❖ 딕셔너리(dictionary)
| key | value |
|---|---|
| bug | An error in a program that prevents the program from running as expected. |
| function | A piece of code that you can easily call over and over again. |
| loop | The action of doing something over and over again. |
- 키(key) : 사전에서 단어에 해당
- 값(value) : 사전에서 단어의 정의에 해당
dictionary = {key: value}
dictionary = {
key1: value1,
key2: value2,
key3: value3,
}키와 값의 쌍이 여러 개 있는 딕셔너리를 읽기 쉽도록 작성하는 방법
- 맨 위에 여는 중괄호 작성
- 각 쌍마다 들여쓰기
- 쉼표 후 다음 줄에 그 다음 쌍 작성
(맨 마지막 항목에도 쉼표로 마쳐야 나중에 새 항목 추가하기 편리함) - 닫는 중괄호는 딕셔너리가 시작되는 부분과 같은 들여쓰기로 작성
programming_dictionary = {
"Bug": "An error in a program that prevents the program from running as expected.",
"Function": "A piece of code that you can easily call over and over again.",
}
# 딕셔너리의 특정 값 불러오기
print(programming_dictionary["Bug"])
# 딕셔너리에 코드로 새로운 키와 값 추가하기
programming_dictionary["Loop"] = "The action of doing something over and over again."
print(programming_dictionary)
# 딕셔너리의 값 수정하기
programming_dictionary["Bug"] = "A moth in your computer."
print(programming_dictionary["Bug"])
# 딕셔너리로 반복문 수행하기
for key in programming_dictionary:
print(f"{key}: {programming_dictionary[key]}")
# 딕셔너리를 완전히 비우기
programming_dictionary = {}
print(programming_dictionary)#
An error in a program that prevents the program from running as expected.
#
{'Bug': 'An error in a program that prevents the program from running as expected.', 'Function': 'A piece of code that you can easily call over and over again.', 'Loop': 'The action of doing something over and over again.'}
#
A moth in your computer
#
Bug: A moth in your computer.
Function: A piece of code that you can easily call over and over again.
Loop: The action of doing something over and over again.
#
{}
- 딕셔너리의 특정 값 불러오기
- [ ]에 키를 넣음 (리스트에서는 인덱스)
- 키 입력 시 주의할 점
- 오타로 존재하지 않는 키를 입력하면 에러 발생
- 올바른 자료형을 입력해야 함
- 딕셔너리에 코드로 새로운 키와 값 추가하기 (직접추가 x )
- [ ]에 키를 넣고, 등호와 값 입력
- 빈 딕셔너리를 먼저 만든 후, 필요할 때마다 키와 값을 추가하는 방법이 자주 쓰임
- 딕셔너리의 값 수정하기
- 새로운 값을 추가하는 것과 비슷(등호 뒤에 바꿀 값 입력)
- 딕셔너리로 반복문 수행하기
- 반복문으로 단순히 원소(키와 값의 쌍)를 출력하면 키값만 반복 출력됨
- 값을 출력하려면 [ ]와 키를 이용해야 함
- 딕셔너리를 완전히 비우기
- 빈 딕셔너리로 바꿔주면 됨
- 게임을 재시작해서 점수와 능력을 초기화할 때와 같은 상황에서 유용
💯 coding exercises
Grading program
학생들의 시험 점수에 성적을 매기는 프로그램
- 키 : 학생들의 이름
- 값 : 학생들의 시험 점수
- 시험 점수를 성적으로 변환하여 새 딕셔너리를 생성
- 91 ~ 100 : "Outstanding"
- 81 ~ 90 : "Exceeds Expectations"
- 71 ~ 80 : "Acceptable"
- 70 or lower : "Fail"
student_scores = {
"Harry": 81,
"Ron": 78,
"Hermione": 99,
"Draco": 74,
"Neville": 62,
}
# 🚨 Don't change the code above 👆
# TODO-1: Create an empty dictionary called student_grades.
student_grades = {}
# TODO-2: Write your code below to add the grades to student_grades.👇
for name in student_scores:
score = student_scores[name]
if score >= 91:
student_grades[name] = "Outstanding"
elif score >= 81:
student_grades[name] = "Exceeds Expectations"
elif score >= 71:
student_grades[name] = "Acceptable"
else:
student_grades[name] = "Fail"
# 🚨 Don't change the code below 👇
print(student_grades){'Harry': 'Exceeds Expectations', 'Ron': 'Acceptable', 'Hermione': 'Outstanding', 'Draco': 'Acceptable', 'Neville': 'Fail'}
❖ 리스트와 딕셔너리 중첩(nesting)
리스트 또는 딕셔너리 안에 또 다른 리스트 또는 딕셔너리를 넣는 것
# 딕셔너리 {key : value}
capitals = {
"France": "Paris",
"Germany": "Berlin",
}
# 딕셔너리 안에 리스트 중첩 (딕셔너리의 값 = 리스트)
# {key : [List]}
travel_log = {
"France": ["Paris", "Lille", "Dijon"],
"Germany": ["Berlin", "Hamburg", "Stuttgart"],
}
# 딕셔너리 안에 딕셔너리 중첩 (바깥 딕셔너리의 값 = 두 쌍의 키와 값으로 이루어진 안쪽 딕셔너리)
# {key : {Dict}}
travel_log = {
"France": {"cities_visited": ["Paris", "Lille", "Dijon"], "total_visits": 12},
"Germany": {"cities_visited": ["Berlin", "Hamburg", "Stuttgart"], "total_visits": 5},
}
# 리스트 안에 여러 개의 딕셔너리들을 중첩
# [{key1 : value, key2 : [List], key3 : {Dict}}, {...}, {...}]
travel_log = [
{
"country": "France",
"cities_visited": ["Paris", "Lille", "Dijon"],
"total_visits": 12,
},
{
"country": "Germany",
"cities_visited": ["Berlin", "Hamburg", "Stuttgart"],
"total_visits": 5,
},
]💯 coding exercises
Dictionary in List
여행 기록에 방문한 국가의 정보를 추가하는 프로그램
- 함수의 매개변수로 국가 이름, 방문 횟수, 방문한 도시를 넣으면 리스트 속 딕셔너리에 추가하기
- 리스트의 한 원소 = 키와 값의 쌍이 3개가 있는 딕셔너리
- 딕셔너리의 값이 리스트일 경우, 리스트 안의 어떤 원소인지 인덱스[ ] 로 지정
country = input() # Add country name
visits = int(input()) # Number of visits
list_of_cities = eval(input()) # create list from formatted string
travel_log = [
{
"country": "France",
"visits": 12,
"cities": ["Paris", "Lille", "Dijon"]
},
{
"country": "Germany",
"visits": 5,
"cities": ["Berlin", "Hamburg", "Stuttgart"]
},
]
# Do NOT change the code above 👆
# TODO: Write the function that will allow new countries
# to be added to the travel_log.
def add_new_country(visited_country, visited_times, visited_city):
new_country = {} # 빈 딕셔너리 생성
new_country["country"] = visited_country
new_country["visits"] = visited_times
new_country["cities"] = visited_city
travel_log.append(new_country) # 리스트에 원소처럼 추가
# Do not change the code below 👇
add_new_country(country, visits, list_of_cities)
print(f"I've been to {travel_log[2]['country']} {travel_log[2]['visits']} times.")
print(f"My favourite city was {travel_log[2]['cities'][0]}.")❚Brazil
❚2
❚["Sao Paulo", "Rio de Janeiro"]
I've been to Brazil 2 times.
My favourite city was Sao Paulo.
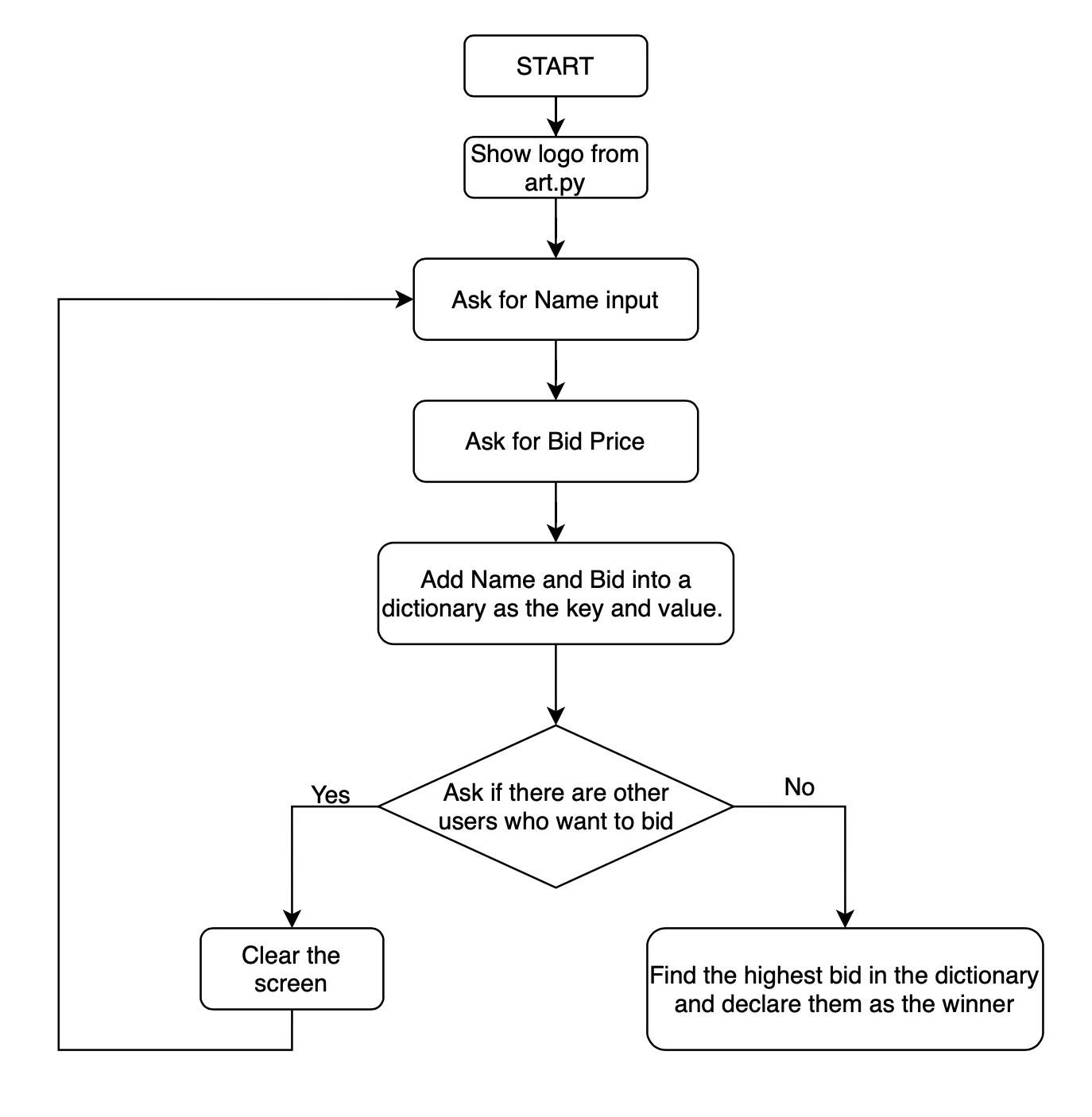
🗂️ Day9 프로젝트: 비밀경매 프로그램
최종 낙찰되어서 경매가 끝날 때까지 다른 사람의 입찰가를 알 수 없는 비밀 경매 프로그램
🔍 유의 사항
- replit 모듈로 입력할 때마다 콘솔창을 지워서 다른 사람의 입찰가를 알 수 없게 하기
- 참여자의 이름 : 키, 낙찰가 : 값
- 딕셔너리를 이용한 반복문으로 누가 최고가를 입찰했는지 찾기
- 순서도
📄 art.py
아스키 아트 로고 저장⌨️ 작성한 코드
from replit import clear
#HINT: You can call clear() to clear the output in the console.
import art
print(art.logo)
print("Welcome to the secret auction program.")
bids = {}
highest_bidder = ""
highest_bid = 0
bidding_done = False
while not bidding_done:
name = input("What is your name? : ")
price = int(input("What is your bid? : $"))
bids[name] = price
is_next = input("Are there any other bidders? Type 'yes' or 'no' : ").lower()
if is_next == "yes":
clear()
elif is_next == "no":
bidding_done = True
for name in bids:
if highest_bid < bids[name]:
highest_bidder = name
highest_bid = bids[name]
print(f"The winner is {highest_bidder} with a bid of ${highest_bid}!")
else:
bidding_done = True
print("Type 'yes' or 'no'. Try again.")[ 출력 결과 ]
___________
\ /
)_______(
|"""""""|_.-._,.---------.,_.-._
| | | | | | ''-.
| |_| |_ _| |_..-'
|_______| '-' `'---------'` '-'
)"""""""(
/_________\
.-------------.
/_______________\
Welcome to the secret auction program.
What is your name? : ❚angela
What is your bid? : $❚100
Are there any other bidders? Type 'yes' or 'no' : ❚yesWhat is your name? : ❚blake
What is your bid? : $❚98
Are there any other bidders? Type 'yes' or 'no' : ❚yesWhat is your name? : ❚charlie
What is your bid? : $❚103
Are there any other bidders? Type 'yes' or 'no' : ❚no
The winner is charlie with a bid of $103!🖍️ 답안
from replit import clear
from art import logo
print(logo)
bids = {}
bidding_finished = False
def find_highest_bidder(bidding_record):
highest_bid = 0
winner = ""
# bidding_record = {"Angela": 123, "James": 321}
for bidder in bidding_record:
bid_amount = bidding_record[bidder]
if bid_amount > highest_bid:
highest_bid = bid_amount
winner = bidder
print(f"The winner is {winner} with a bid of ${highest_bid}")
while not bidding_finished:
name = input("What is your name?: ")
price = int(input("What is your bid?: $"))
bids[name] = price
should_continue = input("Are there any other bidders? Type 'yes or 'no'.\n")
if should_continue == "no":
bidding_finished = True
find_highest_bidder(bids)
elif should_continue == "yes":
clear()
"""
FAQ: My console doesn't clear()
This will happen if you’re using an IDE other than replit.
I’ll cover how to use PyCharm in Day 15.
That said, you can write your own clear() function or configure your IDE like so:
https://www.udemy.com/course/100-days-of-code/learn/lecture/19279420#questions/16084076
"""경매 종료 후 가장 높은 입찰가와 가격을 제시한 입찰자를 추적하는 반복문을 함수로 만듦