연결 리스트 (Linked List)
배열(Array)는 생성 시 길이가 고정되어 있다. (정적 메모리 할당)
이를 보완하기 위해, 연결 리스트는 아이템을 삽입해야 하는 상황이 오면, 그만큼의 공간을 동적으로 할당받는다.
각 노드는 해당 노드의 정보인 info와, 다음 노드를 가리키는 next 변수를 가짐.
-
Single Linked List: 기본 연결 리스트.
-
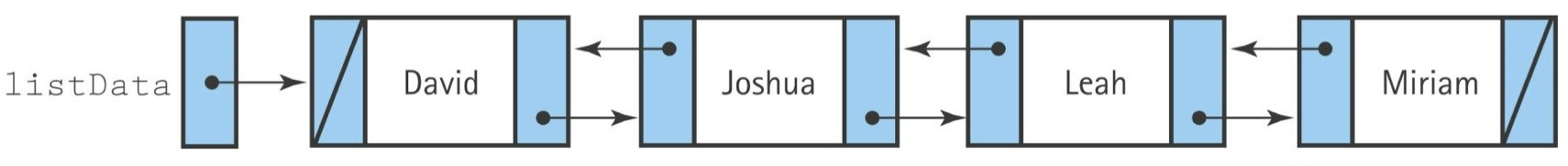
Doubly Linked List: 한 노드가 successor를 가리키는 pointer와 predecessor를 가리키는 pointer 모두 가짐
-
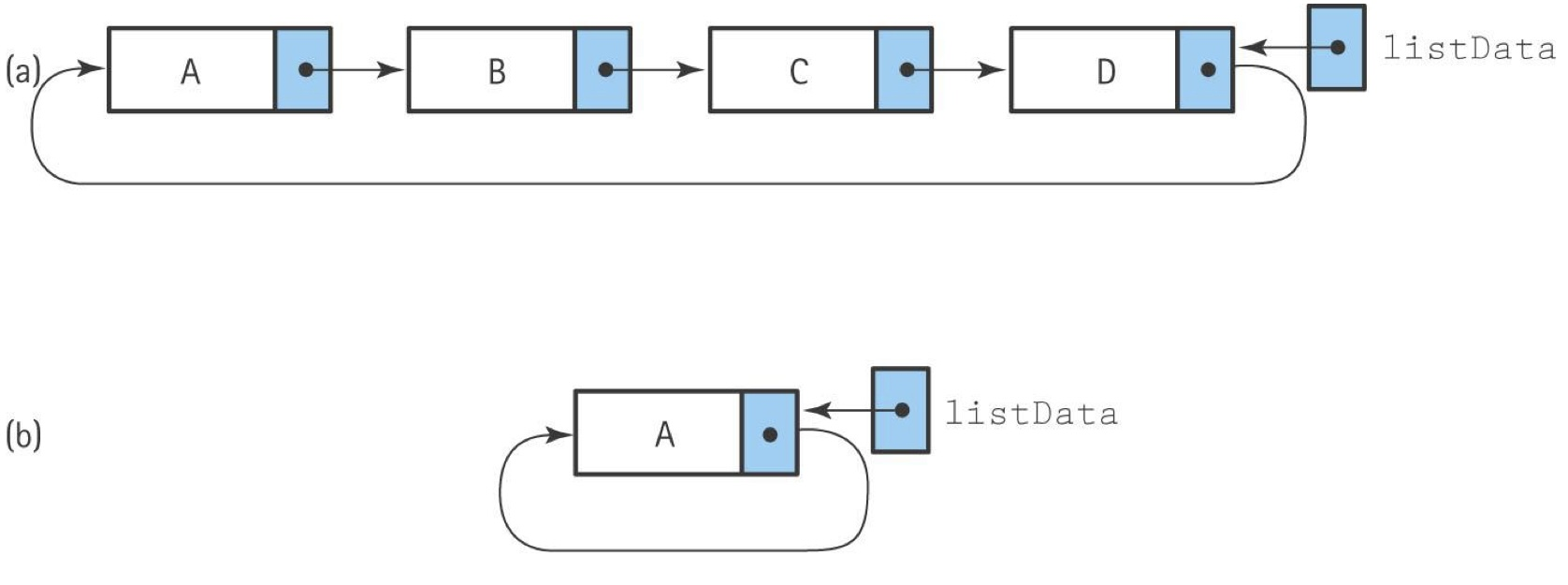
Circular Linked List: 모든 노드가 successor를 가짐, 마지막 노드의 successor는, 가장 처음 노드
구현
LinkedList.h
#pragma once
#include "NodeType.h"
template<class ItemType>
class LinkedList
{
public:
LinkedList();
~LinkedList();
void MakeEmpty();
bool IsFull() const;
int LengthIs() const;
void RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found);
void InsertItem(ItemType item);
void DeleteItem(ItemType item);
void ResetList();
void GetNextItem(ItemType& item);
private:
NodeType<ItemType>* listData; // 맨 첫 번째 데이터
int length;
NodeType<ItemType>* currentPos;
};LinkedList.cpp
#include "LinkedList.h"
#include <stdexcept>
template<class ItemType>
LinkedList<ItemType>::LinkedList()
{
length = 0;
listData = nullptr;
currentPos = nullptr;
}
template<class ItemType>
LinkedList<ItemType>::~LinkedList()
{
NodeType<ItemType>* tempNode;
currentPos = listData;
while (currentPos != nullptr)
{
tempNode = currentPos;
currentPos = currentPos->next;
delete tempNode;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
void LinkedList<ItemType>::MakeEmpty()
{
NodeType<ItemType>* tempNode;
currentPos = listData;
while (currentPos != nullptr)
{
tempNode = currentPos;
currentPos = currentPos->next;
delete tempNode;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
bool LinkedList<ItemType>::IsFull() const
{
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
try
{
// 새로운 Node를 받는 것이 가능함 => false
location = new NodeType<ItemType>;
delete location;
return false;
}
catch (std::bad_alloc exception)
{
// Node를 받으려 해도 안 받아질 때 => true
return true;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
int LinkedList<ItemType>::LengthIs() const
{
return length;
}
template<class ItemType>
void LinkedList<ItemType>::RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found)
{
bool moreToSearch;
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
location = listData;
found = false;
moreToSearch = (location != nullptr);
while (moreToSearch && !found)
{
if (item == location->info)
{
item = location->info;
found = true;
}
else
{
location = location->next;
moreToSearch = (location != nullptr);
}
}
}
template<class ItemType>
void LinkedList<ItemType>::InsertItem(ItemType item)
{
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
location = new NodeType<ItemType>;
location->info = item;
location->next = listData;
listData = location;
length++;
}
template<class ItemType>
void LinkedList<ItemType>::ResetList()
{
currentPos = listData;
}
template<class ItemType>
void LinkedList<ItemType>::GetNextItem(ItemType& item)
{
item = currentPos->info;
currentPos = currentPos->next;
}Delete 시 주의 사항
(item == location->info)가 아닌, (item == (location->next)->info)
왜냐하면, 어느 노드를 삭제하면, 해당 노드를 가리킨 이전 노드의 next 포인터도 변경해 주어야 하는데,
전자의 경우처럼 진행할 경우, 이전 노드로 되돌아갈 수 없기 때문이다
template<class ItemType>
void LinkedList<ItemType>::DeleteItem(ItemType item)
{
NodeType<ItemType>* location = listData;
NodeType<ItemType>* tempLocation;
if (item == listData->info)
{
tempLocation = location;
listData = listData->next;
}
else
{
while (!(item == (location->next)->info))
location = location->next;
tempLocation = location->next;
location->next = (location->next)->next;
}
delete tempLocation;
length--;
}비교
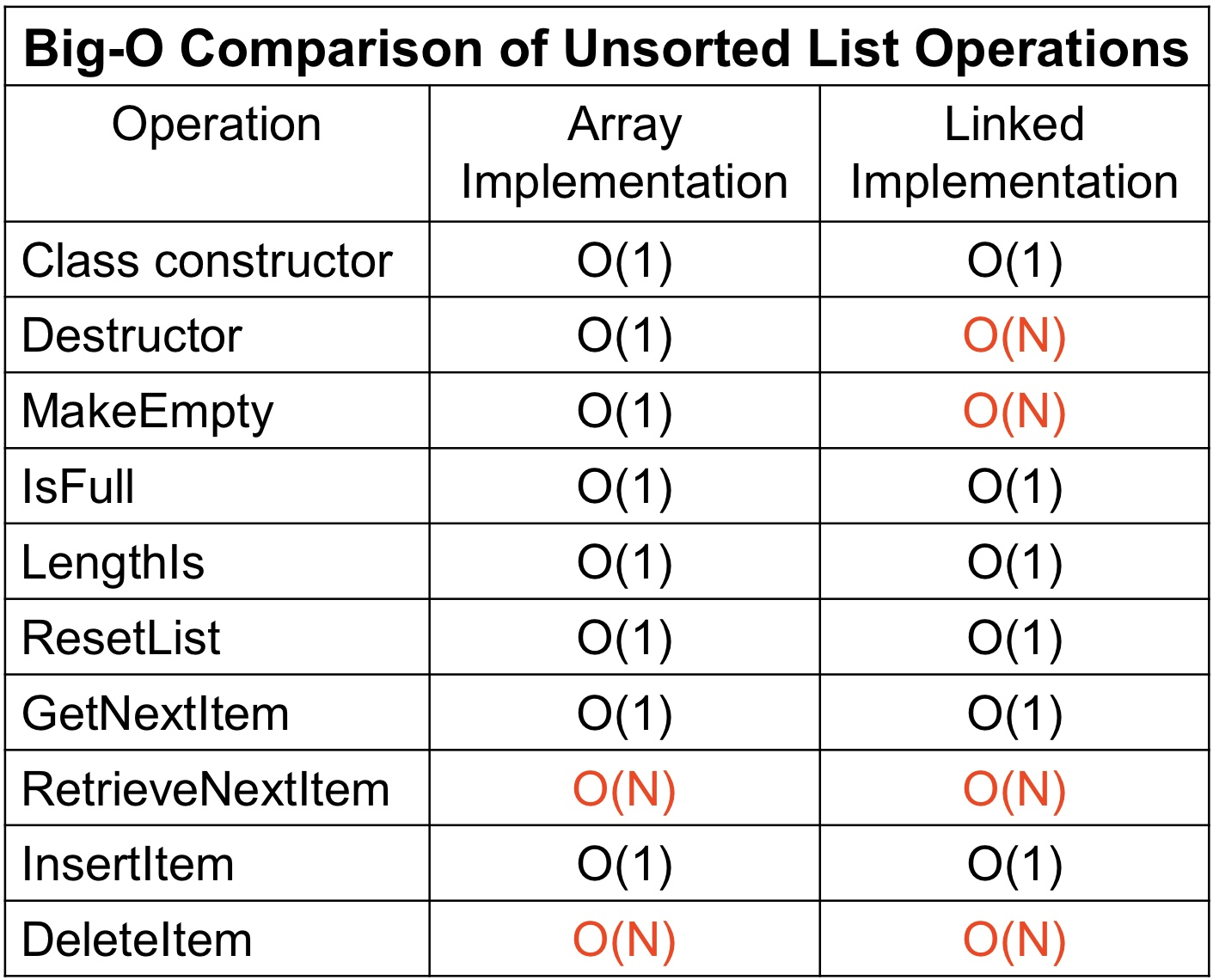
- 데이터 접근 시, Array는 Random Access를 지원하고 Linked List는 Sequential Access를 지원한다. 때문에 특정 요소에 접근하는 경우 Array가 효율적이며, Linked List는 좋지 않다.
- 검색에도 문제가 생긴다. Binary Search를 사용하지 못하며, 순차적으로 접근해야 하기 때문에 O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다.
표에도 나와 있듯 Linked List가 Array보다 시간복잡도가 안 좋을 수 있다. 그러나 Linked List는 공간의 효율성에서 이득을 취했기 때문에, 상황에 따라 방법을 선택하면 된다.
참고
