https://learnopencv.com/fine-tuning-yolov12/

Fine-Tuning YOLOv12: Comparison with YOLOv11 & Darknet-Based YOLOv7
이 글은 최신 객체 탐지 모델인 YOLOv12, YOLOv11, 그리고 Darknet 기반 YOLOv7을 HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋에 맞게 미세 조정(fine-tuning)하는 과정을 다루고 있습니다. HRSC2016-MS는 다양한 크기, 밀도, 방향을 가진 선박의 항공 이미지를 포함하고 있어 모델 학습에 도전적인 데이터셋입니다.
- HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋 이해:
- 이 데이터셋은 다양한 크기와 방향의 선박 이미지를 포함하여, 모델의 일반화 능력을 평가하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 데이터셋 전처리 및 변환:
- 주석을 XML 형식에서 YOLO 형식의 텍스트 파일로 변환합니다.
- 데이터셋을 무작위로 섞어(train, test, val 세트로) 모델의 일반화 능력을 향상시킵니다.
- YOLO 및 Darknet 형식에 맞게 데이터셋을 재구성합니다.
- YOLOv12, YOLOv11, Darknet 기반 YOLOv7의 미세 조정:
- 각 모델에 대한 구성 설정 및 학습 절차를 설명합니다.
- 평가 지표를 통해 모델 성능을 비교합니다.
- mAP 점수 비교 및 결과 시각화:
- 각 모델의 mAP(mean Average Precision) 점수를 비교하여 성능을 평가합니다.
- 훈련 및 손실 그래프를 시각화하여 모델의 학습 과정을 분석합니다.
5.결론 및 주요 시사점:
- 적절한 데이터 전처리와 구조화가 모델의 정확도 향상에 직접적으로 기여함을 강조합니다.
- 데이터셋의 편향을 다루고, 작은 객체 탐지를 개선하며, 데이터셋을 무작위로 섞어 일반화를 보장하는 것이 중요함을 제시합니다.
이 글은 HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋의 도전과제를 다루며, 데이터 준비와 구조화의 중요성을 강조하고 있습니다. 이를 통해 모델의 정확도를 향상시키는 방법을 제시합니다.
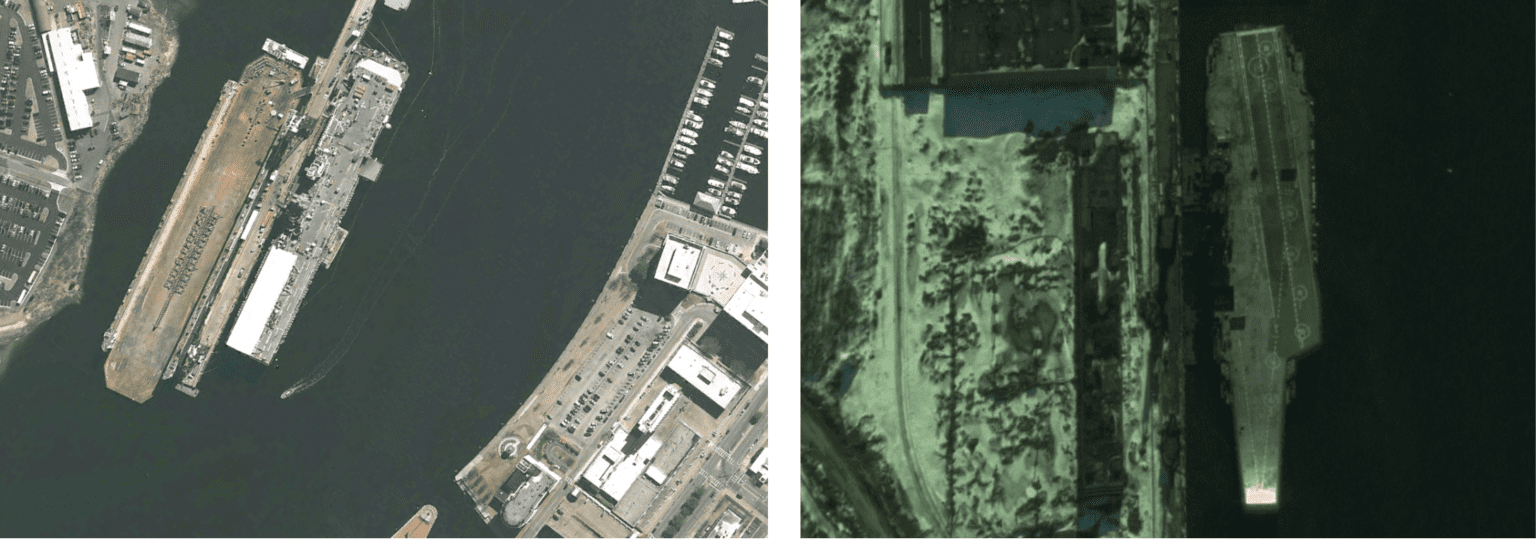
Understanding the HRSC2016-MS Dataset
먼저 데이터셋에 대한 이해가 필요합니다
HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋은 해양 객체 탐지(Maritime Object Detection)를 위한 데이터셋으로, 항공 이미지에서 선박(Ship)을 탐지하는 작업에 사용됩니다.
특징 및 주요 내용
- 단일 클래스 데이터셋
- HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋은 오직 하나의 클래스(Ship) 만 포함합니다. 즉, 모델이 탐지해야 할 객체는 모든 유형의 선박(Ships) 입니다.
- 다양한 선박 크기 및 밀도
- 데이터셋에는 크기가 매우 다른 선박들이 포함되어 있습니다. 또한, 밀집된 선박(여러 척이 모여 있는 경우)과 고립된 선박 모두 존재합니다.
- 다양한 방향(Orientation)
- HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋의 큰 특징 중 하나는 선박의 방향(Rotation)이 다양하다는 점입니다. 선박이 수직, 대각선, 수평 등 다양한 각도로 배치되어 있어, 일반적인 사각형 바운딩 박스 기반의 객체 탐지 모델이 어려움을 겪을 수 있습니다.
- 객체 탐지 모델 평가에 적합
- 선박은 다양한 크기와 방향으로 존재하기 때문에, YOLO, Faster R-CNN, SSD 같은 객체 탐지 모델의 성능을 평가하는 데 유용합니다. 특히 앵커 기반(Anchor-based) 모델과 앵커 프리(Anchor-Free) 모델의 성능을 비교하는 데 자주 사용됩니다.

적절한 데이터 전처리와 구조화 방법 (YOLOv12, YOLOv11, YOLOv7 기준)
HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋을 YOLO 기반 모델(YOLOv12, YOLOv11, YOLOv7)에서 최적화하기 위해 적절한 데이터 전처리와 구조화가 필요합니다. 이 과정에서 중요한 요소들을 단계별로 정리하면 다음과 같습니다.
1. 데이터 전처리 (Preprocessing)
1.1 어노테이션 변환 (Annotation Conversion)
HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋은 XML 형식(Pascal VOC 형식)을 사용합니다. 하지만 YOLO 모델은 텍스트 기반 어노테이션 형식을 요구합니다. 따라서 다음과 같은 변환 과정이 필요합니다.
- XML → YOLO 텍스트 형식 변환:
- XML 파일에서 객체의 경계 상자(Bounding Box) 좌표를 추출
- 이를 YOLO 형식(객체 클래스, x_center, y_center, width, height)으로 변환
- 모든 값은 이미지 크기에 대한 상대 좌표(0~1)로 변환
class_id x_center y_center width height
1.2 데이터셋 분할 (Dataset Split)
모델의 일반화를 위해 데이터를 적절히 분할해야 합니다. 일반적으로 다음과 같은 비율을 사용합니다.
- Train Set (80%): 모델 훈련용
- Validation Set (10%): 하이퍼파라미터 조정 및 검증용
- Test Set (10%): 최종 모델 평가용
데이터 분할 시 고려할 점:
- 클래스 별 분포가 유지되도록 무작위 샘플링(Random Sampling) 적용
- K-fold Cross Validation(k-겹 교차 검증) 적용 가능
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import os
import shutil
# 데이터셋 경로
image_dir = "path/to/images"
label_dir = "path/to/labels"
# 파일 리스트 로드
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(image_dir) if f.endswith('.jpg')]
train_files, val_test_files = train_test_split(image_files, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
val_files, test_files = train_test_split(val_test_files, test_size=0.5, random_state=42)
# 데이터셋 이동 함수
def move_files(file_list, src_img_dir, src_lbl_dir, dest_img_dir, dest_lbl_dir):
os.makedirs(dest_img_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(dest_lbl_dir, exist_ok=True)
for file in file_list:
shutil.move(os.path.join(src_img_dir, file), os.path.join(dest_img_dir, file))
shutil.move(os.path.join(src_lbl_dir, file.replace('.jpg', '.txt')), os.path.join(dest_lbl_dir, file.replace('.jpg', '.txt')))
# 데이터셋 분할 실행
move_files(train_files, image_dir, label_dir, "dataset/train/images", "dataset/train/labels")
move_files(val_files, image_dir, label_dir, "dataset/val/images", "dataset/val/labels")
move_files(test_files, image_dir, label_dir, "dataset/test/images", "dataset/test/labels")1.3 데이터 증강 (Data Augmentation)
작은 데이터셋에서는 데이터 증강(Data Augmentation)이 필수적입니다. 특히 HRSC2016-MS 데이터셋처럼 객체 크기와 방향이 다양한 경우, 여러 증강 기법을 적용할 수 있습니다.
✅ 적용 가능한 데이터 증강 기법
- 좌우 반전 (Horizontal Flip)
- 회전 (Rotation)
- 스케일 변환 (Scaling)
- 노이즈 추가 (Gaussian Noise)
- HSV 색상 변환 (Color Jitter)
- CutMix 및 MixUp 적용 (데이터 합성 기법)
YOLOv12 및 YOLOv11에서는 기본적으로 Mosaic Augmentation과 MixUp을 활용하여 작은 객체 탐지 성능을 향상시킵니다.
from albumentations import (
HorizontalFlip, Rotate, RandomBrightnessContrast, RandomScale, GaussNoise, Compose
)
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 데이터 증강 함수
def augment_image(image):
transform = Compose([
HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
Rotate(limit=20, p=0.5),
RandomScale(scale_limit=0.2, p=0.5),
RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.3),
GaussNoise(var_limit=(10.0, 50.0), p=0.3)
])
augmented = transform(image=image)
return augmented['image']
# 이미지 로드 및 증강 적용 예시
image = cv2.imread("example.jpg")
augmented_image = augment_image(image)
cv2.imwrite("augmented_example.jpg", augmented_image)2. 데이터 구조화 (Dataset Organization)
YOLO 기반 모델을 훈련하려면, 데이터 디렉토리 구조를 적절히 구성해야 합니다.
디렉토리 구조 예시 (YOLO 형식)
dataset/
├── train/
│ ├── images/
│ │ ├── image1.jpg
│ │ ├── image2.jpg
│ ├── labels/
│ ├── image1.txt
│ ├── image2.txt
├── val/
│ ├── images/
│ ├── labels/
├── test/
│ ├── images/
│ ├── labels/YOLO 모델을 훈련할 때 필요한 설정 파일을 생성합니다.
train.txt, val.txt, test.txt 생성
import os
def create_data_list(image_dir, output_file):
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
for img_file in os.listdir(image_dir):
if img_file.endswith('.jpg'):
f.write(f"{image_dir}/{img_file}\n")
create_data_list("dataset/train/images", "train.txt")
create_data_list("dataset/val/images", "val.txt")
create_data_list("dataset/test/images", "test.txt")YOLO 데이터 설정 파일 (data.yaml)
train: /path/to/dataset/train.txt
val: /path/to/dataset/val.txt
nc: 10 # 클래스 개수 (HRSC2016-MS 기준)
names: ['ship', 'boat', 'yacht', 'cargo', 'cruise', 'ferry', 'submarine', 'tanker', 'warship', 'other']Fine-Tuning YOLOv12 on the HRSC2016-MS Dataset
최근 YOLOv12 모델(Ultralytics 구현)을 사용한 실험 설정을 기반으로, 성능 최적화를 위해 적용된 구성 요소를 분석해 보겠습니다.
1. 모델 구성 (Model Configuration)
✅ YOLOv12 (Ultralytics Implementation) 사용
-
Ultralytics YOLOv12는 최신 YOLO 모델로, 기존 YOLO 시리즈보다 더 빠르고 정확한 객체 탐지 성능을 제공함.
-
어텐션(Aggregated Attention Mechanism) 기법이 추가되어 작은 객체 탐지 성능이 개선됨.
✅ 이미지 크기 설정: 640×640
- 640×640 해상도는 속도와 정확도의 균형을 맞추는 최적의 크기.
- YOLO 모델은 입력 이미지를 고정된 크기로 변환하여 훈련하므로, 너무 큰 크기는 계산 비용을 증가시키고, 너무 작은 크기는 객체 탐지 성능을 저하시킬 수 있음.
- 일반적으로 사용되는 YOLO 이미지 크기:
- 640×640 → 가장 많이 사용되는 크기 (속도와 정확도의 균형)
- 416×416 → 속도 우선 (경량 모델)
- 1280×1280 → 정확도 우선 (더 높은 mAP, 하지만 속도 저하)
2. 훈련 파이프라인 (Training Pipeline)
✅ Batch Size: 8
- 배치 크기(batch size)는 모델이 한 번에 처리하는 이미지 개수를 의미.
- 일반적으로 배치 크기가 크면 모델의 일반화 성능이 높아지고, 작으면 메모리 사용량이 감소하지만 수렴 속도가 느려질 수 있음.
- 배치 크기 8은 GPU VRAM이 제한된 환경에서 적절한 설정.
- 다른 배치 크기와의 비교:
Batch size 4 → 더 안정적인 훈련, 하지만 속도 느림.
Batch size 16 → 더 빠른 훈련, 하지만 과적합 가능성 증가.
✅ Epochs: 100
- Epoch(에포크)란 전체 데이터셋을 몇 번 반복하여 학습하는지를 의미.
- 일반적으로 50~150 epochs 정도가 적절하며, 100 epochs는 일반적인 YOLO 훈련 과정에서 적절한 값.
조기 종료(Early Stopping)를 적용하면 최적의 에포크에서 훈련을 중단할 수 있음.
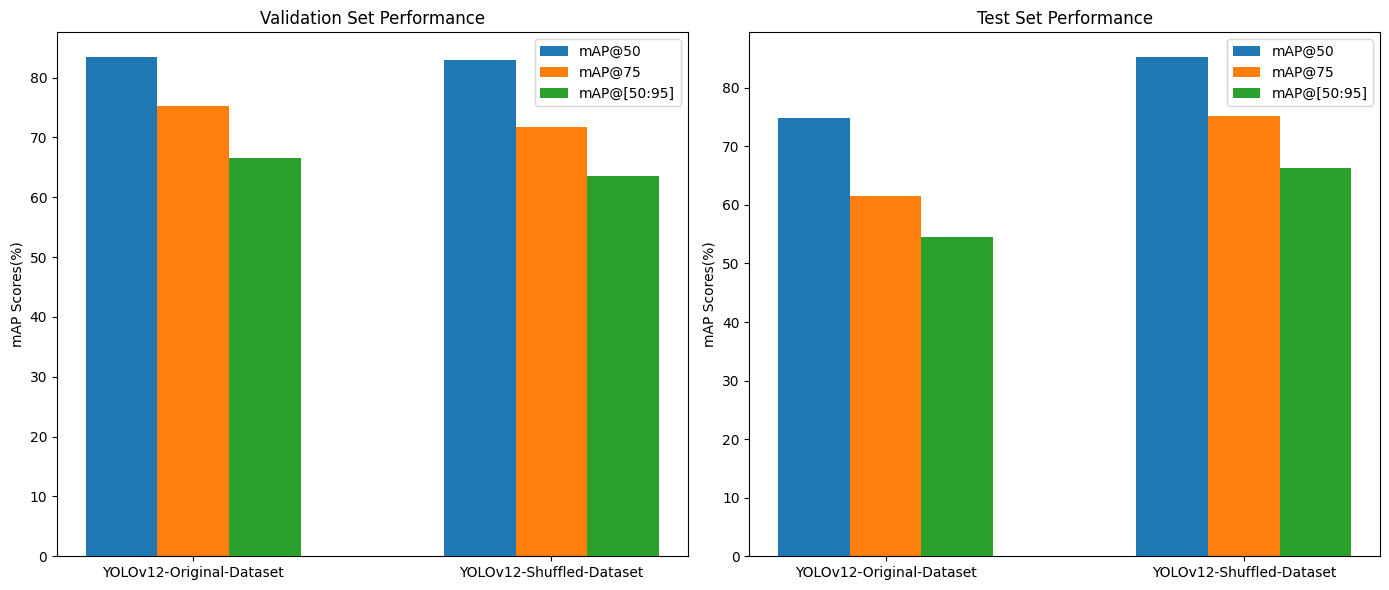
Evaluation Metrics
Inference Results on Few Images
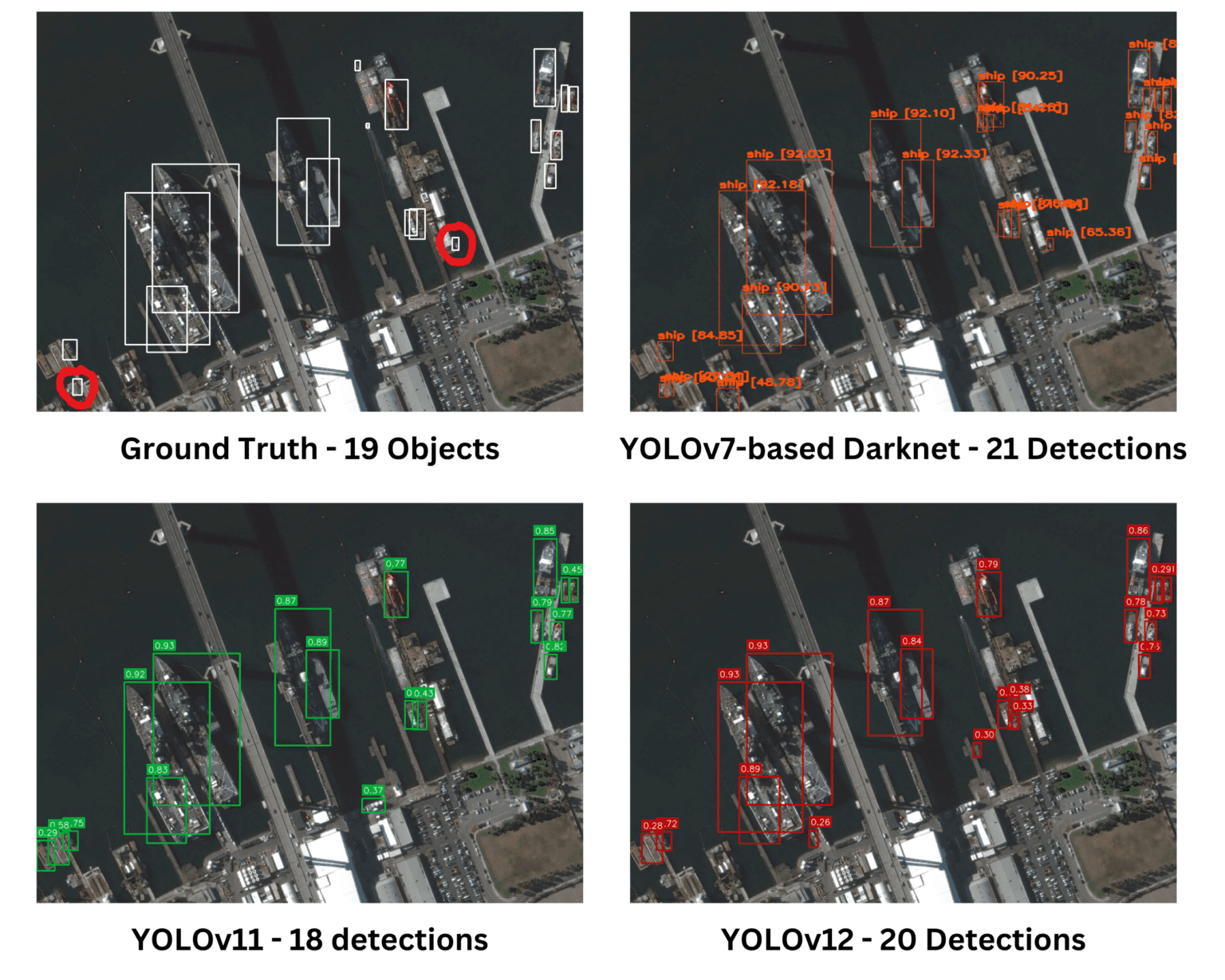

세 개의 모델 모두 주어진 실제(Ground Truth) 이미지에서 유사한 성능을 보였다. Darknet은 다른 모델들이 놓치거나 덜 정확하게 탐지한 작은 객체들을 더 정확하게 식별하는 성능을 보였다.
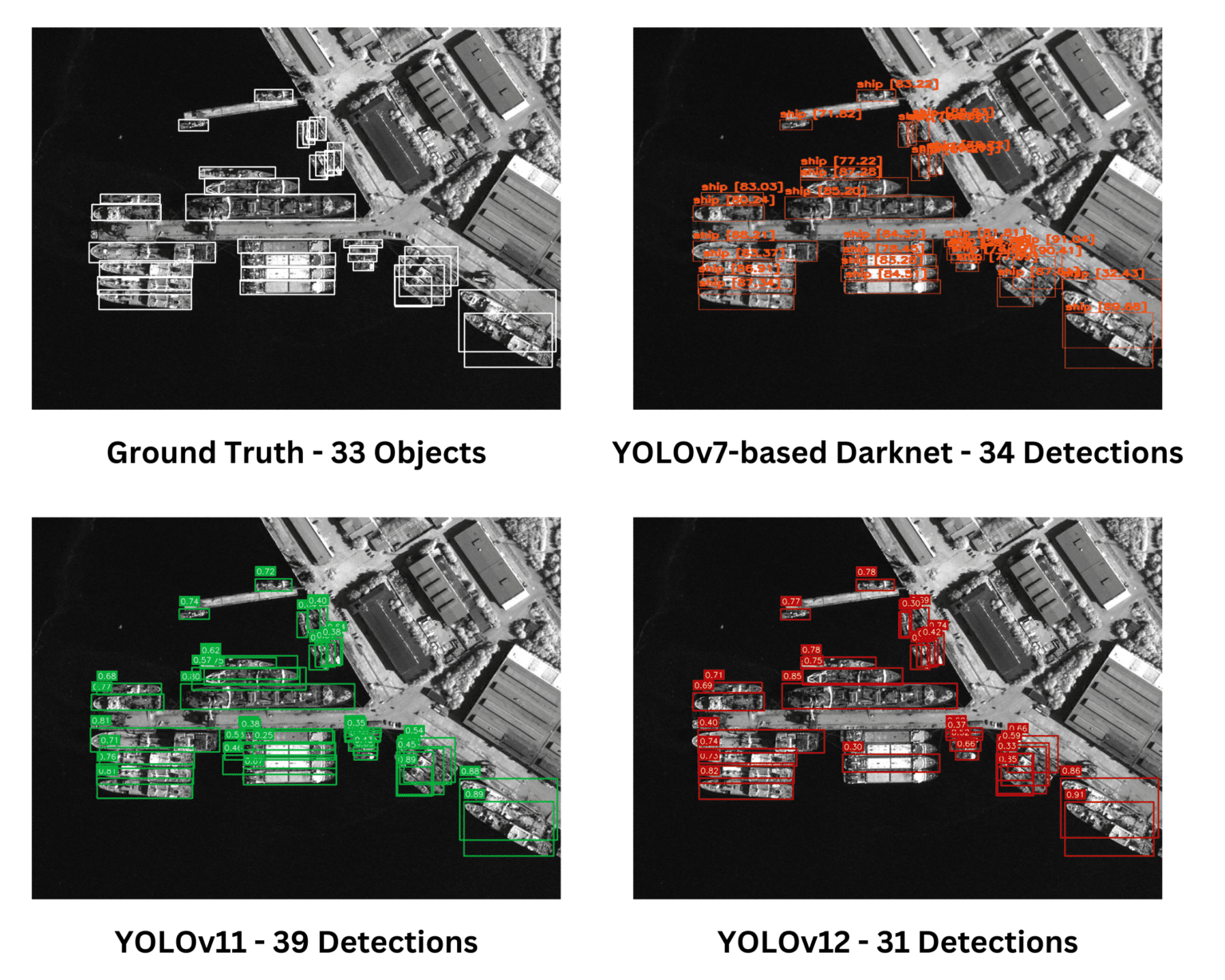

평가된 모든 모델은 밀집된 작은 객체를 탐지하는 데 강력한 성능을 보였다. 그러나 YOLOv11은 중복 탐지(overlapping detections)를 나타냈으며, 이는 불필요하거나 덜 정확한 예측을 의미할 수 있다. 전반적으로, 모델들은 다양한 수준의 중복과 정확도를 보이며 탐지 작업을 효과적으로 수행했다.
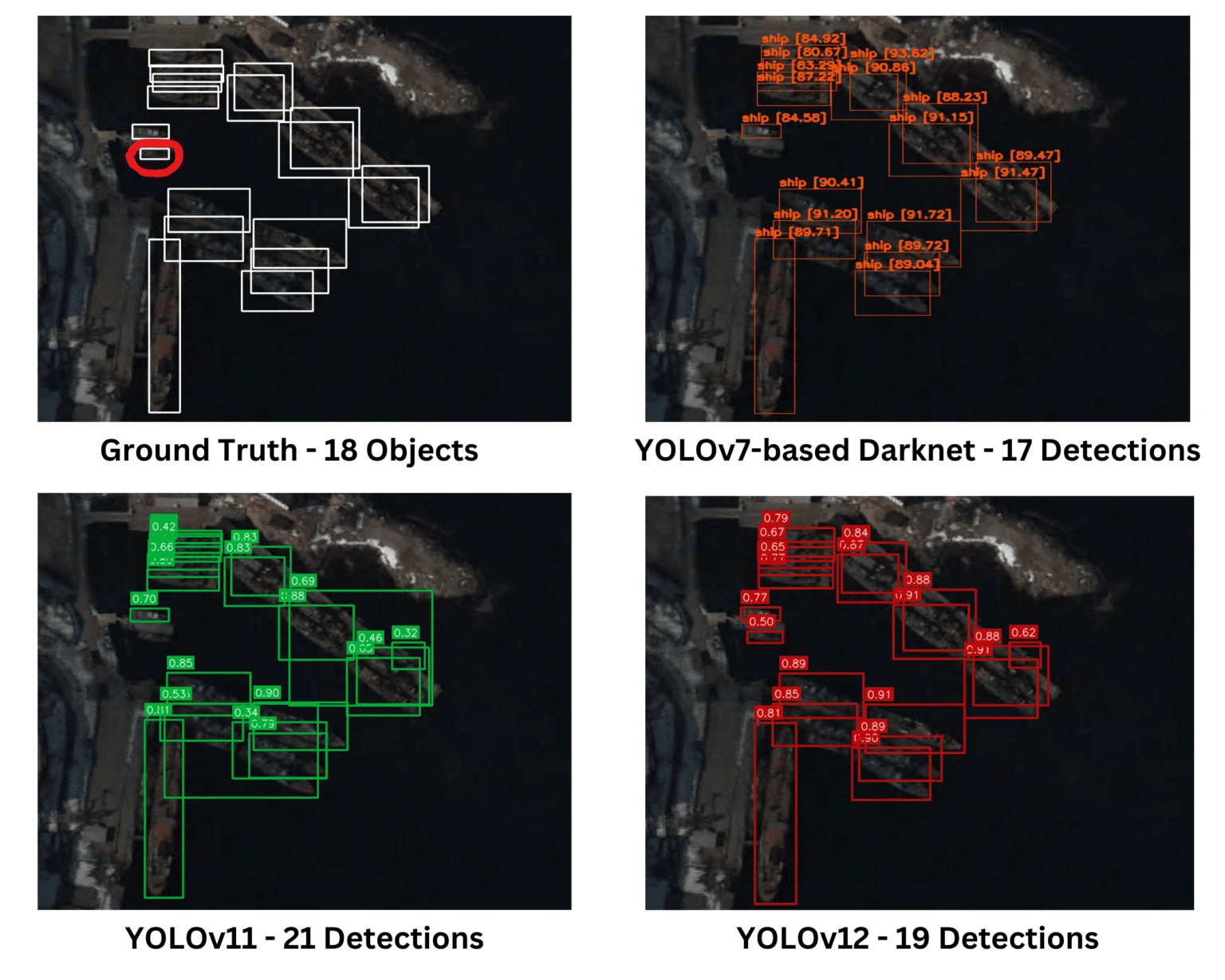

YOLOv12는 Ground Truth 이미지에서 표시된 객체를 탐지할 수 있었던 유일한 모델이었다. 전반적으로 모든 모델이 객체 탐지에서 유사한 성능을 보였지만, YOLOv11은 여전히 중복 탐지(overlapping detections)를 발생시켜 불필요한 예측이나 정확도 감소 가능성을 나타냈다.
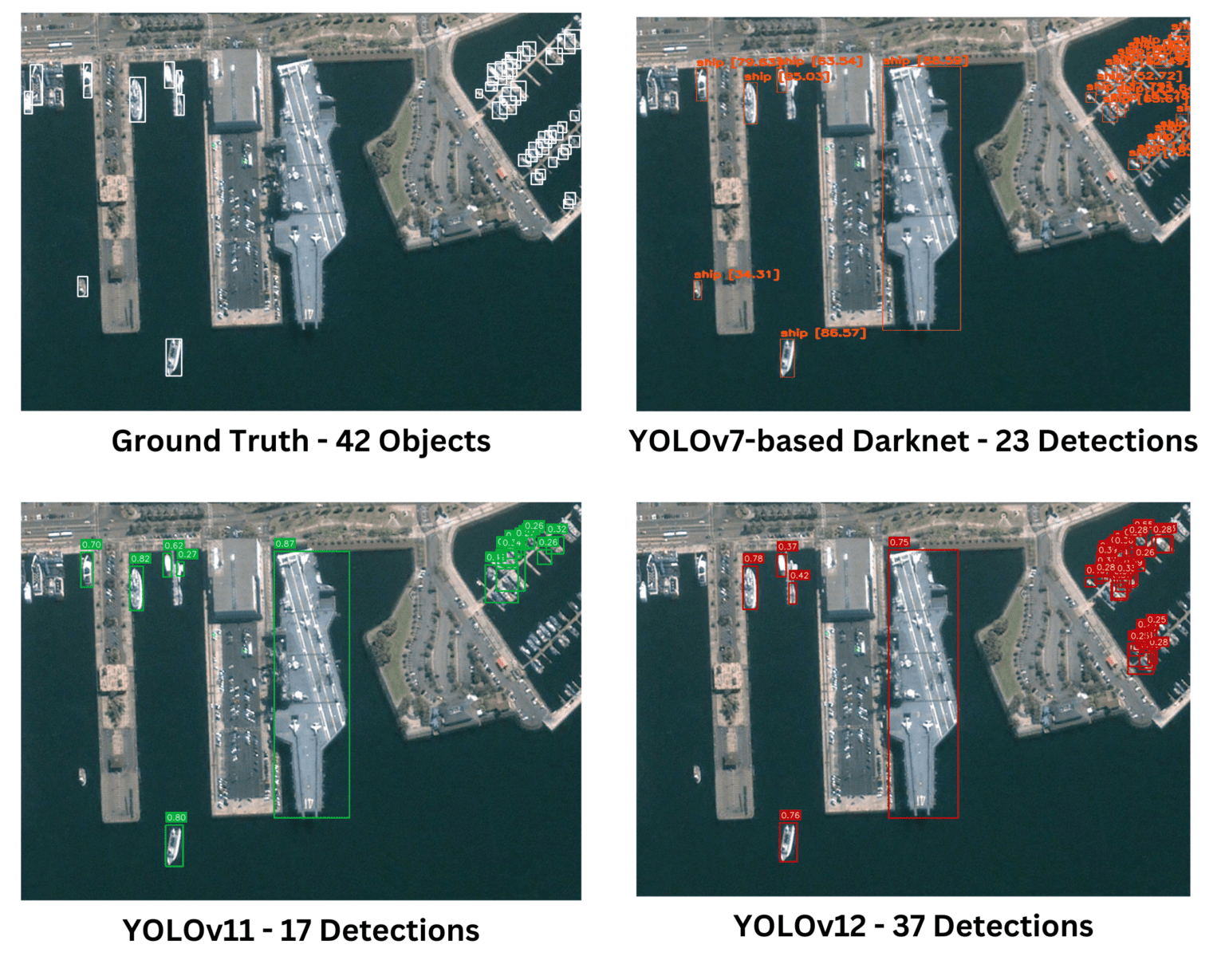

주어진 이미지는 특히 밀집된 작은 객체 탐지 상황에서 객체 탐지 모델을 평가하는 데 이상적인 테스트 사례이다. 단순한 비교에서는 YOLOv12가 더 많은 객체를 탐지했기 때문에 다른 모델보다 우수해 보일 수 있다. 그러나 자세한 분석 결과, YOLOv12의 많은 탐지가 중복되었거나 불필요한 예측(오검출)임이 밝혀졌다. 반면, Darknet 기반 YOLOv7은 탐지한 객체 수는 적었지만, 오검출과 중복이 최소화된 높은 정확도를 보였다. 객체 탐지 모델의 성능을 평가할 때는 단순한 탐지 개수가 아니라, 정확도(Precision), 재현율(Recall), 오검출율(False Detection Rate) 등을 종합적으로 고려해야 한다.
