Digital-to-Analog Conversion
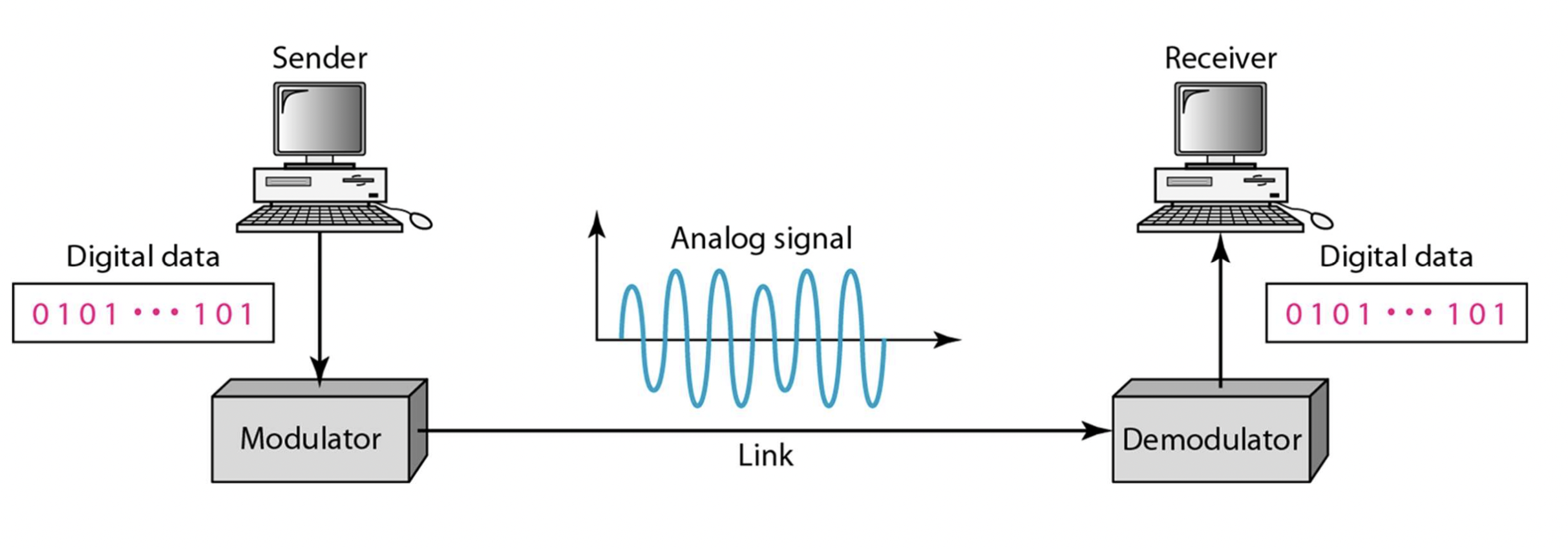
- Digital data can be encoded using these 3 characteristics
- Amplitude
- Frequency
- Phase
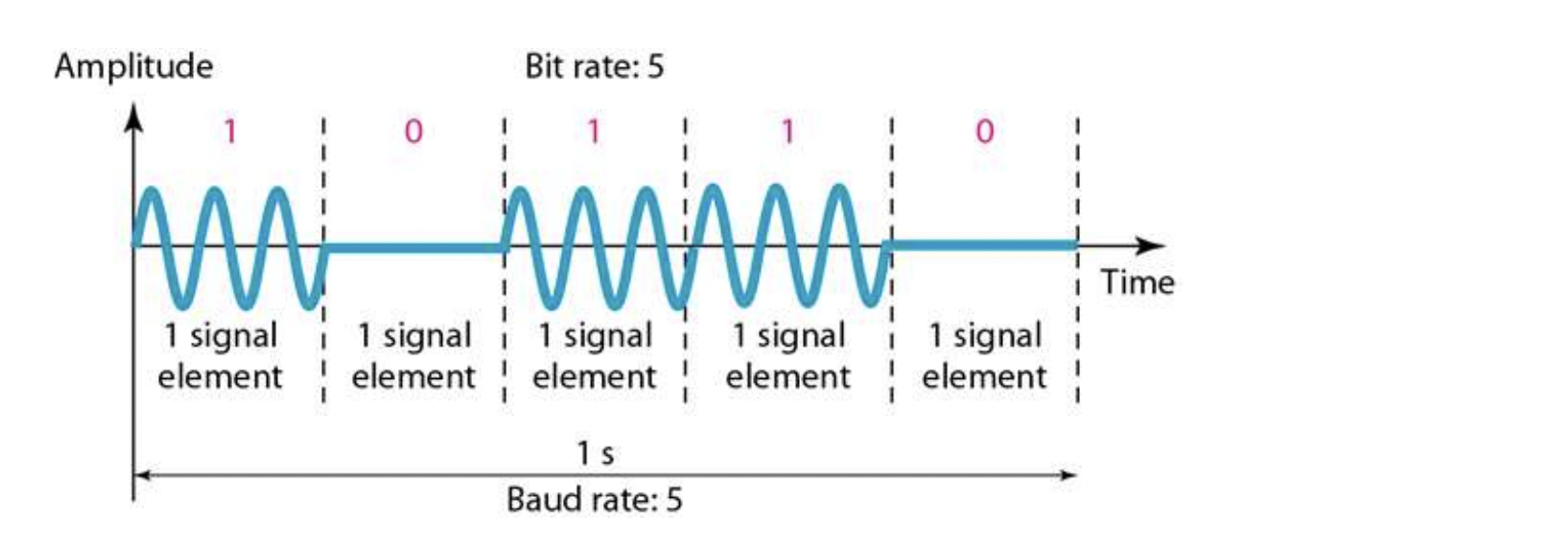
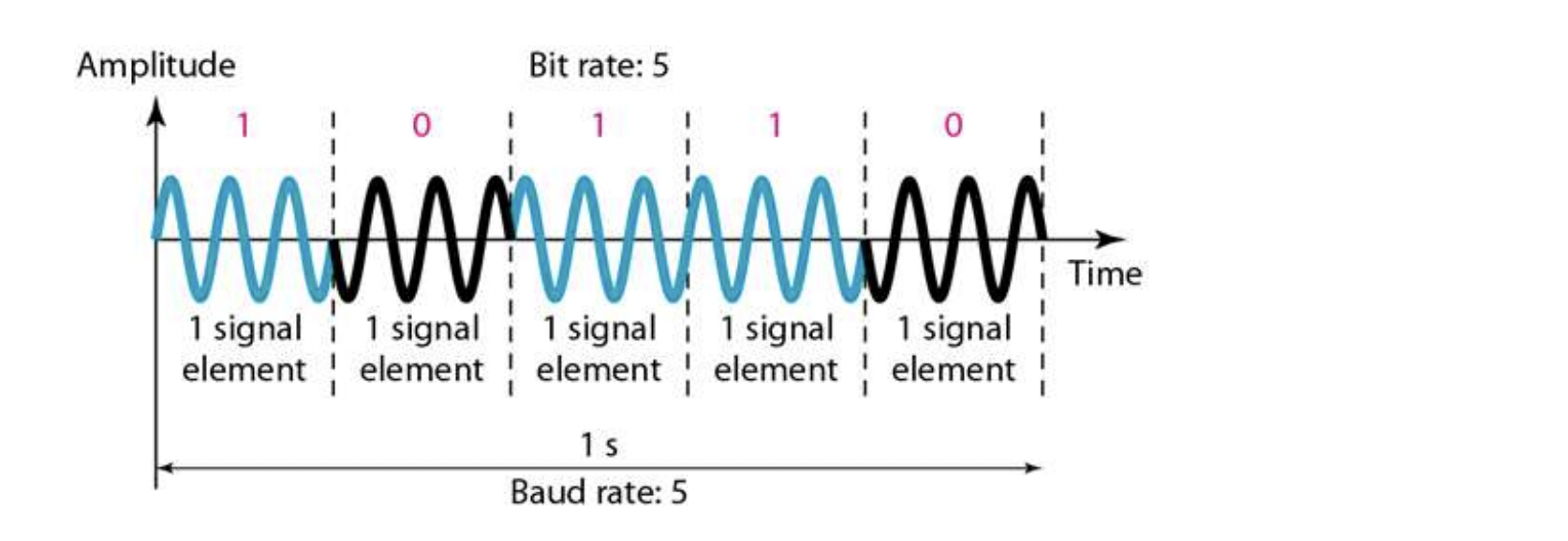
- Data element : bit
- Signal element : the smallest unit of signal that represents one or more bits
(주의. digital에서와 정의가 다르다)
그래서, 항상 bit rate >= baud rate
왜냐하면, 최소한 1개로는 표현할 수 있고, 2개로도 1bit 표현하니까.
1bit를 표현할 수 있는 최소 단위 느낌으로 생각하자.
// signal element의 정의 차이가 아직 잘 이해가 안된다..
- N : Data transmission rate (bit rate)
- S : Signal transmission rate (baud rate)
- S = N x 1/r
Q. An analog signal carries 4 bits of data per signal element. If baud rate is 1000 baud, what is the data transmission rate?
A. 4000 bps
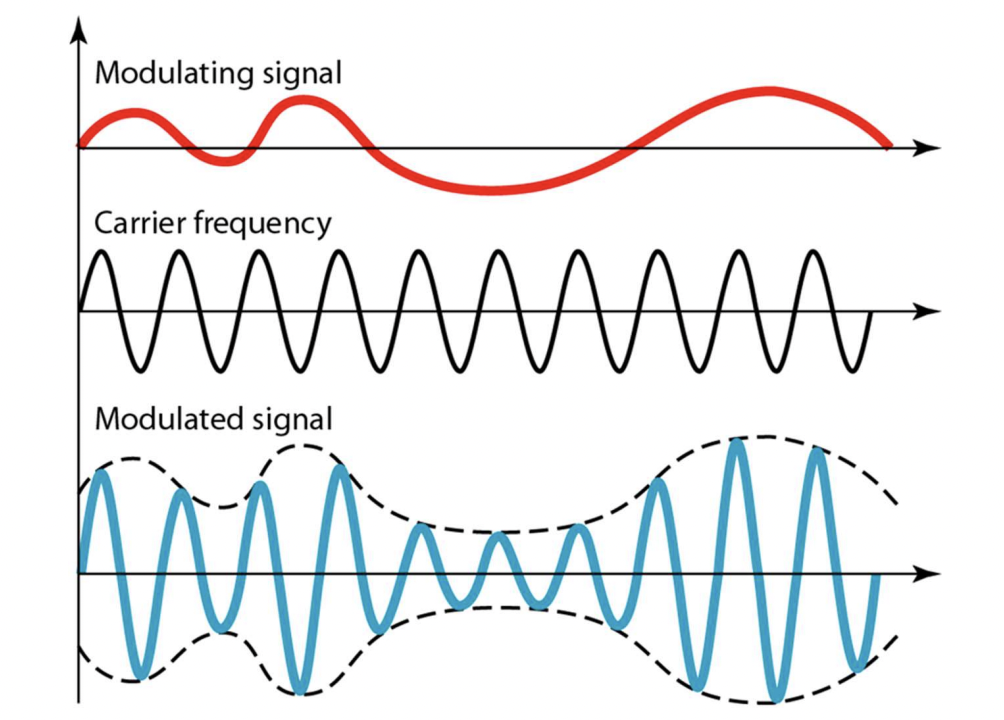
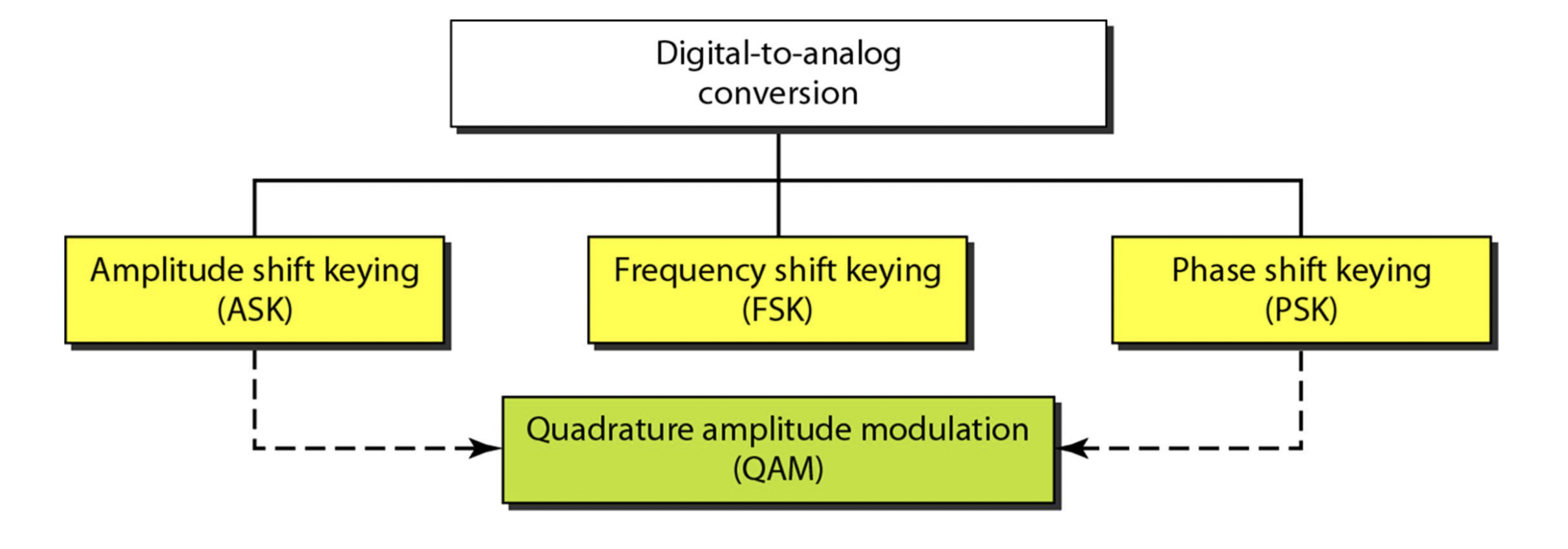
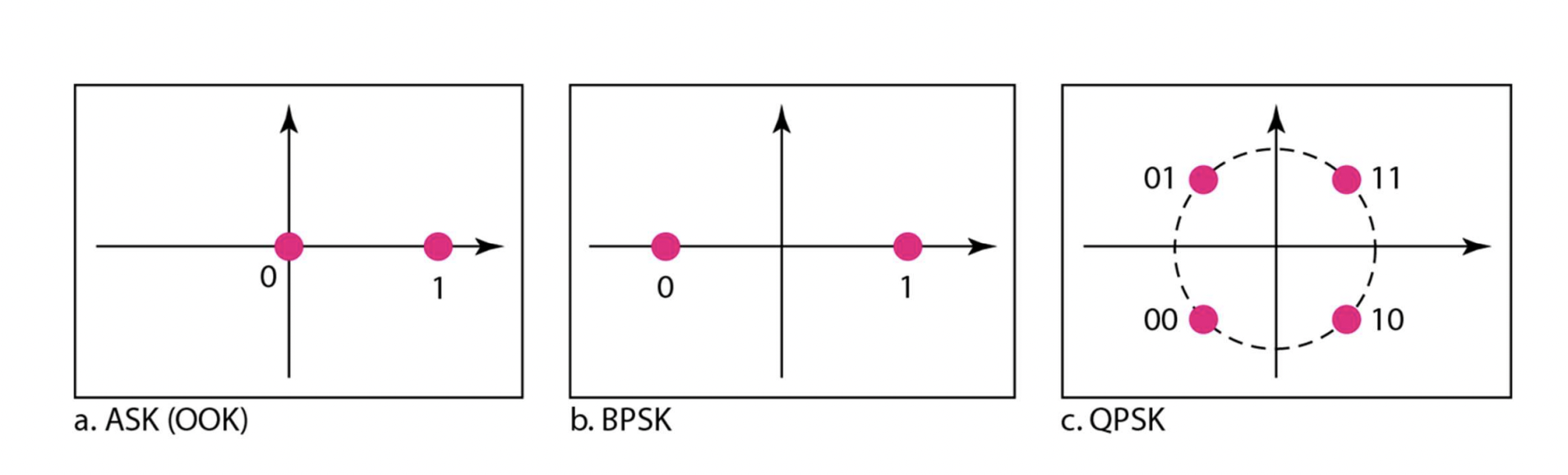
ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying)
- Change amplitude of the carrier signal to encode data
- carrier signal : the analog signal that carries the data
- carrier frequency : frequency of the carrier signal
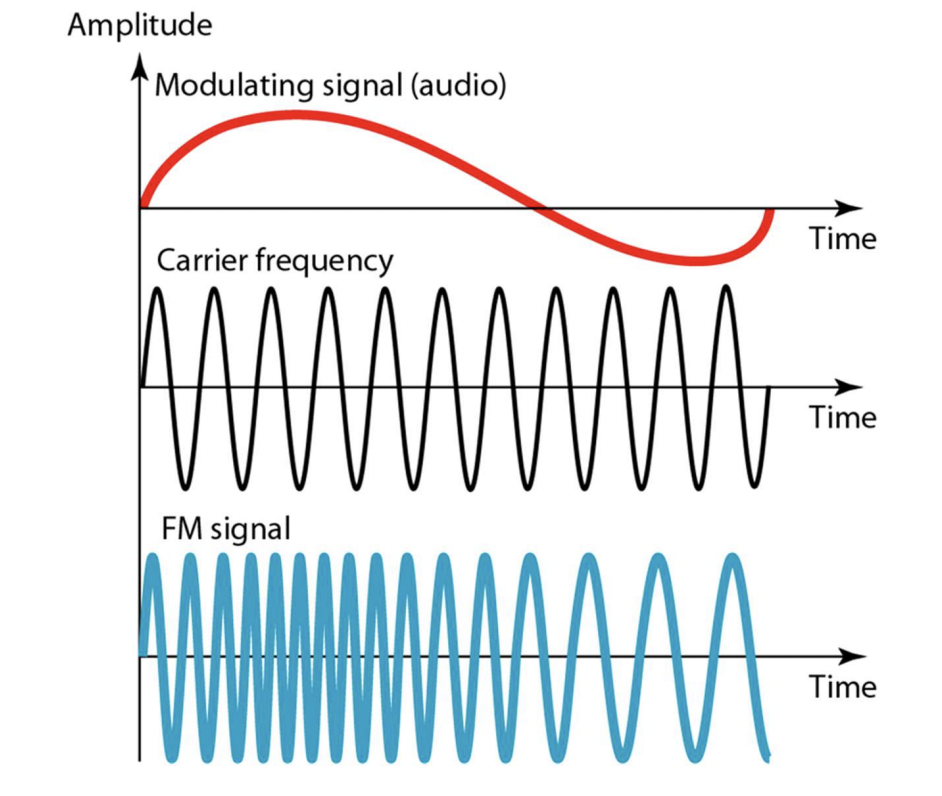
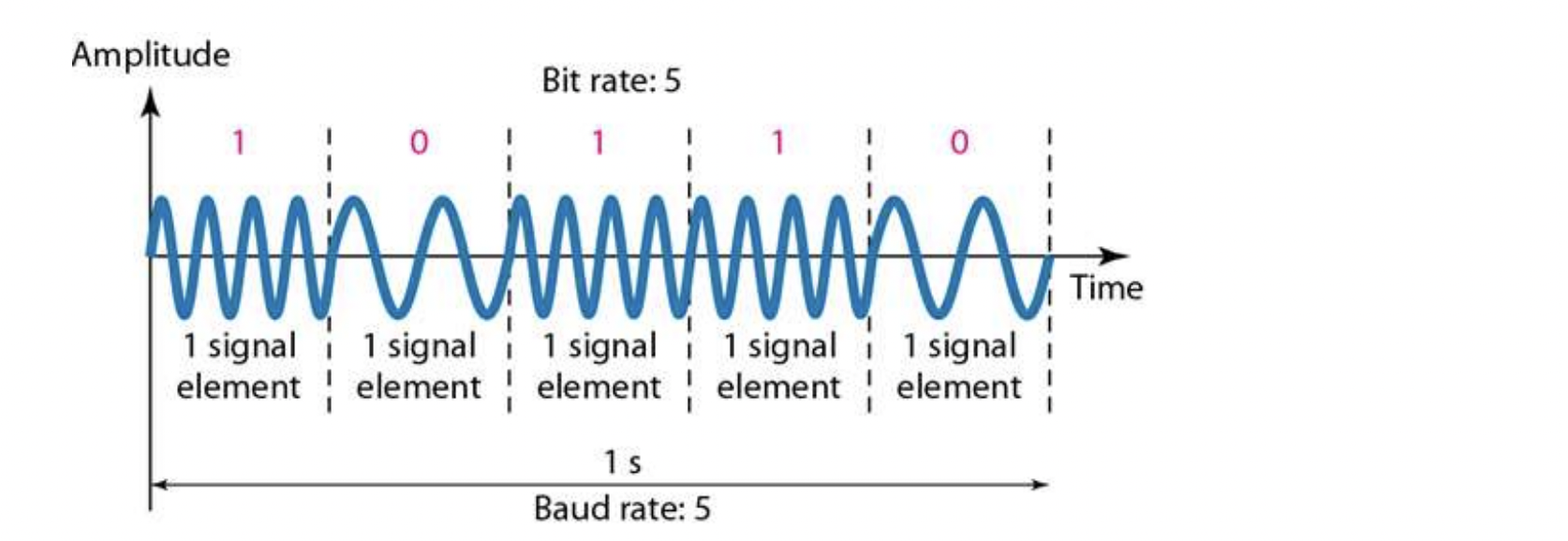
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)
- Change frequency of the carrier signal to encode data
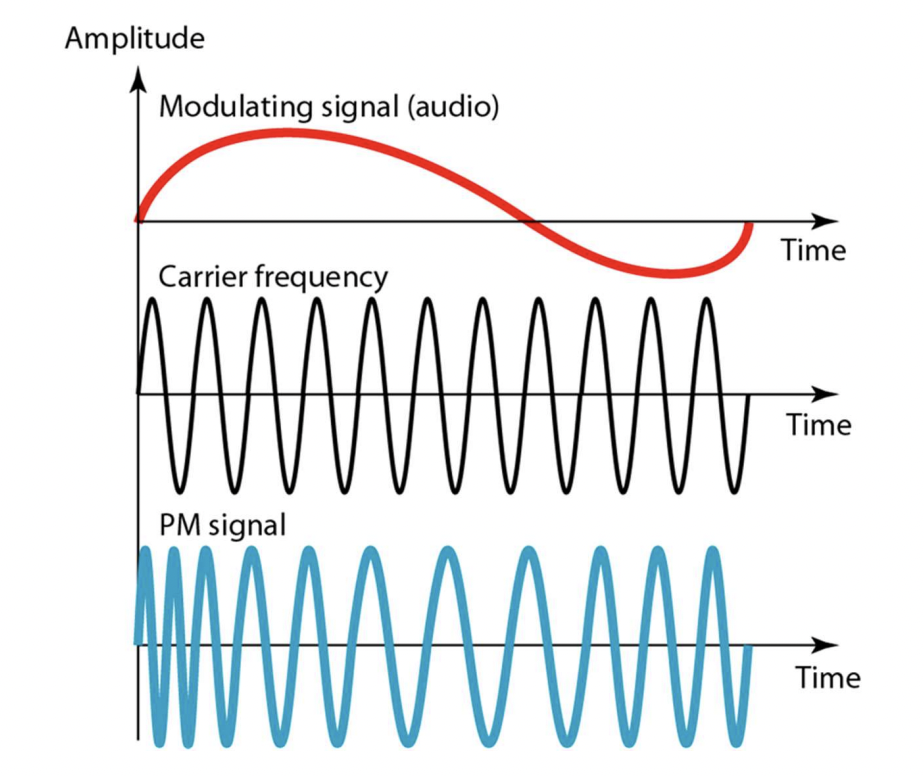
PSK (Phase Shift Keying)
- Change phase of the carrier signal to encode date
BPSK vs. QPSK
BPSK (Binary PSK)
: use 2 different phases to encode 0 and 1
0도, 180도
이렇게 하니까 속도가 너무 안나와
QPSK (Quadrature PSK)
: use 4 different phases to encode 00, 01, 10, 11
2 bits per signal element
45도, 135도, -45도, -135도
Q. data was transmitted at 12Mbps using QPSK modulation. What is the baud rate?
A. signal element 1개당 2개의 bit를 보낸다.
baud rate는 1/2배. => 6Mbps
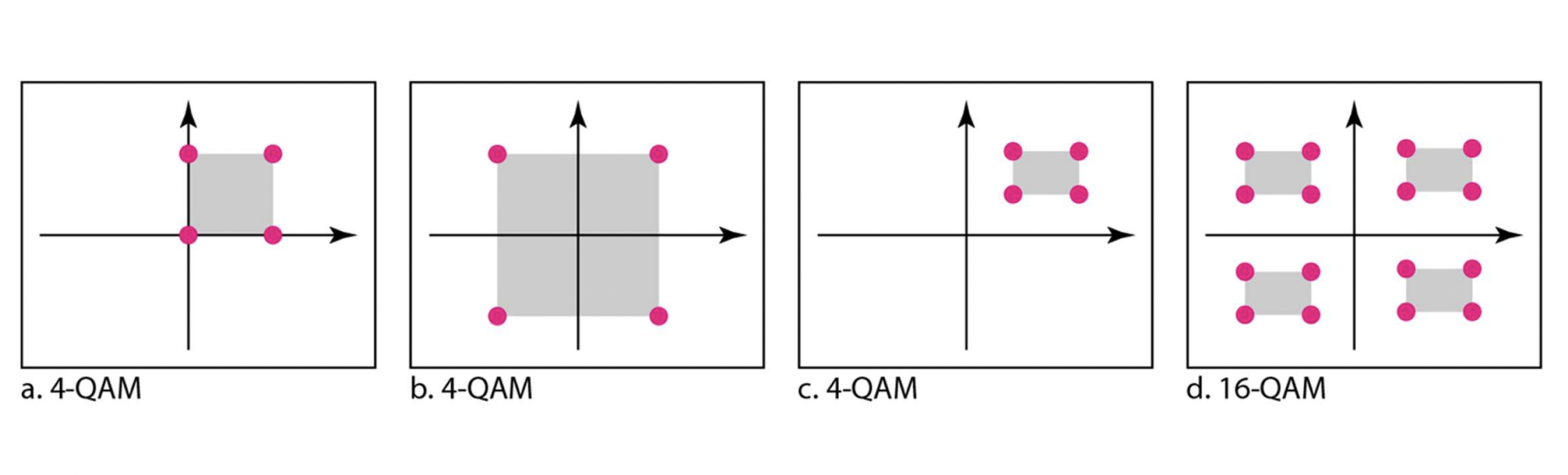
Constellation Diagram
QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation)
QAM = QPSK + ASK
-
Use both amplitude shift and phase shift on carrier signal to encode data
-
n-QAM : n개의 점을 이용한다.
- n개의 signal element를 이용해서 log2n개의 bit를 encode한다.
- n이 커질수록 위상 차가 거의 없어지기 때문에 왜곡이 일어나기 쉽다.
Analog-to-Analog Conversion