Paper link : https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.1784.pdf
Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets
-
cGAN은 GAN모델에 추가적인 정보 y를 input noise 에 결합하여 generator와 discriminator에 입력하며 다음과 같은 식으로 표현합니다.
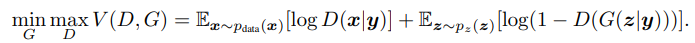
-
위의 식은 GAN모델의 목적함수에 조건식을 추가함으로써 Noise에 따라 임의로 데이터를 생성하는 것이 아닌 일정 수준 사용자가 의도한 대로 데이터가 생성될 수 있도록 합니다.
- 논문에는 조건부 확률에 대한 식이 기재되었지만 실제 구현에서는 generator와 discriminator에 추가 정보를 삽입하는 방식으로, 위의 식과 차이가 있습니다.
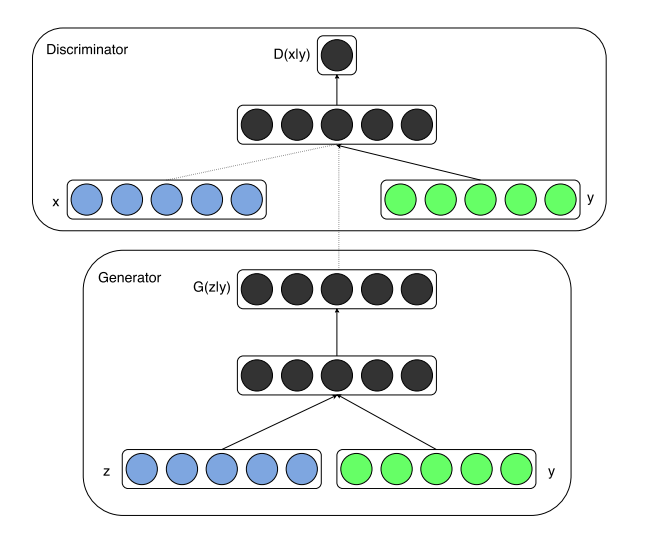
- 논문에는 조건부 확률에 대한 식이 기재되었지만 실제 구현에서는 generator와 discriminator에 추가 정보를 삽입하는 방식으로, 위의 식과 차이가 있습니다.
-
입력되는 추가 정보 y의 종류나 형태에 제약이 없지만, 일반적으로 class에 대한 정보나 class의 수만큼 채널을 추가 삽입합니다.
pytorch 구현
MNIST
- 논문에서는 MNIST 데이터셋에 대한 예시가 있습니다.
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(img_size + condition_size, hidden_size3)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(hidden_size3, hidden_size2)
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(hidden_size2, hidden_size1)
self.linear4 = nn.Linear(hidden_size1, 1)
self.leaky_relu = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.leaky_relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.leaky_relu(self.linear2(x))
x = self.leaky_relu(self.linear3(x))
x = self.linear4(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x- Discriminator의 입력층에 condition_size만큼 추가 채널을 삽입합니다.
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(noise_size + condition_size, hidden_size1)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(hidden_size1, hidden_size2)
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(hidden_size2, hidden_size3)
self.linear4 = nn.Linear(hidden_size3, img_size)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear2(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear3(x))
x = self.linear4(x)
x = self.tanh(x)
return x-
Generator에서도 마찬가지로 입력층에 condition_size만큼 추가 채널을 삽입합니다.
-
condition_size는 0~9의 10개의 Class를 가지는 MNIST데이터셋에서는 Tensor(10)만큼의 크기를, 즉 10의 크기만큼을 추가로 입력하게 됩니다.
-
추가된 10의 크기만큼의 채널에 학습과정 중 추가되는 정보는 class에 대한 정보입니다. 예를 들어, 0~9 중 2에 대한 이미지를 생성하는 경우 [0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]와 같이 one-hot encoding된 정보를 추가 입력함으로써 네트워크 상에서 현재 class 2에 대한 학습이 이루어짐을 알림으로써 생성을 제어하게 됩니다.
개인적 이해
- 개인적으로 이해한 바이며 논문에서 설명한 내용과 다를 수 있습니다.
- cGAN의 흐름도는 다음과 같이 표현됩니다.
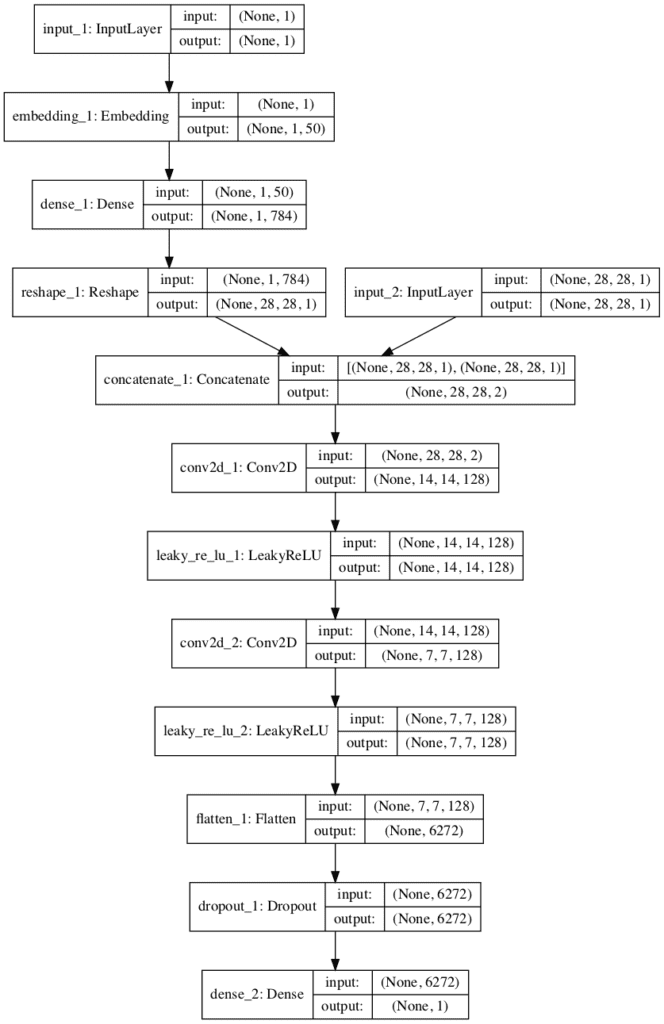
- feature map을 다음과 같다고 가정합니다.
-
one-hot encoding된 0차원 텐서를 데이터의 feature map과 concaternate할 수 있도록 동일 형태로 encoding합니다.
-
GAN 모델에서는 가상의 데이터를 생성하기 위해 Upsampling과정을 거치며, 이 과정 중 concaternate된 feature map을 계산합니다.
- 계산 결과 생성된 행렬은 즉, 3번째 class와 연관된 feature들이며 학습과정에서 이 feature를 이용하여 데이터를 생성함으로써 특정 class에 대한 데이터 생성을 제어할 수 있다고 생각합니다.
