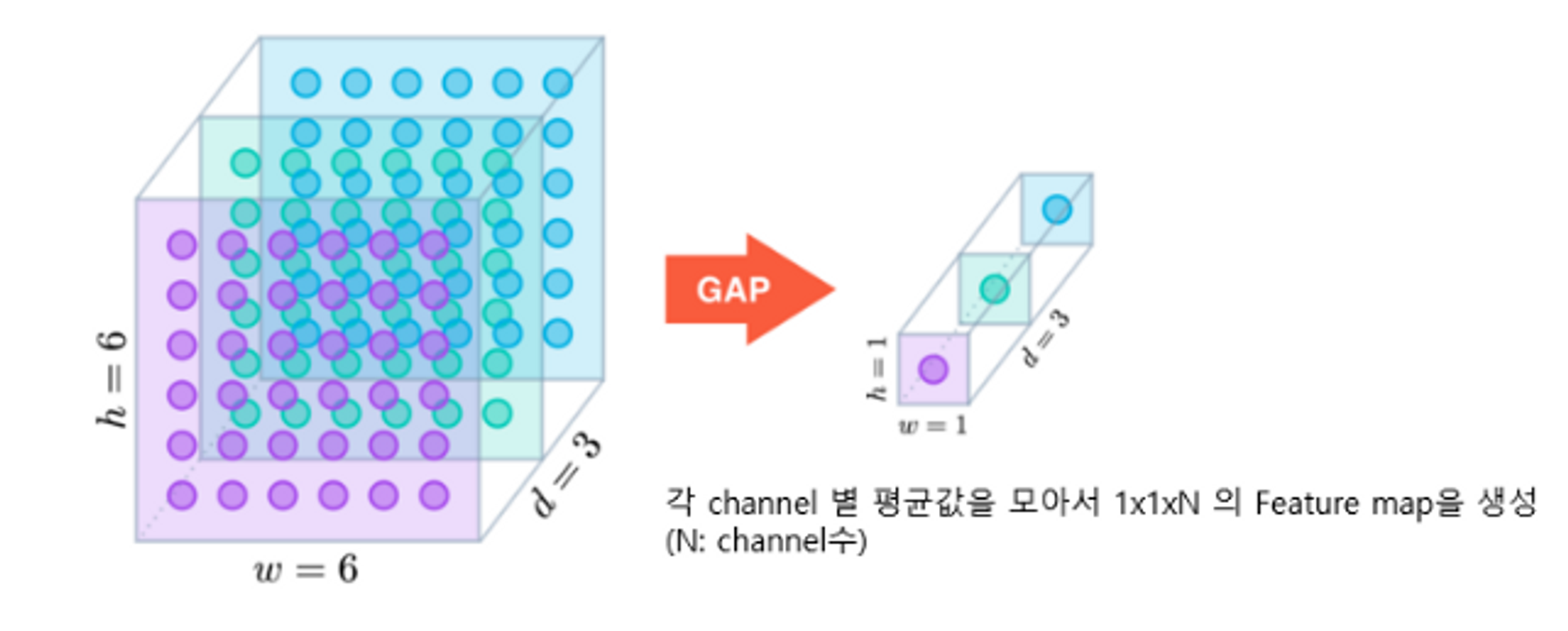
GlobalAveragePooling (GAP)
- CNN의 결과는 3차원이다. → 이 결과를 Dense Layer는 1차원을 받기 때문에 이전에는 Flatten Layer를 사용하여 1차원으로 변경하였다. → 이제는 Flatten 대신 GlobalAverage를 사용할 것이다.
- 각 Channel 별 평균값을 모아서 1x1xN의 Feature map을 생성(N:channel수)
- 4x4x512 → flatten하면 8192개가되고 → unit512인 Dense Layer에 입력 시 8193(+bias) X 512 = 4194816개의 weight가 생긴다. → 처리해야할 파라미터가 너무 많아진다.
but
- 4x4x512→GlobalAverage를 사용하여 1x1x512 → unit512인 Dense Layer에 입력 시 513(+bias)X512 = 262656개의 weight가 생긴다. → flatten사용 시 보다 처리해야 할 파라미터가 줄어든다.
Pretrained Model
- 이전에 누군가가 다른목적을 위해 만들어 학습까지 해놓은 모델이다.
- 내가 만들려는 모델과 비슷한 경우 Pretrained Model을 내가 해결하려는 모델에 포함시켜 사용한다.
- 이런 방식을 Transfer Learning(전이학습)이라고 한다.
Keras에서 제공하는 Pretrained Model
- tensorflow.keras.applications 패키지를 통해 제공
- Modules
- 각 모델별 입력 Image 전처리 함수 제공(이미지 넣어 내가 전처리해서 줄게!)
- Functions
- 각 모델 생성함수
- 이미 만들어진 모델이니 여기서 학습된 상황과 동일하면 그냥 학습하지않고 사용해도된다.
- 모델 생성함수의 주요 매개변수
weights: 우리가 아닌 기존의 모델에 학습된 weight 지정(생략가능)include_top: fully connected layer(분류기)를 포함할지 여부. True 포함시킴, False: 포함 안 시킴- False를 지정하면 Feature Extractor인 Convolution Layer들로만 구성된 모델이 생성된다.
input_shape: Input(입력) 이미지의 크기 shape. 3D 텐서로 지정. (높이, 너비, 채널). 기본값: (224,224,3)
딥러닝 모델기반 application 개발시 대부분 Transfer Learning(전이학습)을 이용한다.
왜냐하면 다양한 분야의 모델들이 구현되어 공개 되어 있으며 학습된 Parameter들도 제공되고 있기때문이다.
→ paperswithcode에서 State Of The Art(SOTA) 논문들과 그 구현된 모델을 확인할 수 있다.
State Of The Art(SOTA): 특정 시점에 특정 분야에서 가장 성능이 좋은 모델을 말한다.
그럼 Pretrained Model을 예제로 보자.
from tensorflow.keras.applications import VGG16
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input, decode_predictions
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
import numpy as np
# VGG16 모델을 ImageNet 가중치와 입력 크기 (224, 224, 3)로 불러옵니다.
vgg16 = VGG16(weights='imagenet', input_shape=(224, 224, 3))
# 이미지를 불러와 전처리 작업을 수행합니다.
img_path = 'test_img/bicycle.jpg'
input_array = img_to_array(load_img(img_path, target_size=(224, 224)))[np.newaxis, ...]
input_tensor = preprocess_input(input_array)
# 이미지를 VGG16 모델을 사용하여 추론합니다.
pred = vgg16.predict(input_tensor)
# 예측된 클래스 인덱스를 출력합니다.
print("추론한 클래스 index:", pred[0].argmax(axis=-1))
# 상위 3개의 클래스와 해당 확률을 출력합니다.
label_cls = decode_predictions(pred, top=3)
for idx, (_, cls_name, proba) in enumerate(label_cls[0], start=1):
print(f"{idx}. {cls_name}: {proba*100:.2f}%")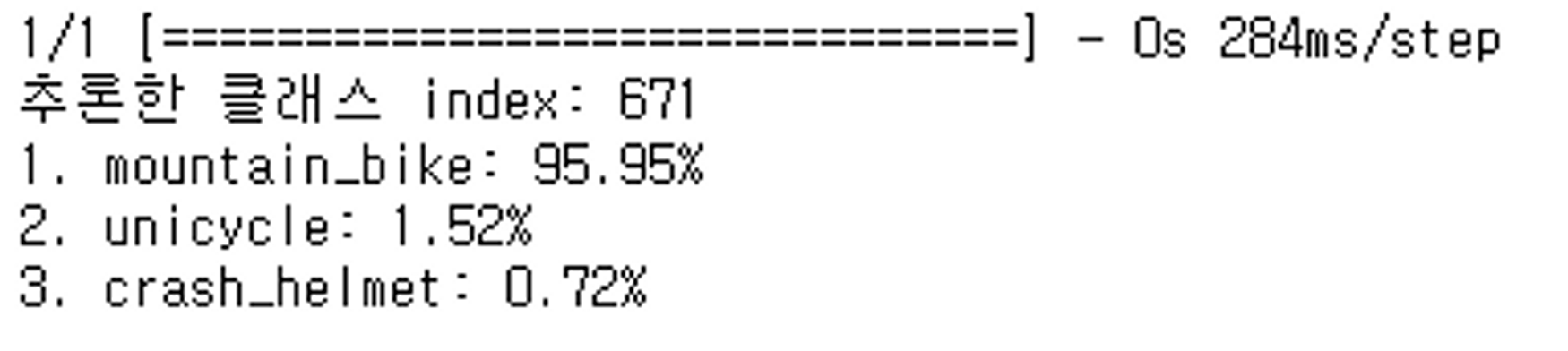
Transfer learning (전이학습)
- 사전에 학습된 모델의 구조와 파라미터를 재사용해서 새로운 모델를 만든 뒤 해결하려는 문제를 위해 내 데이터(Custom data)를 재학습시킨다.
- 보통 Pretrained Model에서 Feature Extraction(CNN) 부분을 사용한다.
- Computer Vision 문제의 경우 Bottom 쪽의 Convolution Layer(Feature Extractor)들은 이미지에 나타나는 일반적인 특성을 추출하므로 다른 대상을 가지고 학습했다고 하더라도 재사용할 수 있다.
- Top 부분 Layer 부분은 특히 출력 Layer의 경우 대상 데이터셋의 목적에 맞게 변경 해야 하므로 재사용할 수 없다.

⇒ 순전파시에만 학습시키고 역전파시에는 학습을 시키지 않겠다는 것이다.
⇒ 이미 다양한 이미지를 가지고 학습이 완료되어있는것이기 때문에 학습을 시키지 않아되고 순전파시에만 변경되는 weight만 재학습시키고 굳이 역전파까지 할 필요없다는 것이다.
# VGG16 모델 로드
vgg16_2 = applications.VGG16(include_top=True)
# VGG16 모델의 학습 가능 여부 확인
vgg16_2.trainable
# 출력: True
# VGG16 모델의 모든 레이어를 학습 불가능하게 설정
vgg16_2.trainable = False
# 학습 불가능으로 설정한 VGG16 모델의 구조 출력
vgg16_2.summary()
# "block1_conv1" 레이어 가져오기
conv1 = vgg16_2.get_layer("block1_conv1")
# "block1_conv1" 레이어의 학습 가능 여부 확인
conv1.trainable
# 출력: False
# "block1_conv1" 레이어를 학습 가능하도록 설정
conv1.trainable = True
# "block1_conv1" 레이어의 학습 가능 여부 확인
conv1.trainable
# 출력: True
# 학습 가능한 설정 이후 VGG16 모델의 구조 출력
vgg16_2.summary()이미지 다운로드
!pip install gdown --upgrade
import gdown
import os
from zipfile import ZipFile
url = 'https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1YIxDL0XJhhAMdScdRUfDgccAqyCw5-ZV'
fname = 'cats_and_dogs_small.zip'
gdown.download(url, fname, quiet=False)
with ZipFile('cats_and_dogs_small.zip') as zf:
zf.extractall("data/cats_and_dogs_small") # 압축풀 디렉토리 경로를 넣어서 푼다.전처리 및 데이터셋 로드
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator, load_img, img_to_array
import numpy as np
IMAGE_SIZE = 224
N_EPOCH = 10
N_BATCH = 100
def predict_func(image_path, model, preprocess_input):
"""
이미지 경로를 받아서 모델을 이용해 추론결과를 반환하는 함수
[parameter]
image_path: str - 추론한 이미지의 경로
model: Model객체 - 개/고양이 분류를 위해 학습된 딥러닝 모델
preprocess_input: function - 이미지 전처리 함수 객체
[반환값]
tuple: (예측확률, 예측라벨, 예측라벨이름)
"""
class_name = ["cat", "dog"]
# 이미지 로딩후 배열로 변환
img_array = img_to_array(load_img(image_path, target_size=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE)))[np.newaxis, ...]
# 전처리
input_tensor = preprocess_input(img_array)
# 추론
pred = model.predict(input_tensor)
result_proba = pred[0, 0] # 2차원[[0.7]] => 0.7
result_class = np.where(result_proba >= 0.5, 1, 0) # 1 # 2진분류:np.where(), 다중분류: np.argmax()
result_class_name = class_name[result_class] # dog
return result_proba, result_class, result_class_name
def get_generator(preprocess_input):
"""
cat/dog 데이터의 train/validation/test 용 ImageDataGenerator를 반환하는 함수
[parameter]
preprocess_input: function - 전처리용 함수
[return]
tuple: (train_dataset_iterator, val_dataset_iterator, test_dataset_iterator)
"""
train_dir = 'data/cats_and_dogs_small/train/'
val_dir = 'data/cats_and_dogs_small/validation/'
test_dir = 'data/cats_and_dogs_small/test/'
# ImageDataGenerator 생성 - train: image augmentation을 적용, 공통: preprocessing_input 함수 적용
train_gen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input,
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='constant'
)
val_gen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
test_gen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
train_iter = train_gen.flow_from_directory(train_dir, target_size=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE), batch_size=N_BATCH, class_mode='binary')
val_iter = val_gen.flow_from_directory(val_dir, target_size=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE), batch_size=N_BATCH, class_mode='binary')
test_iter = test_gen.flow_from_directory(test_dir, target_size=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE), batch_size=N_BATCH, class_mode='binary')
return train_iter, val_iter, test_iter
# ImageDataGenerator 생성
train_iter, val_iter, test_iter = get_generator(applications.vgg16.preprocess_input)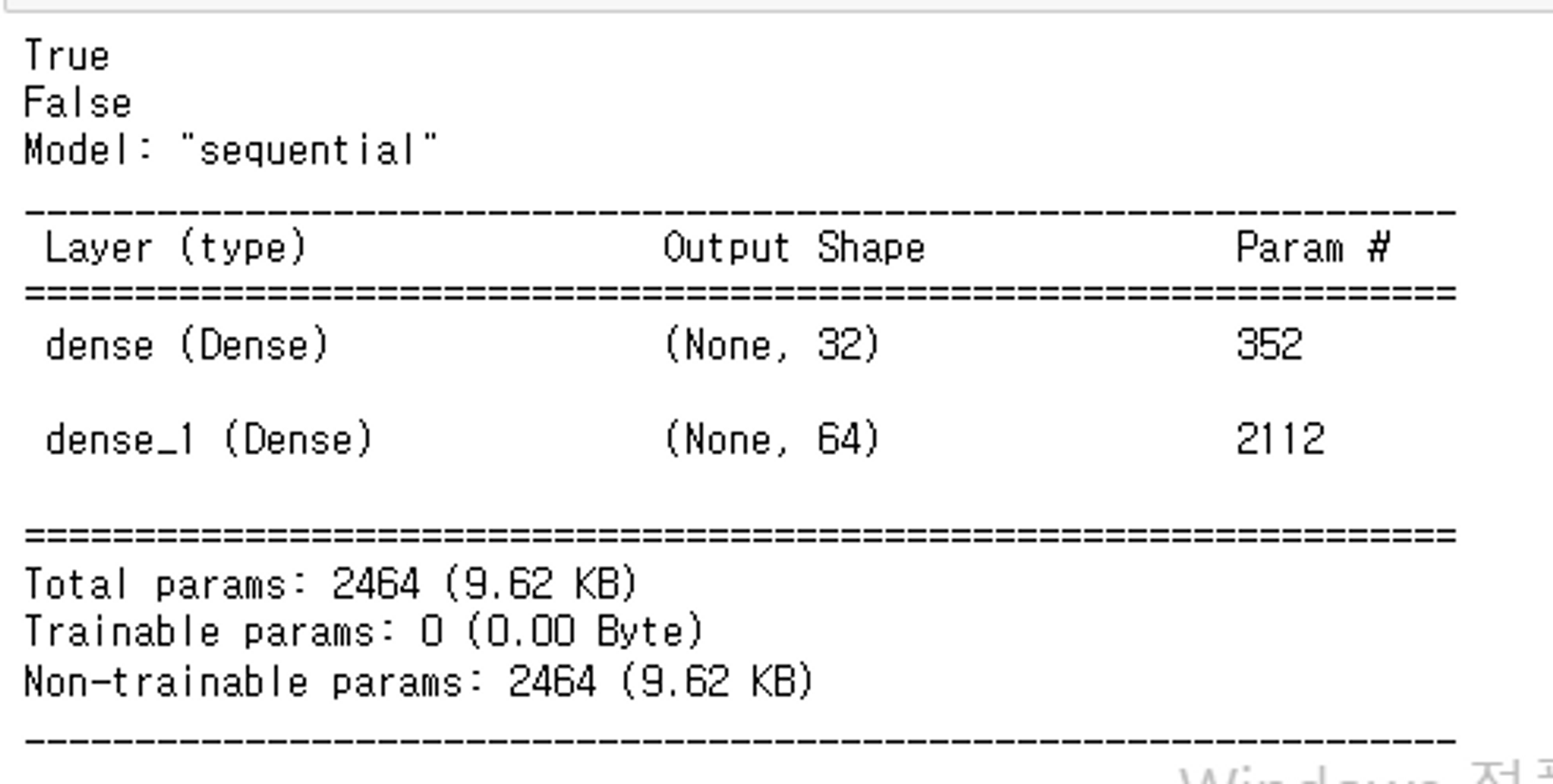
모델정의
- frozon
- 학습시 파라미터가 업데이트 되지 않도록 한다.
model.trainable = Falselayer.trainable = False
dense1 = layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')
temp_model = keras.Sequential()
temp_model.add(layers.InputLayer(input_shape=(10, )))
temp_model.add(dense1)
temp_model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))
print(temp_model.trainable)
temp_model.trainable = False
print(temp_model.trainable)
temp_model.summary()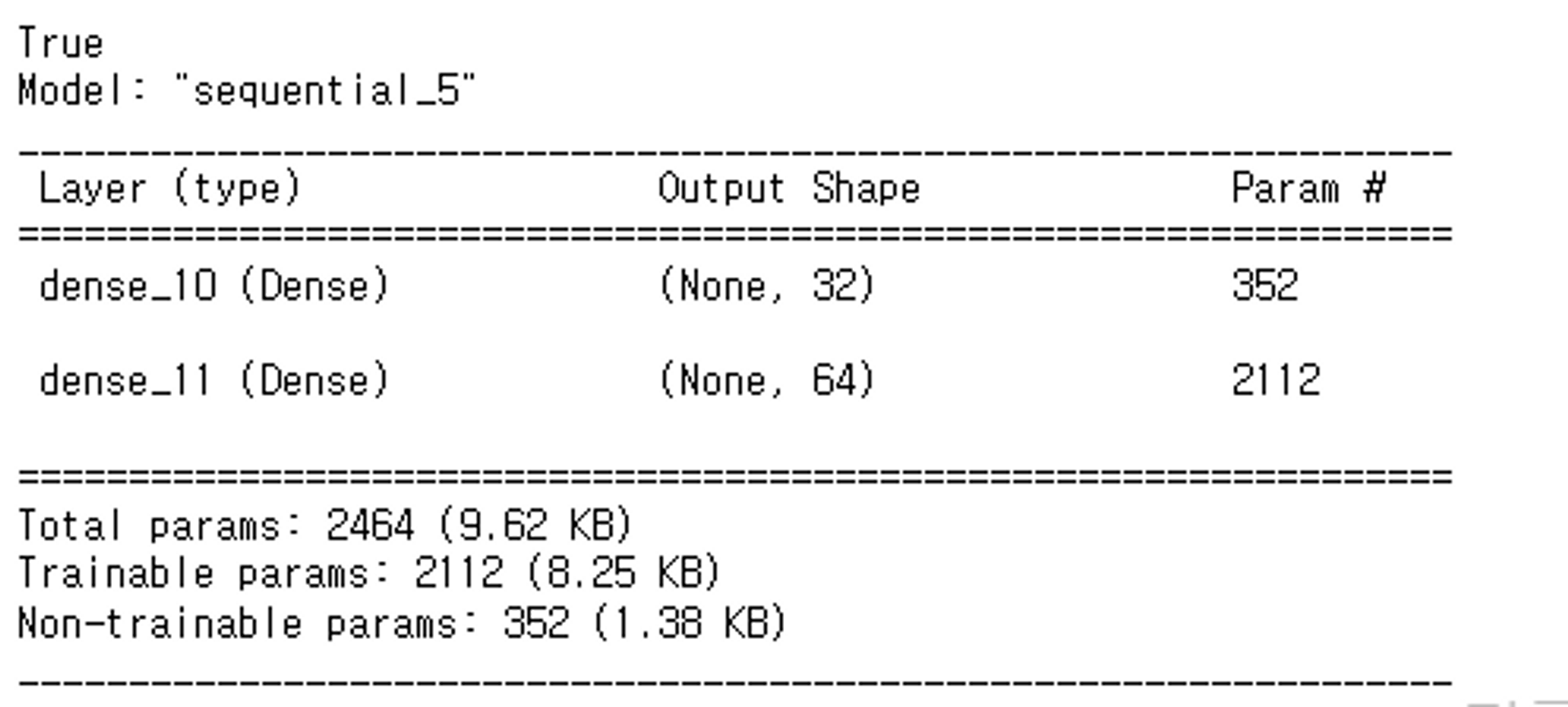
특정 trainable 속성을 변경
dense1 = layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')
print(dense1.trainable)
dense1.trainable = False # 특정 layer의 trainable 속성을 변경
temp_model = keras.Sequential()
temp_model.add(layers.InputLayer(input_shape=(10, )))
temp_model.add(dense1)
temp_model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))
temp_model.summary()
model에 model 추가
final_model = keras.Sequential()
final_model.add(layers.InputLayer(input_shape=(10, )))
final_model.add(temp_model) # 모델을 Layer로 추가.
final_model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
final_model.summary()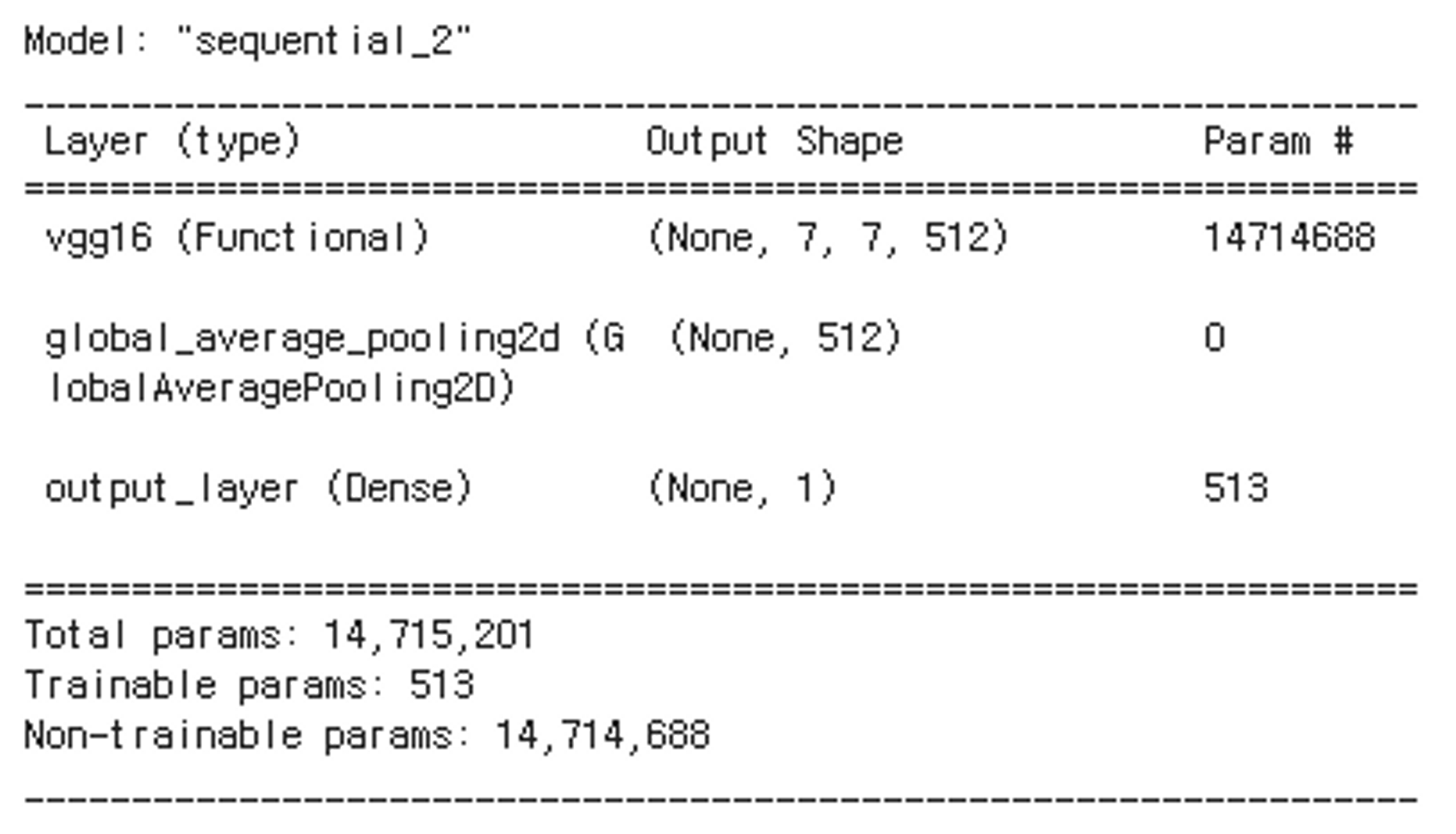
Cats and Dogs 분류 모델 정의
def get_model_1(backbone):
"""
매개변수로 Feature Extractor(Backbone) 모델을 받아서 개/고양이를 분류하는 모델을 생성.
[parameter]
backbone: Model - Pretrained backbone 네트워크 모델
[return]
model 객체 - 추론기를 추가한 모델
"""
# 모델 정의
model = keras.Sequential()
backbone.trainable = False
model.add(backbone)
model.add(layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D())
model.add(layers.Dense(units=1, activation='sigmoid', name='output_layer'))
# 모델 컴파일
model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE),
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
backbone = applications.VGG16(include_top=False, input_shape=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3))
model_1 = get_model_1(backbone)
model_1.summary()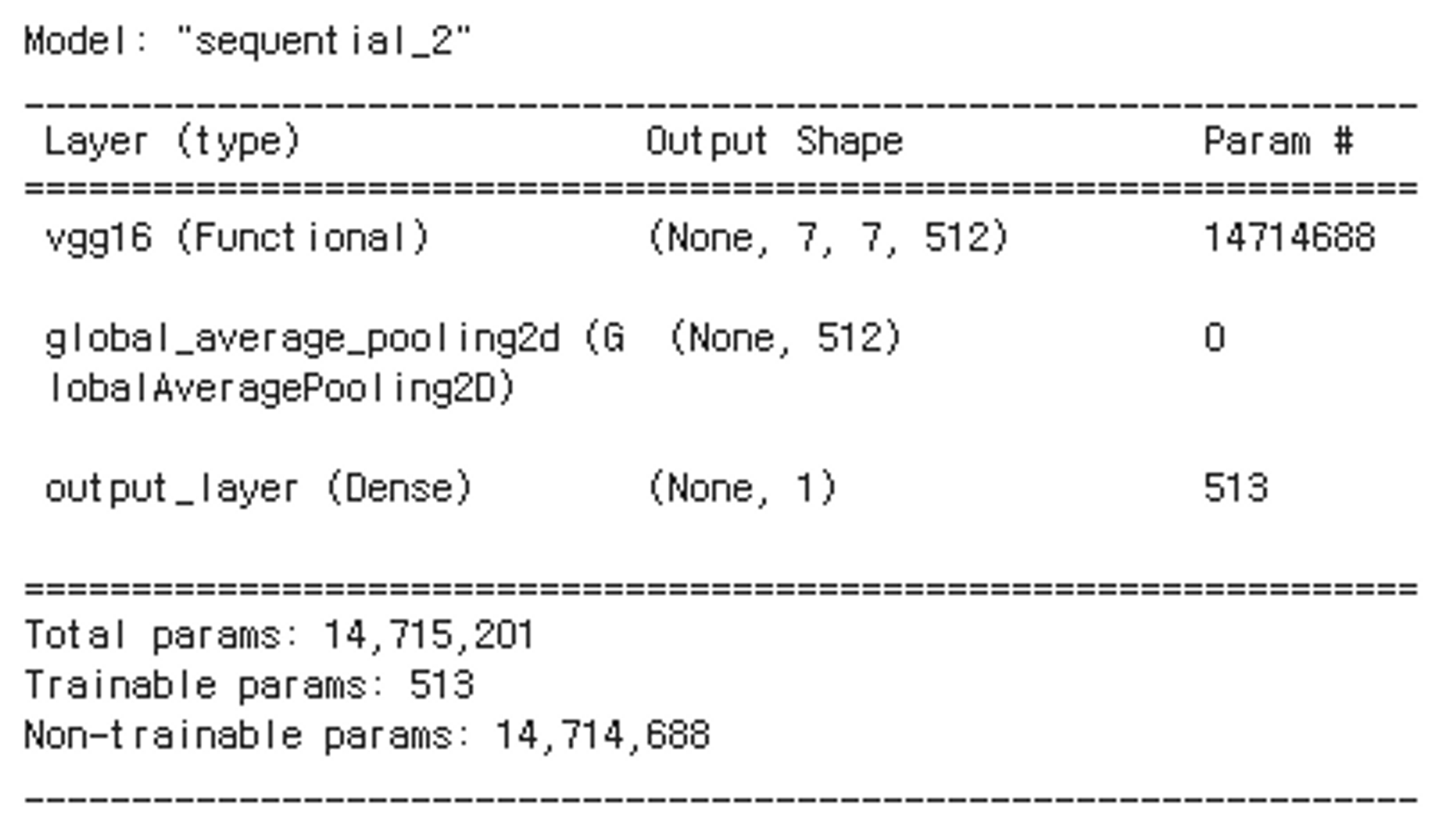
학습& 평가
g_drive_root = "/content/drive/MyDrive"
save_path = os.path.join(g_drive_root, 'SAVED_MODELS', 'cat_dog_transfer_learning')
mc_callback = keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(save_path, save_best_only=True, save_weights_only=True, verbose=1)
es_callback = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(patience=10, verbose=2)
hist = model_1.fit(train_iter,
epochs=N_EPOCH,
steps_per_epoch=len(train_iter),
validation_data=val_iter,
validation_steps=len(val_iter),
callbacks=[mc_callback, es_callback])
model_1.evaluate(test_iter)
새로운 데이터 추론
img_path = 'dog.jpg'
predict_func(img_path, model_1, applications.vgg16.preprocess_input)
Fine-tuning(미세조정)
- Transfer Learning을 위한 Pretrained 모델을 내 데이터셋(Custom Dataset)으로 재(추가)학습시키는 것을 fine tunning 이라고 한다. → Feature Extractor(backbone)의 가중치들도 조정한다.
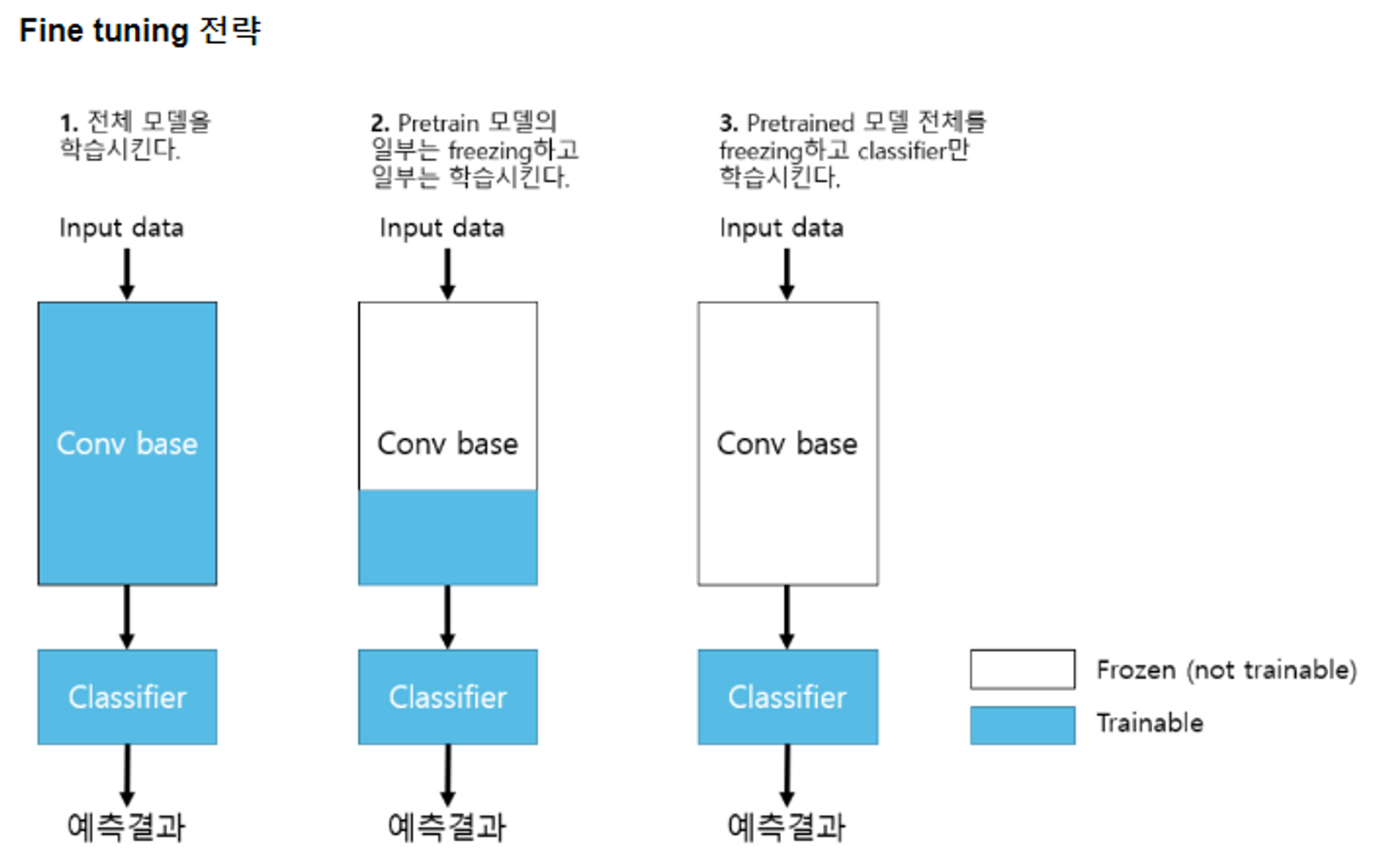
⇒ 추론기는 3경우 모두 학습시키는 것을 볼 수 있다.
- Custom dataset: 내가 학습시키고자 하는 dataset 1번 2번 전략을 Fine tuning 이라고 한다.
데이터 셋은 크고,유사도가 낮다는 것 → Pretrained은 자동차이고 Custom은 뼈일 경우 유사도가 낮다.
데이터 셋은 크고 유사도가 높다 → Pretrained은 택시이고 Custom은 스포츠가 인경우 같은 자동차라 겹치는 부분이 많지만 데이터가 많으므로 일부분은 학습시켜준다.
많은 도움이 되었습니다, 감사합니다.