문제 링크
문제
티어: 골드 4
알고리즘: dfs, 그래프
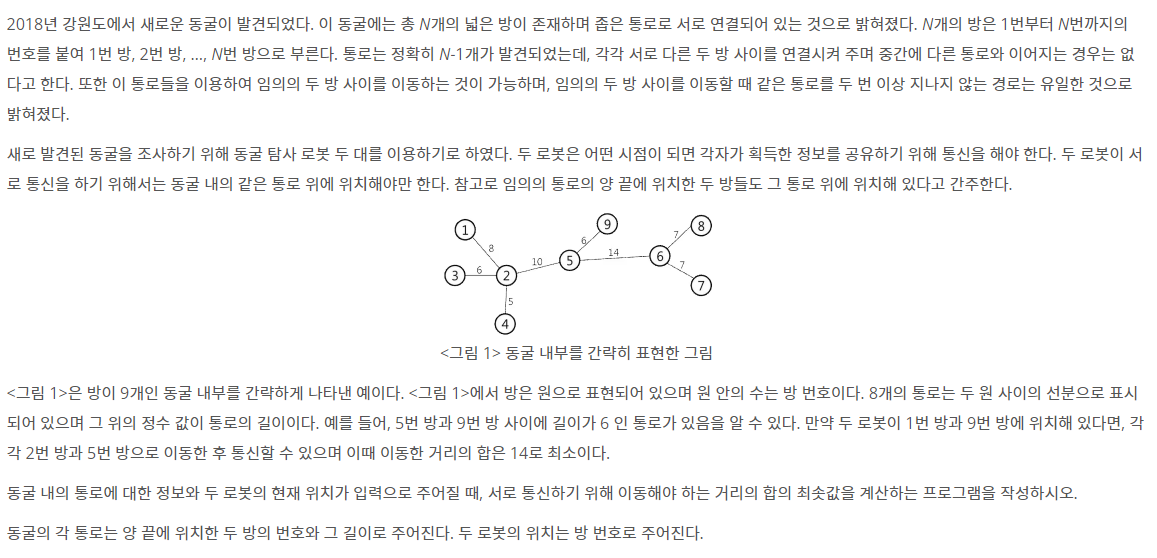
입력
표준 입력으로 동굴의 방의 개수 N과 두 로봇이 위치한 방의 번호가 세 개의 양의 정수로 공백으로 분리되어 첫 줄에 주어진다. 이후 동굴의 통로 N-1개가 한 줄에 하나씩 주어진다. 각 통로는 세 개의 양의 정수로 공백으로 분리되어 한 줄에 주어지며, 앞 두 정수는 통로의 양 끝에 위치한 방의 번호를, 세 번째 정수는 그 통로의 길이를 의미한다.
출력
표준 출력으로 두 로봇이 서로 통신하기 위해 현재 위치에서 이동해야 하는 거리의 합의 최솟값을 정수로 출력한다.
제한
모든 서브태스크에서 1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000이며, 통로의 길이는 1,000을 넘지 않는다.
풀이
두 로봇이 서로 통신하기 위해 현재 위치에서 이동해야 하는 거리의 합의 최솟값을 출력해야 한다.
두 로봇을 A, B라고 부르겠다.
나는 dfs를 이용해서 A와 B가 다른 모든 정점으로 가는데 비용을 각각 구해주고, 두 정점과 연결된 모든 통로를 체크하면서, 최솟값을 출력했다.
예를 들어 3 5와 연결된 통로가 있다면 aDistance[3] + bDistance[5]의 값이 통신하기 위한 이동 거리가 된다.
모든 통로는 N-1이기 때문에 시간 복잡도는 O(N)을 넘지 않는다.
또 다른 방법은 로봇 간의 이동 거리를 구하고, 그 이동 거리에 포함된 가장 긴 통로를 하나 제거하는 방법이다. (그림으로 보면 왜 가장 긴 통로를 제거해야 하는지 쉽게 알 수 있다.)
내 풀이는 dfs를 두 번 사용하지만 후자는 한 번만 사용하기 때문에 더 효율적인 풀이다.
또한 정점으로 가는 경로는 유일하기 때문에 먼저 방문하는 것이 곧 최단 거리다.
(모든 정점은 연결되어 있고, 간선이 N-1이면 정점으로 가는 경로는 유일하다. 트리)
소스 코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int N, A, B;
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
B = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(A == B) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
HashMap<String, Integer> wMap = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0; i<N-1; i++) {
StringTokenizer st2 = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st2.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st2.nextToken());
int w = Integer.parseInt(st2.nextToken());
graph.get(a).add(b);
graph.get(b).add(a);
wMap.put(a + " " + b, w); // a b => w
wMap.put(b + " " + a, w); // b a => w
}
int[] aDistance = new int[N + 1];
int[] bDistance = new int[N + 1];
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
aDistance[i] = -1;
bDistance[i] = -1;
}
aDistance[A] = 0;
bDistance[B] = 0;
dfs(A, aDistance, graph, wMap);
dfs(B, bDistance, graph, wMap);
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : wMap.entrySet()) {
StringTokenizer keyTokens = new StringTokenizer(entry.getKey(), " ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(keyTokens.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(keyTokens.nextToken());
min = Math.min(min, aDistance[a] + bDistance[b]);
}
System.out.println(min);
}
static void dfs(int v, int[] distance, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph, HashMap<String, Integer> wMap) {
for(int i=0; i<graph.get(v).size(); i++) {
int nextV = graph.get(v).get(i);
if(distance[nextV] == -1) {
//방문하지 않았다면
distance[nextV] = distance[v] + wMap.get(v + " " + nextV);
dfs(nextV, distance, graph, wMap);
}
}
}
}