import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as FConvolution Layer
- 기존 Fully Connected Layer Neural Network는 3차원 데이터를 1차원으로 평면화 하여 다음 layer로 연결
(평면화 과정에서 공간정보가 손실) - 3차원 형태를 유지한 상태로 학습하기 위해 등장한 모델이 CNN(Convolution Neural Network)
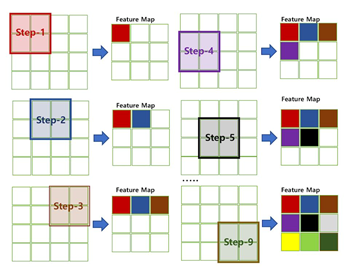
- Convolution Layer는 2차원 이상 데이터 형태를 유지하면서 데이터 내에서 filter(kernal)를 이동(mapping)시켜가며 특징(feature map)을 추출
I. parameters
torch.nn.conv1d(
in_channels, # (1)-1 depth of input
out_channels, # (1)-2 depth of output
kernel_size, # (2) filter=kernel size
stride=1, # (3) filter 이동 step
padding=0, # (4) input 테두리에 적용될 padding size
dilation=1,groups=1,bias=True,padding_mode='zeros',device=None,dtype=None)참조 : https://github.com/vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic/blob/master/README.md
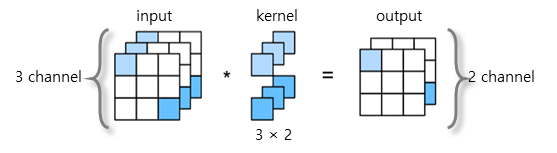
(1) channel ≠ shape(size)
- channel ≒ depth, shape ≒ size
(예. RGB컬러 10×10 이미지 : shape=size=(10,10), channel=depth=3(R,G,B) - kernel numbers = input channel×output channel
(2) kernel_size
- feature를 추출할 view 단위
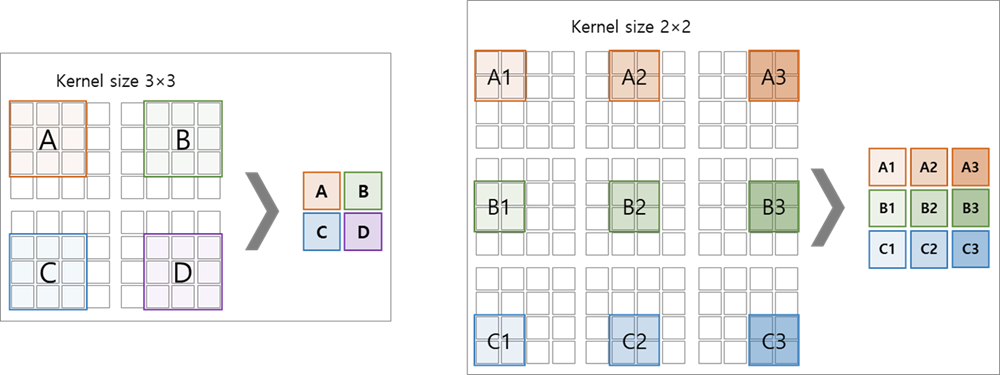
(3) stride
- kernel를 이동시키는 step 단위
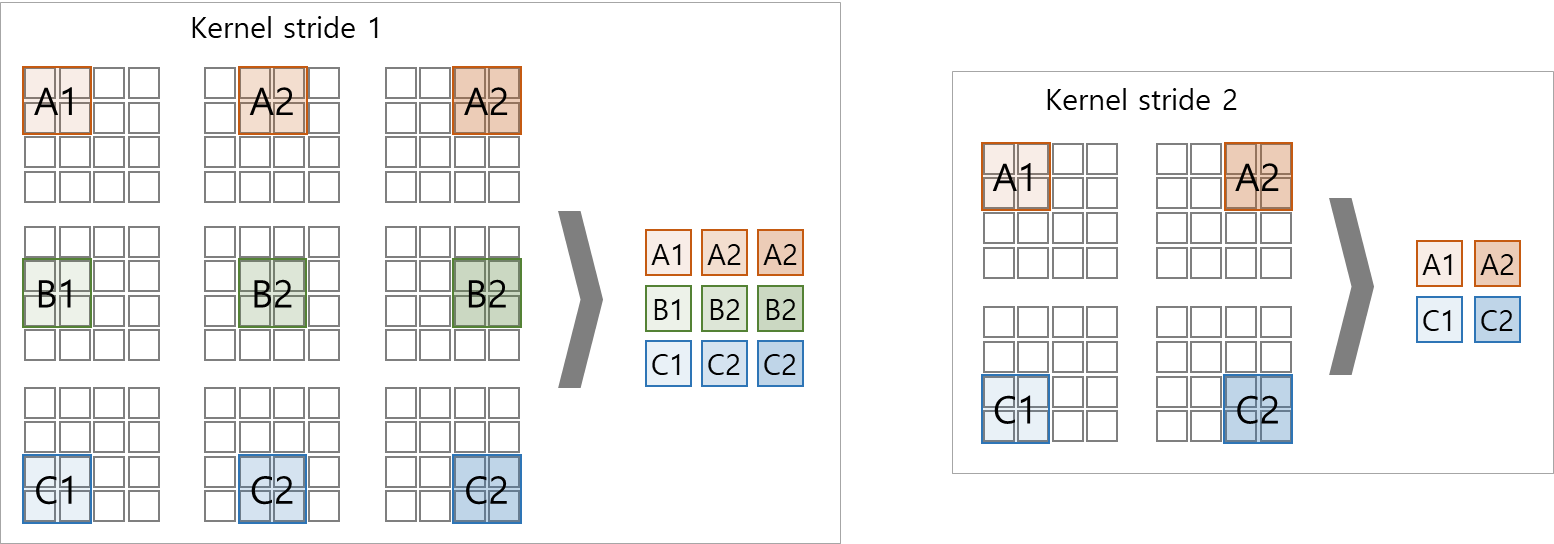
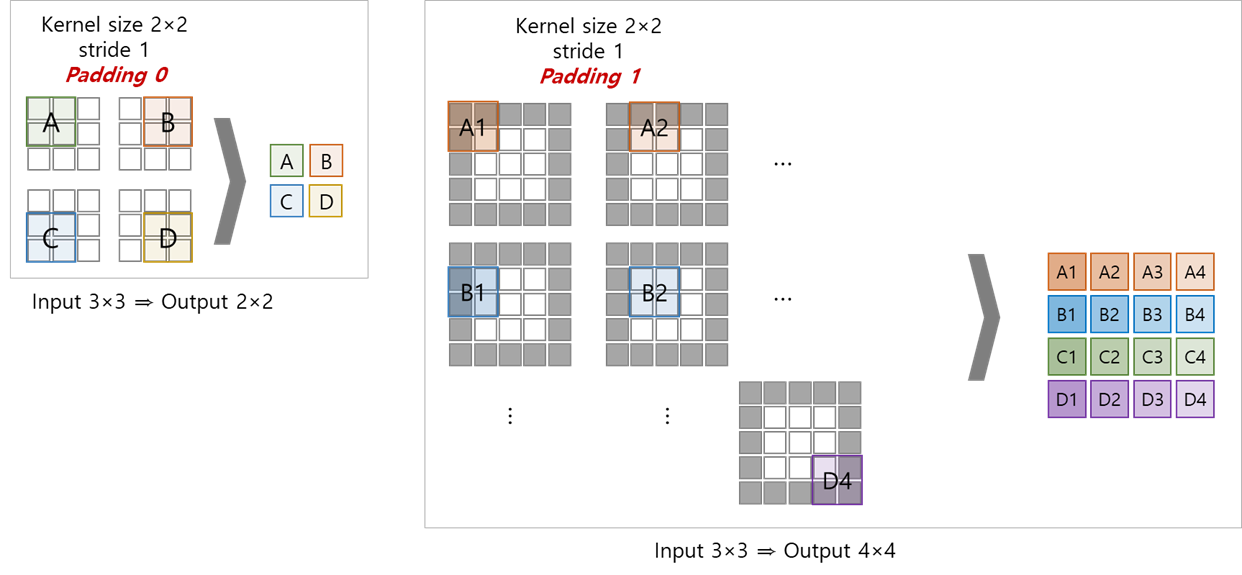
(4) padding
- kernel mapping 시 input size에 비해 output size가 작아짐
mapping 전 input의 외곽에 zero-padding으로 content를 유지하면서 size를 키워 mapping 후 output의 size를 조정함
(※ padding 전 모서리 데이터에 대한 연산 1회 ≫ padding 후 모서리 데이터에 대한 연산 2회 이상으로 증가)
II. types of convolutions
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
[x for x in torch.nn.__dir__() if ('Conv' in x)|('conv' in x)]
#['Conv1d', 'Conv2d', 'Conv3d',
# 'ConvTranspose1d',
# 'ConvTranspose2d',
# 'ConvTranspose3d'](1) dimension of convolution
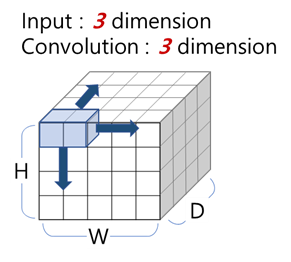
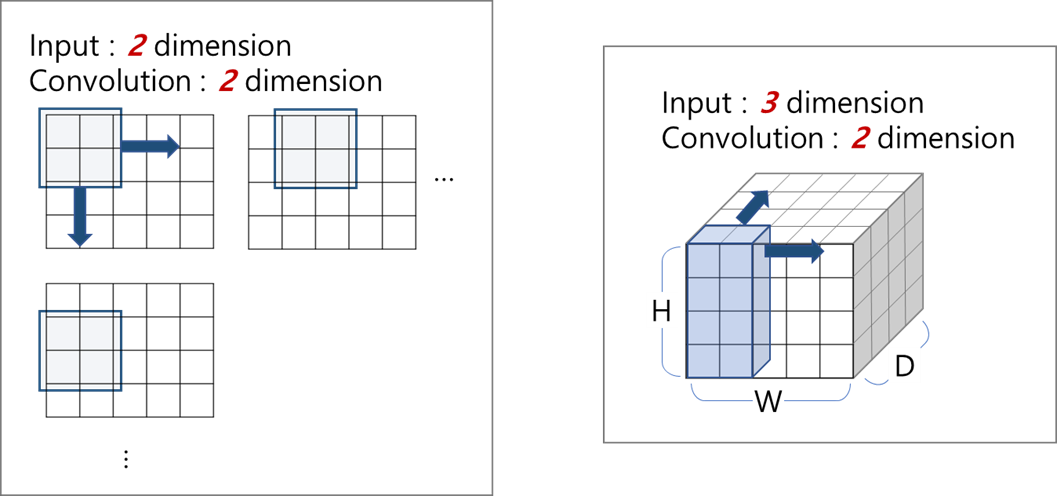
- convolution dimension ≠ input/output dimension
- convolution dimension : the number of direction where to move kernel
-
1d-convolution

-
2d-convolution
-
3d-convolution