Neural Network Implementation with numpy

torch.nn 모듈에 익숙해져 있는 나에게 nn 없이 numpy만으로 2-layer-MLP를 구현해보는 task가 주어지게 되었다. forward는 구현이 매우 쉽지만, backward 구현이 매우 어렵게 느껴졌다..
모델 구조
Linear(1) -> Sigmoid(activation) -> Linear(2) -> Softmax(Final layer) -> Cross Entropy(Loss)Weight initialization
첫 스텝은 weight를 초기화이다. 초기화 방법으로는 Xaiver Initialization을 사용하였으며, 이에 대한 설명은 해당 포스트에서는 생략하도록 하겠다! (코드 구현이 목적이므로)
https://paperswithcode.com/method/xavier-initialization
def initialize_parameters(self, input_dim, num_hiddens, num_classes):
"""
[Inputs]
- input_dim
- num_hiddens: hidden units의 수
- num_classes: 클래스의 수
[Returns]
- params: 초기화된 파라미터들의 딕셔너리
"""
# weight init -> xavier
W1_num = np.sqrt(6 / (input_dim + num_hiddens))
W1 = np.random.uniform(low=-W1_num, high=W1_num, size=(num_hiddens, input_dim))
W2_num = np.sqrt(6 / (num_hiddens + num_classes))
W2 = np.random.uniform(low=-W2_num, high=W2_num, size=(num_classes, num_hiddens))
# bias init
b1 = np.zeros(num_hiddens)
b2 = np.zeros(num_classes)
return {
'W1': W1,
'b1': b1,
'W2': W2,
'b2': b2
}Forward Implementation
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def softmax(X):
logit = np.exp(X - np.amax(X, axis=1, keepdims=True)) # for numerical stability
return logit / np.sum(logit, axis=1, keepdims=True)
def forward(self, X):
"""
[Inputs]
- X: input 행렬 (N, D)
[Returns]
- y: 모델 output
- ff_dict: 각 layer에서의 output
- type: dict
"""
fc1 = X @ self.params['W1'].T + self.params['b1'] # (N, H)
sig = sigmoid(fc1)
fc2 = sig @ self.params['W2'].T + self.params['b2'] # (N, C)
y = softmax(fc2)
ff_dict = {
'fc1': fc1,
'sig': sig,
'fc2': fc2,
'y': y
}
return y, ff_dict- softmax에서는 numerical stability(숫자의 안정성)때문에 각 batch에 해당하는 벡터의 최댓값을 빼야 한다!
- softmax의 주 연산자가 exp()이므로, softmax 적용 시 overflow 현상이 발생하게 된다. 따라서 최댓값을 해당 벡터에 broadcast로 빼주게 되면, 해당 벡터의 각 요소들이 0~1의 값을 갖게 되므로 overflow를 예방할 수 있다.
- 만약 [1e5, 1e10, 1e20] 벡터가 softmax의 입력으로 들어와 overflow가 발생했다고 가정하면, 최댓값을 뺀 경우에는 해당 값들이 에 적용되어 0~1 사이의 값을 갖게 된다. ex) (0에 가까운 어떤 두 수로 표현하기 위한 기호 사용)
- 각 layer에 대한 forward 연산 후, 각 output을 하나의 dictionary에 저장하였다. (backward 시 필요)
Loss Implementation
def loss(self, Y, Y_pred):
"""
[Inputs]
Y: 실제 라벨
Y_pred: 예측된 라벨
[Returns]
loss
"""
loss = -(1 / Y.shape[0]) * np.sum(Y * np.log(Y_pred))
return loss- Cross Entropy를 그대로 구현한 함수이다.
- Cross Entropy는 확률 분포의 불확실성을 측정하는 엔트로피를 활용하여 두 확률 분포 간의 차이를 측정하는 지표이다.
- CE 값이 낮아진다면, 모델이 데이터 분포와 가깝게 학습되었다는 것을 의미
- CE 값이 높아진다면, 모델의 예측 불확실성이 높다는 의미
Backpropagation Implementation
- Backrward 과정은 조금 복잡하므로, 한 step씩 살펴보겠습니다.
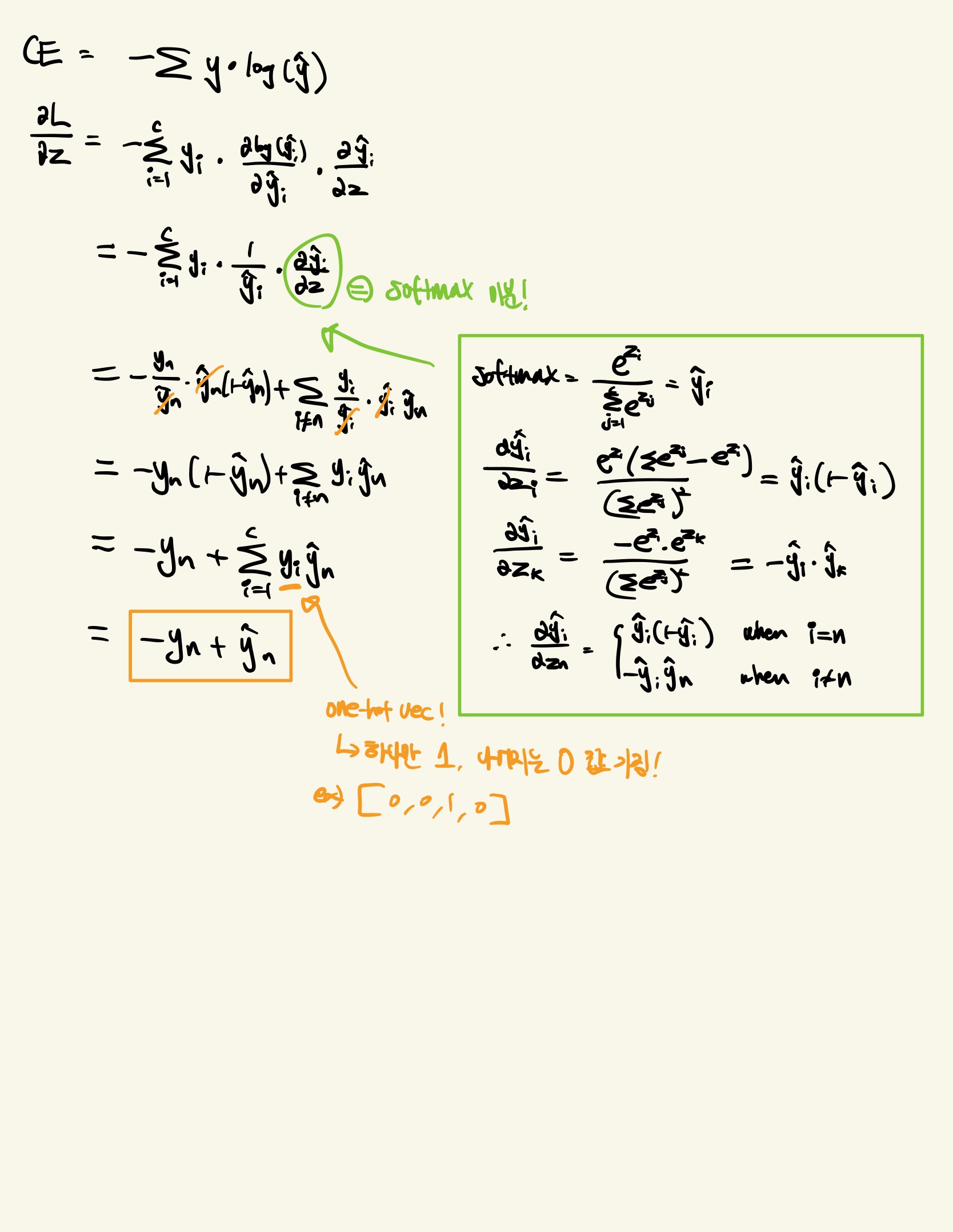
Cross Entropy + Softmax 미분
- 수식 유도 과정을 필기해보았습니다..!
- CE와 Softmax를 같이 쓰게 되면, target - pred와 같이 매우 간단한 형태로 grad를 계산할 수 있습니다!!
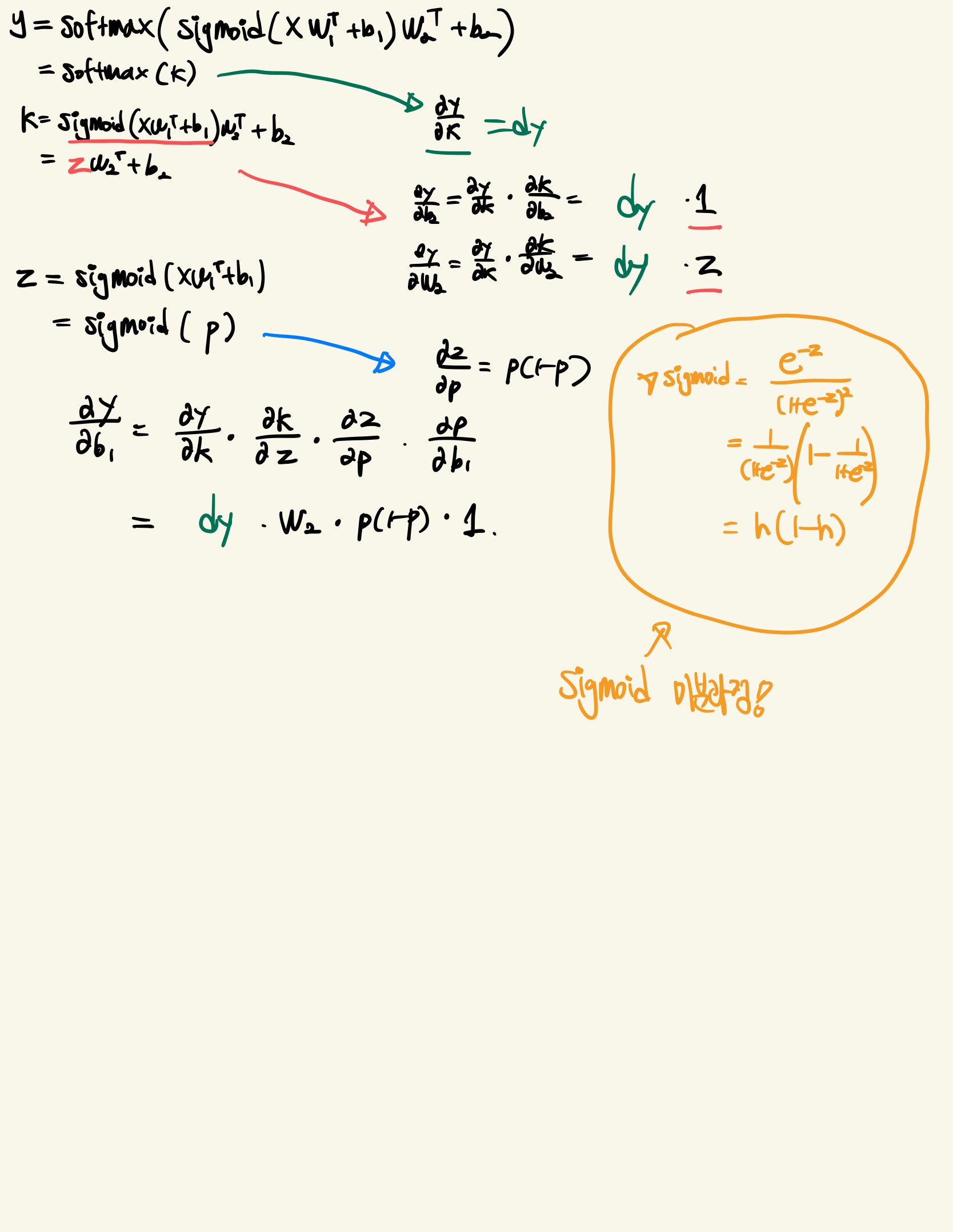
Affine transform, Sigmoid, Affine transform 미분
- 마찬가지로 수식 유도 과정 필기입니다.
- Sigmoid의 미분에 대해서도 추가로 남겨두었습니다.
Code
- 위의 수식을 구현한 코드입니다.
def backward(self, X, Y, ff_dict):
"""
[Inputs]
- X: input 행렬 (B, D)
- Y: label (B, C)
- ff_dict: outputs in forward step
- type: dict
[Returns]
- grads: W2, b2, W1, b1
- type: dict
"""
N = Y.shape[0]
dy = (1/N) * (ff_dict['y'] - Y) # (N, C)
grad_W2 = dy.T @ ff_dict['sig'] # (C, N) X (N, H) -> (C, H)
grad_b2 = np.sum(dy, axis=0) # (C,)
grad_a1 = dy @ self.params['W2'] # (N, H)
grad_z1 = grad_a1 * ff_dict['sig'] * (1 - ff_dict['sig']) # (N, H)
grad_W1 = grad_z1.T @ X # (H, N) X (N, D) -> (H, input_dim)
grad_b1 = np.sum(grad_z1, axis=0) # (H,)
return {
'W2': grad_W2,
'b2': grad_b2,
'W1': grad_W1,
'b1': grad_b1
}Training

- MNIST dataset에 대해 학습 결과, 약 0.9의 정확도로 분류해내는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다! (test data에서도 동일)
- Hyperparameters
- lr: 0.01
- batch_size: 32
- hidden_dimension(model): 128
후기
torch module을 잘 쓰자..! MLP 구현을 torch없이 직접 해보니, torch의 Autograd가 얼마나 강력한 프레임워크인지, 인공지능에서 수학(확률론, 선형대수 등..)이 얼마나 큰 비중을 차지하는지 다시 느낄 수 있었습니다. 직접 학습 과정을 구현해보면서 머신러닝에 대한 전체적인 이해도도 높아졌던 시간이었습니다!
