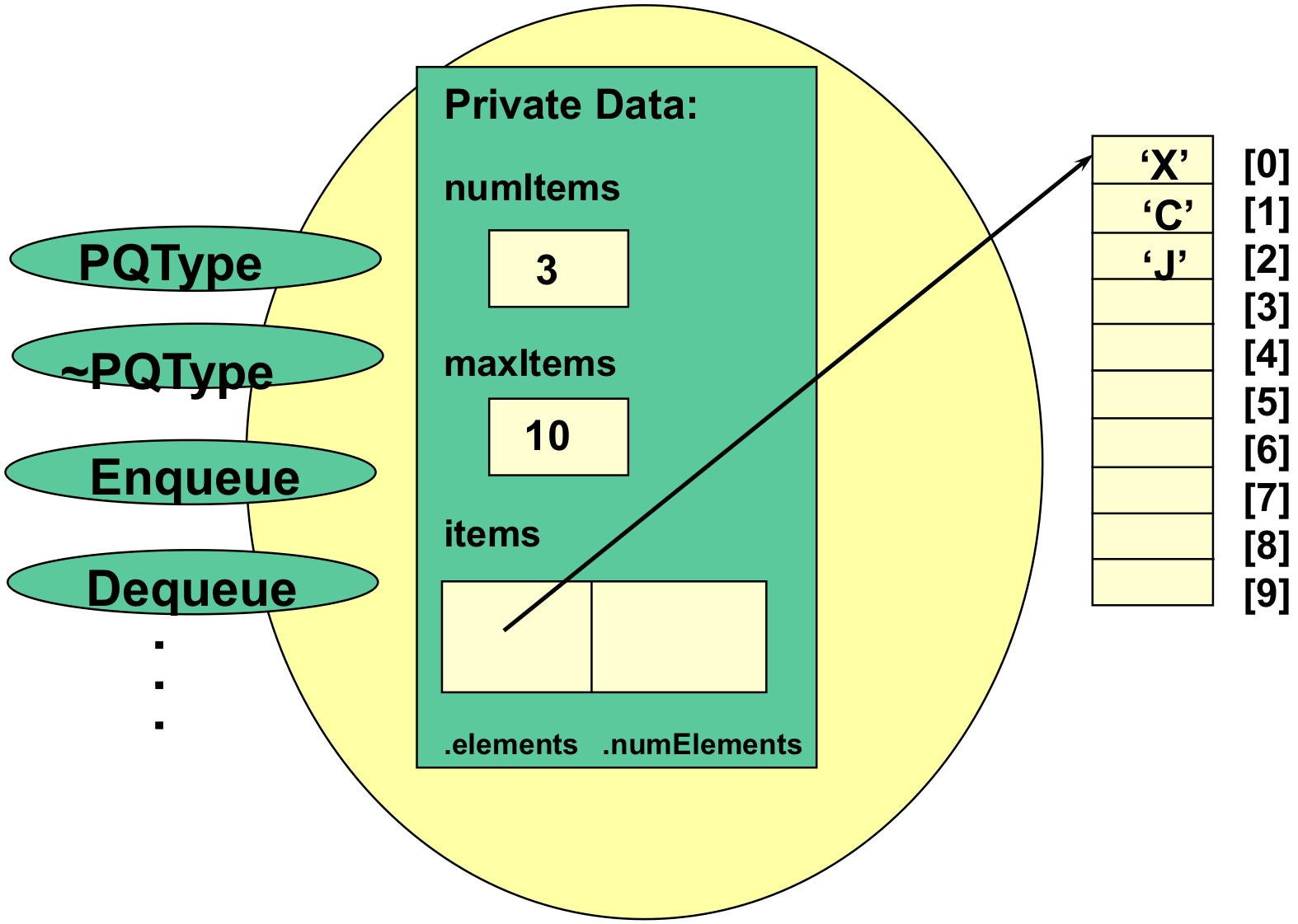
일반적인 Queue는 FIFO(First In First Out)을 따라, 가장 먼저 삽입된 값이 가장 먼저 나온다.
그러나 이와 다르게 Priority Queue는, 우선순위를 유지하여 우선순위가 높은 값이 먼저 나오는 자료구조이다.
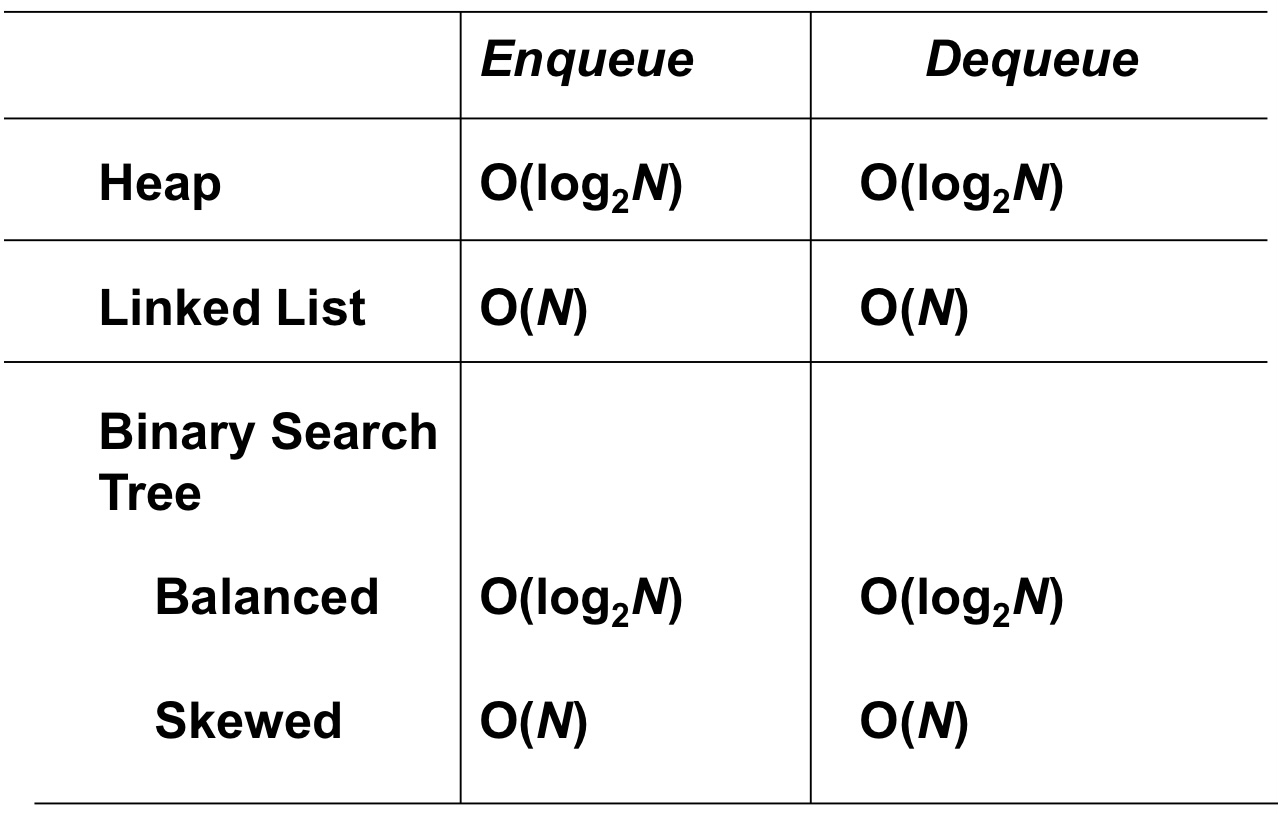
- Unsorted List: Dequeue가 시간이 많이 소요됨. O(n)
- Array-Based Sorted List: Enqueue가 시간이 많이 소요됨. O(n)
- Binary Search Tree: Enqueue / Dequeue 모두 평균적으로 O(log n)만큼의 시간 소요
- Heap: 최악의 케이스에도 O(log n)만큼의 시간을 보장
결론적으로, 데이터 삽입/삭제 모두 빠른 시간을 보장해 주는 자료구조이며
이는 Heap의 정의대로, Heap을 이용하여 구현됨.
코드
HeapType.h
#pragma once
template<class ItemType>
struct HeapType
{
void ReheapDown(int root, int bottom);
void ReheapUp(int root, int bottom);
ItemType* elements; // 배열 동적 할당
int numElements;
};HeapType.cpp
#include "HeapType.h"
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
template<class ItemType>
void HeapType<ItemType>::ReheapDown(int root, int bottom)
{
// 전제조건: root노드가 Heap의 특성을 위배함.
int maxChild;
int rightChild;
int leftChild;
leftChild = root * 2 + 1;
rightChild = root * 2 + 2;
if (leftChild <= bottom)
{
if (leftChild == bottom) // 자식이 하나일 경우
maxChild = leftChild;
else // 자식이 두 개인 경우
{
// maxChild: 두 자식 중 큰 자식을 택함.
if (elements[leftChild] <= elements[rightChild])
maxChild = rightChild;
else
maxChild = leftChild;
// root보다 큰 값을 갖는 자식과, root를 swap하고
// 해당 자식을 ReheapDown함으로써 원위치로 보냄.
if (elements[root] < elements[maxChild])
{
swap(elements[root], elements[maxChild]);
ReheapDown(maxChild, bottom);
}
}
}
}
template<class ItemType>
void HeapType<ItemType>::ReheapUp(int root, int bottom)
{
// 전제조건: 마지막 레벨의 가장 오른쪽 노드가
// Heap의 특성을 위배함.
int parent;
if (bottom > root) // tree가 비어 있지 않고 존재함
{
parent = (bottom - 1) / 2;
if (elements[parent] < elements[bottom])
{
// parent와 rightmost bottom 값을 바꾸고, 다시 ReheapUp 진행
swap(elements[parent], elements[bottom]);
ReheapUp(root, parent);
}
}
}PQType.h
#pragma once
class FullPQ {};
class EmptyPQ {};
template<class ItemType>
class PQType
{
public:
PQType(int max);
~PQType();
void MakeEmpty();
bool IsEmpty() const;
bool IsFull() const;
void Enqueue(ItemType newItem);
void Dequeue(ItemType& item);
private:
int length;
HeapType<ItemType> items;
int maxItems;
};PQType.cpp
#include "PQType.h"
template<class ItemType>
PQType<ItemType>::PQType(int max)
{
maxItems = max;
items.elements = new ItemType[max];
length = 0;
}
template<class ItemType>
void PQType<ItemType>::MakeEmpty()
{
length = 0;
}
template<class ItemType>
PQType<ItemType>::~PQType()
{
delete[] items.elements;
}
template<class ItemType>
bool PQType<ItemType>::IsEmpty() const
{
return length == 0;
}
template<class ItemType>
bool PQType<ItemType>::IsFull() const
{
return length == maxItems;
}
template<class ItemType>
void PQType<ItemType>::Dequeue(ItemType& item)
{
if (length == 0)
throw EmptyPQ;
else
{
item = items.elements[0];
items.elements[0] = items.elements[length - 1];
length--;
items.ReheapDown(0, length - 1);
}
}
template<class ItemType>
void PQType<ItemType>::Enqueue(ItemType newItem)
{
if (length == maxItems)
throw FullPQ;
else
{
length++;
items.elements[length - 1] = newItem;
items.ReheapUp(0, length - 1);
}
}