자바스크립트 객체 지향 프로그래밍 (Object-oriented programming)
JS 웁!!을 배워보자
프로토타입 기반 언어?
JavaScript는 프로토타입 기반 언어(prototype-based language)입니다.
모든 객체들이 메소드와 속성들을 상속 받기 위한 템플릿으로써 프로토타입 객체(prototype object)를 가진다는 의미입니다. MDN
이번 프로토타입은 MDN이나 모던자바스크립트 튜토리얼.. 블로그를 봐도 정말 너무너무 어렵다.!!!
(분명 한글로 되어있는데 .Q.)
프로토타입 prototype
참조하는 대상을 prototype이라 부른다.
자바스크립트의 객체는 [[Prototype]]이라는 숨김 프로퍼티를 갖는다. 이 값은 null이거나 다른 객체에 대한 참조가 되는데, 다른 객체를 참조할 경우 참조 대상을 ‘프로토타입(prototype)이라 부른다.
이는 자바스크립트의 ‘신기한' 특징인데, object에서 속성을 읽으려고 할 때, 해당 속성이 없으면 프로토타입에서 속성을 찾는 특징이 있기 때문이다. 이런 동작을 프로토타입 상속이라고 부른다.
.__proto__
아놔 마크다운 뭔데 T-T .. 땡큐 백틱!
__proto__는 [[Prototype]]용 getter, setter 이다.
(getter, setter가 뭔지 일단 그냥 넘어간다) 프로토타입이 참조하는 대상인건 알겠고, __proto__는 아래 코드와 같이 [[Prototype]]에 접근해 참조 대상을 지정해 줄 수 있다.
다시 말하면, obj.__proto__로 프로토타입에 접근할 수 있다. 주의를 할 부분은..
__proto__는 브라우저를 대상으로 개발하고 있다면 다소 구식이기 때문에 더는 사용하지 않는 것이 좋습니다. _모던 javascript 튜토리얼
__proto__대신에 모던한 메서드(Object.create, Object.getPrototypeOf, Object.setPrototypeOf)들이 있다고 하니까, 개념만 알아 둔다.
let animal = {
eats: true
};
let rabbit = {
jumps: true
};
rabbit.__proto__ = animal;
// rabbit의 프로토타입을 animal로 지정한다.
rabbit.eats // true"rabbit의 프로토타입은 animal입니다." 혹은 "rabbit은 animal을 상속받는다."라고 할 수 있다.
__proto__의 값은 객체나 null만 가능하다.
다른 자료형은 무시된다.
let Human = {
walk() {
alert('사람이 걷습니다')
}
}
let person = {
name: true
}
let actor = {
role: true
}
person.__proto__ = Human
actor.__proto__ = person
actor.walk() // (alert) '사람이 걷습니다'proto의 순환 참조는 허용되지 않는다.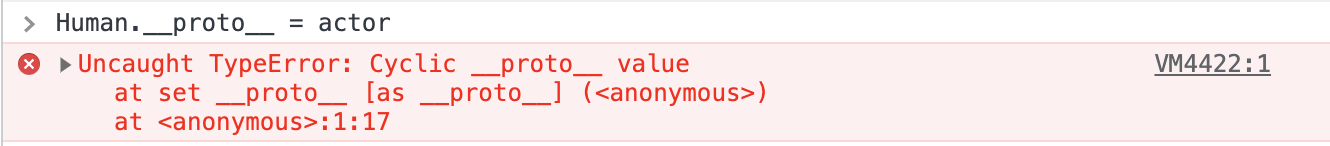
여기까지는 prototype의 개념([[prototype]], proto)과 의 동작 방식이었고,
prototype 프로퍼티에 대해 알아보자면…
.prototype 프로퍼티
우선 User() 클래스와 person1로 인스턴스를 정의한다.
클래스 User 내에서 정의한 메서드를 User.prototype에 저장한다.
현재 프로토타입에는 constructor과 sayHi 메서드가 두 개이다.
class User {
constructor (name) {
this.name = name
}
sayHi() {
let result = `${this.name}, Hello!`
console.log(result)
}
}
let person1 = new User('mina')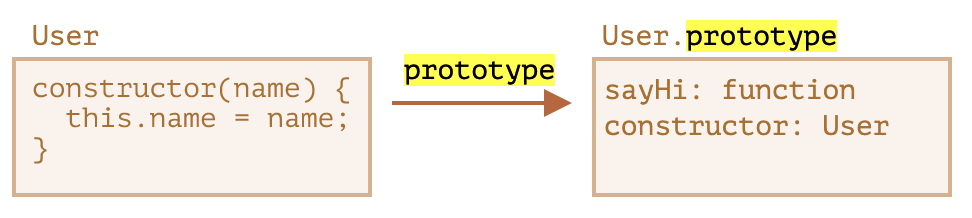
User === User.prototype.constructor // true
// User prototype 생성자와 User 클래스 자체는 동일하다.
User.prototype.sayHi() // undefined, Hello!
// → 함수를 실행하면 this.name은 User 내에서 할당되지 않았기 때문에 undefined함수의 디폴트 프로퍼티 prototype과 constructor 프로퍼티
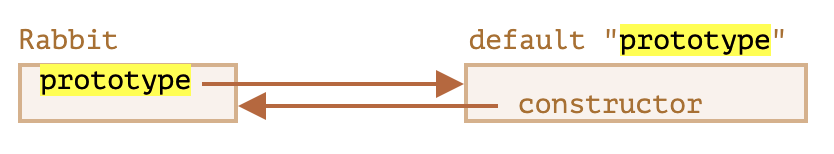
특별히 할당하지 않더라도 모든 함수는 기본적으로 prototype 프로퍼티를 갖는다. 디폴트 prototype은 constructor 프로퍼티 하나만 있는 객체를 가리키는데, constructor 프로퍼티는 함수 자신을 가리킨다.
function Rabbit() {}
// 함수를 생성만 해도 디폴트로 아래와 같이 생성되는 것과 같다
// Rabbit.prototype = { constructor: Rabbit}
// Rabbit.prototype.constructor === Rabbit → true
let rabbit = new Rabbit() // new 생성자 함수를 통해 객체를 rabbit에 상속한다.
// rabbit.constructor === Rabbit → true
// rabbit 객체도 constructor 프로퍼티를 사용할 수 있는데, 이때 [[Prototype]]를 거친다. prototype 프로퍼티 값을 덮어쓰지 않도록 주의한다.
function Rabbit() {}
Rabbit.prototype = {
jumps: true
}
let rabbit = new Rabbit()
// rabbit.constructor === Rabbit → false이런 상황을 방지하고, constructor의 기본 성질을 제대로 활용하려면 prototype 전체를 덮어쓰지 않고 디폴트 prototype에 원하는 프로퍼티를 추가, 제거해야 한다.
function Rabbit() {}
Rabbit.prototype.jumps = true
// rabbit.constructor === Rabbit → true만약 덮어쓰면 수동으로 constructor에 Rabbit을 다시 할당하면 된다.
Rabbit.prototype.constructor = Rabbit더 공부해보고 싶은 부분?
::TODO::
1. extends 와 super 키워드를 이용해서 상속
2. 프로토타입 체이닝이 일어나는 과정
3. 커스텀 객체를 만들었을 경우 일부만 상속되는 것은 왜 그런지.
출처
클래스와 기본 문법 | 모던 javascript 튜토리얼
프로토타입 상속 | 모던 javascript 튜토리얼
Object prototypes | MDN
함수의 prototype 프로퍼티 | 모던 javascript 튜토리얼
