R-CNN(Region-based Convolution Neural Networks)
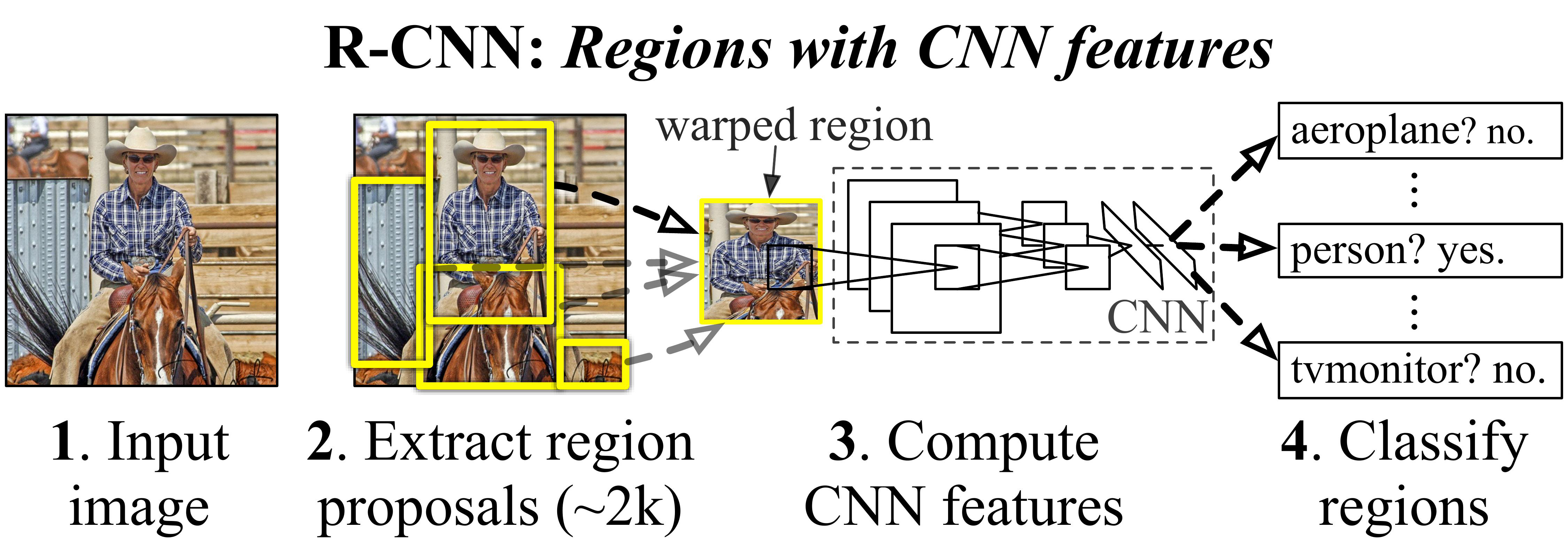
R-CNN은 2014년에 처음 소개된 Object Detection 모델로 Region을 input으로 CNN 모델을 사용한다. 이 모델은 기존의 Object Detection 방법들과 달리 딥러닝을 이용하여 객체의 위치를 정확히 찾아내고 분류한다.
RCNN의 주요 구성 요소
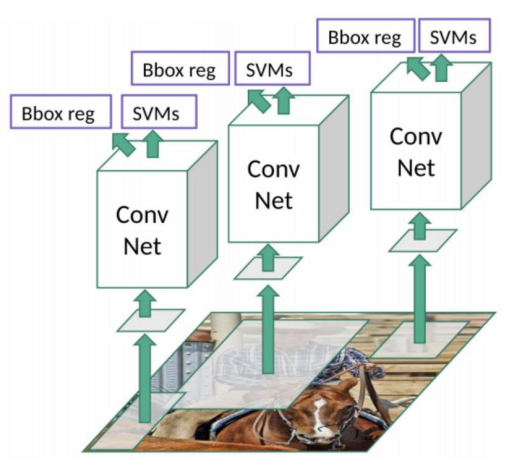
- 1. Region Proposals 추출하기 : Selective Search와 같은 알고리즘을 사용하여 이미지에서 잠재적인 Region Proposals를 추출한다.
- 2. CNN Feature 추출 : 각각의 후보 영역을 같은 크기로 변환한 후 CNN을 토오가시켜 특성을 추출한다.
- 3. SVM 분류 : 추출된 특성을 기반으로 각 후보 영역에 대해 SVM(Support Vetctor Machine)을 사용하여 객체의 클래스를 분류한다.
- 4. Bounding Box Regression : Bounding Box의 위치를 더 정확하게 조정하기 위해 회귀 모델을 적용한다.
RCNN Train 방법
- 1. CNN Pre-train : R-CNN은 Pre-trained 된 CNN(ex: AlexNet, VGG)을 사용하여 이미지의 특성을 추출한다. 이 단계는 일반적으로 ImageNet과 같은 대규모 데이터셋에서 수행된다.
- 2. Fine-tuning for Object Detection : Pre-trained 된 CNN 모델을 Object Detect 작업에 맞게 Fine-tuning한다. 이때 Selective Search로 추출된 후보 영역을 사용한다.
- 3. SVM train : CNN을 통해 얻은 특성에 대해 각 클래스별로 SVM을 train한다. 이 SVM은 각 후보 영역이 특정 클래스에 속하는지 여부를 판별한다.
- 4. Bounding Box Regression : Bounding Box의 위치를 조정하기 위해 Regression 모델을 train한다. 이 모델은 CNN의 feature를 입력으로 받아 Bounding Box의 좌표를 조정한다.
Loss function
- 1. Classification Loss : SVM을 훈련할 때 사용되며 객체가 어떤 클래스에 속하는지를 정확하게 분류하기 위한 것이다. 일반적으로 hinge loss가 사용된다.
- 2. Regression Loss : Bounding Box Regression을 위해 사용되며 Ground Truth와 예측된 Bounding Box의 위치 간 차이를 최소화하기 위한 것이다. 이를 위해 L1 loss나 L2 loss가 사용될 수 있다.
R-CNN의 장단점
- 높은 Detection 정확도 : 동시대의 다른 알고리즘 대비 매우 높은 Detection 정확도.
- 너무 느린 Detection 시간과 복잡한 아키텍처 및 학습 프로세스
- 하나의 이미지마다 selective search를 수행하여 2000개의 region 영역 이미지들 도출
- 개별 이미지별로 2000개씩 생성된 region 이미지를 CNN Feature map 생성
- 각기 따로 노는 구성요소들 : Selective search, CNN Feature Extractor, SVM, Bounding box regressor로 한 프로세스를 거쳐서 학습 및 Object Detection이 되어야함
- 1장의 이미지를 Object Detection 하는데 약 50초 소요
R-CNN 이후 Object Detection 연구 방향성
- Deep Learning 기반 Object Detection 성능 입증
- Region Proposal 기반 성능 입증
- Detection 수행 시간을 줄이고 복잡하게 분리된 개별 아키텍처를 통합 할 수 있는 방안
R-CNN 개선 방안
- 2000 개의 Region Proposal 이미지를 CNN으로 Feature Extration 하지 않고 원본 이미지만 CNN으로 Feature Map 생성 뒤에 원본 이미지의 Selective search로 추천된 영역의 이미지만 Feature Map으로 매핑하여 별도 추출한다.
R-CNN 수행 시간 개선 방안 문제점
CNN은 서로 다른 사이즈의 Image를 수용하지 않는데 가장 큰 이유는 Flatten Fully Connection Input의 크기가 고정되어야 하기 때문이다.
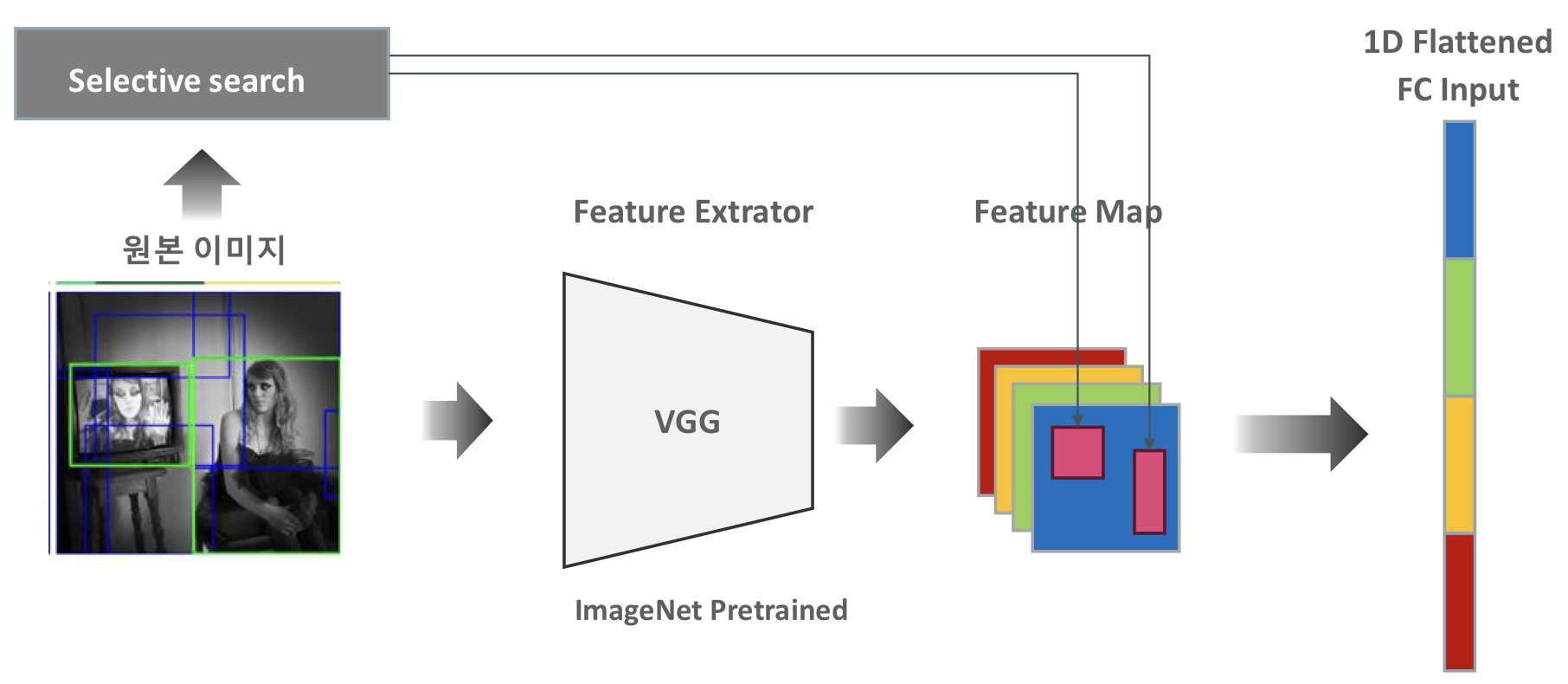
서로 다른 크기의 Region Proposal 이미지 개선 방안
Feature 맵으로 투영된 서로 다른 크기를 가진 Region proposal 이미지를 SPP Net의 고정된 크기 Vector로 변환하여 FC에 1D Flattend 된 input을 제공한다.
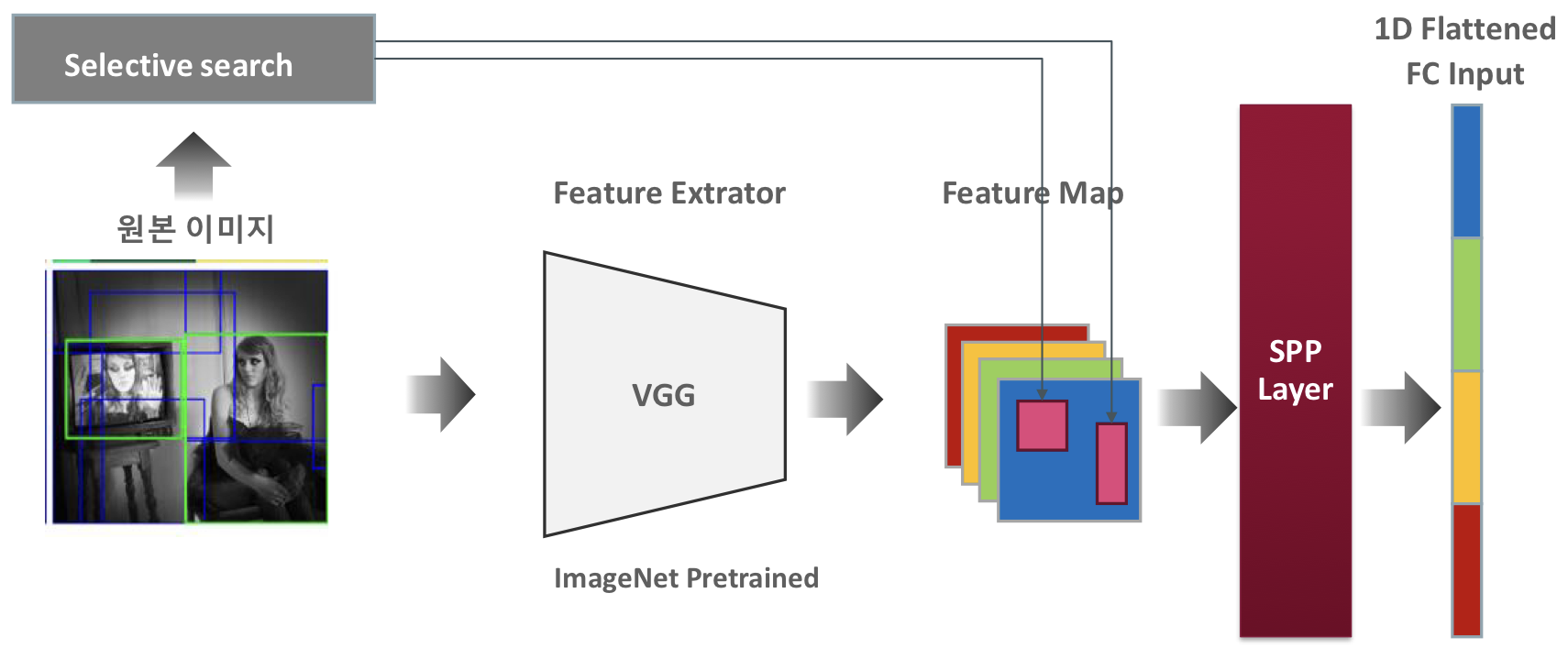
SPP(Spatial Pyramid Pooling) Net
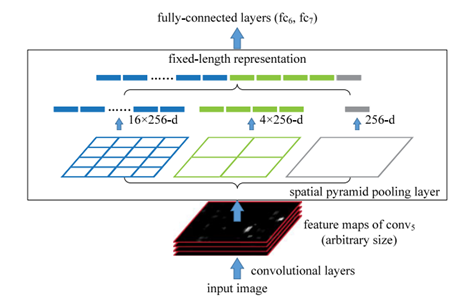
SPPNet(Spatial Pyramid Pooling Network)은 CNN의 뒷부분에 Spatial Pyramid Pooling 레이어를 도입함으로써 다양한 크기와 비율의 입력 이미지에 대응할 수 있게한다. 이는 이미지를 고정된 크기로 변환하지 않고도 Convolution 레이어를 통과한 Feature map의 크기와 비율에 관계없이 일정한 길이의 Feature vector를 생성할 수 있게 해준다.
Spatial Pyramid Matching
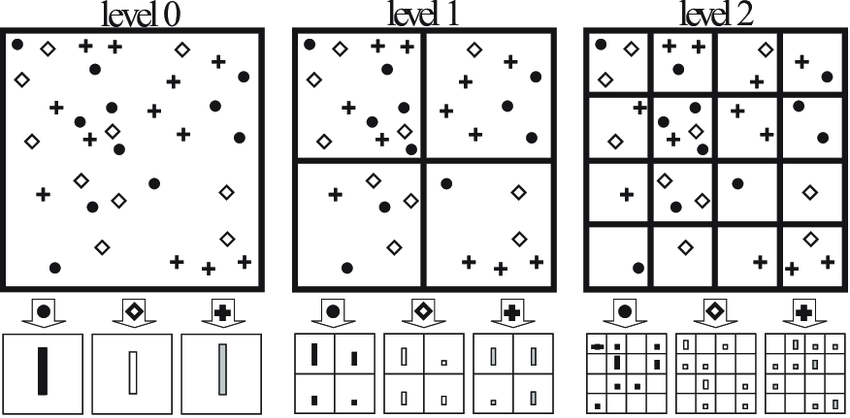
Spatial Pyramid Matching은 이미지를 여러단계의 피라미드로 분할하고 각 단계에서 특성을 추출하는 방법이다. 이미지를 다양한 크기의 grid로 분할하고 각 grid에서 pooling을 수행하여 feature를 집계한다. 이러한 과정을 여러 크기의 grid에 대해 반복함으로써 다양한 스케일에서 feature를 포착한다.
Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Spatial Pyramid Pooling은 CNN을 통관한 후의 특성 맵에 적용되며 다양한 크기의 Feature map에 적용되며 다양한 크기의 Feature map을 고정된 크기의 Feature vector로 변환한다. Feature map을 다양한 크기의 grid로 분할하고 각 grid 내에서 pooling을 수행하여 모든 grid의 pooling 결과를 연결하여 고정된 크기의 feature vector를 생성한다.
SPPNet Object Detection
- 다양한 크기의 객체 처리 : SPPNet은 다양한 크기와 비율의 객체를 효과적으로 처리할 수 있어 Object Detection에서 더 높은 정확도를 달성할 수 있다.
- 속도와 효율성 향상 : 전통적인 CNN은 고정된 크기의 입력을 필요로 하기 때문에 다양한 크기의 이미지를 처리하기 위해 여러번의 전처리가 필요했지만 SPPNet은 이러한 과정을 단순화하여 처리속도와 효율성을 크게 향상시킨다.
- Object Detection : SPPNet은 기존의 Object detection 모델과 결합되어 더 정교하고 효율적인 Object detection 시스템을 구축하는데 사용될 수 있다.
R-CNN과 SPPNet 비교
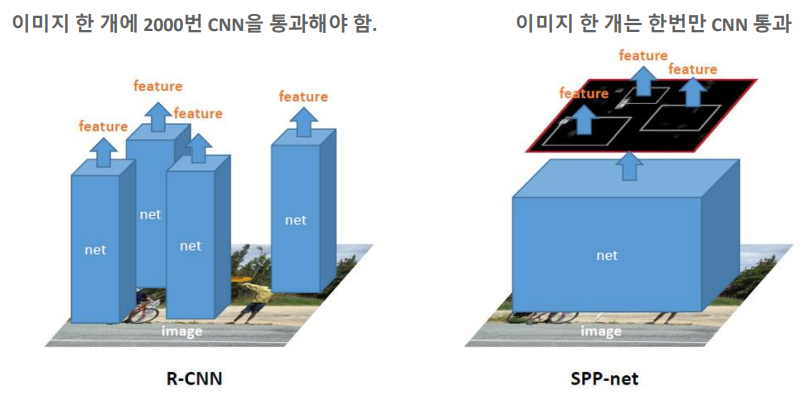
R-CNN의 주요 단점은 계산 효율성이다. 이미지의 각 후보 영역에 대해 별도로 CNN을 통과시켜야 하기 때문에 시간이 매우 소요되는데 SPPNet은 이미지 한개당 하나의 CNN을 통과해 모든 후보 영역에 대한 feature를 추출하면서 R-CNN에 비해 더 빠른 처리가 가능하다.
Fast R-CNN
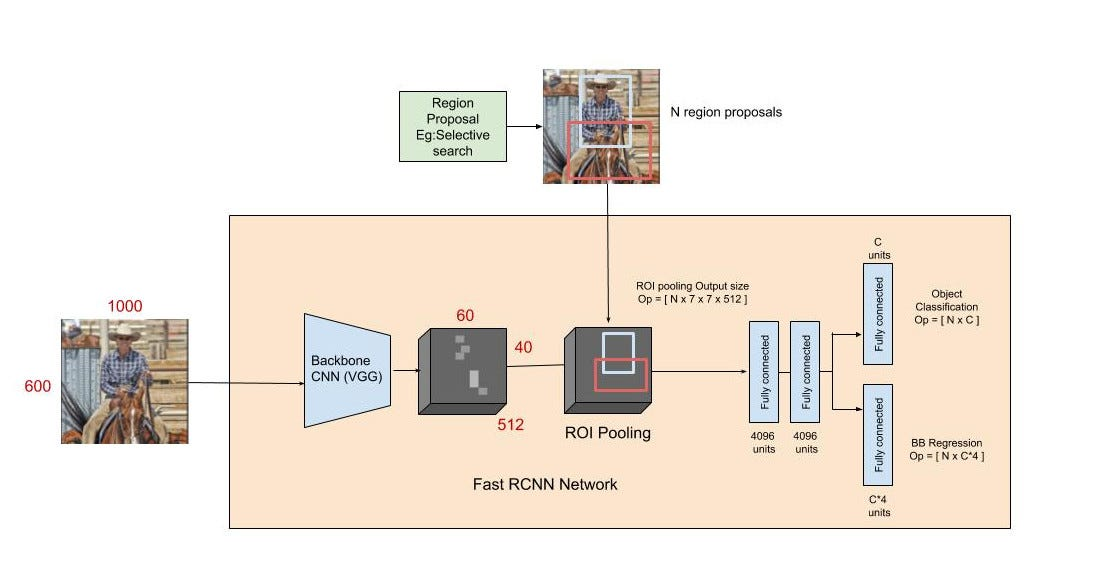
Fast R-CNN은 R-CNN과 SPPNet의 핵심 아이디어를 결합하여 Object Detection의 속도와 성능을 동시에 향상시킨 모델로 각 이미지에서 여러 객체와 그 위치를 식별하고 분류한다. 이 모델의 핵심은 효율적인 feature extraction과 통합된 train과정이다.
Fast R-CNN의 주요 구성 요소
- 1. 전체 이미지 feature extraction : 전체 이미지에 대해 한번의 CNN 연산을 수행하여 feature map을 생성한다.
- 2. ROI(Region of Interest) pooling 레이어 : Selective Search로 생성된 후보 영역을 feature map에 투영하고 각 후보 영역에 대한 feature를 고정된 크기의 벡터로 변환한다.
- 3. Object Classification, Bounding Box Regression : ROI pooling을 통해 얻은 고정된 크기의 벡터를 사용하여 객체의 클래스를 분류하고 Bounding Box의 위치를 정밀하게 조정한다. 이 두 작업은 동시에 수행되며 이는 Fast R-CNN의 중요한 특징 중 하나이다.
ROI(Region of Interest) Pooling
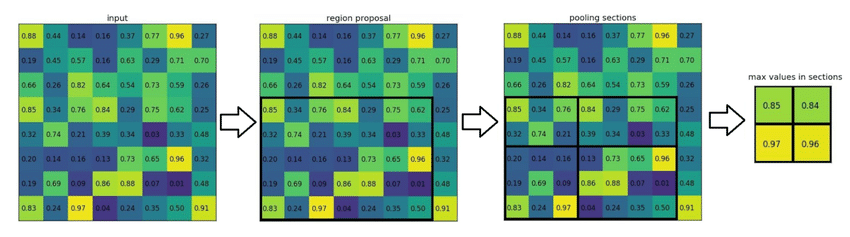
ROI Pooling은 feature map 상의 관심 영역(ROI)에 대하여 공간적으로 불변한 특성을 추출하는 과정이다. 이 기법은 CNN을 통과한 뒤의 feature map에서 정의된 ROI에 적용되며 각 ROI를 동일한 크기의 벡터로 사양하는 데 사용된다. 이로 인해 네트워크는 다양한 크기와 비율의 객체를 효과적으로 처리할 수 있게 된다.
ROI 작동 원리
- ROI 정의 : 이미지 내에서 객체가 존재할 것 으로 추정되는 영역, 즉 ROI가 정의된다. 이는 Selective Search, Region Proposal Newrok(RPN) 등의 방법을 통해 이루어진다.
- 특성 맵에 투영 : 정의된 ROI는 원본 이미지에서 feature map으로 투영된다. 이는 특성 맵상에서 해당 객체가 위치하는 영역을 찾는 과정이다.
- Pooling 영역 분할 : 각 ROI는 고정된 크기(ex: )의 Pooling 영역으로 분할된다. 분할된 각 영역은 feature map 상의 실제 크기와 비율에 따라 가변적인 크기를 가진다.
- Pooling 연산 수행 : 각 분할된 영역 내에서 Max Pooling이나 Average Pooling 과 같은 Pooling 연산을 수행한다. 이는 각 영역에서 가장 두드러진 feature 혹은 평균적인 feature를 추출한다.
- 고정된 크기의 feature vector 생성 : 모든 Pooling 연산의 결과를 concatenate하여 각 ROI에 대한 고정된 크기의 벡터를 생성한다.
ROI Pooling의 중요성
- 공간적 불변성 : ROI 풀링은 객체의 위치가 달라도 동일한 특성을 추출할 수 있도록 해준다.
- 다양한 크기의 처리 : 이 기법을 통해 네트워크는 다양한 크기의 입력 이미지를 처리할 수 있게 되며 이는 Object Detection의 범용성과 정확도를 높인다.
- 계산효율성 : 고정된 크기의 feature vector를 사용함으로써 후속 분류 및 회귀 작업을 위한 계산 비용이 감소한다.
Multi-task loss
Fast R-CNN의 train 과정에서 사용되는 손실 함수는 multi-task loss로 classification loss와 Bounding Box regression loss의 합으로 구성된다 이는 모델이 classification과 Bounding Box의 위치를 동시에 학습하도록 한다.
Faster R-CNN
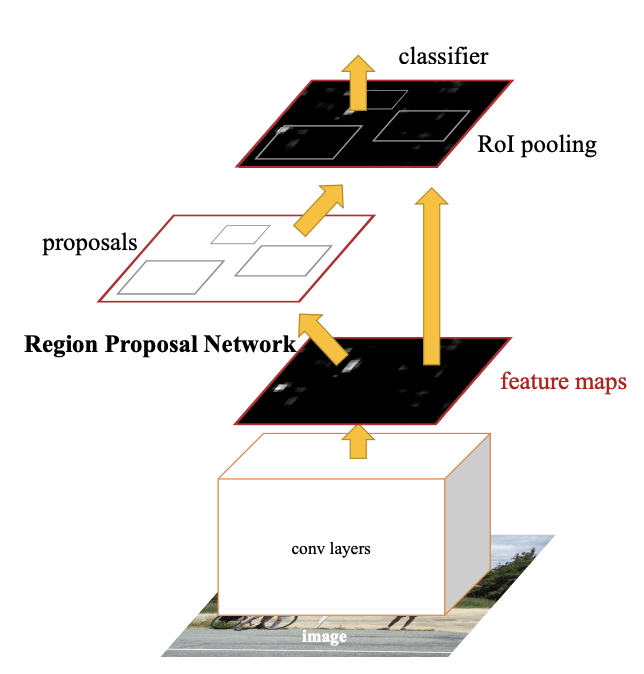
Faster R-CNN은 Anchor Box와 RPN(Region Proposal Network)가 도입된 Object Detection 신경망 구조다.
Anchor Box
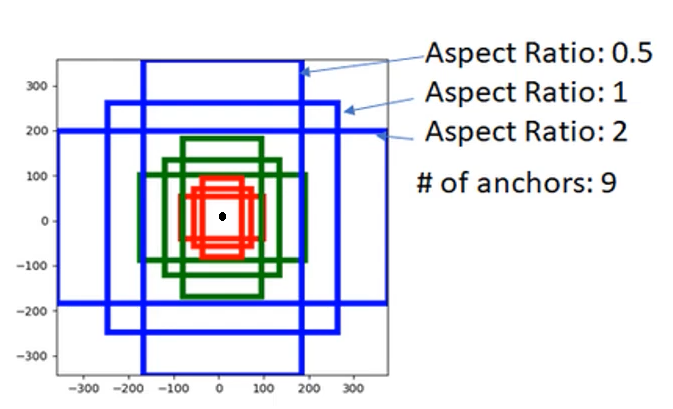
Anchor Box는 다양한 형태와 크기의 물체를 식별할 수 있는 기준 Box로서 이미지상의 모든 위치에 대해 미리 정의된 여러 크기와 비율을 가진다.
- 다양성 : Anchor Box는 다양한 aspect ratio를 가짐으로써 이미지 내의 다양한 객체를 감지할 수 있도록 한다.
- 위치 인코딩 : Anchor는 feature map 상의 각 위치에 대응되며 해당 위치에서 감지될 수 있는 개체의 크기와 비율을 인코딩한다.
RPN(Region Proposal Network) 구성
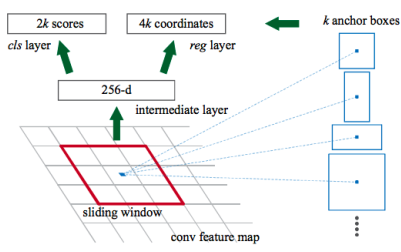
RPN은 Anchor Box를 기반 실시간으로 영역 제안을 생성한다.
- 1. feature map 생성 : Backbone 네트워크(ex: VGG 또는 ResNet)를 통해 생성된 feature map 위에 RPN을 적용한다.
- 2. Sliding Window : feature map에 Sliding Window를 적용하여 각 위치에서의 특성을 추출한다.
- 3. Anchor Box 적용 : 각 Sliding Window 위치에서 여러 Anchor Box를 적용하고 각 Box에 대한 Objectness Score와 Bounding Box Regressions를 예측한다.
- 4. 객체 존재 확률과 Bounding Box 조정 : 이 두 예측은 각 Anchor Box가 실제 객체를 포함하는지와 그 객체의 정확한 위치를 결정하는 데 사용된다.
Faster R-CNN의 Train
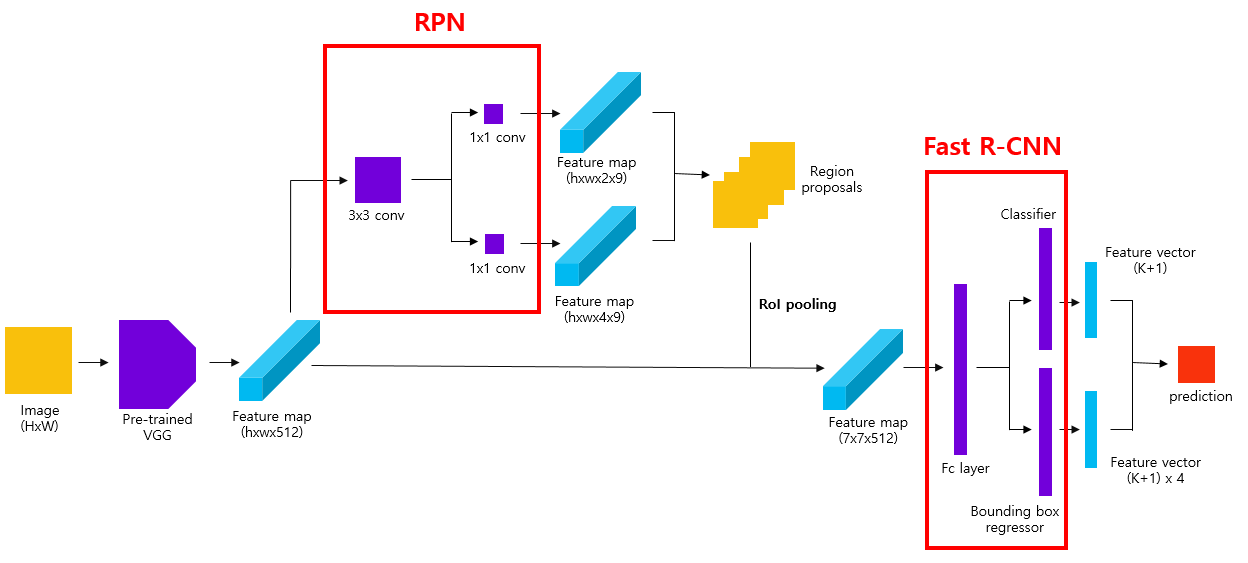
Faster R-CNN은 통합된 Train 방법을 사용하여 RPN과 Fast R-CNN을 동시에 Train한다.
- 1. RPN Train : feature map에 RPN을 적용하여 객체의 존재 확률과 Bounding Box 조정값을 예측한다.
- 2. Fast R-CNN Train : RPN에서 생성된 후보 영역을 사용하여 Fast R-CNN을 훈련한다. 이는 객체의 클래스를 예측하고 Bounding Box의 위치를 더욱 정밀하게 조정하는 데 사용된다.
- 3. 다목적 loss function : loss function은 RPN의 classification과 regression loss 그리고 Fast R-CNN의 classification과 regression을 모두 포함한다.
- 4. end-to-end 최적화 : RPN과 Fast R-CNN을 하나의 네트워크로 통합하여 전체 네트워크를 End-to-End로 train시킬 수 있다.
Faster R-CNN 실습
OpenCV DNN 패키지를 이용하여 Faster R-CNN 기반의 Object Detection 수행
- Tensorflow에서 Pretrained 된 모델 파일을 OpenCV에서 로드하여 이미지와 영상에 대한 Object Detection 수행
입력 이미지로 사용 될 이미지 출력
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
img = cv2.imread('../data/beatles01.jpg')
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
print('image shape:', img.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
Tensorflow에서 Pretrained 된 Inference모델(Frozen graph)와 환경파일을 다운로드 받은 후 이를 이용해 OpenCV에서 Inference 모델 생성
- https://github.com/opencv/opencv/wiki/TensorFlow-Object-Detection-API 에 다운로드 URL 있음.
- pretrained 모델은 http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28.tar.gz 에서 다운로드 후 압축 해제
- pretrained 모델을 위한 환경 파일은 https://github.com/opencv/opencv_extra/blob/master/testdata/dnn/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28.pbtxt 에서 다운로드
- download된 모델 파일과 config 파일을 인자로 하여 inference 모델을 DNN에서 로딩함.
dnn에서 readNetFromTensorflow()로 tensorflow inference 모델을 로딩
cv_net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow('../pretrained/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28/frozen_inference_graph.pb',
'../pretrained/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28.pbtxt.txt')coco 데이터 세트의 클래스 id별 클래스 명 지정
# OpenCV Yolo용
labels_to_names_seq = {0:'person',1:'bicycle',2:'car',3:'motorbike',4:'aeroplane',5:'bus',6:'train',7:'truck',8:'boat',9:'traffic light',10:'fire hydrant',
11:'stop sign',12:'parking meter',13:'bench',14:'bird',15:'cat',16:'dog',17:'horse',18:'sheep',19:'cow',20:'elephant',
21:'bear',22:'zebra',23:'giraffe',24:'backpack',25:'umbrella',26:'handbag',27:'tie',28:'suitcase',29:'frisbee',30:'skis',
31:'snowboard',32:'sports ball',33:'kite',34:'baseball bat',35:'baseball glove',36:'skateboard',37:'surfboard',38:'tennis racket',39:'bottle',40:'wine glass',
41:'cup',42:'fork',43:'knife',44:'spoon',45:'bowl',46:'banana',47:'apple',48:'sandwich',49:'orange',50:'broccoli',
51:'carrot',52:'hot dog',53:'pizza',54:'donut',55:'cake',56:'chair',57:'sofa',58:'pottedplant',59:'bed',60:'diningtable',
61:'toilet',62:'tvmonitor',63:'laptop',64:'mouse',65:'remote',66:'keyboard',67:'cell phone',68:'microwave',69:'oven',70:'toaster',
71:'sink',72:'refrigerator',73:'book',74:'clock',75:'vase',76:'scissors',77:'teddy bear',78:'hair drier',79:'toothbrush' }# OpenCV Tensorflow Faster-RCNN용
labels_to_names_0 = {0:'person',1:'bicycle',2:'car',3:'motorcycle',4:'airplane',5:'bus',6:'train',7:'truck',8:'boat',9:'traffic light',
10:'fire hydrant',11:'street sign',12:'stop sign',13:'parking meter',14:'bench',15:'bird',16:'cat',17:'dog',18:'horse',19:'sheep',
20:'cow',21:'elephant',22:'bear',23:'zebra',24:'giraffe',25:'hat',26:'backpack',27:'umbrella',28:'shoe',29:'eye glasses',
30:'handbag',31:'tie',32:'suitcase',33:'frisbee',34:'skis',35:'snowboard',36:'sports ball',37:'kite',38:'baseball bat',39:'baseball glove',
40:'skateboard',41:'surfboard',42:'tennis racket',43:'bottle',44:'plate',45:'wine glass',46:'cup',47:'fork',48:'knife',49:'spoon',
50:'bowl',51:'banana',52:'apple',53:'sandwich',54:'orange',55:'broccoli',56:'carrot',57:'hot dog',58:'pizza',59:'donut',
60:'cake',61:'chair',62:'couch',63:'potted plant',64:'bed',65:'mirror',66:'dining table',67:'window',68:'desk',69:'toilet',
70:'door',71:'tv',72:'laptop',73:'mouse',74:'remote',75:'keyboard',76:'cell phone',77:'microwave',78:'oven',79:'toaster',
80:'sink',81:'refrigerator',82:'blender',83:'book',84:'clock',85:'vase',86:'scissors',87:'teddy bear',88:'hair drier',89:'toothbrush',
90:'hair brush'}labels_to_names = {1:'person',2:'bicycle',3:'car',4:'motorcycle',5:'airplane',6:'bus',7:'train',8:'truck',9:'boat',10:'traffic light',
11:'fire hydrant',12:'street sign',13:'stop sign',14:'parking meter',15:'bench',16:'bird',17:'cat',18:'dog',19:'horse',20:'sheep',
21:'cow',22:'elephant',23:'bear',24:'zebra',25:'giraffe',26:'hat',27:'backpack',28:'umbrella',29:'shoe',30:'eye glasses',
31:'handbag',32:'tie',33:'suitcase',34:'frisbee',35:'skis',36:'snowboard',37:'sports ball',38:'kite',39:'baseball bat',40:'baseball glove',
41:'skateboard',42:'surfboard',43:'tennis racket',44:'bottle',45:'plate',46:'wine glass',47:'cup',48:'fork',49:'knife',50:'spoon',
51:'bowl',52:'banana',53:'apple',54:'sandwich',55:'orange',56:'broccoli',57:'carrot',58:'hot dog',59:'pizza',60:'donut',
61:'cake',62:'chair',63:'couch',64:'potted plant',65:'bed',66:'mirror',67:'dining table',68:'window',69:'desk',70:'toilet',
71:'door',72:'tv',73:'laptop',74:'mouse',75:'remote',76:'keyboard',77:'cell phone',78:'microwave',79:'oven',80:'toaster',
81:'sink',82:'refrigerator',83:'blender',84:'book',85:'clock',86:'vase',87:'scissors',88:'teddy bear',89:'hair drier',90:'toothbrush',
91:'hair brush'}이미지를 preprocessing 수행하여 Network에 입력하고 Object Detection 수행 후 결과를 이미지에 시각화
img.shape
# 원본 이미지가 Faster RCNN기반 네트웍으로 입력 시 resize됨.
# scaling된 이미지 기반으로 bounding box 위치가 예측 되므로 이를 다시 원복하기 위해 원본 이미지 shape정보 필요
rows = img.shape[0]
cols = img.shape[1]
# cv2의 rectangle()은 인자로 들어온 이미지 배열에 직접 사각형을 업데이트 하므로 그림 표현을 위한 별도의 이미지 배열 생성.
draw_img = img.copy()
# 원본 이미지 배열 BGR을 RGB로 변환하여 배열 입력. Tensorflow Faster RCNN은 마지막 classification layer가 Dense가 아니여서 size를 고정할 필요는 없음.
cv_net.setInput(cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img, swapRB=True, crop=False))
# Object Detection 수행하여 결과를 cvOut으로 반환
cv_out = cv_net.forward()
print(cv_out.shape)
# bounding box의 테두리와 caption 글자색 지정
green_color=(0, 255, 0)
red_color=(0, 0, 255)
# detected 된 object들을 iteration 하면서 정보 추출
for detection in cv_out[0,0,:,:]:
score = float(detection[2])
class_id = int(detection[1])
# detected된 object들의 score가 0.5 이상만 추출
if score > 0.5:
# detected된 object들은 scale된 기준으로 예측되었으므로 다시 원본 이미지 비율로 계산
left = detection[3] * cols
top = detection[4] * rows
right = detection[5] * cols
bottom = detection[6] * rows
# labels_to_names_seq 딕셔너리로 class_id값을 클래스명으로 변경.
caption = "{}: {:.4f}".format(labels_to_names_0[class_id], score)
print(caption)
#cv2.rectangle()은 인자로 들어온 draw_img에 사각형을 그림. 위치 인자는 반드시 정수형.
cv2.rectangle(draw_img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color=green_color, thickness=2)
cv2.putText(draw_img, caption, (int(left), int(top - 5)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.4, red_color, 1)
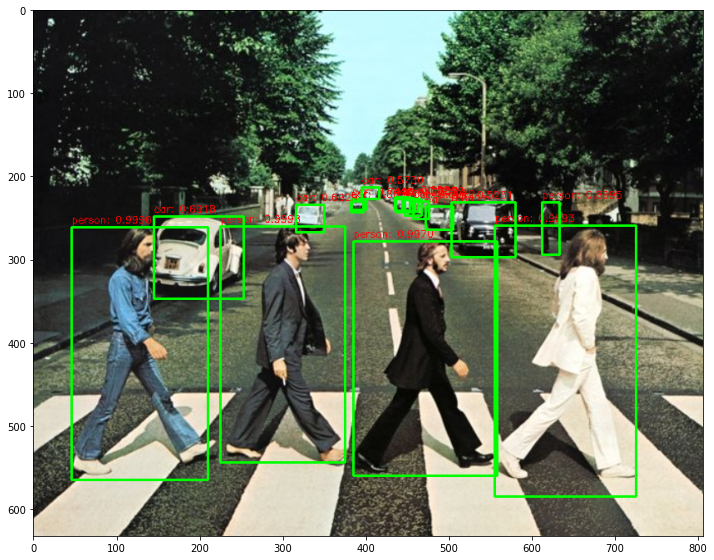
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(draw_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)(1, 1, 100, 7)
person: 0.9998
person: 0.9996
person: 0.9993
person: 0.9970
person: 0.8995
car: 0.8922
car: 0.7602
car: 0.7415
car: 0.6929
car: 0.6918
car: 0.6896
car: 0.6717
car: 0.6521
car: 0.5730
car: 0.5679
car: 0.5261
car: 0.5012
단일 이미지의 objec detection을 함수로 생성
import time
def get_detected_img(cv_net, img_array, score_threshold, use_copied_array=True, is_print=True):
rows = img_array.shape[0]
cols = img_array.shape[1]
draw_img = None
if use_copied_array:
draw_img = img_array.copy()
else:
draw_img = img_array
cv_net.setInput(cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img_array, swapRB=True, crop=False))
start = time.time()
cv_out = cv_net.forward()
green_color=(0, 255, 0)
red_color=(0, 0, 255)
# detected 된 object들을 iteration 하면서 정보 추출
for detection in cv_out[0,0,:,:]:
score = float(detection[2])
class_id = int(detection[1])
# detected된 object들의 score가 함수 인자로 들어온 score_threshold 이상만 추출
if score > score_threshold:
# detected된 object들은 scale된 기준으로 예측되었으므로 다시 원본 이미지 비율로 계산
left = detection[3] * cols
top = detection[4] * rows
right = detection[5] * cols
bottom = detection[6] * rows
# labels_to_names 딕셔너리로 class_id값을 클래스명으로 변경. opencv에서는 class_id + 1로 매핑해야함.
caption = "{}: {:.4f}".format(labels_to_names_0[class_id], score)
print(caption)
#cv2.rectangle()은 인자로 들어온 draw_img에 사각형을 그림. 위치 인자는 반드시 정수형.
cv2.rectangle(draw_img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color=green_color, thickness=2)
cv2.putText(draw_img, caption, (int(left), int(top - 5)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.4, red_color, 1)
if is_print:
print('Detection 수행시간:',round(time.time() - start, 2),"초")
return draw_img# image 로드
img = cv2.imread('../data/beatles01.jpg')
print('image shape:', img.shape)
# tensorflow inference 모델 로딩
cv_net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow('../pretrained/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28/frozen_inference_graph.pb',
'../pretrained/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28.pbtxt.txt')
# Object Detetion 수행 후 시각화
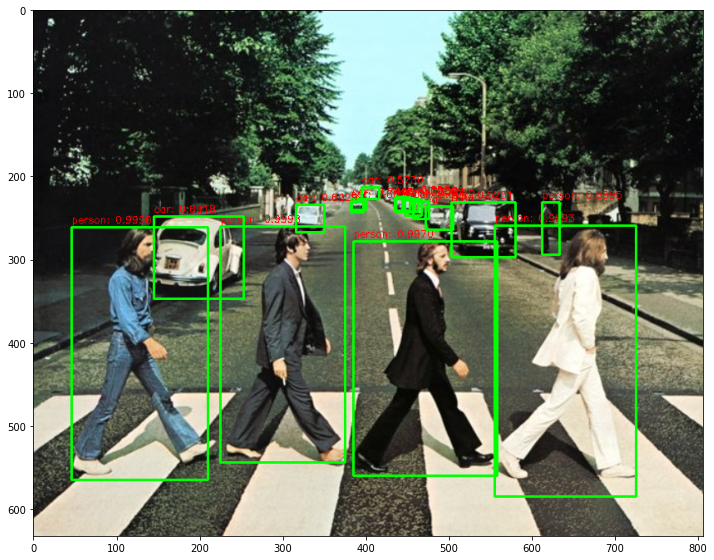
draw_img = get_detected_img(cv_net, img, score_threshold=0.5, use_copied_array=True, is_print=True)
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(draw_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)image shape: (633, 806, 3)
person: 0.9998
person: 0.9996
person: 0.9993
person: 0.9970
person: 0.8995
car: 0.8922
car: 0.7602
car: 0.7415
car: 0.6929
car: 0.6918
car: 0.6896
car: 0.6717
car: 0.6521
car: 0.5730
car: 0.5679
car: 0.5261
car: 0.5012
Detection 수행시간: 0.62 초
다른 image 테스트
img = cv2.imread('../data/baseball01.jpg')
print('image shape:', img.shape)
# tensorflow inference 모델 로딩
cv_net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow('../pretrained/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28/frozen_inference_graph.pb',
'../pretrained/faster_rcnn_resnet50_coco_2018_01_28.pbtxt.txt')
# Object Detetion 수행 후 시각화
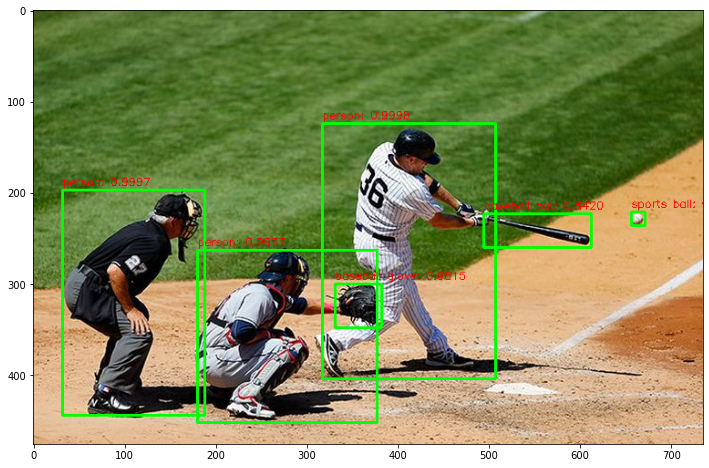
draw_img = get_detected_img(cv_net, img, score_threshold=0.5, use_copied_array=True, is_print=True)
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(draw_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)image shape: (476, 735, 3)
person: 0.9998
person: 0.9997
person: 0.9977
baseball glove: 0.9815
sports ball: 0.8867
baseball bat: 0.8420
Detection 수행시간: 0.54 초
Video Inference
VideoCapture 와 VideoWriter 설정하기
- VideoCapture를 이용하여 Video를 frame별로 capture 할 수 있도록 설정
- VideoCapture의 속성을 이용하여 Video Frame의 크기 및 FPS설정
- VideoWriter를 위한 인코딩 코덱 설정 및 영상 write를 위한 설정
video_input_path = '../data/John_Wick_small.mp4'
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_input_path)
frame_cnt = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
print('총 Frame 갯수:', frame_cnt)video_input_path = '../data/John_Wick_small.mp4'
video_output_path = '../data/John_Wick_small_cv01.mp4'
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_input_path)
codec = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
vid_size = (round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
vid_fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS )
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(video_output_path, codec, vid_fps, vid_size)
frame_cnt = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
print('총 Frame 갯수:', frame_cnt)총 Frame 별로 iteration 하면서 Object Detection 수행 개별 frame 별로 단일 이미지 Object Detection과 유사
# bounding box의 테두리와 caption 글자색 지정
green_color=(0, 255, 0)
red_color=(0, 0, 255)
while True:
hasFrame, img_frame = cap.read()
if not hasFrame:
print('더 이상 처리할 frame이 없습니다.')
break
rows = img_frame.shape[0]
cols = img_frame.shape[1]
# 원본 이미지 배열 BGR을 RGB로 변환하여 배열 입력
cv_net.setInput(cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img_frame, swapRB=True, crop=False))
start= time.time()
# Object Detection 수행하여 결과를 cv_out으로 반환
cv_out = cv_net.forward()
frame_index = 0
# detected 된 object들을 iteration 하면서 정보 추출
for detection in cv_out[0,0,:,:]:
score = float(detection[2])
class_id = int(detection[1])
# detected된 object들의 score가 0.5 이상만 추출
if score > 0.5:
# detected된 object들은 scale된 기준으로 예측되었으므로 다시 원본 이미지 비율로 계산
left = detection[3] * cols
top = detection[4] * rows
right = detection[5] * cols
bottom = detection[6] * rows
# labels_to_names_0딕셔너리로 class_id값을 클래스명으로 변경.
caption = "{}: {:.4f}".format(labels_to_names_0[class_id], score)
#print(class_id, caption)
#cv2.rectangle()은 인자로 들어온 draw_img에 사각형을 그림. 위치 인자는 반드시 정수형.
cv2.rectangle(img_frame, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color=green_color, thickness=2)
cv2.putText(img_frame, caption, (int(left), int(top - 5)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, red_color, 1)
print('Detection 수행 시간:', round(time.time()-start, 2),'초')
vid_writer.write(img_frame)
# end of while loop
vid_writer.release()
cap.release() video detection 전용 함수 생성
def do_detected_video(cv_net, input_path, output_path, score_threshold, is_print):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(input_path)
codec = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
vid_size = (round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
vid_fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, codec, vid_fps, vid_size)
frame_cnt = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
print('총 Frame 갯수:', frame_cnt)
green_color=(0, 255, 0)
red_color=(0, 0, 255)
while True:
hasFrame, img_frame = cap.read()
if not hasFrame:
print('더 이상 처리할 frame이 없습니다.')
break
img_frame = get_detected_img(cv_net, img_frame, score_threshold=score_threshold, use_copied_array=False, is_print=is_print)
vid_writer.write(img_frame)
# end of while loop
vid_writer.release()
cap.release()do_detected_video(cv_net, '../data/John_Wick_small.mp4', '../data/John_Wick_small_02.mp4', 0.2, False)총 Frame 갯수: 58
car: 0.9882
car: 0.9622
person: 0.9495
car: 0.9266
car: 0.8772
motorcycle: 0.6607
car: 0.3988
car: 0.3763
bicycle: 0.3498
person: 0.2871
car: 0.2583
car: 0.2150
book: 0.2069
car: 0.9881
car: 0.9643
person: 0.9581
car: 0.9318
car: 0.8992
motorcycle: 0.5682
person: 0.4459
car: 0.4418
bicycle: 0.4216
car: 0.4189
person: 0.2940