데이터 분석과 python
주의: 행 렬 == row col == ↓→
Numpy
fundamental package for scientific computing in Python
Numpy가 제공하는 것
- 다차원 배열
ndarray- 파이썬 기본 배열과 다름(list와 다르게 생김)
- 여전히 c와 같은 compile language 보단 느림
- 파생 객체
masked arraysmatrices - 빠른 연산을 가능케 하는 기본 도구 모음
Numpy 배열의 특징
- 생성될 때 정해지는 크기(memory allocation)
- 동일한 데이터 타입 → 동일한 메모리
- 대용량 데이터를 가지고 빠른 수학적/과학적 계산 가능
배열 모양

- 24의 위치: [1][3][2]
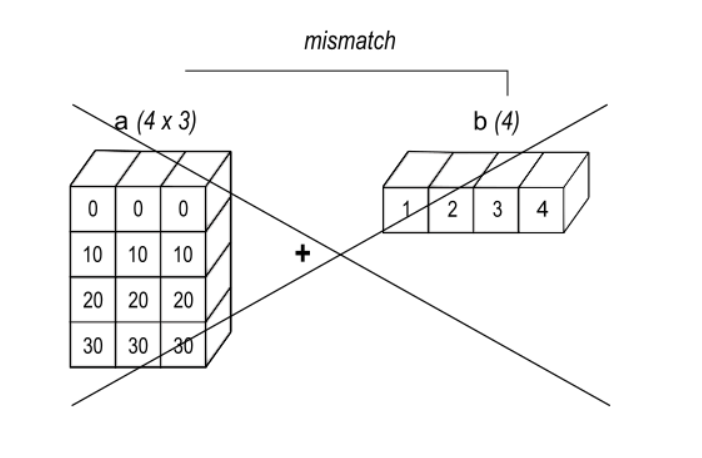
브로드캐스팅(Broadcasting)
두 array가 있을 때, 둘이 연산 가능할 때 호환되는 현상
- 두 array가 있을 때, 둘이 연산을 할 수 있을 때 →
크기가 같을 때or둘 중 하나가 1(크기)일때 - Vectorization과 Broadcasting은 한 번에 일어난다.
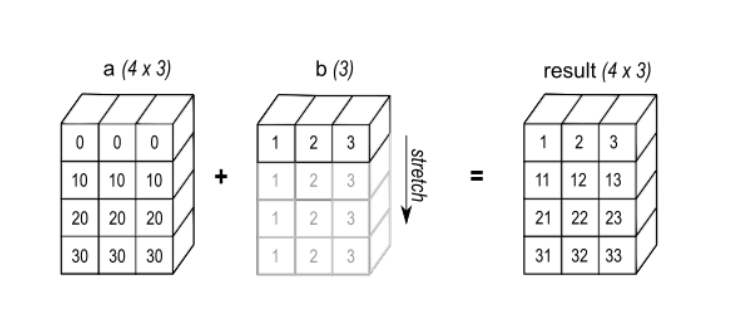
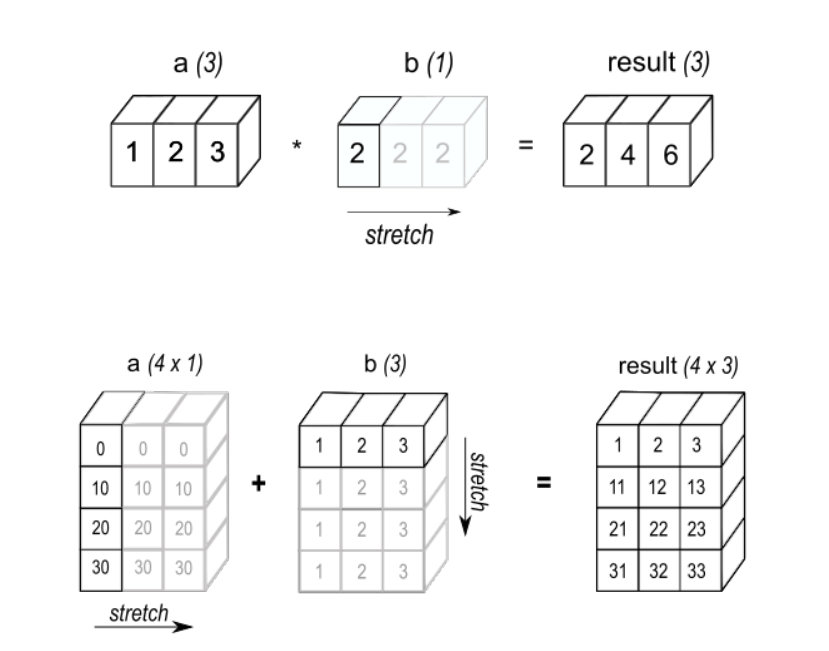
브로드캐스팅 가능 예
브로드캐스팅 불가능 예

Vector화
동일 크기의 두 배열에 있는 각 element의 곱을 구하는 문제
// In C
c = []
for i in range(len(a)):
c.append(a[i] * b[i])for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
c[i][j] = a[i][j] * b[i][j];
}
}↓
#in numpy
c = a * b주의: Dot Product가 아닌 같은 크기, 같은 위치 배열 기준
Numpy 배열 생성
목적이 다른 곳에서 데이터를 가져와 사용하기 위함
- 6가지 방식 존재
- 다른 python 구조(list, tuple 등) 에서 변환
- Numpy 자체 제공 함수로 생성:
arangeoneszeros - 기존 배열 복제, 결합, 수정
- Disk에서 배열 불러오기
- 문자열이나 버퍼를 이용해 Raw Bytes로부터 배열 생성
- 특수 라이브러리 함수 사용:
SciPypandasOpenCV
다른 Python 구조에서 변환
import numpy as np
a1D = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
a2D = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
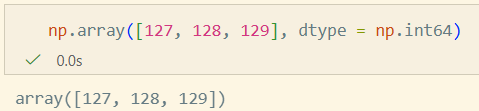
a3D = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])numpy.array를 사용할 때에는dtype을 사용하자(주로np.int64사용)
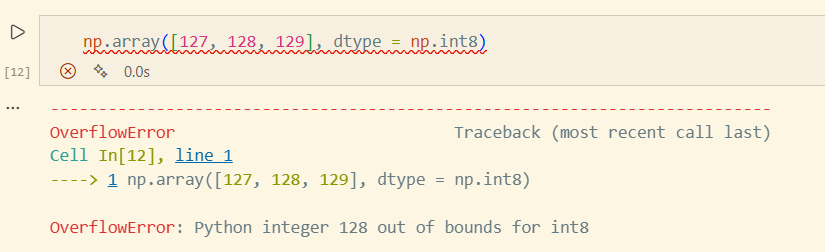 참고: np.int8 : -127~128
참고: np.int8 : -127~128
 u21: 유니코드 21자리
u21: 유니코드 21자리

- [-3, -3, -3] 이 unsigned Int 형식으로 처리되어서 해당 값이 출력
- 자체적으로 32비트 값이 지정되어 있는 것은 같다.
- 그 값을 읽는 방식을 다르게 지정했기때문에 발생한 현상
- c_signed64에선 b값이 int32 → a는 uint64 이므로 int 64로 변환되기 때문에 정상적으로 기대한 값 출력
Numpy 자체 제공 함수
arange, linspace

주의: float16과같이 너무 작은 비트수를 float로 표현하면 오차 발생으로 인한 이상한 값이 튀어나올수도..)
eye


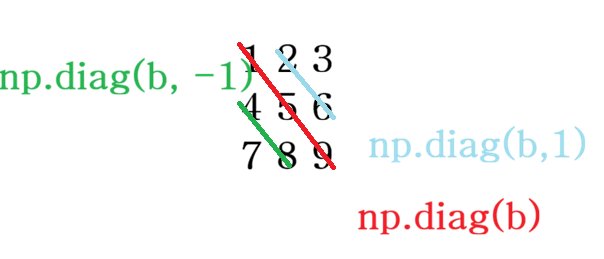
diag
공분산 행렬에서 분산 값만 추출하는 경우, 다중회귀분석에서 가중치를 부여할 때 사용
SVD(특이값분해)에서도 사용


np.diag([1, 2, 3], 1)에서 1에 -1값을 넣으면 왼쪽으로도 shift 가능




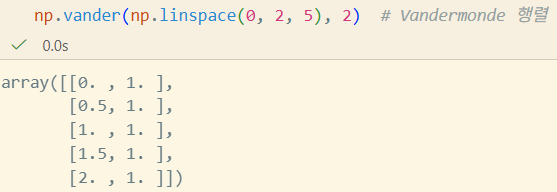
vander


zeros


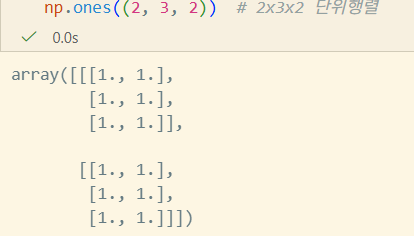
ones

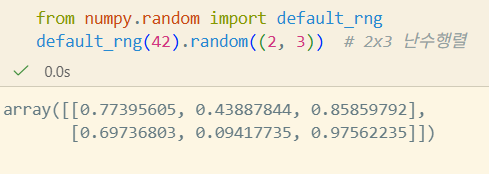
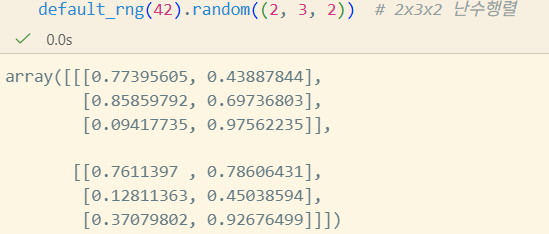
default_rng
indices

기존 배열을 복제, 결합, 수정




Disk에서 배열 불러오기
CSV 읽기
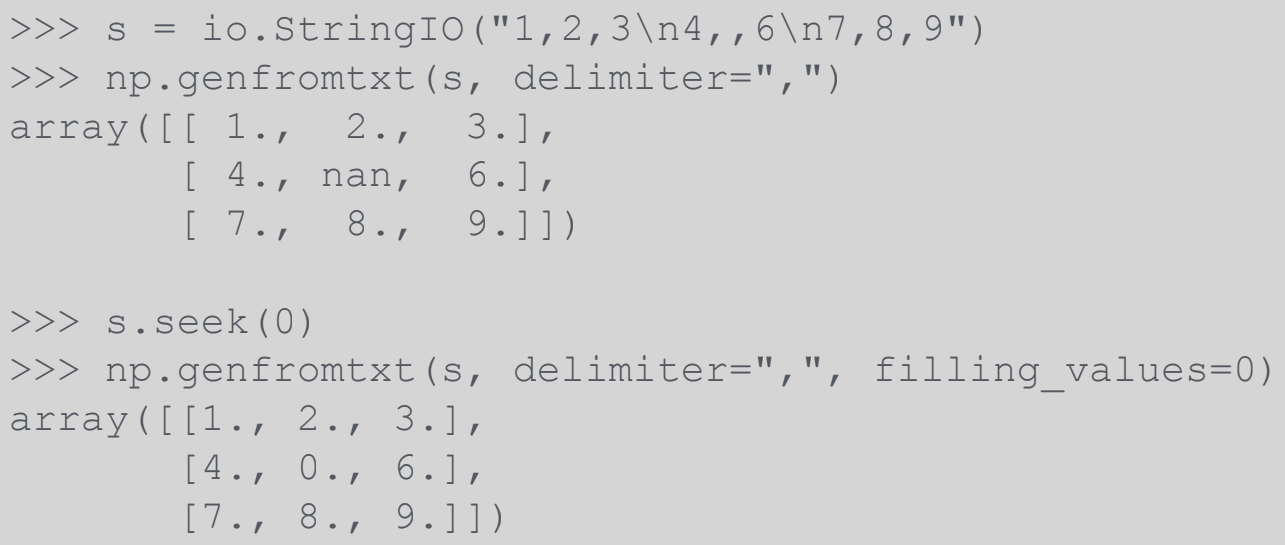
loadtxt: 빠진 값이 없는 정형화된 자료, float/int 중심genfromtxt: 값이 빠진 경우, 복잡한 dtype지정, 결측값 처리 등 유연성 높음
JSON
- Numpy는 JSON serializable 하지 않다(JSON Encoding 불가)
- json.JSONEncoder 사용
pickle
- 가급적 피해라(확장성 떨어짐)
- pickle은 잘못 생성된 데이터에 안전하지 못함
numpy.save,numpy.load사용할 때allow_pickle=False설정
Numpy 배열의 자료형

void는 null로 끝나지 않음을 주의
Numpy 배열 인덱스
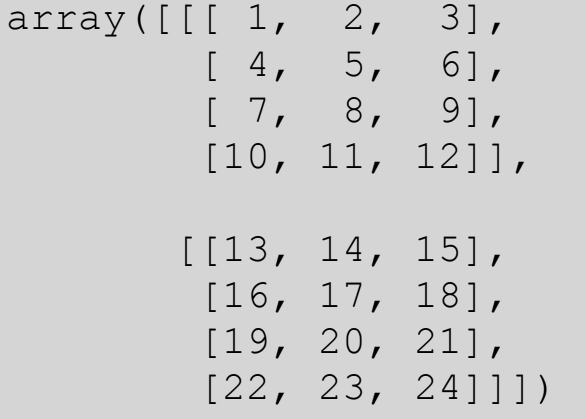
x[0, 1, 2]==x[0][1][2]- [0, 1, 2]가 더 빠르다([0][1][2]는 앞의거까지 evaluation 처리때문에 느림)
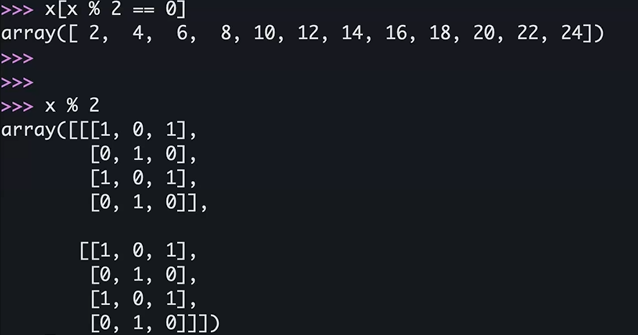
x[-1, -1, -1]→ 24x[0]x[x % 2 == 0]vectorization
x[[True, False]]vectorization- True인 부분의 인덱스만
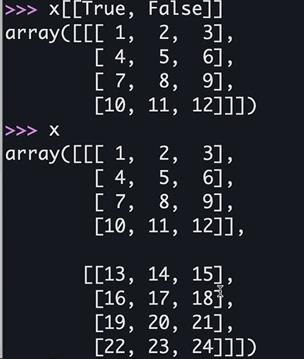
- True인 부분의 인덱스만
Numpy 배열 슬라이스
- 배열의 Slice는 View
start:stop:step...은:의 확장이다
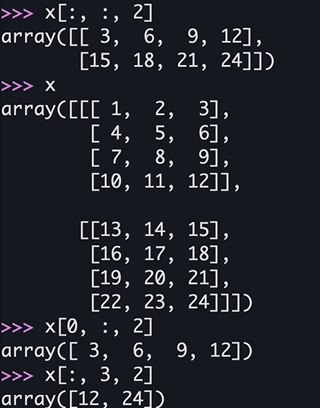
x[:, :, 0]==x[..., 0]
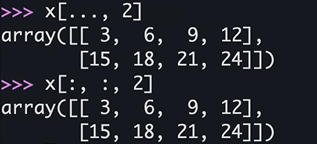
x[:, 0]는 다르다
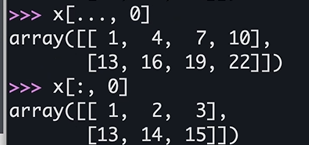
x[0, 0, [0, 2]]==x[0, 0, 0:3:2]
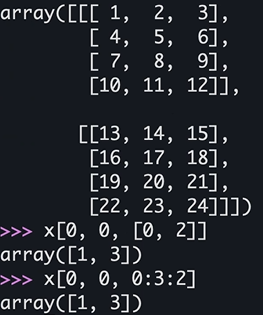
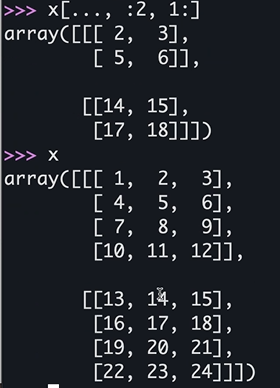
x[0, [0, 2], 1]
Numpy 함수
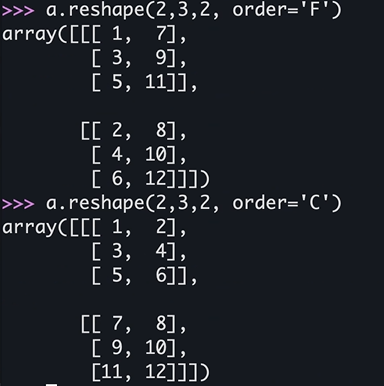
reshape
numpy.reshape(a, /, shape = None, order = 'C', newshape = None, copy = None)
# order에서 C는 C언어 기준 (깊은 depth 부터)
# F는 Fortran 기준 (바깥 depth 부터)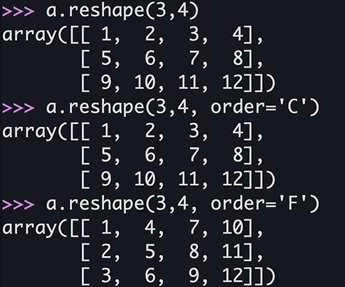
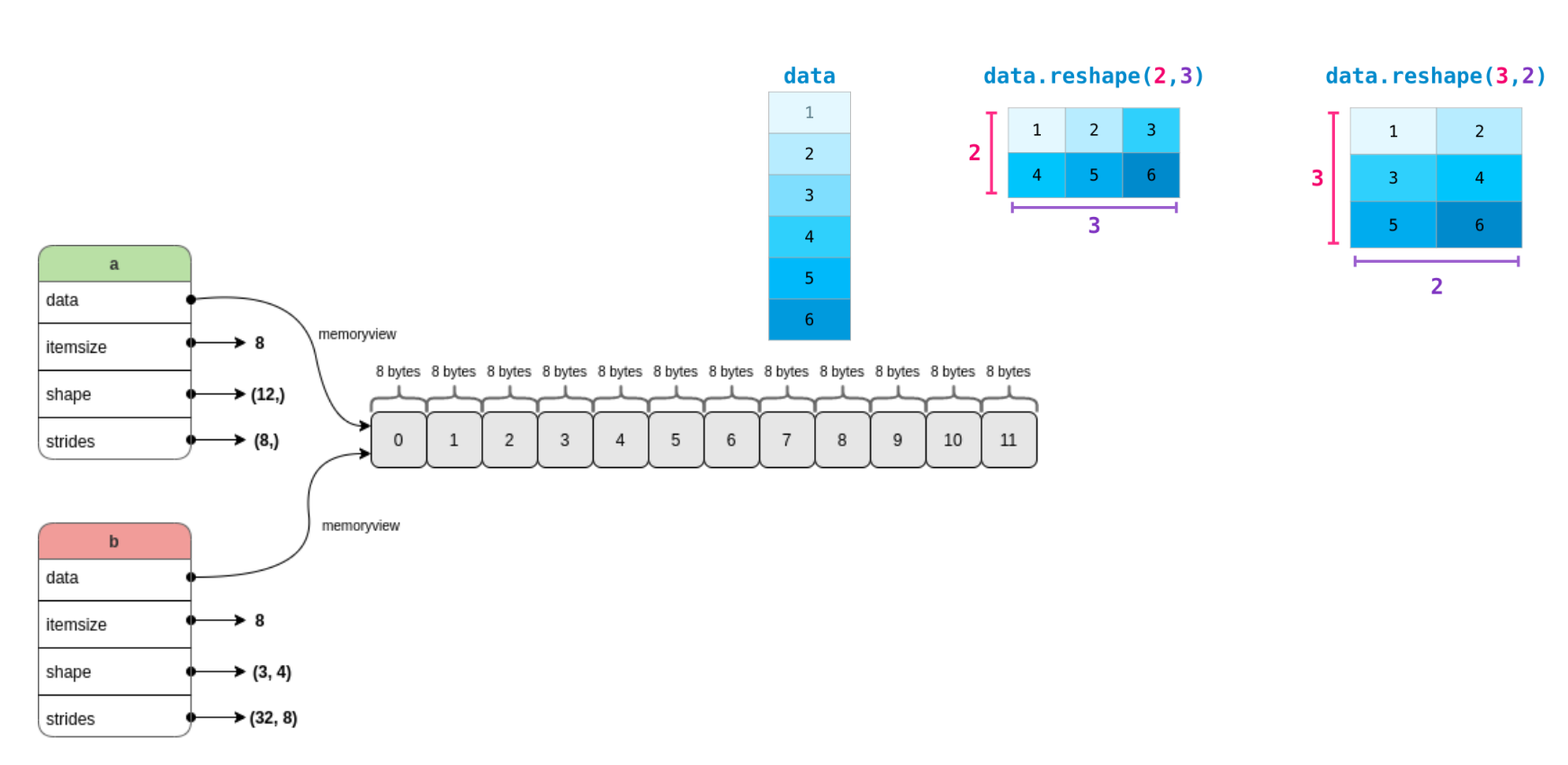
- a에서 reshape 통해 b 됨
- shape: (12,) → (3, 4)
- 3 x 4 가 됨
- strides: (8,) → (32, 8)
- 다음 elem을 찾으려면 8칸을 가면 된다는 의미 → 첫번째-두번째 elem의 메모리 차이가 32만큼 차이
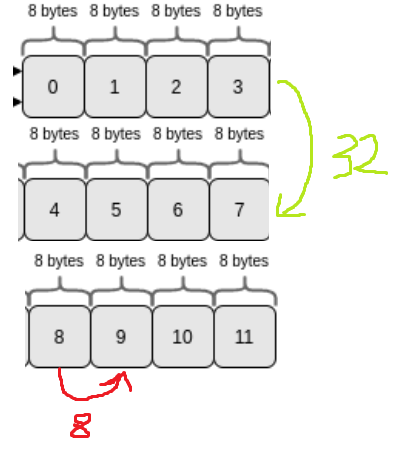
- 다음 elem을 찾으려면 8칸을 가면 된다는 의미 → 첫번째-두번째 elem의 메모리 차이가 32만큼 차이
- shape: (12,) → (3, 4)
flatten, ravel, flat
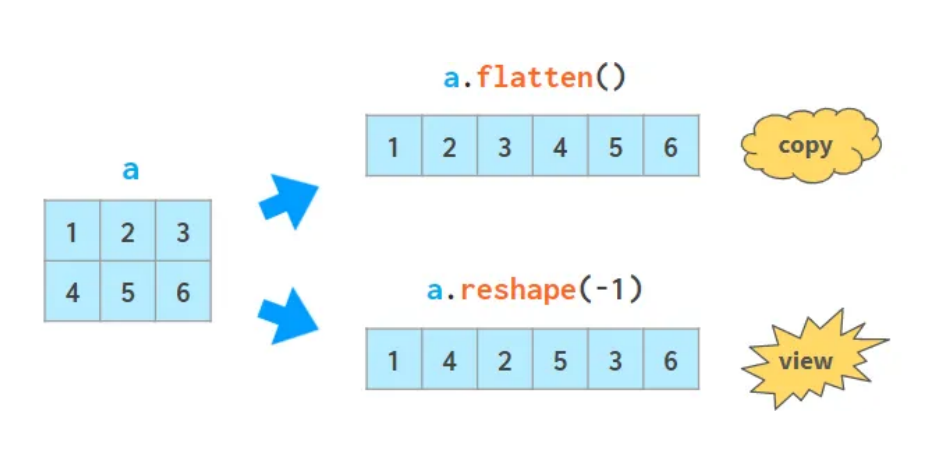
ndarray.flatten(order = 'C') #copy 반환
ndarray.flat() #Iterator 반환: 내부적으로 함수가 반환됨 → direct access는 불가, loop만 가능
numpy.ravel(a, order = 'C') #필요할때만 copy해서 반환transpose, moveaxis, swapaxes
축 뒤집기
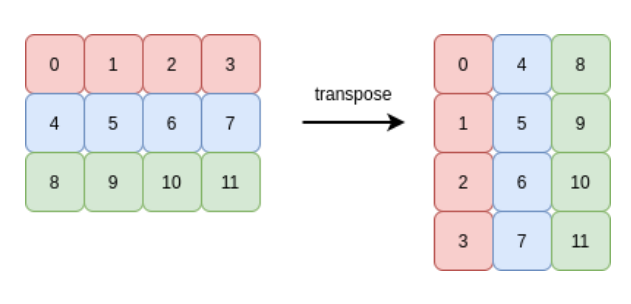
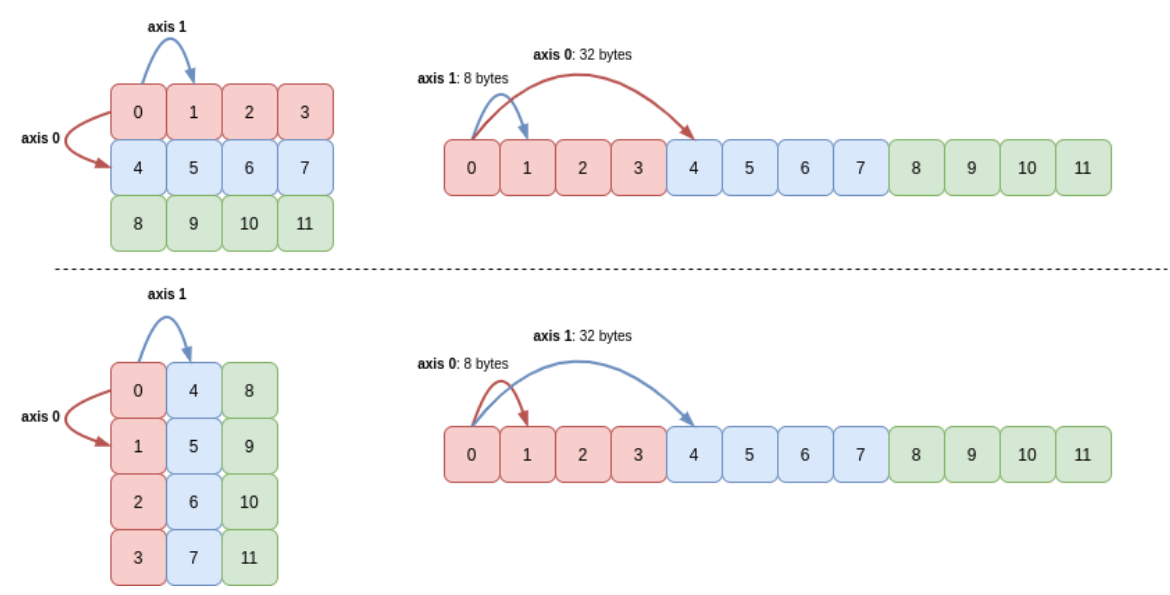
numpy.transpose(a, axes = None)
numpy.moveaxis(a, source, destination)
numpy.swapaxes(a, axis0, axis1)min, max, sum
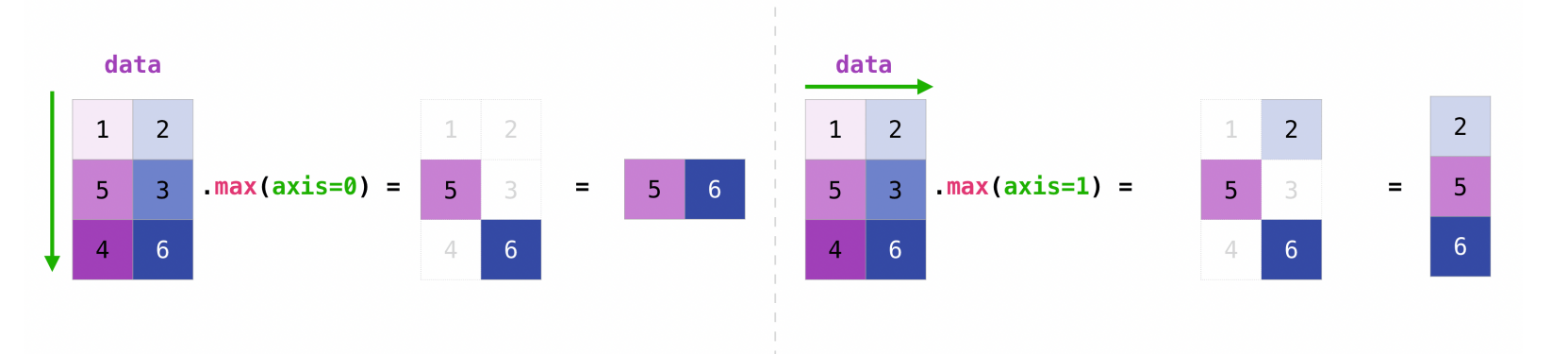
numpy.min(a, axis=None, out=None, keepdims= , initial= , where= )
numpy.max(a, axis=None, out=None, keepdims= , initial= , where= )
numpy.sum(a, axis=None, dtype=None, out=None, keepdims= , initial= , where= )Pandas
데이터 분석 포커싱
개요
- DataFrame을 잘쓰면 pandas를 잘쓰는것
- 자유로운 컬럼의 삽입 및 삭제
- 빠른 읽기 쓰기: CSV, text, MS Excel,SQL, database, HDF5
- 강력한 group by(SQL만큼까지는 아님)
- 지능적인 데이터 정렬과 누락된 데이터 처리
- 고성능 병합 및 조인
- 유연한 데이터 재구성과 피벗
- Hierarchical axis indexing
- 탁월한 시계열 기능 *시계열: 시간에 따른 데이터
- 라벨 기반 슬라이싱, 고급 인덱싱, 부분 선택
- 성능 최적화
사용처
- 복잡한 분석 로직이 필요할 때
- 시계열 Resamplig, Rolling, 분해
- Group by 연산
- 데이터 시각화
- ML(머신러닝), 통계분석 목적일 때
- 데이터 구조 호환
- 결측치 처리
- 강력한 문자열 처리
- regular expression
DataStructure
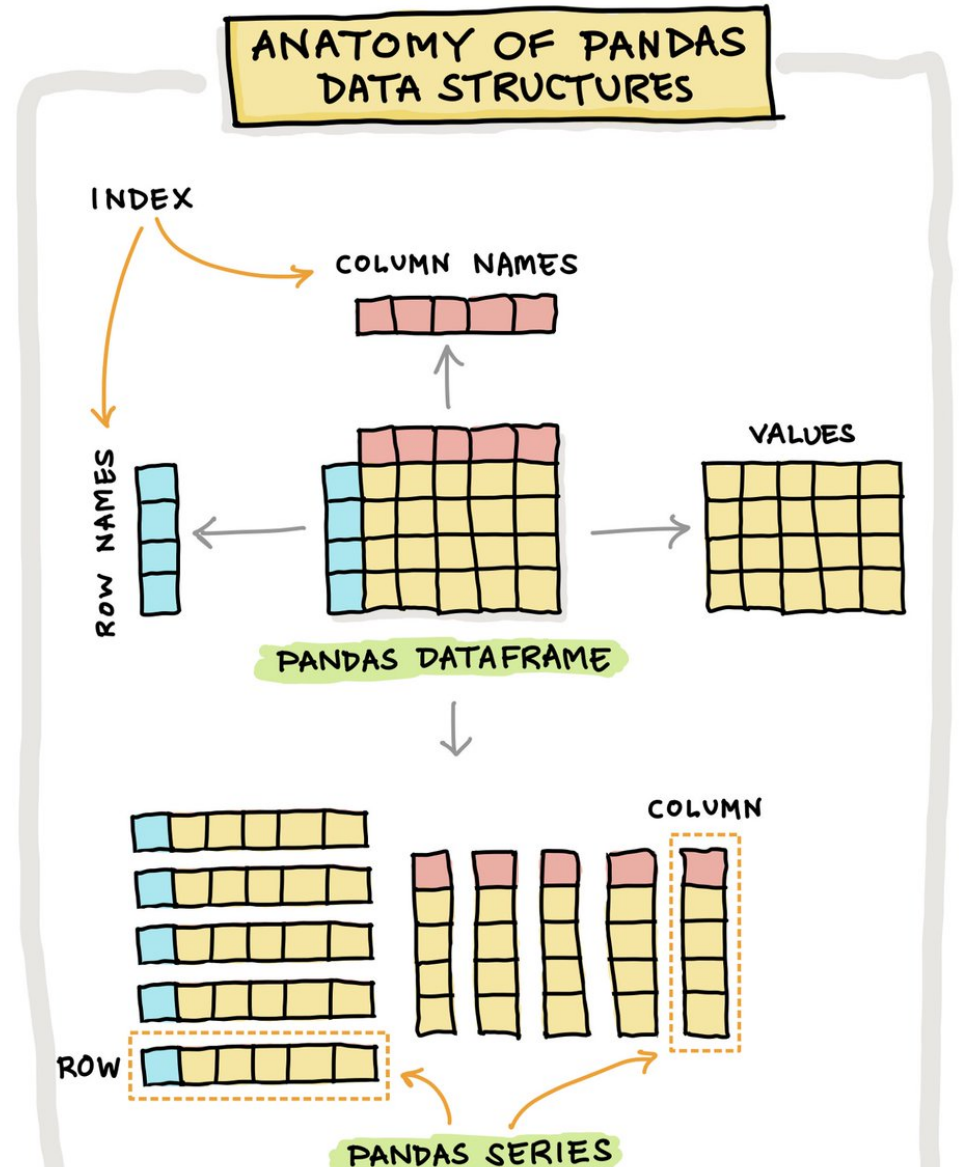
3-Dimension은 Pandas에 존재하지 않음
- Series는 Any Data Type
- Row, Column은 모두 Series로 이루어져 있음
- index는 숫자 뿐만이 아닌, Label로도 Access 가능
- 설정 안하면 0, 1, 2..로 default로 잡힘

- String값일때 dtype이 object라고 나옴
df['열이름']라 하면 숫자 인덱스가,dfi['열이름']라고 한다면 String 인덱스가 나온다.- 레이블로 할 땐
loc, 인덱스 숫자로 할 땐iloc- iloc으로 하면 stop 포함 X
- loc으로 하면 stop 포함 O
Series
class pandas.Series(data=None, index=None, dtype=None, name=None, copy=None, fastpath=<no_default>data: array-like, iterable, dict, scalarindex: array-like, index, RangeIndex(default)- Hashable(Immutable)해야만 하고, Data와 같은 길이
dtype: str, numpy.dtype, ExtensionDtypename: Hashablecopy: 입력 data의 copy 여부. Series나 1d-ndarray일때만 적용- python의 list면 무조건 copy
- Series나 1d-ndarray일땐 view가 적용될 수 있기 때문
Series 생성법
Array Input
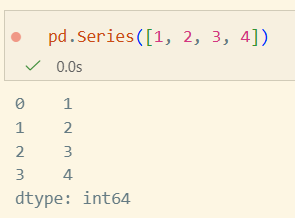

Dict Input
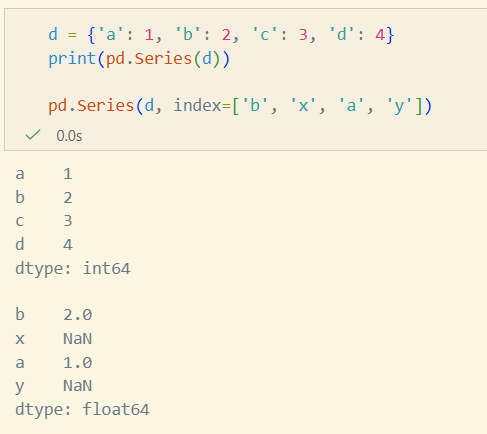
copy parameter, index 변경

Series 선택
Indexing/Selection
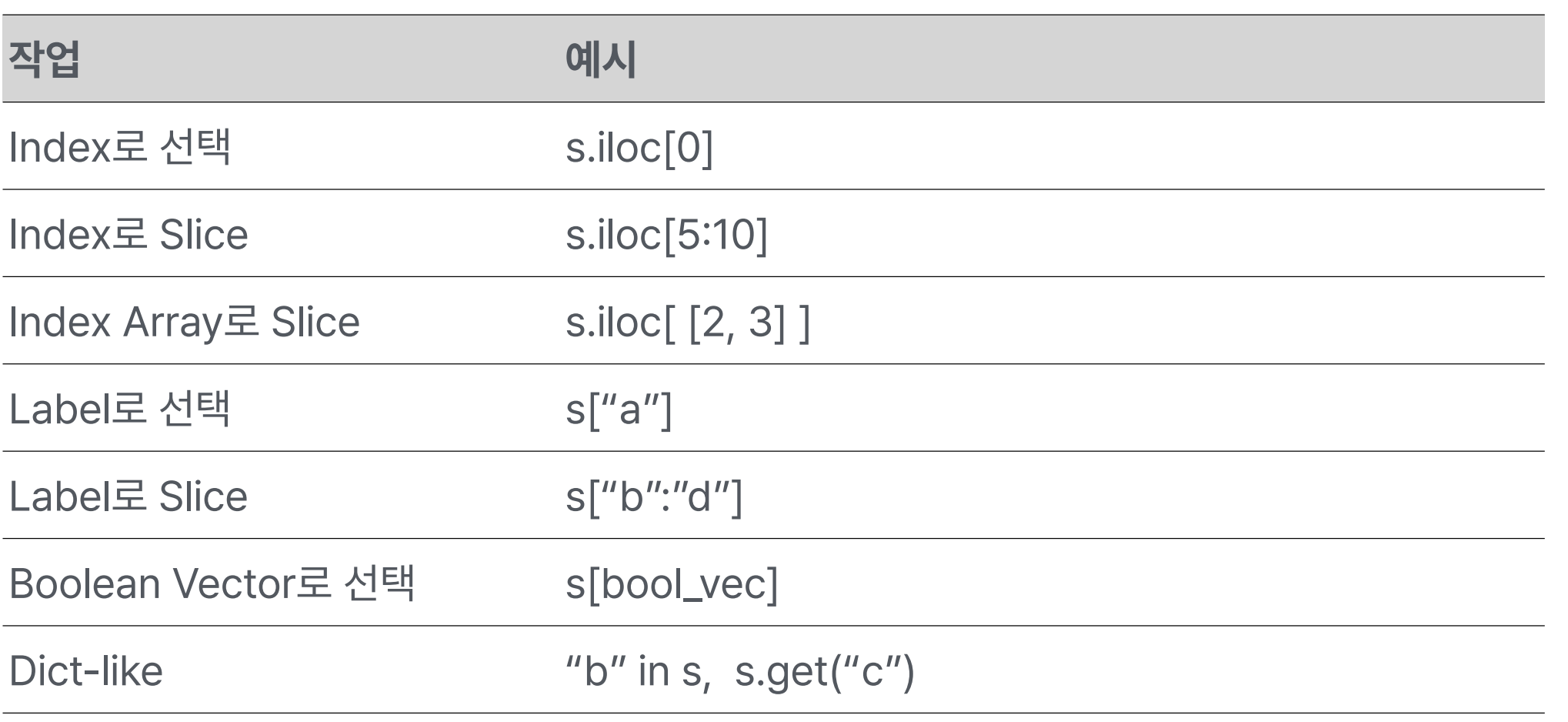
Series 연산
Vectorization & Label alignment
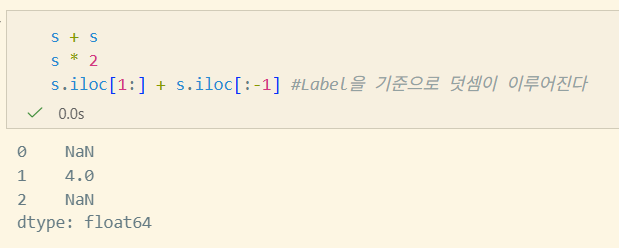
DataFrame
class pandas.DataFrame(data=None, index=None, columns=None, dtype=None, copy=None)data: ndarray, iterable, dict, DataFrameindex: index, array-like, RangeIndex(Default)columns: index, array-like, RangeIndex(Default)dtype: str, numpy.dtype, ExtensionDtypecopy: 입력 data의 copy 여부
DataFrame 생성법
Dict input
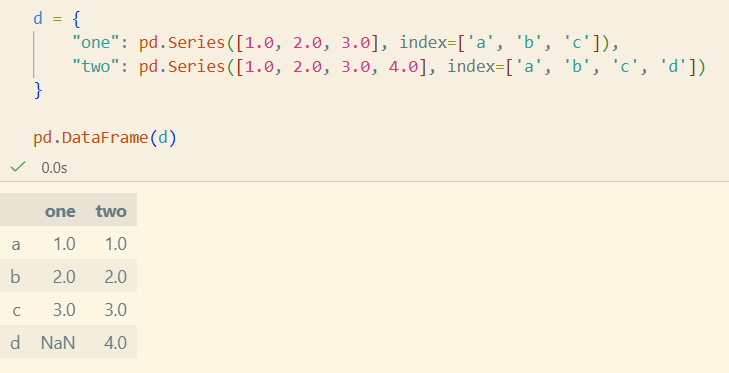
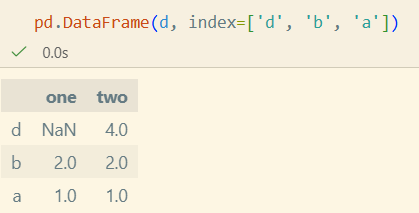

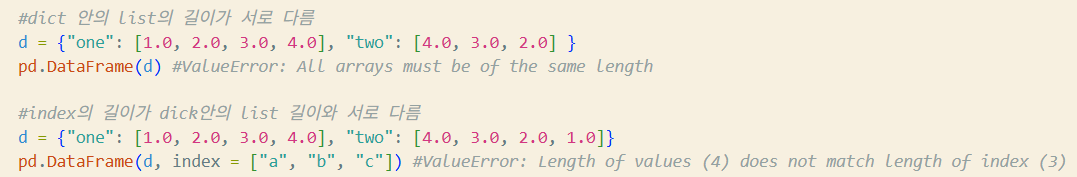
- index를 주지않으면 길이가 다를 때 error
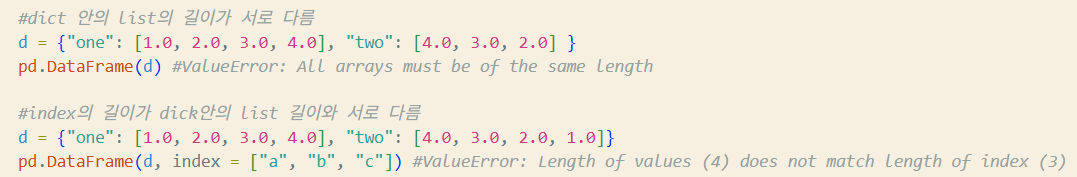
List of dict input
Column의 선택, 추가, 삭제
- DataFrame을 Series의 Dict처럼 다룰 수 있다.
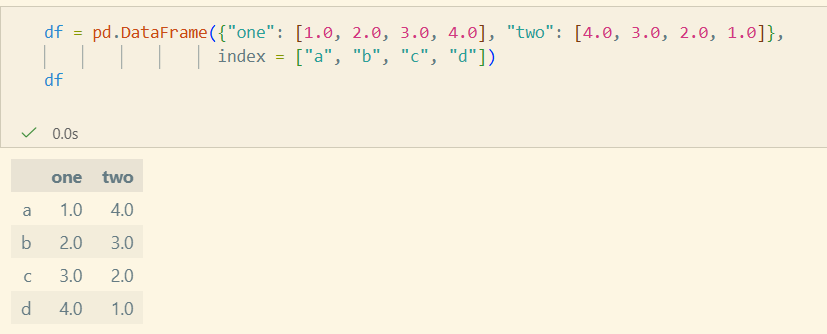
선택
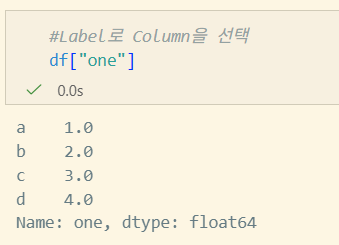
추가

 하단의 삭제 이후의 연산임
하단의 삭제 이후의 연산임
삭제
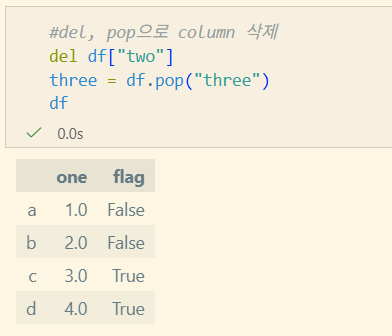
Indexing/Selection
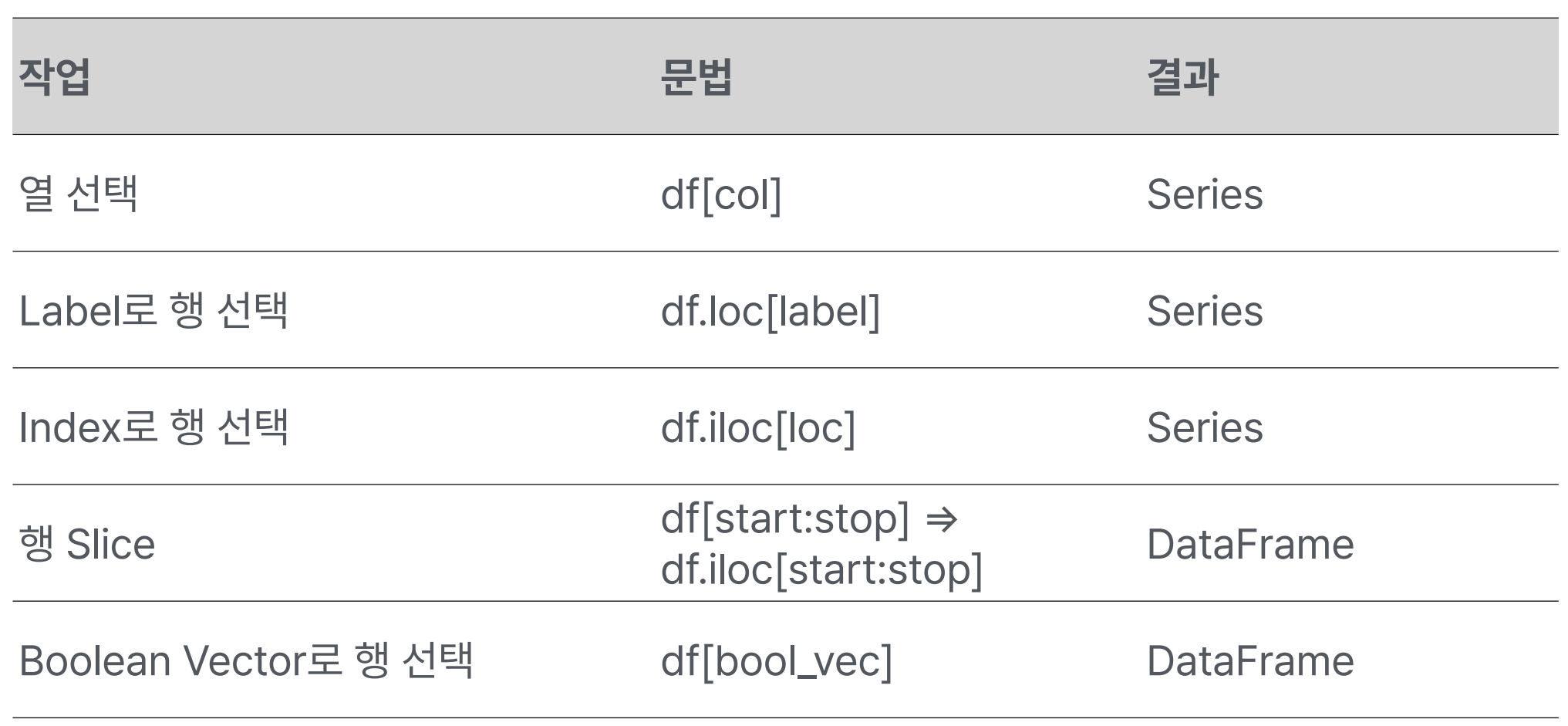
- 행 Slice의
df[start:stop]보다는df.iloc[start:stop]을 사용함이 맥락적으로 바람직하다.
I/O tools
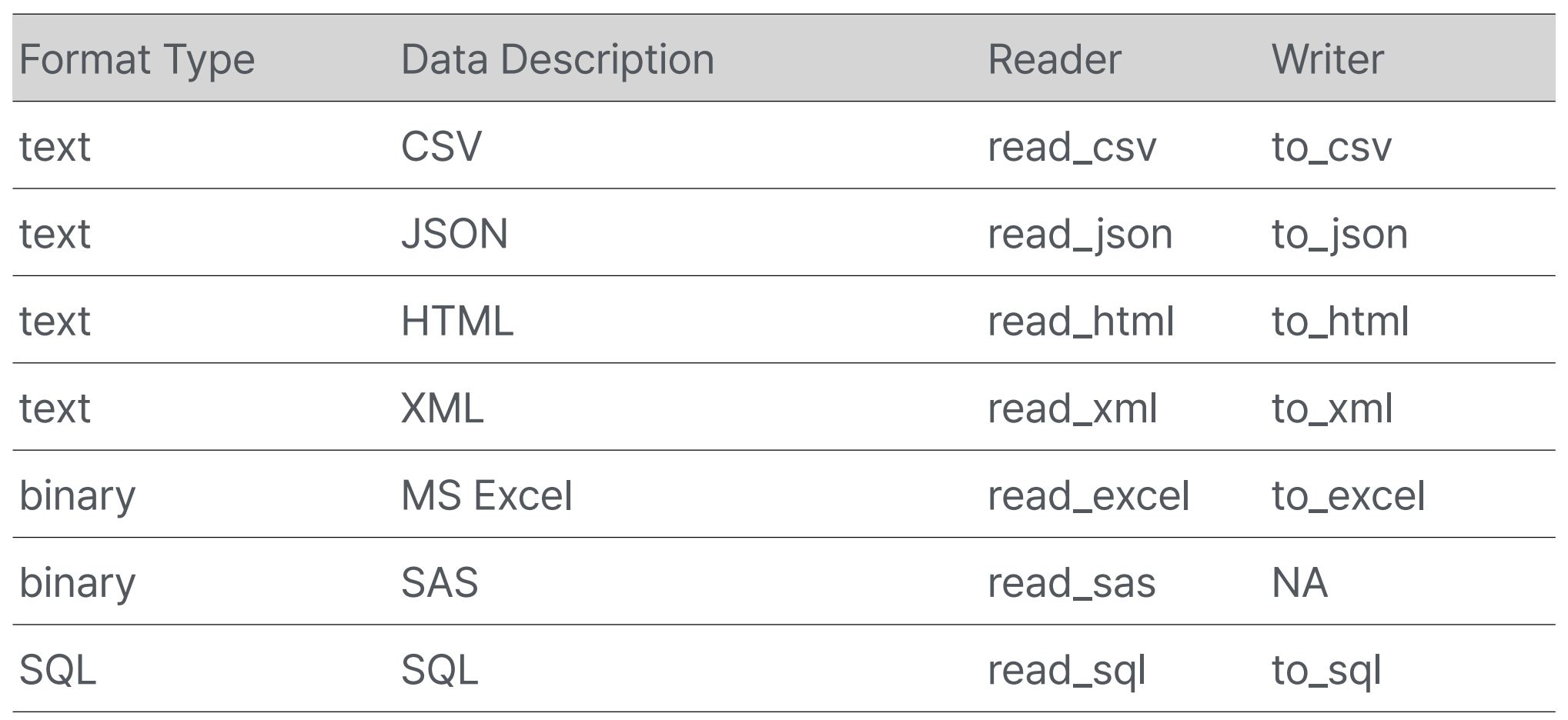
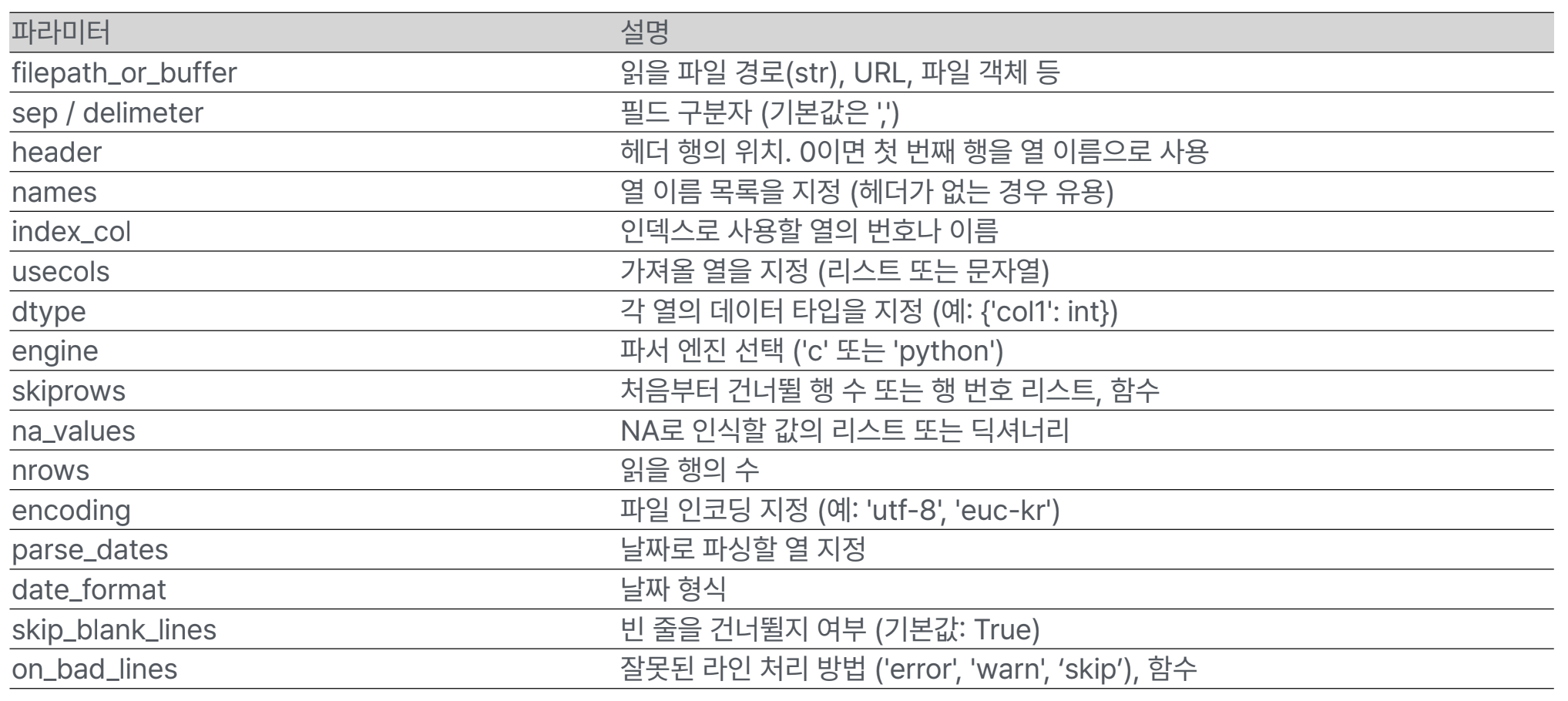
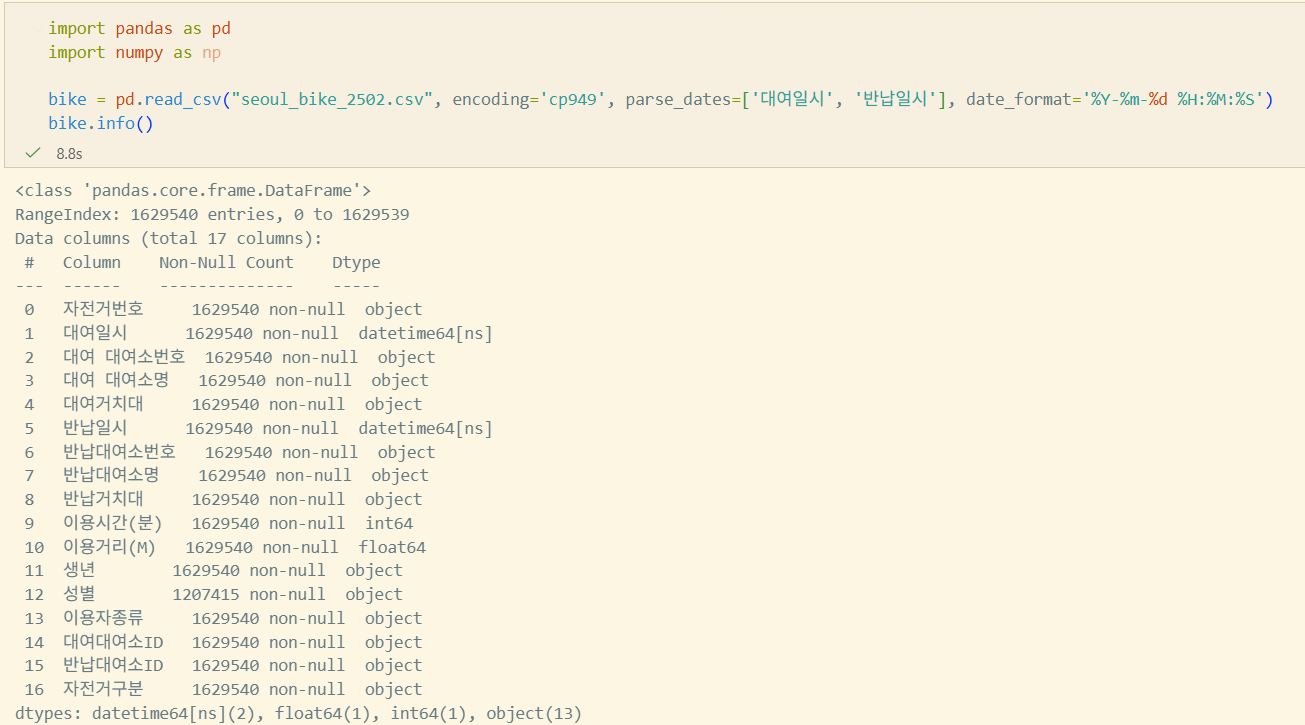
read_csv()
read_sql_table()
탐색
head/tail
DataFrame.head(n=5) #[:n]을 반환
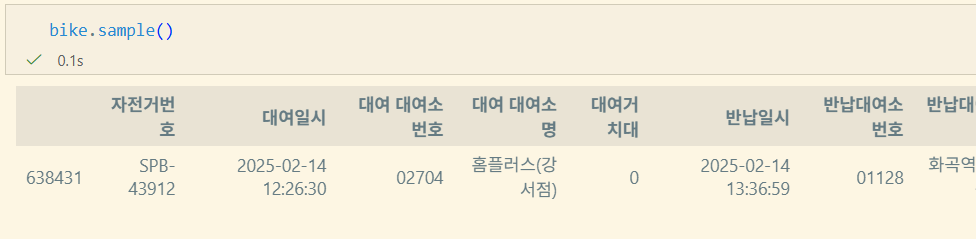
DataFrame.tail(n=5) #[-n:]을 반환sample
DataFrame.sample(n=None, frac=None, replace=False, weights=None, random_state=None, axis=None, ignore_index=False)n: int형, 반환할 item의 개수. frac과 같이 쓰지 않음.frac: float형, 전체 대비 반환할 비율. frac > 1일 수 있다. n과 같이 쓰지 않음.replace: bool형, 한 번 이상 같은 행이 sampling 될 수 있는지 설정weights: str, ndarray-like 형. 가중치를 부여한 column 이름random_state: int, array-like, BitGenerator, np.random.RandomState, np.random.Generatoraxis: 0 orindex, 1 orcolumns, Noneignore_index: bool. 반환값의 index 제거 여부
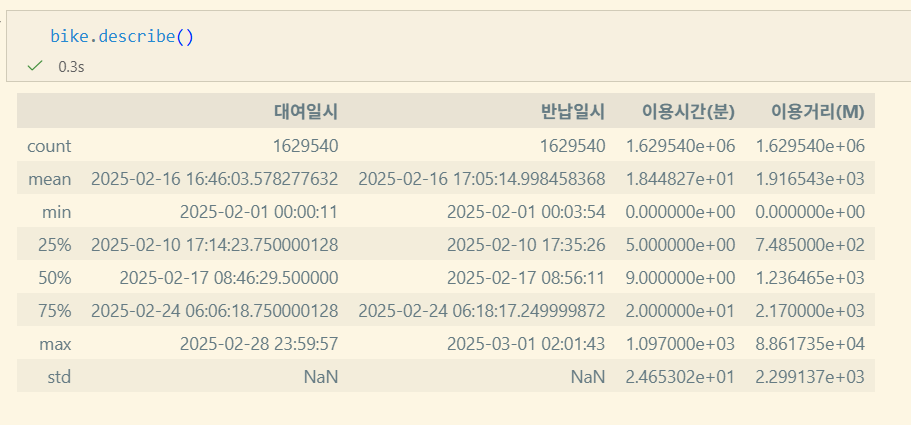
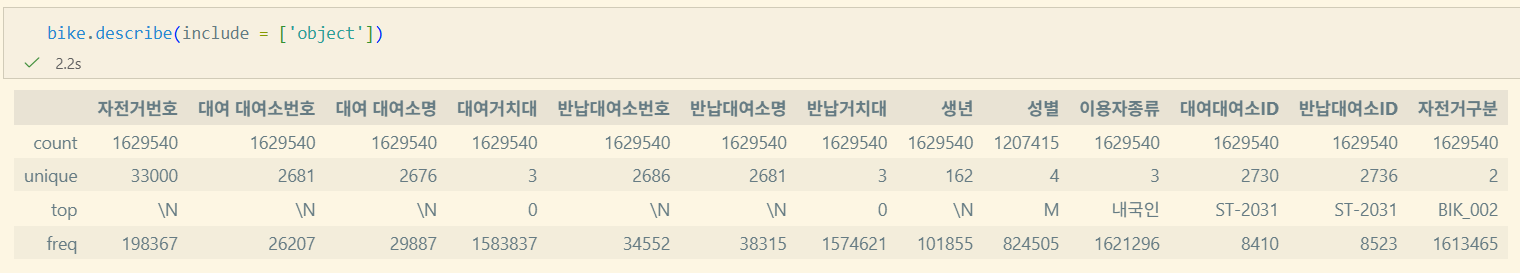
describe
DataFrame.describe(percentiles=None, include=None, exclude=None)percentiles: list-like of numbersinclude: all, list-like of dtypes, Noneexclude: list-like of dtypes, None
결측값 처리
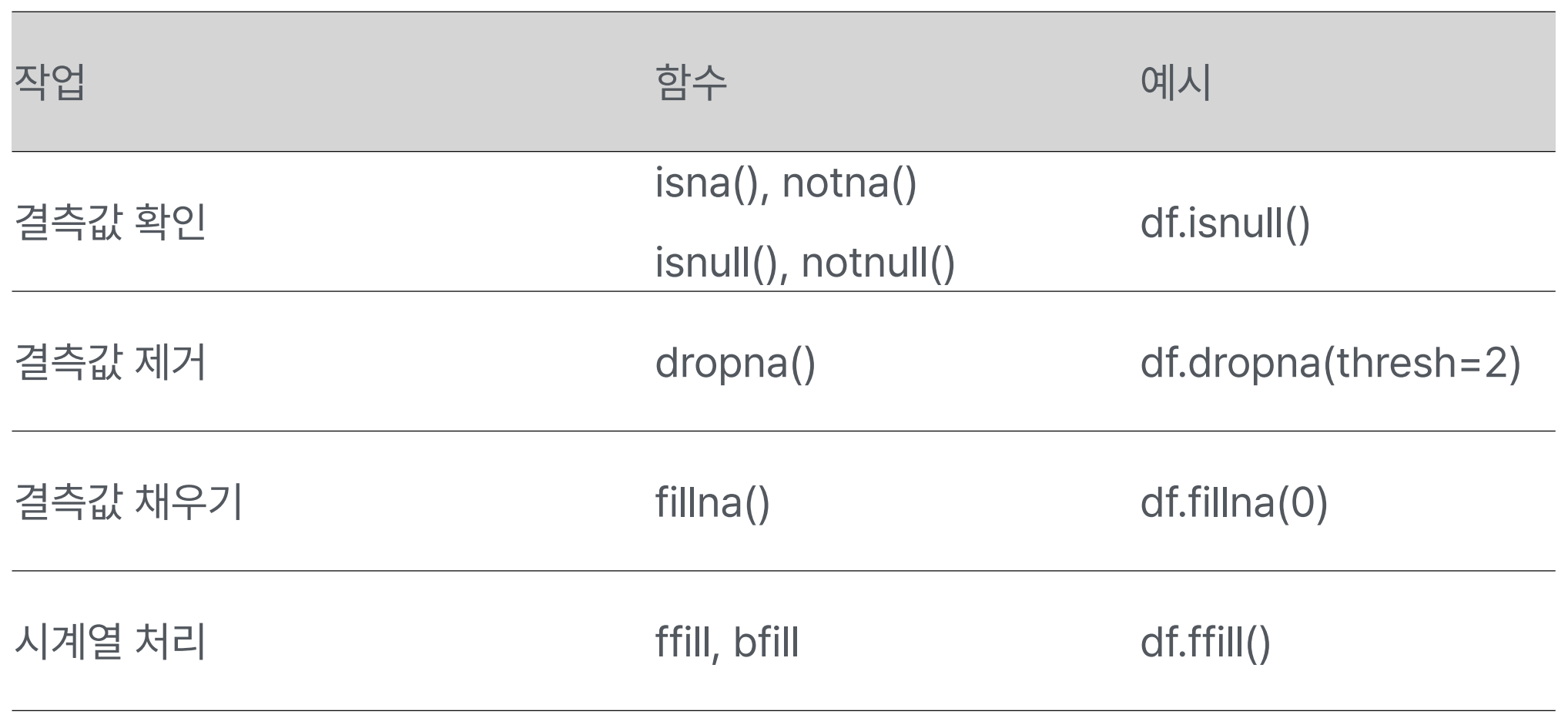
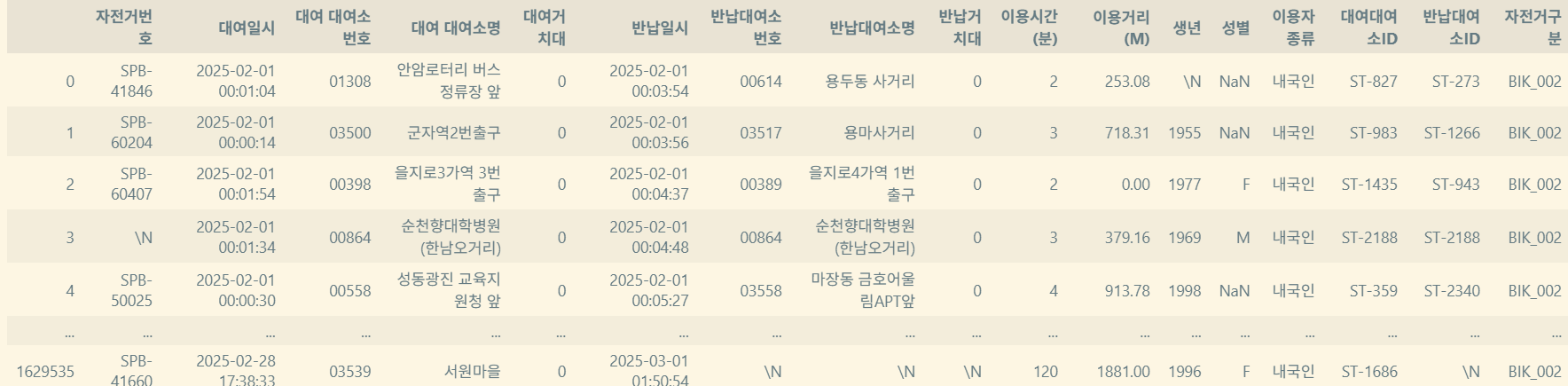
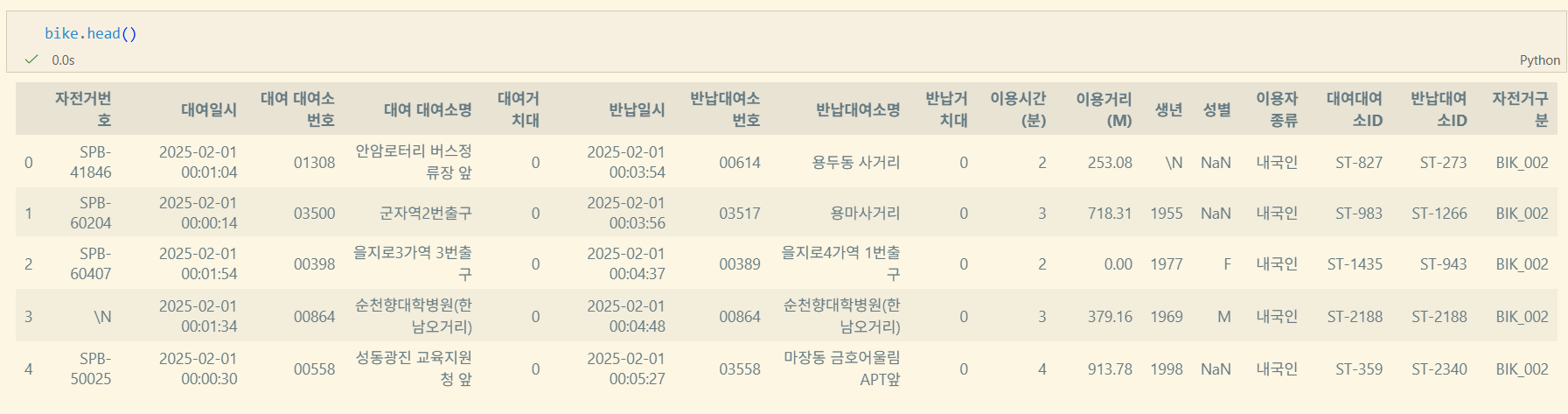
example - 서울시 공공 데이터
https://data.seoul.go.kr/dataList/OA-15182/F/1/datasetView.do

데이터 분석 시 sort는 많이 사용하지 않는다고 한다. 굳이 하려면
DataFrame.sort_values

pandas 데이터 전처리
원시 데이터를 분석 가능하도록 정리하는 과정
필요성
- 원시 데이터는 정형화 되어있지 않은 경우가 다수
- 결측치, 이상치 존재
- 통일되지 않은 값: 남/남자, 경북/경상북도
- 이후 작업의 정확도 및 성능 향상
- 데이터 분석, 머신러닝/딥러닝, 대시보드 구축
- 데이터 전처리가 분석의 70% 차지
자료형 변환
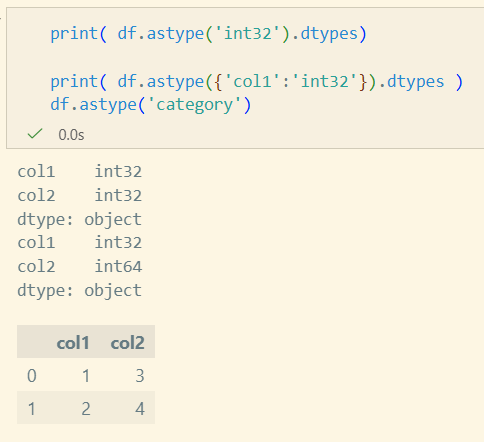
DataFrame.astype(dtype, copy=None, errors='raise')
Series.astype(dtype, copy=None, errors='raise')dtype: str, data type, Series or Mapping or column name → data typecopy: 쓰지 않는 것이 좋음(명시X). copy-on-write로 대체될 예정errors: 'raise', 'ignore'- 이외
to_datetime,to_numeric,to_timedelta,convert_dtypes존재
Grouping
Split - Apply - Combine
pandas documentation
- Split
- 각 데이터를 Group으로 나눔
- Apply
- Aggretion: 각 Group의 통계 계산 (mean, sum..)
- Transformation: 값 변경(각각의 elem 값 변경)
- Filtration: Group 단위의 Filtering. Group 전체 삭제 가능
- Combine
- 작업한 결과물을 통합
다만 굳이? pandas를 이용하는 것 보다 sql의 join, group by를 사용하는 것이 낫다.
Split

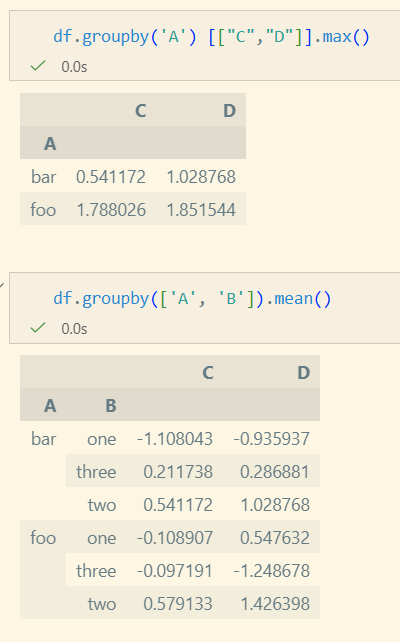
groupby
DataFrame.groupby(by=None, axis=<no_default>,
level=None, as_index=True, sort=True, group_keys=True, observed=<no_default>, dropna=True)by: mapping, function, label, pd.Grouper, listlevel: int, level name, sequence, MultiIndex인 경우as_index: False인 경우 index가 column에 저장. 기본 index 사용sort: 결과 index sort 여부group_keys: 결과 index의 key 사용 여부. False인 경우 기본 index 사용
Apply
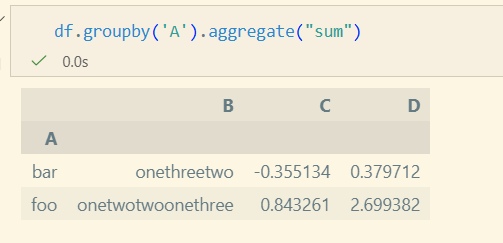
Aggregation
group 단위로 값이 계산되어 하나의 Scalar 값이 반환
- aggregate/agg를 사용하여 다양한 적용 가능
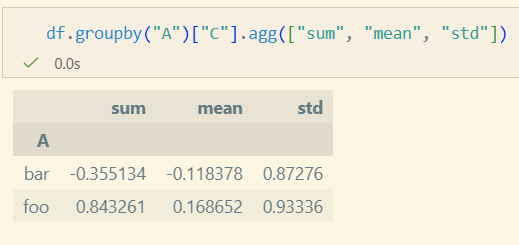
Built-in Aggregation Methods
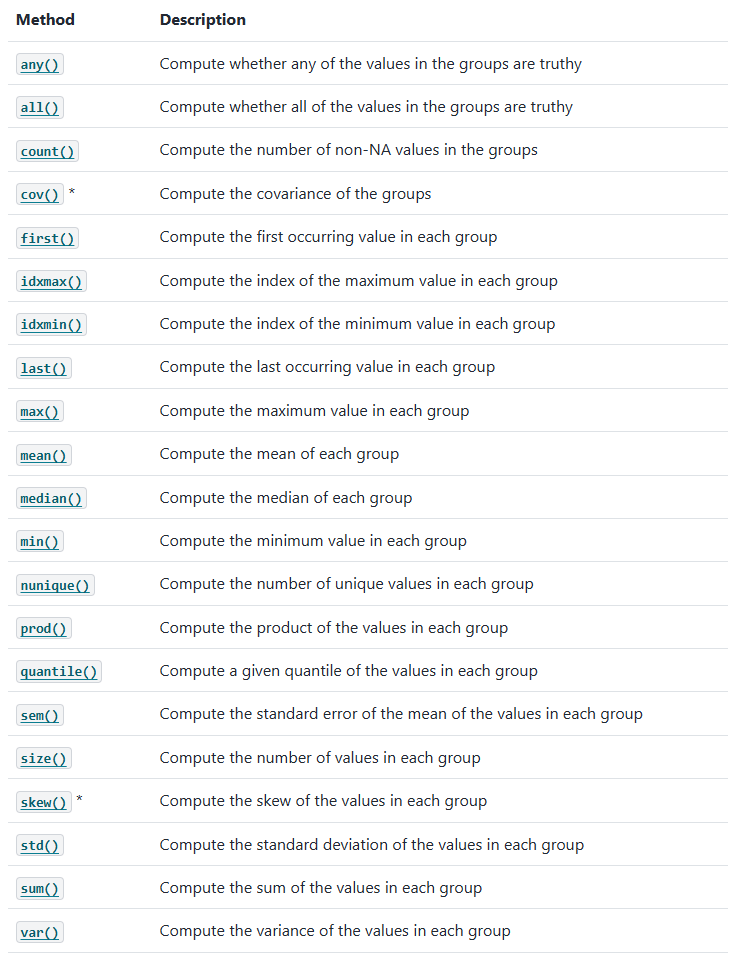
Transformation
각 Row에 대해 Group 단위로 Function 적용
In [125]: speeds
Out[125]:
class order max_speed
falcon bird Falconiformes 389.0
parrot bird Psittaciformes 24.0
lion mammal Carnivora 80.2
monkey mammal Primates NaN
leopard mammal Carnivora 58.0
In [126]: grouped = speeds.groupby("class")[["max_speed"]]
In [127]: grouped.transform("cumsum")
Out[127]:
max_speed
falcon 389.0
parrot 413.0
lion 80.2
monkey NaN
leopard 138.2
In [128]: grouped.transform("sum")
Out[128]:
max_speed
falcon 413.0
parrot 413.0
lion 138.2
monkey 138.2
leopard 138.2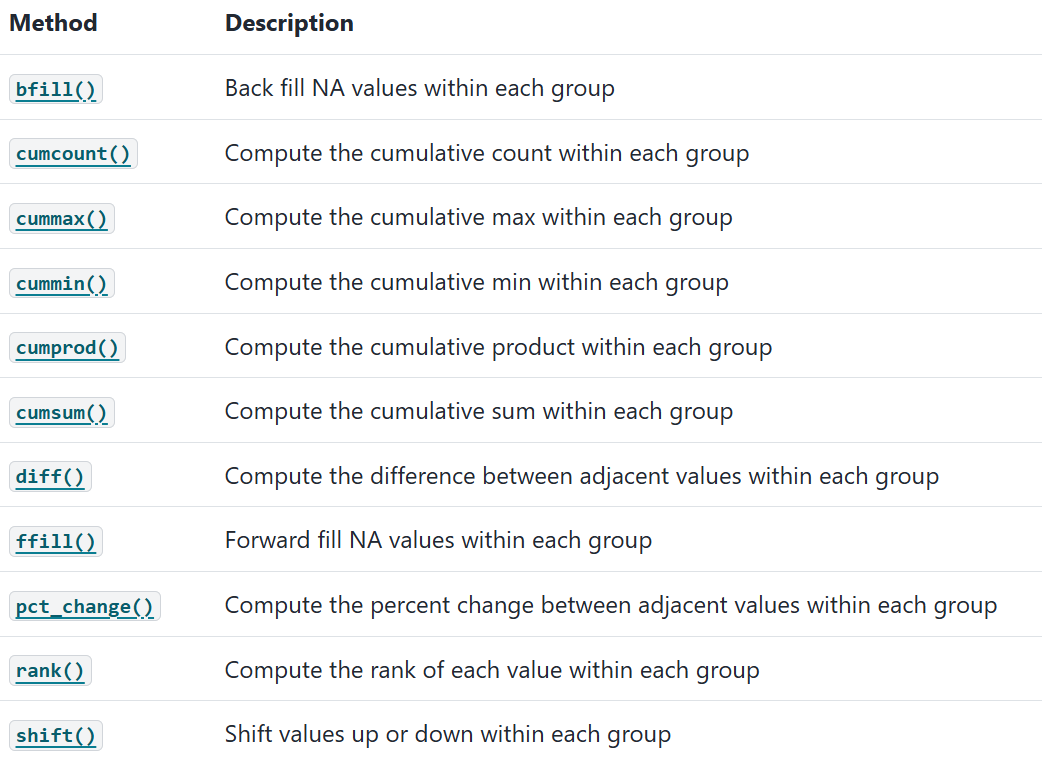
Apply
Group 전체, 혹은 일부를 제거
In [188]: dff = pd.DataFrame({"A": np.arange(8), "B": list("aabbbbcc")})
In [189]: dff.groupby("B").filter(lambda x: len(x) > 2) #filter을 사용하여 user defined function 적용 가능
Out[189]:
A B
2 2 b
3 3 b
4 4 b
5 5 b
apply 함수
DataFrameGroupBy.apply(func, *args, include_groups=True, **kwargs)func: callableinclude_groups: func를 group 단위로 적용할지 여부args,kwargs: func에 전달되는 인자들
>>> df = pd.DataFrame({'A': 'a a b'.split(),
... 'B': [1, 2, 3],
... 'C': [4, 6, 5]})
>>> df.groupby('A', group_keys=True)[['B', 'C']].apply(lambda x: x / x.sum())
B C
A
a 0 0.333333 0.4
1 0.666667 0.6
b 2 1.000000 1.0import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
"A": ["a", "a", "b"],
"B": [1, 2, 3],
"C": [5, 6, 7]
})
def show_arg(x):
print(x)
return x.sum() # x / x.sum() 으로 바꾸어 보고 결과를 비교해 보자!!
print("include_groups=True")
# include_groups=True (기본값): 그룹 컬럼(A)이 함수에 전달되는 데이터프레임에 포함됨
result1 = df.groupby("A").apply(show_arg)
print(result1)
# include_groups=False: 그룹 컬럼(A)이 함수에 전달되는 데이터프레임에서 제외됨
print("\ninclude_groups=False")
result2 = df.groupby(“A").apply(show_arg, include_groups=False)
print(result2)



GroupBy
https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/groupby.html
