Virtual memory can be seen as an array of characters whose size is 2^32 (in 32-bit computer)
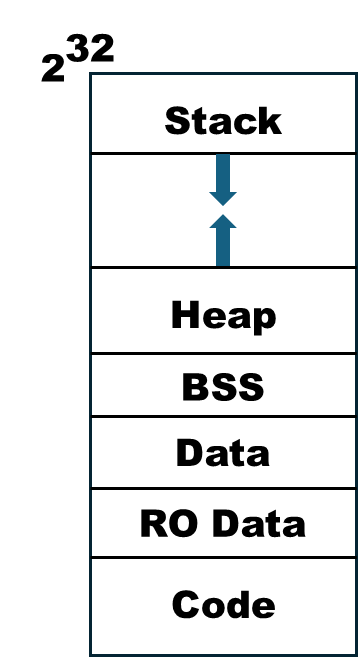
- Stack
- Automatically managed memory; when a function returns, its stack memory is released.
- Stores local variables, parameters, and return addresses for function calls.
- Heap
- Area for dynamically allocated memory
- The programmer manages memory allocation and deallocation (e.g., using
malloc/freein C).
- BSS(Block Started by Symbol)
- Contains uninitialized global and static variables.
- Memory is initialized to zero before use but doesn't have an explicit allocation until it's assigned.
- Data
- Includes initialized global and static variables.
- These variables have assigned values when the program starts.
- RO Data
- Keeps read-only constant data.
- Includes string literals and constant arrays, which cannot be modified.
- Code
- Stores instructions of a program.
- The CPU reads instructions from this section.
- Typically read-only and cannot be modified.
