Data Mining - Association discovery
Association discovery
- 주어진 transaction set에서 동시에 사건이 일어나는(co-occurrence) item에 대한 rule을 찾음으로써 co-occurrence하게 발생할 item을 예측할 수 있다.
- Cross-selling에 관한 가능성을 식별할 수 있다.
- Implication의 의미는 동시에 일어난 것을 의미하며, 항상 인과 관계를 의미하지 않는다.
Association analysis key issue
- 큰 data에서 패턴을 찾는 작업은 계산적으로 굉장히 비싸다
- 몇몇의 발견된 패턴은 의미 없는 것일 수도 있다. (potentially spurious)
용어
- Set of all items : I = {i_1,i_2,…,i_d}
- Set of transactions : T = {t_1,t_2,…,t_n}
- k-itemset : k개의 item을 가지고 있는 itemset
- null set : 비어 있는 item set
- transaction width : 현재 상태에 존재하는 아이템의 개수
Association Rule
- Implication의 표현은 X → Y의 형태로 표현한다.
- 같은 Itemset으로 수많은 binary partition을 만들 수 있다.
Support count (σ)
- Frequency of occurrence of an itemset
- σ(X) : X를 Itemset에 포함하고 있는 transaction 수 |{t_i |X ⊆t_i,t_i∈T}|
Support & confidence
Support, function denoted by s
- Support, s(X → Y) = σ(X∪Y)/N
- Low support : rule이 우연히 일어났다고 평가한다. 구매 시점이 우연히 같았다고 평가한다. Cross-selling 가능성 낮음
- Frequent itemset : minsup 이상의 support 값을 가지는 itemset, 우연히 일어나지 않는 itemset
Confidence, function denoted by c
- Confidence, c(X → Y) = σ(X∪Y)/(σ(X))
- X → Y와 같은 Rule의 신뢰성을 나타낸다.
- X과 주어졌을 때 Y가 일어날 조건부 가능성을 나타낸다.
- X가 단독으로 일어날 확률과 X,Y가 동시에 일어날 확률을 계산함으로써 Rule의 신뢰성 획득
Association rule mining task
- Support, confidence의 값이 각각 minsup, minconf 이상의 값을 가지는 rule을 의미 있는 rule이라고 판단한다.
Brute-force 접근법
- 가능한 모든 룰을 나열하고 각각에 대한 confidence, support 값을 계산하고 임계값과 비교한다.
0 Minsup과 minconf의 값을 넘기지 못한 rule을 prune(가지치기)한다
- 계산적으로 비효율적이며 진행이 불가능할 수 있다. Computationally prohibitive
- 가능한 모든 룰의 수 : R=3^d-2^(d+1)+1 (d는 아이템의 수)
Decoupling two metrics
- 같은 아이템으로 만들어진 룰은 같은 s의 값을 가진다.
- Support 값을 먼저 계산한 뒤, minsup을 넘긴 rule에 대해서만 confidence를 계산한다.
- Frequent itemset generation
- support값을 먼저 계산한 후, 임계 값을 넘지 못하는 item 조합을 제거하고 의미 있는 itemset만을 남긴다.
- Rule generation
- 의미 있는 frequent itemset에 대하여 confidence를 계산하여 룰을 생성한다.
- 여전히 frequent itemset generation은 계산적으로 비싸다 >> 다른 방법이 필요하다
Reducing number of candidate
Brute-force approach (비효율적 방법)
- Lattice(2^d-1개의 조합)안에 있는 itemset은 frequent itemset의 후보가 될 수 있다.
- 데이터 베이스를 스캔하여 각각의 후보에 대하여 support값을 계산한다.
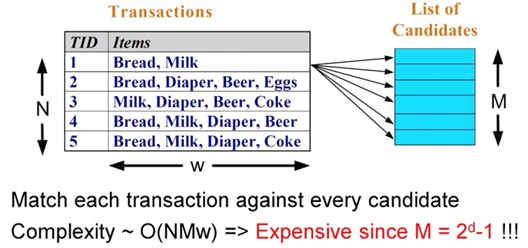
- 후보를 줄이는 방법 / M을 줄이는 방법
- 비교 회수를 줄이는 방법 / NM을 줄이는 방법
A priori(해보지 않고도 알 수 있는) principle / Reducing candidate
- 하나의 itemset이 frequent하다면 그 itemset의 부분 집합도 frequent하다
- 어떤 itemset이 frequent가 아니라면 그것의 superset도 frequent가 아니다
- Pruned superset

Anti-monotonicity property
- X가 Y의 부분집합이라면, f(Y)는 f(X)를 넘지 못한다.
Apriori algorithm
- Generate frequent itemsets of length 1
- Repeat until no new frequent itemsets are identified
- Generate length (k+1) candidate itemsets from length k frequent itemsets
- Prune candidate itemsets containing subsets of length k that are infrequent (Apriori algorithm)
- Count support of each candidate by scanning DB
- Eliminate candidates that are infrequent, leaving only those that are frequent


