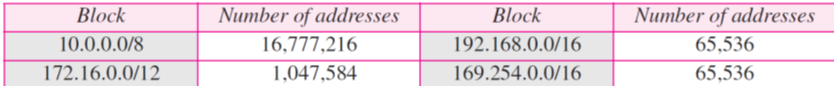
5-3 Classless Addressing
- Classful addressing의 subnetting, supernetting으로도 주소 고갈 문제를 완전히 해결하지는 못한다.
- 장거리는 IPv6, 단거리는 IPv4이지만 classless addressing 방법으로 보완 중
- Classless addressing의 block은 가변적
-
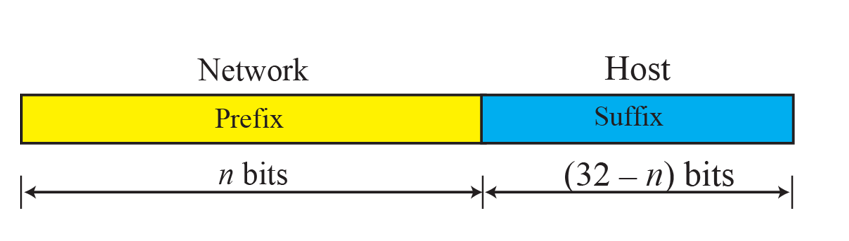
Prefix == Netid / Suffix == Hostid
-
Prefix는 1~32bit까지 가능
-
Classful방식 에서 Classless방식으로 변화함에 따라 과거 Class A는 /8을 붙이는 형태로 변화함
Classful과 classless의 차이
classful은 Subnet으로 나누었다고 해도 하나의 네트워크로 본다.
즉, Network - Subnet - Host 구조
Classless는 쉽게 말해 classful + subnetting이라고 생각할 수 있다.
즉, Class 구분이 없는 Network - Host 구조
- subnetting을 했을 경우와 마찬가지로 prefix length를 뒤에 표시해야 함.
- prefix length가 클수록 block의 길이는 작아짐.
- block의 길이를 알기 위해서는 block에 속한 address와 prefix length를 알아야 함.
ex5.22
What is the prefix length and suffix length if the whole Internet is considered as one single block with 4,294,967,296 addresses?
(하나의 block이 4,294,967,296개의 주소를 가질 때, prefix와 suffix의 길이는?)
:
- 일 떄, x = 32이다.
- 따라서 suffix의 길이가 32bit여야 함으로 prefix의 길이는 0
(prefix의 길이는 1~32이지만 이번 문제는 prefix와 suffix의 개념을 파악하느 문제임으로 예외로 함)
ex5.23
What is the prefix length and suffix length if the Internet is divided into 4,294,967,296 blocks and each block has one single address?
(하나의 address를 가진 4,294,967,296개의 block. prefix와 suffix의 길이는?)
:
- ex5.22와는 반대로 prefix 32bit, suffix 0
ex5.27
One of the addresses in a block is 167.199.170.82/27. Find the number of addresses in the network, the first address, and the last address.
(주소의 수, 첫 주소, 마지막 주소 찾기)
:
- 주어진 address와 prefix length를 통해 Network address를 찾는다.
-> prefix length가 27이기 때문에 Network mask는 앞부터 27개는 1, 나머지는 0이다.
| address | 167 | 199 | 170 | 82 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| address | 10100111 | 11000111 | 10101010 | 01010010 |
| Network mask | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11100000 |
| &&연산(first address) | 10100111 | 11000111 | 10101010 | 01000000 |
| Last address | 10100111 | 11000111 | 10101010 | 01011111 |
The number of addresses in the network:
First address : 167.199.170.64/27
Last address : 167.199.170.95/27
ex5.28
One of the addresses in a block is 17.63.110.114/24. Find the number of addresses, the first address, and the last address in the block.
(주소의 수, 첫 주소, 마지막 주소 찾기)
:
- 이 예제의 경우 prefix length가 24로 byte 단위로 떨어지기 때문에 2진수 변환을 하지 않고 해결 가능하다.
Network mask : 255.255.255.0
The number of addresses in the network:
Fisrst address : 17.63.110.0/24
Last address : 17.63.110.255/24
ex5.29
One of the addresses in a block is 110.23.120.14/20. Find the number of addresses, the first address, and the last address in the block.
(주소의 수, 첫 주소, 마지막 주소 찾기)
:
| address | 110 | 23 | 120 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| address | 01101110 | 00010111 | 01111000 | 00001110 |
| Network mask | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11110000 | 00000000 |
| &&연산(first address) | 01101110 | 00010111 | 01110000 | 00000000 |
| Last address | 01101110 | 00010111 | 01111111 | 11111111 |
The number of addresses in the network:
Fisrst address : 110.23.112.0/20
Last address : 110.23.127.255/20
ex5.30
An ISP has requested a block of 1000 addresses. The following block is granted.
:
- 위 예제의 경우, 1000은 2의 제곱수로 표현 되지 않는다. 따라서 1000개의 address를 가지기 위해서는 1024()개의 address를 가지는 block을 구성해야 한다.
- 위 경우, prefix length는 32 - 10 = 22
ex5.32
An organization is granted the block 130.34.12.64/26. The organization needs four subnetworks, each with an equal number of hosts. Design the subnetworks and find the information about each network.
(하나의 block을 동일한 address수를 가진 네 개의 subnetworks로 나누어라.)
:
- 네 개의 subnetworks를 만들기 위해서는 .
즉, 2bit를 더 prefix length에 할당해야 함.

-
기존 Network address에서 2bit를 subnet으로 활용
-
suffix 부분을 모두 0으로 하면 해당 subnet의 첫 번째 address,
모두 1로 하면 해당 subnet의 마지막 address.block이 가진 address 수 :
각 subnet이 가진 address 수 :subnet1 : 130.34.12.64/28 ~ 130.34.12.79/28
subnet2 : 130.34.12.80/28 ~ 130.34.12.95/28
subnet3 : 130.34.12.96/28 ~ 130.34.12.111/28
subnet4 : 130.34.12.112/28 ~ 130.34.12.127/28 -
Original block을 위와 같이 Subblocks로 구성 가능.
ex5.33
An organization is granted a block of addresses with the beginning address 14.24.74.0/24. The organization needs to have 3 subblocks of addresses to use in its three subnets as shown below:
One subblock of 120 addresses.
One subblock of 60 addresses.
One subblock of 10 addresses.
(하나의 block을 서로 다른 수의 address를 가진 subblock들로 나누어라.) -
block이 가진 address 수 :
-
Subblock들은 각각
120 ->
60 ->
10 ->
개의 address를 가지도록 구성되어야 한다.

- 128 -> 64 -> 16 순으로 Subnet을 구성했다.
- 48개의 address가 남는다.
subnet1(120/128) : 14.24.74.0/25 ~ 14.24.74.127/25
subnet2(60/64) : 14.24.74.128/26 ~ 14.24.74.191/26
subnet3(10/16) : 14.24.74.192/28 ~ 14.24.74.207/28
Unused(48) : 14.24.74.208 ~ 14.24.74.255
ex5.34
Assume a company has three offices: Central, East, and West. The Central office is connected to the East and West offices via private, WAN lines. The company is granted a block of 64 addresses with the beginning address 70.12.100.128/26. The management has decided to allocate 32 addresses for the Central office and divides the rest of addresses between the two other offices.
(하나의 block을 세 office에 적합한 크기의 Subnet으로 구성하기)
:

- Orignal Block의 범위는
- East와 West는 각 16개의 address를 가져야 한다.
Central block : 70.12.100.128/27 ~ 70.12.100.159/27
East block : 70.12.100.160/28 ~ 70.12.100.175/28
West block : 70.12.100.176/28 ~ 70.12.100.191/28
ex5.35
An ISP is granted a block of addresses starting with 190.100.0.0/16(65,536 addresses). The ISP needs to distribute these addresses to three groups of customers as follows:
- The first group has 64 customers; each needs approximately 256 addresses.
- The second group has 128 customers; each needs approximately 128 addresses.
- The third group has 128 customers; each needs approximately 64 addresses.
We design the subblocks and find out how many addresses are still available after these allocations.
(세 subblock을 구성하고 이후에 남은 addresses는?)
:
- first group : subblock 64개, suffix 8bit
- second group : subblock 128개, suffix 7bit
- third group : subblock 128개, suffix 6bit
-> Subnetting의 목적은 효율적인 사용을 위함이다. 따라서 subblock의 수가 아닌 suffix의 수에 맞춰 subblock을 구성한다.
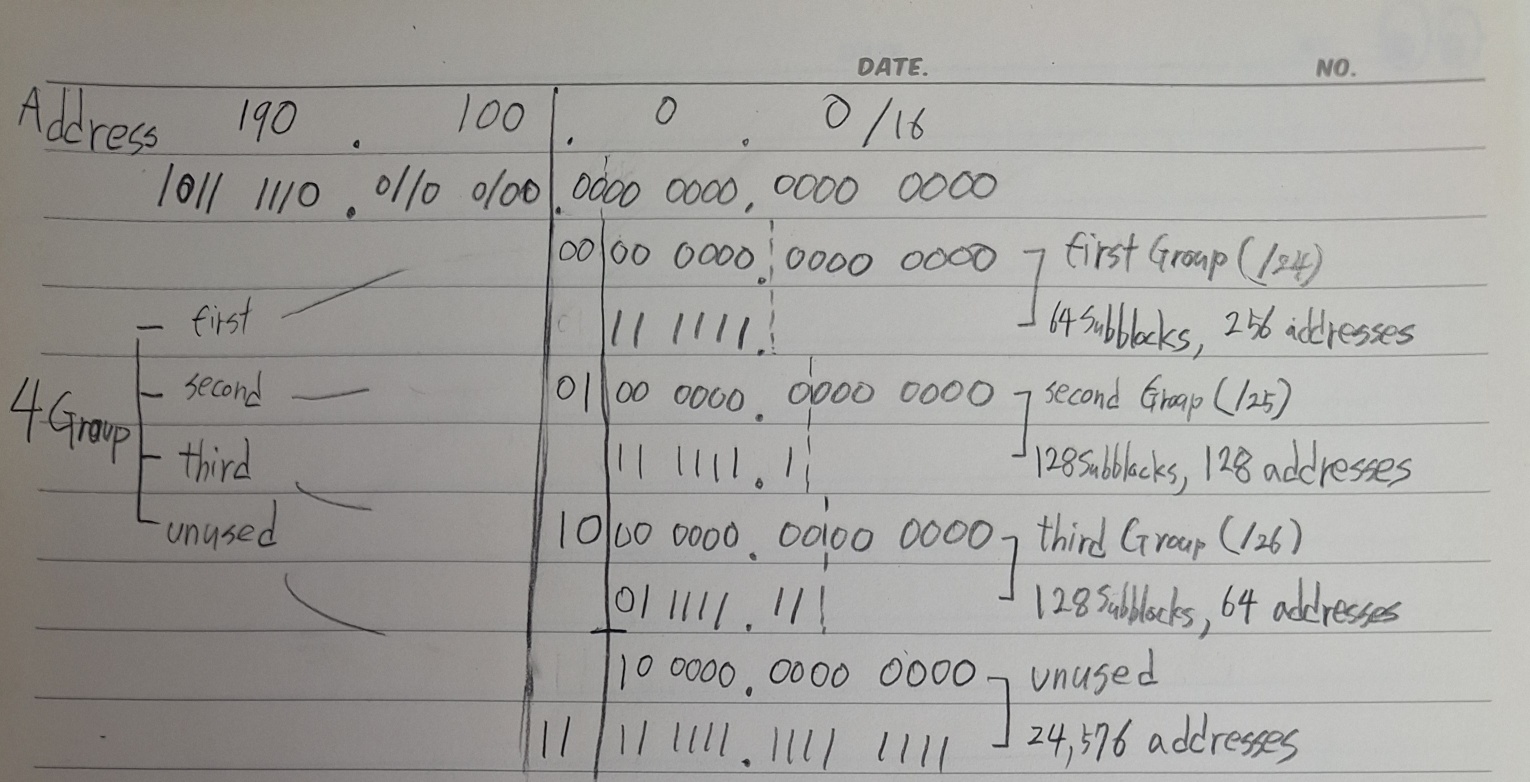
1) suffix의 2비트를 이용하여 Network를 4 group(first, second, third, unused)으로 나눈다.
2) first group부터 suffix length와 subblock의 수를 고려하여 subnet length 구성
- first group : 190.100.0.0/24 ~ 190.100.63.0/24
- second group : 190.100.64.0/25 ~ 190.100.127.128/25
- third group : 190.100.128.0/26 ~ 190.100.159.192/26
- unused : 190.100.160.0 ~ 190.100.255.255 (24576 addresses)
5-4 Special Addresses
all-zero address
- 0.0.0.0
- 아직 IP주소를 할당받지 않았다는 뜻으로 사용
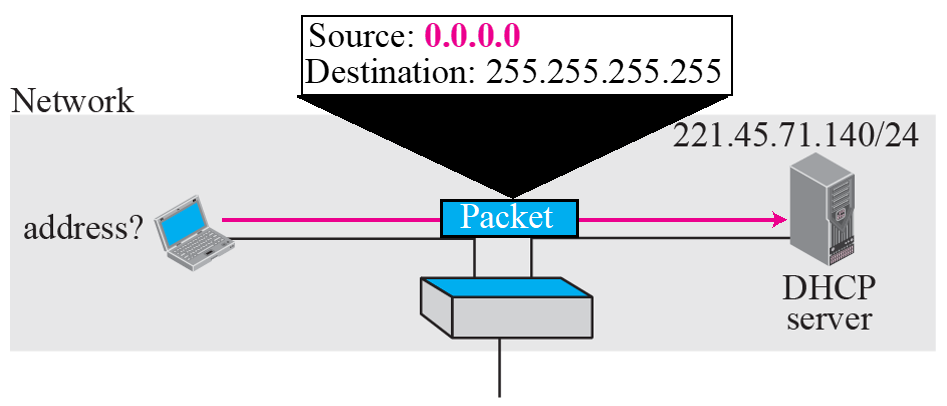
- 위 Packet은 DHCP서버에 IP address를 요청하는 request 메시지이다.
- Source(출발지)의 0.0.0.0은 자신이 IP주소가 없음을 의미한다.
- 위 노트북은 DHCP서버의 주소를 모르기 때문에 broadcast(전체 대상 통신)로 뿌림
Limited broadcast address
- 255.255.255.255
- 자신이 속해있는 Network안 모든 address에 전파
- 라우터가 위 주소를 차단하기 때문에 라우터 넘어서는 전파되지 않는다.
Direct broadcast address
- x. y. z. 255(/24) (맨 마지막 부분만 255 (host 부분만))
- broadcast하고자 하는 네트워크에 전파 (네트워크(라우터)를 넘어갈 수 있음)
ex) 서울대 네트워크(100.100.0.0/16) -> 100.100.255.255/16 전송 -> 서울대 네트워크 broadcast
local Loopback address
- 127.x.y.z (127. 으로 시작)
- Application layer에서 Network layer까지만 가고 다시 돌아옴
- Process1에서 응답을 되돌려 줌
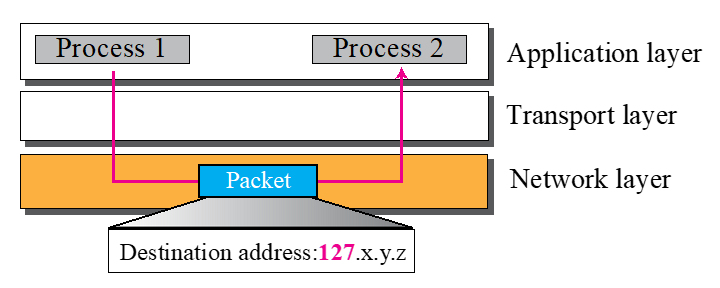
- 실제 LAN카드가 없어도 있는 것 처럼 응답을 되돌려줌
- Network 동작 테스트 용도로 주로 사용
Address for private networks
- 사설주소
- 인터넷 접속 불가, 내부적으로 Network의 PC간 통신을 위해 사용 (내부)
- 인터넷 접속을 위해선 IANA로부터 할당받은 공식 IP address를 사용 (외부)
- 방화벽 구축으로 외부 접근을 방어할 수 있음
ex) Home Network의 경우도 여러개의 Private IP와 하나의 공식 IP로 이루어져 있음
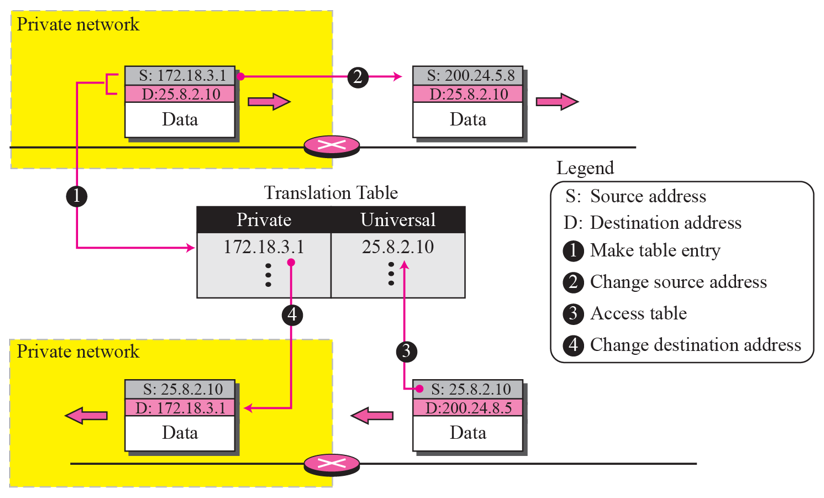
5-5 NAT (Network Address Translation)
- ISP(skt, kt 등)를 통한 위 주소 할당 방식(Classless)의 문제점
- 더 큰 범위의 IP가 필요한 경우, 전후 address가 이미 할당되어 있다면 확장이 어려움
-> NAT
NAT
- 여러개의 PC가 하나의 공인 IP로 Internet에 접속 가능하도록 하는 것
- IP address가 할당된 모든 PC가 항상 동시간 대에 동작하지는 않는다는 점을 활용

- 여러개의 PC를 private address를 사용하여 Network 구축 (172.x.y.z)
- NAT router(공유기)를 사용해 하나의 공식 IP로 Internet과 통신 (200.24.5.8)
- 하나의 IP로 여러개의 PC 활용가능.
NAT의 역할
- 172.18.3.1 PC가 Internet 통신을 원함 -> Source에 자신의 주소를 적어 전달 -> NAT router가 Source에 적힌 주소를 공식 IP로 변경하여 Internet에 전달
- Internet에서 패킷 도착 -> NAT router에서 Destination address를 사설로 변경 후 전달
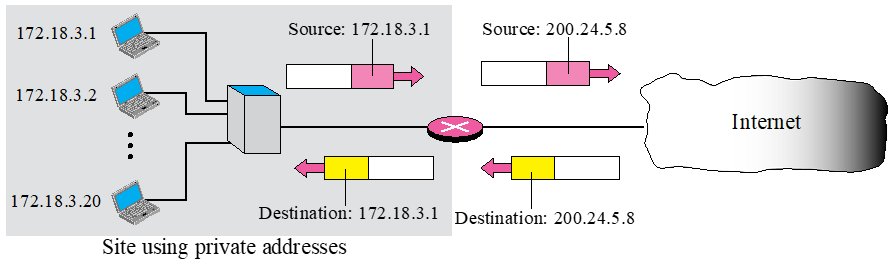
문제점 1
: NAT router는 200.24.5.8 -> 172.18.3.1 임을 어떻게 아는가?
- Table 작성
- 사설 주소와 목적지 주소를 적은 Table을 통해 확인
문제점 2
: 2개 이상의 PC가 같은 목적지 주소에 접속한다면 NAT router는 그 PC들을 어떻게 구분하는가?
- Table 요소 추가
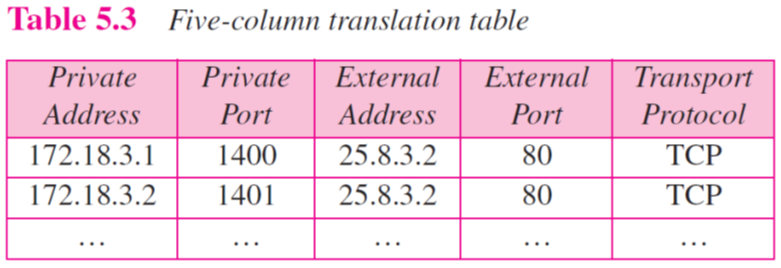
- Private port 기입
- 외부로 패킷을 보낼 때 NAT router에서 할당한 Private port number를 table에 기록
- Internet으로 부터 오는 패킷에는 Destination address와 Private port number가 같이 포함되어 있음
Port forwading
-
외부에서 사설주소의 서버로 접속할 수 있도록 하는 것 (일반적으로는 접속 불가)
- 외부에서는 공식 주소 외 사설 주소는 알지 못하기 때문
-
외부의 특정 port와 사설 주소의 특정 port를 연결시켜 주는 것
ex) NAT router에 9000번 port로 패킷이 들어오면 내부 8080번 port로 전송해라