



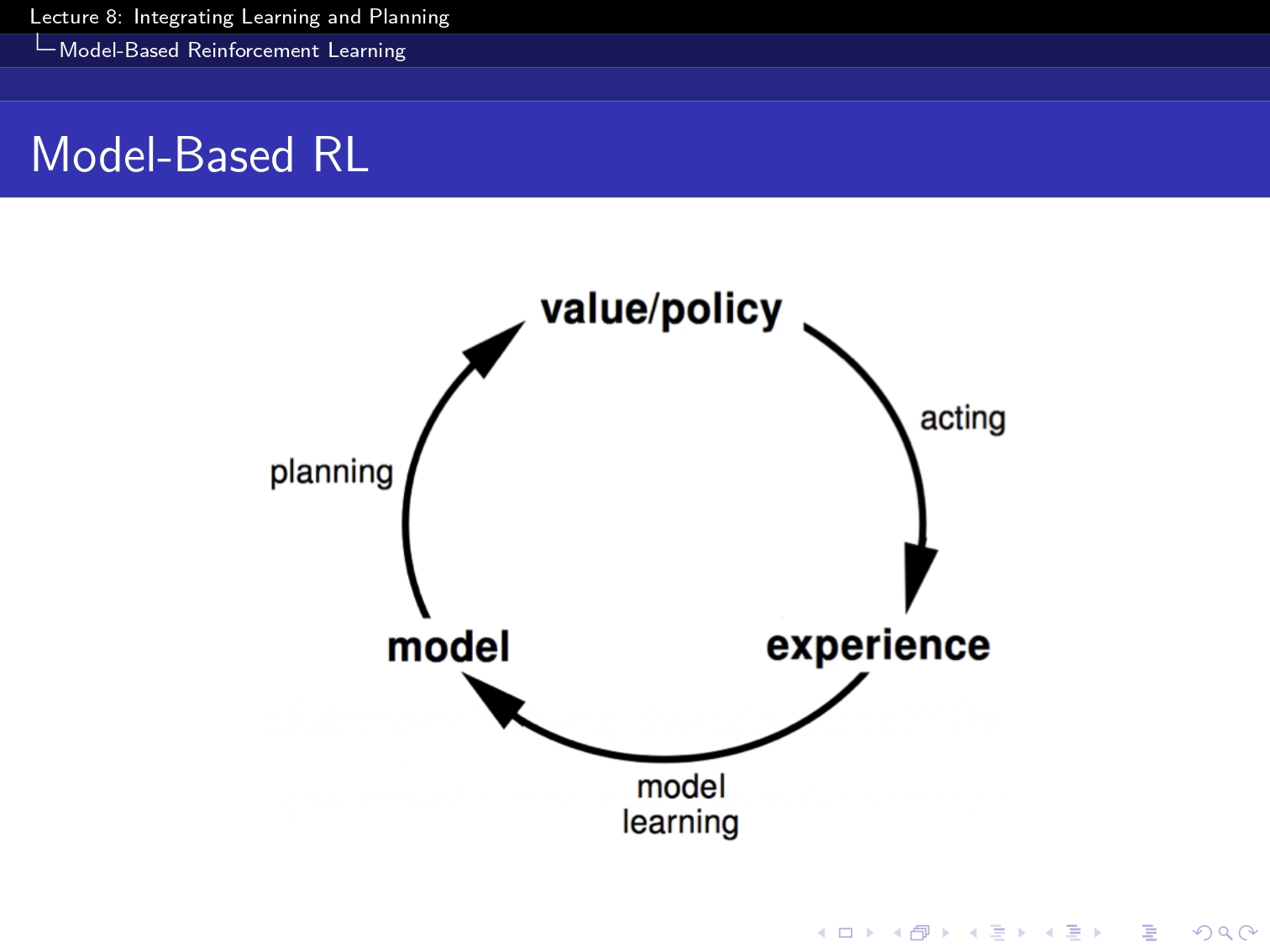

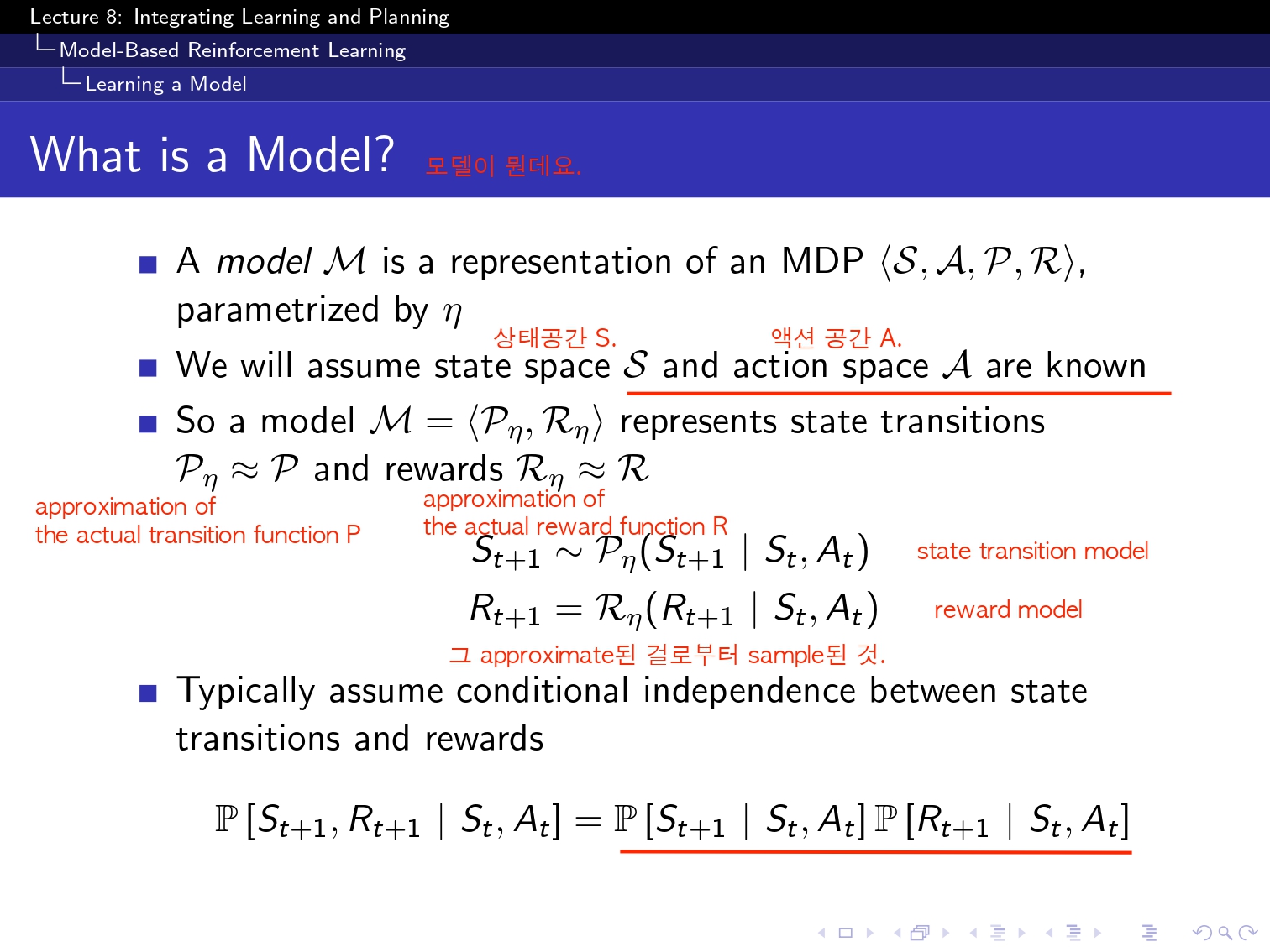
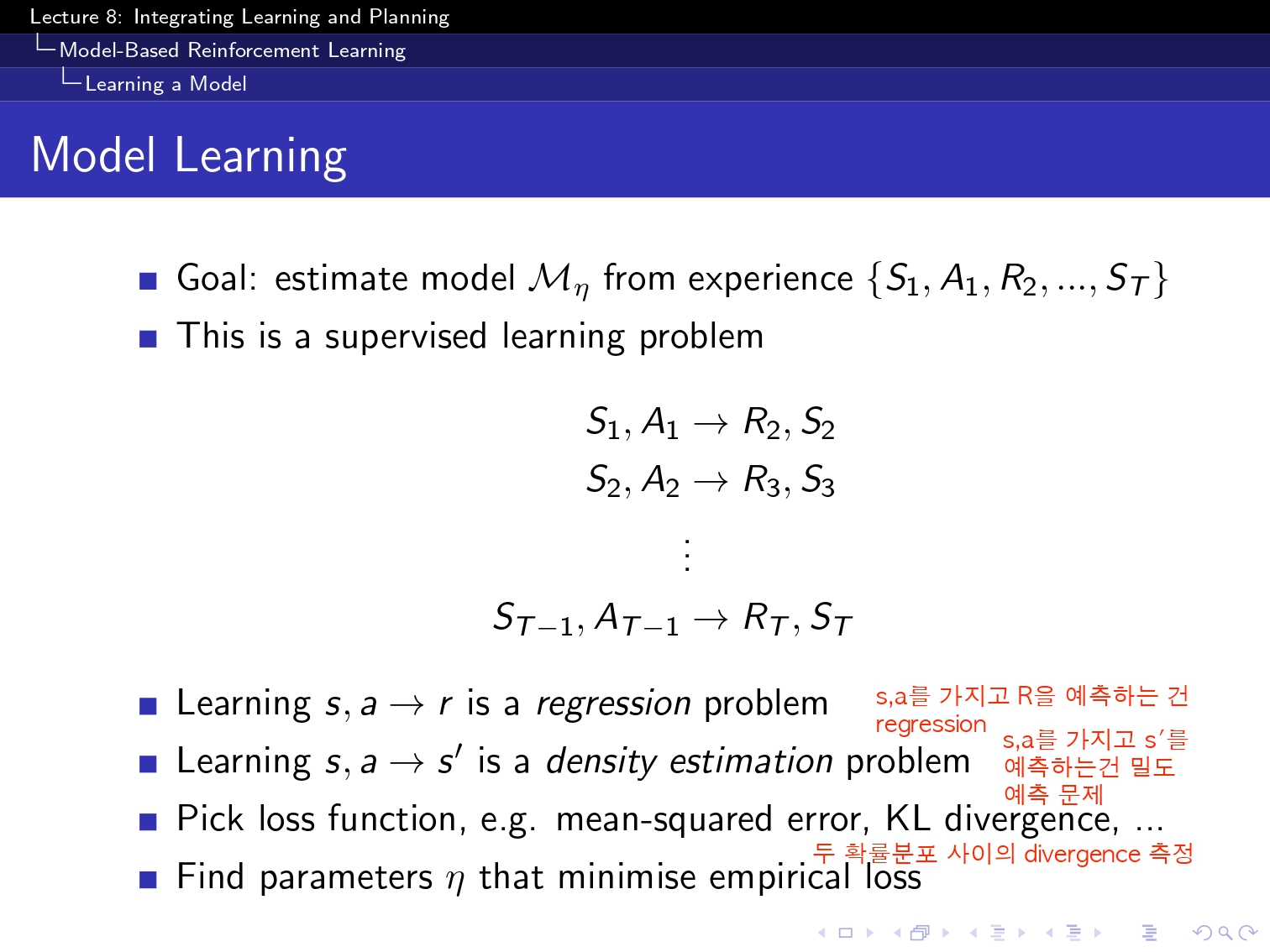







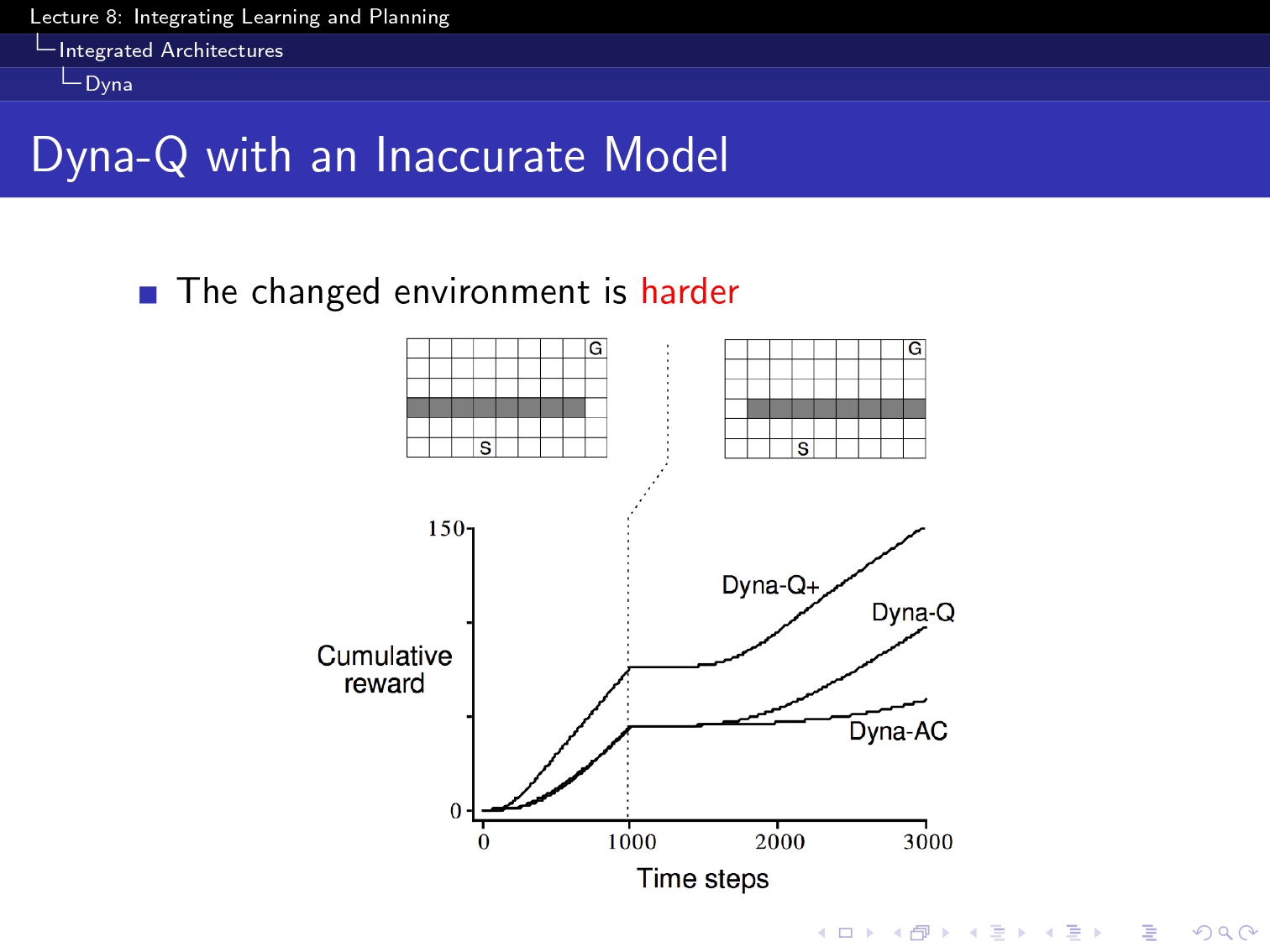
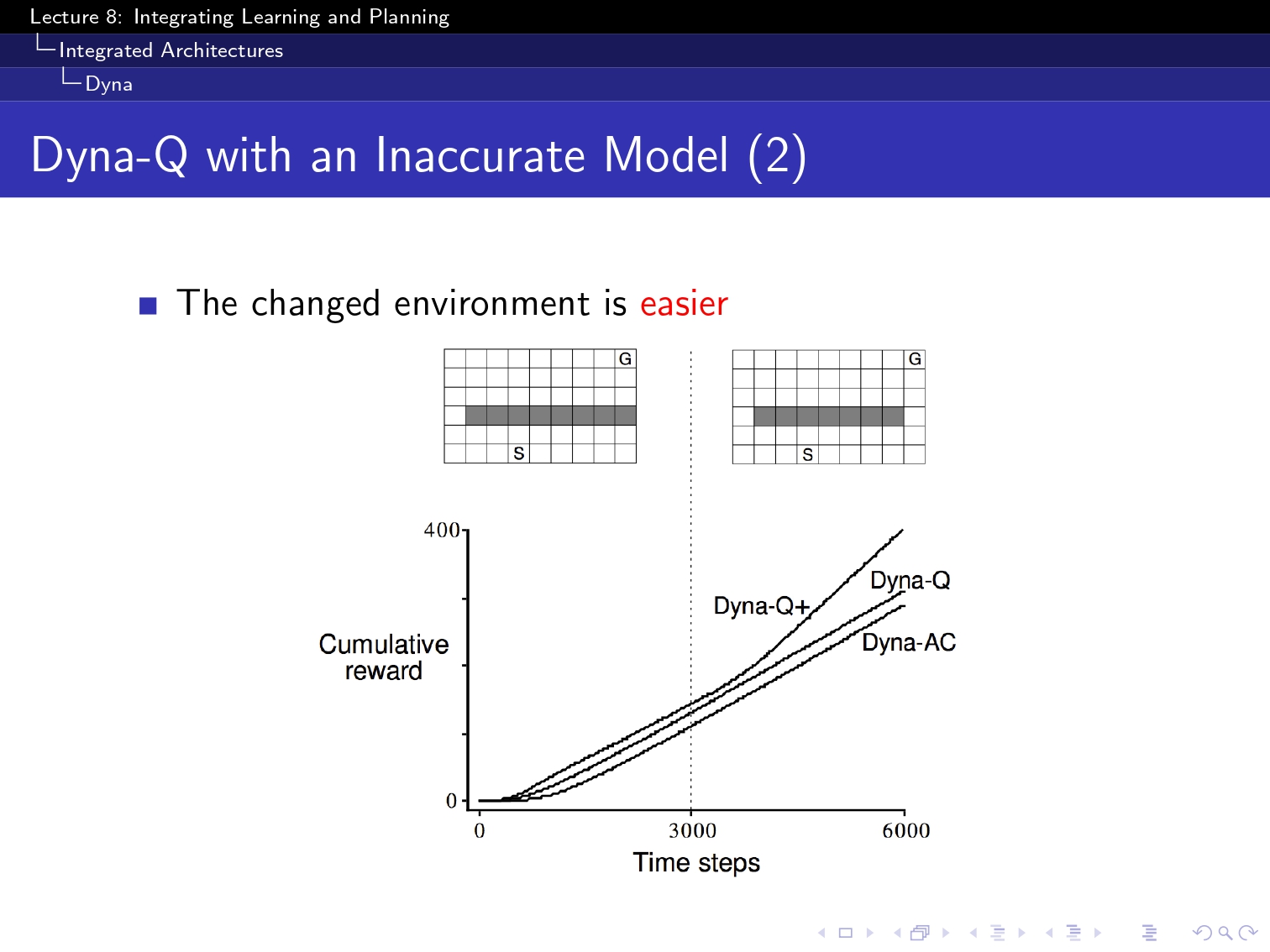
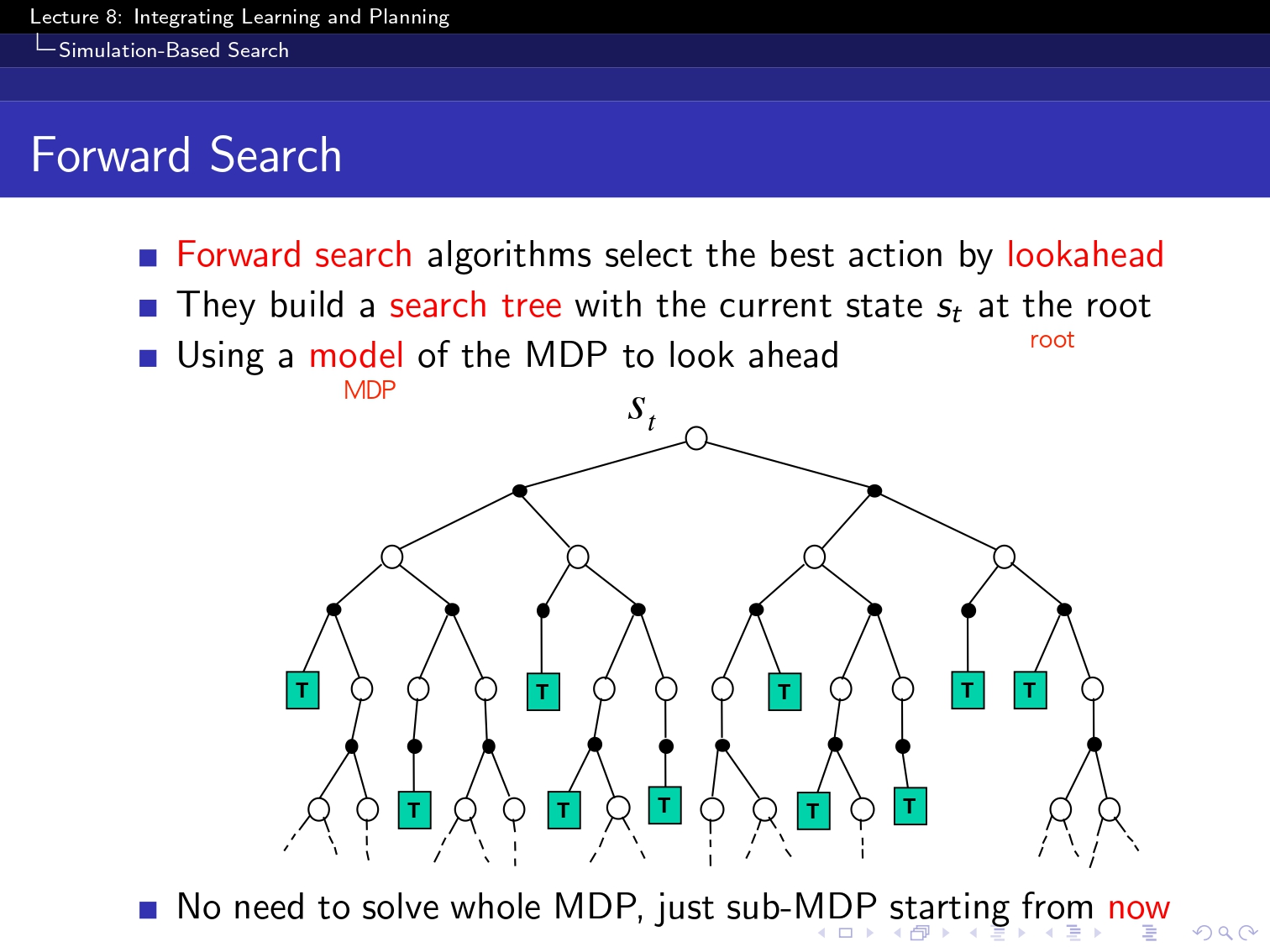
(요기 이 simulation based 부분은 아직 구현을 하지 못했고 강의를 끝까지는 못 들어성 다음 부분으로 넘겨보겠습니당...!)
그리고 저번까지는 계속해서 그냥 ppt에 나와있는 기본코드를 구현하는 것에 그쳤는데, 여기 나와있는 그 미로 탐험이 개인적으로 재미있어보이더라구요??
그래서 구현을 한번 해보았습니당ㅎㅎㅎ
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import argparse
# 미로 크기 설정 (6x9 미로)
maze = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], # 벽 (1)
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], # 길 (0)
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
])
start = (2, 0)
goal = (0, 8)
actions = ['up', 'down', 'left', 'right']
action_map = {0: 'up', 1: 'down', 2: 'left', 3: 'right'}
# 미로 출력 함수
def plot_maze(maze, agent_position, ax=None, agent_plot=None,title=None):
if ax is None or agent_plot is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
ax.imshow(maze, cmap='binary')
ax.scatter(goal[1], goal[0], c='green', s=100, marker='x')
agent_plot = ax.scatter(agent_position[1], agent_position[0], c='red', s=100, marker='*')
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-0.5, maze.shape[1], 1), minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-0.5, maze.shape[0], 1), minor=True)
ax.grid(which='minor', color='black', linestyle='-', linewidth=2)
plt.ion()
plt.show()
return ax, agent_plot
agent_plot.set_offsets([agent_position[1], agent_position[0]])
if title:
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=14)
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.01)
return ax, agent_plot
# 에이전트 이동 함수
def move_agent(agent_position, direction):
x, y = agent_position
if direction == 'up' and x > 0 and maze[x-1, y] != 1:
return (x-1, y)
elif direction == 'down' and x < maze.shape[0] - 1 and maze[x+1, y] != 1:
return (x+1, y)
elif direction == 'left' and y > 0 and maze[x, y-1] != 1:
return (x, y-1)
elif direction == 'right' and y < maze.shape[1] - 1 and maze[x, y+1] != 1:
return (x, y+1)
return agent_position
# 상태 인덱스 변환
def state_index(state):
return state[0] * maze.shape[1] + state[1]
# Q-테이블 및 모델 초기화
num_states = maze.shape[0] * maze.shape[1]
num_actions = len(actions)
Q = np.zeros((num_states, num_actions))
Model = {}
# ε-greedy 정책
def epsilon_greedy_policy(Q, state, epsilon):
if np.random.rand() < epsilon:
return np.random.choice(num_actions)
return np.argmax(Q[state])
# Dyna-Q 알고리즘
def DynaQ(planning_step, num_episodes, alpha=0.1, gamma=0.9, epsilon=0.1):
global Q, Model
ax, agent_plot = plot_maze(maze, start) #일단 maze만들고
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state = start
state_idx = state_index(state) #idx를 통해 table을 만들어야하니.
num_step = 1
while state != goal:
action = epsilon_greedy_policy(Q, state_idx, epsilon)
next_state = move_agent(state, action_map[action])
next_state_idx = state_index(next_state)
reward = 1 if next_state == goal else -0.01 #reward는 goal에 도착할때만!
# Q 업데이트
Q[state_idx, action] += alpha * (reward + gamma * np.max(Q[next_state_idx]) - Q[state_idx, action]) #Q-learning에서 봤듯이.
# 환경 모델 업데이트
Model[(state_idx, action)] = (next_state_idx, reward) #next랑 reward
# Planning 단계
for _ in range(planning_step):
sampled_state_idx, sampled_action = list(Model.keys())[np.random.randint(len(Model))] #요거 어케할지 몰라서 지피티참고
sampled_next_state_idx, sampled_reward = Model[(sampled_state_idx, sampled_action)] #next랑 reward저장되어잇는고임
Q[sampled_state_idx, sampled_action] += alpha * (sampled_reward + gamma * np.max(Q[sampled_next_state_idx]) - Q[sampled_state_idx, sampled_action])
state = next_state
state_idx = next_state_idx
planning_title = f"episode {episode + 1}, step {num_step}"
ax, agent_plot = plot_maze(maze, state, ax, agent_plot,planning_title)
num_step += 1
print(f"Episode {episode + 1} completed with {num_step} steps!")
return Q
# 메인 함수
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Simple maze with Dyna-Q")
parser.add_argument("--planning_step", type=int, default=5, help="Number of planning steps")
parser.add_argument("--num_episodes", type=int, default=10, help="Number of training episodes")
args = parser.parse_args()
global Q, Model
Q = np.zeros((num_states, num_actions)) # Q-테이블 초기화
Model = {} # 환경 모델 초기화
final_Q = DynaQ(args.planning_step, args.num_episodes)
print("\nFinal Q-table:")
print(final_Q)
if __name__ == "__main__":
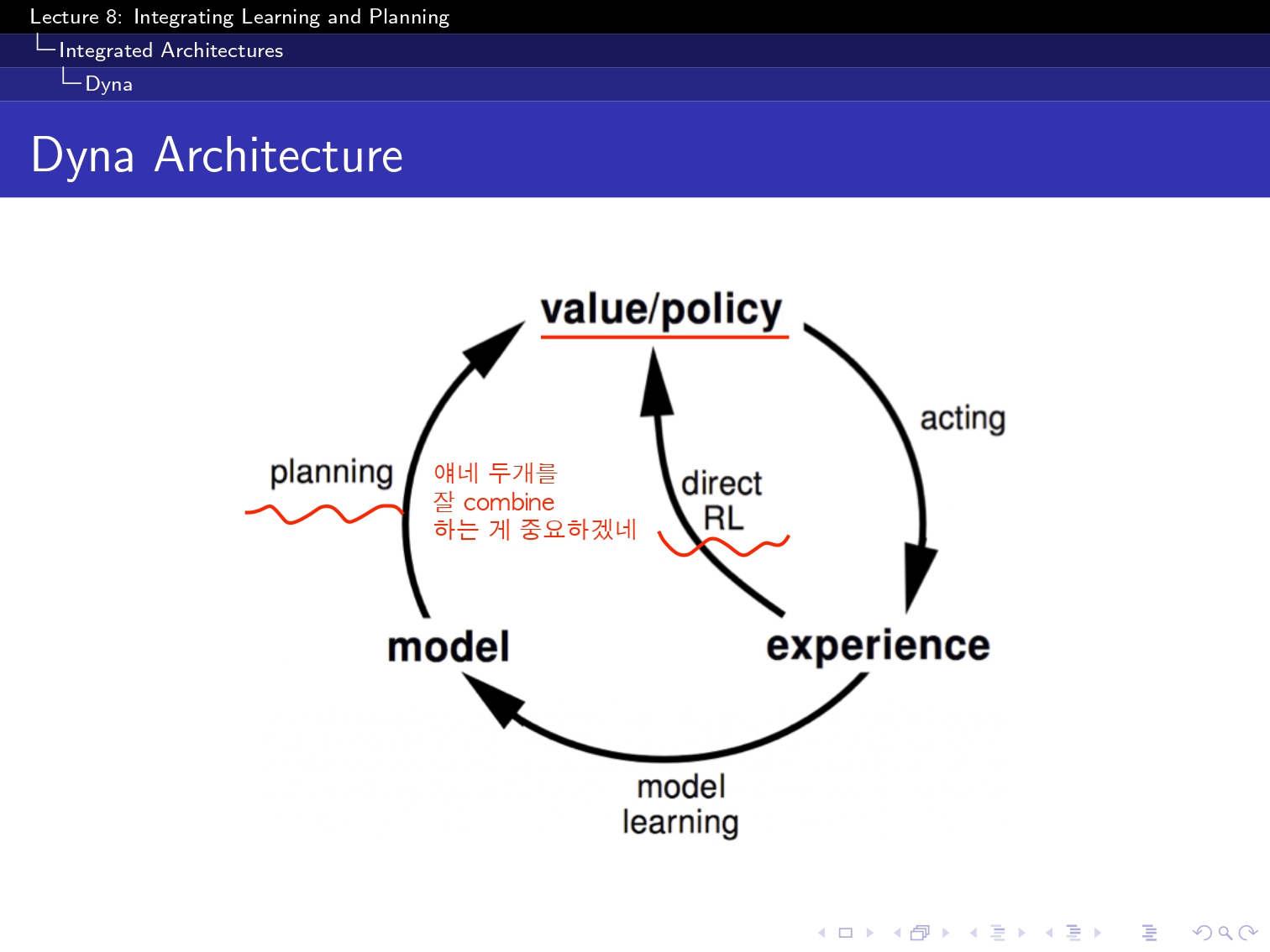
main()이전과는 다른 점은, Model[(state_idx,action)]이 추가 되었다는 것인데요.
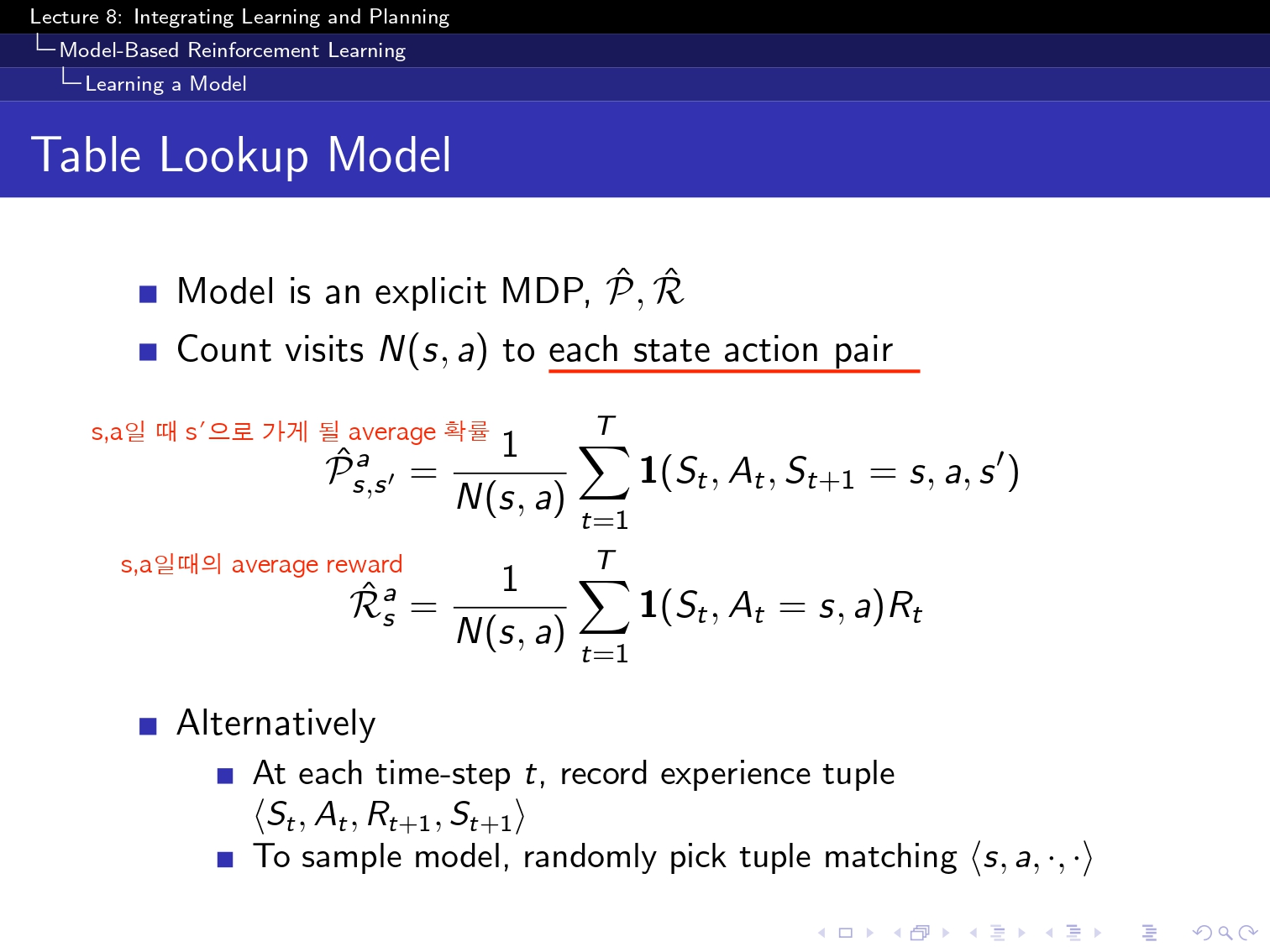
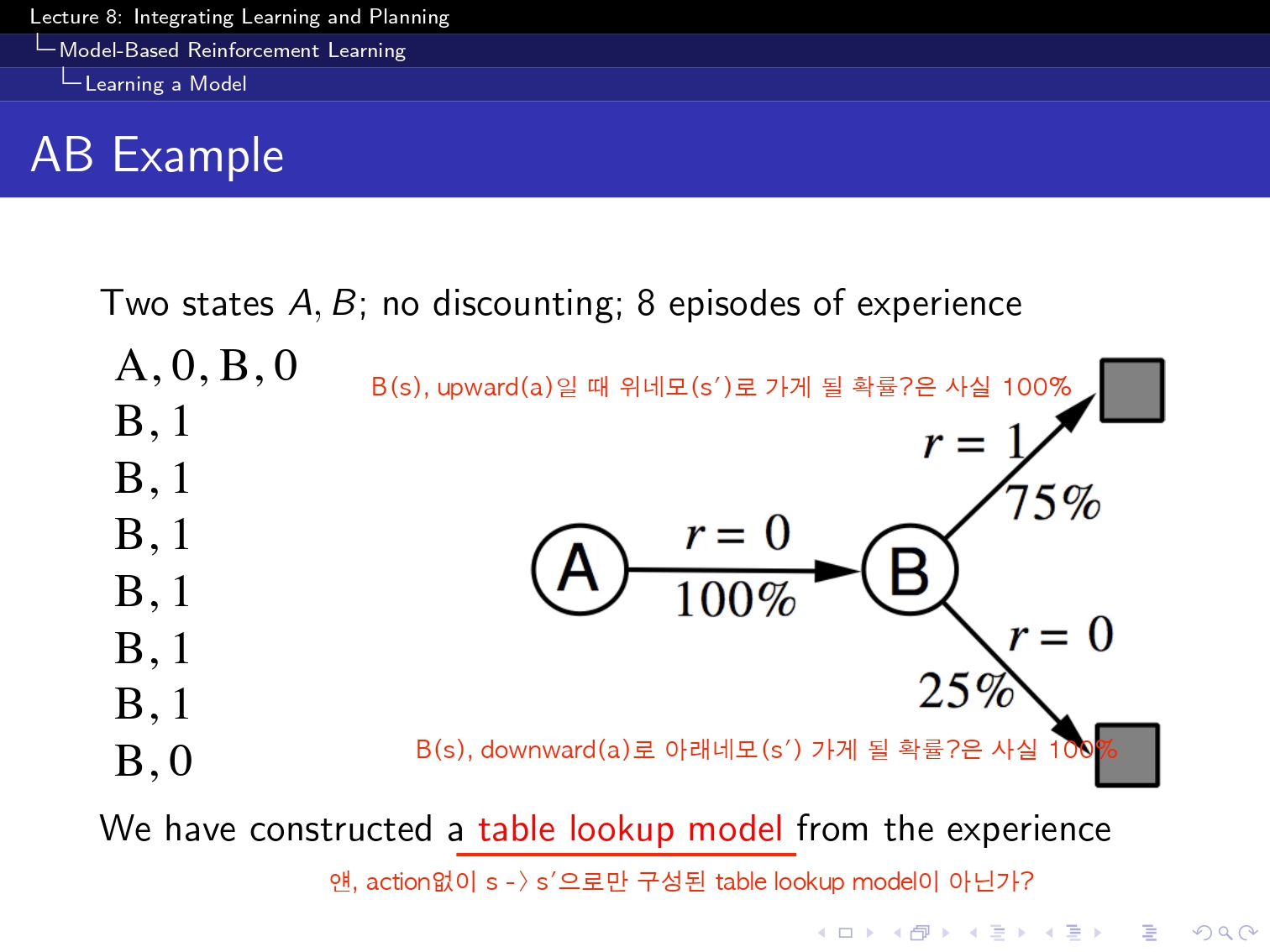
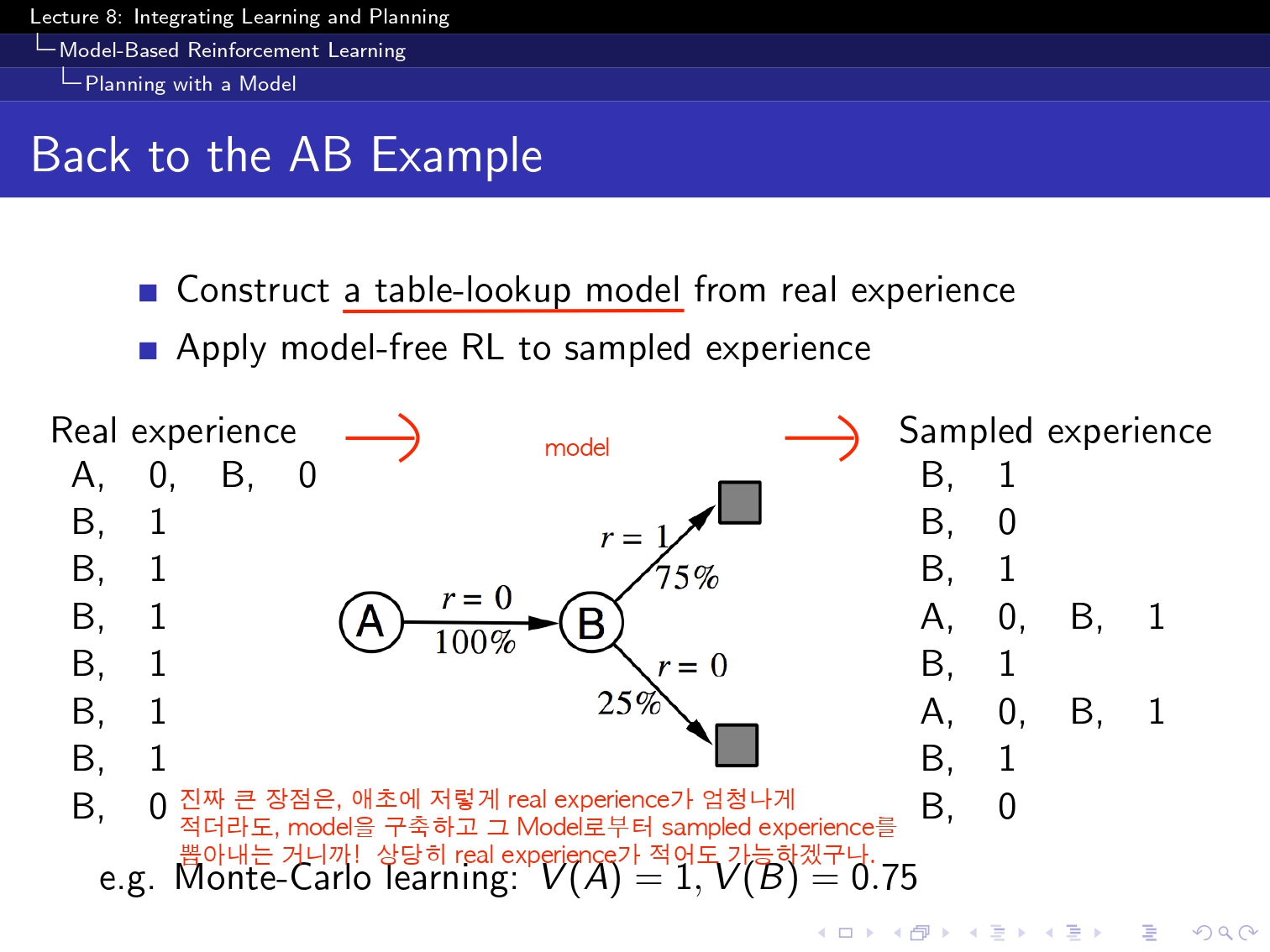
여기서 Model은 정말 다양한 모델을 쓸 수 있지만 일단 ppt에서 Model에도 table lookup도 있다고 해서 일단은 table lookup방식으로 해보았습니다! ! ! !
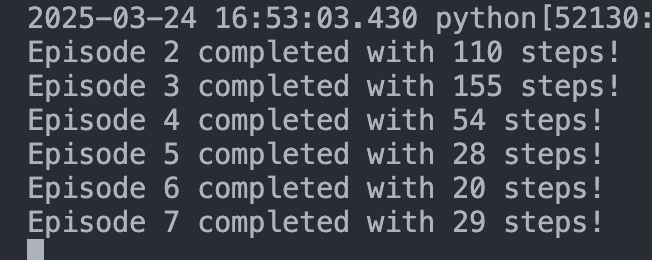
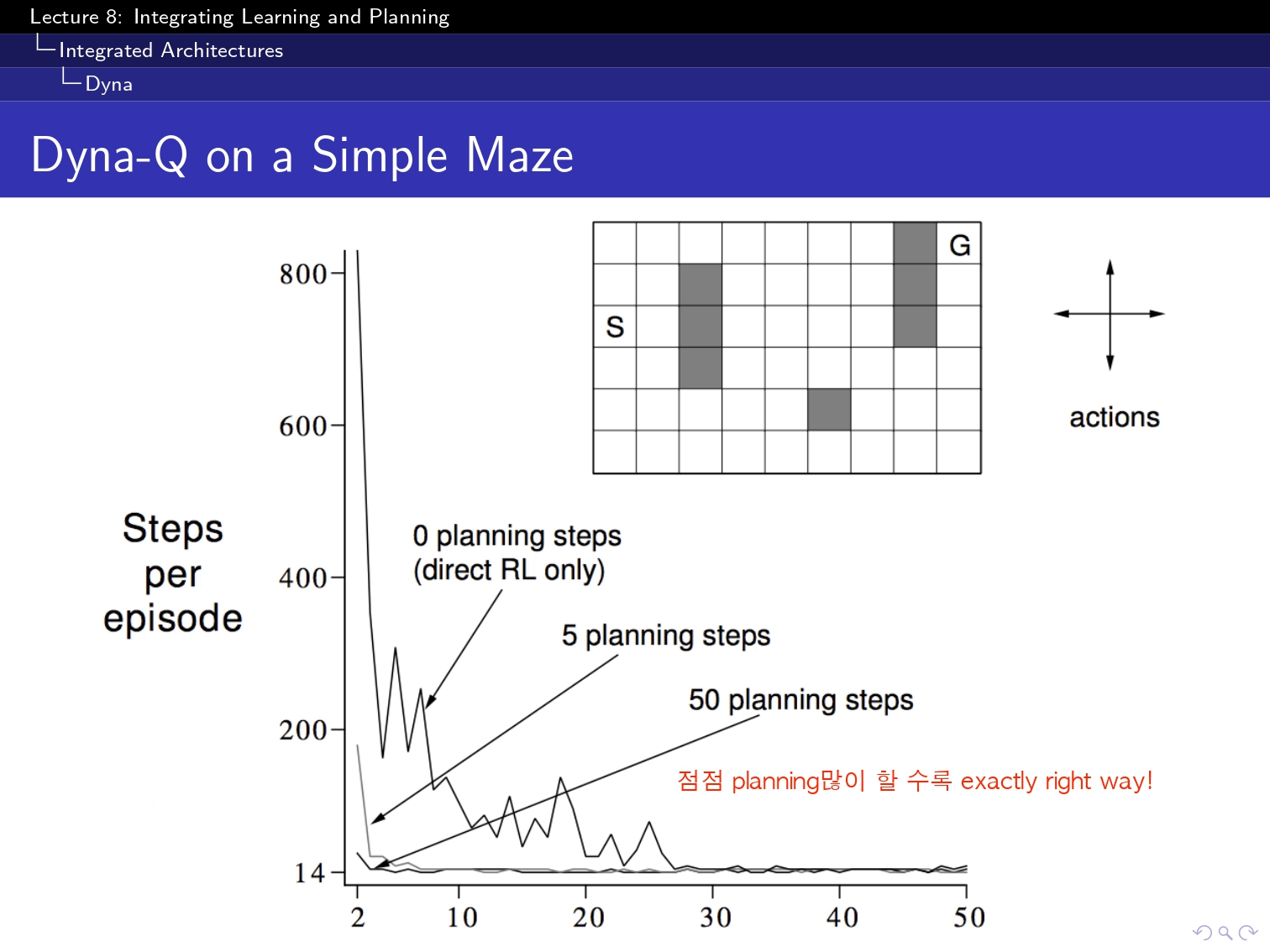
이런식으로 점점 수렴하는 것을 알 수 있습니다!!!
