Delivery and Forwarding of IP Packets
Delivery
Delivery: Packet의 처리 하는 것(목적지까지 전달)
- 네트워크 계층은 physical network의 packet 처리를 감독한다.
- Delivery는 direct와 indirect가 있다.
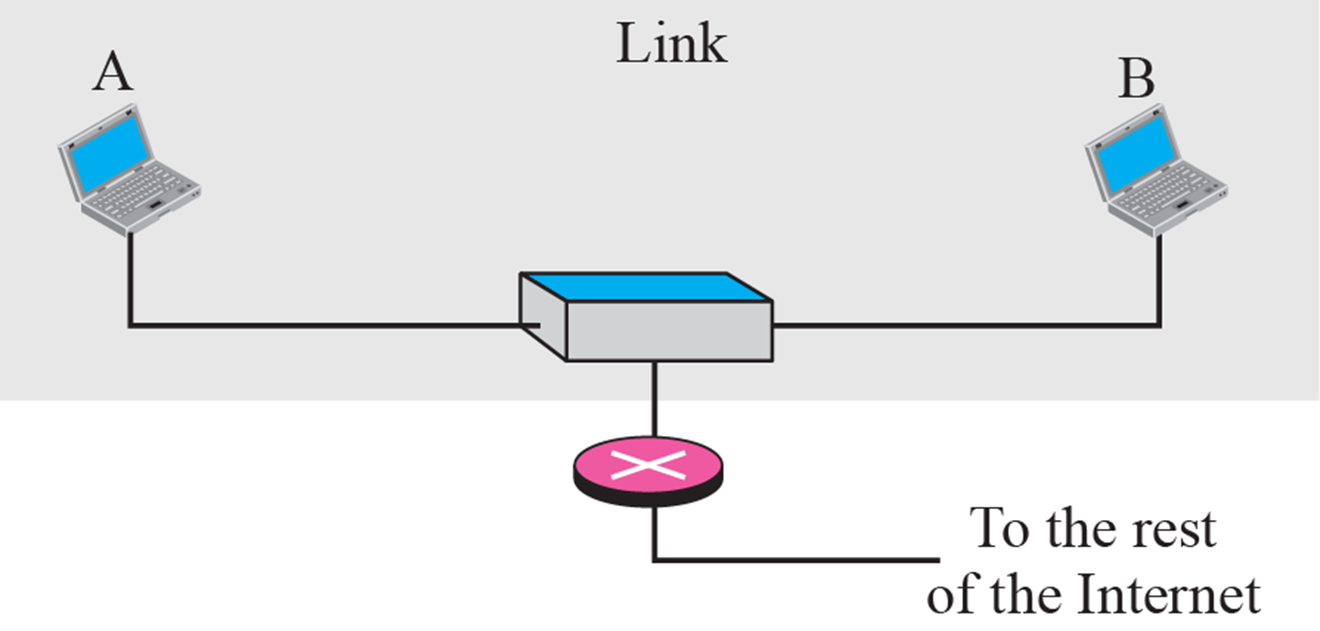
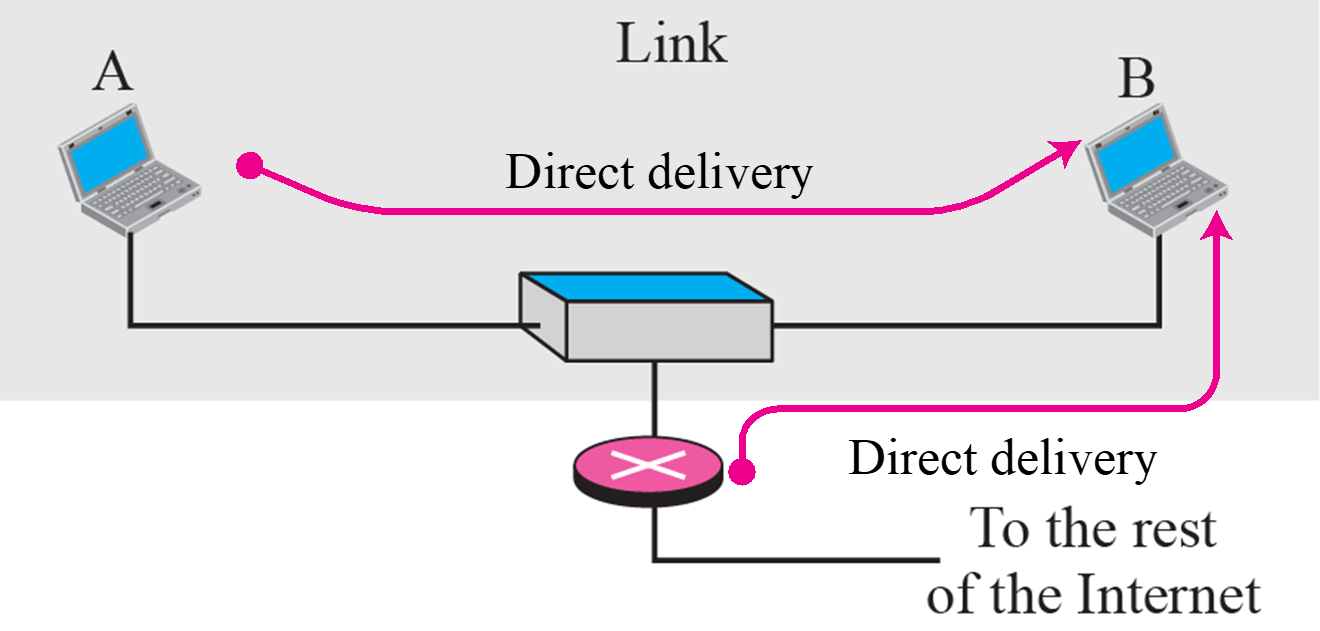
Direct delivery
- 같은 네트워크 내부에서 사용
- ARP를 통해 MAC주소 획득 후 전달(2계층)
- frame을 broadcast로 뿌려서 전달
1계층: 비트 스프링
2계층: 프레임
3계층: IP 패킷
4계층: TCP세그먼트, UDP 데이터그램이터그램
5계층: 메시지
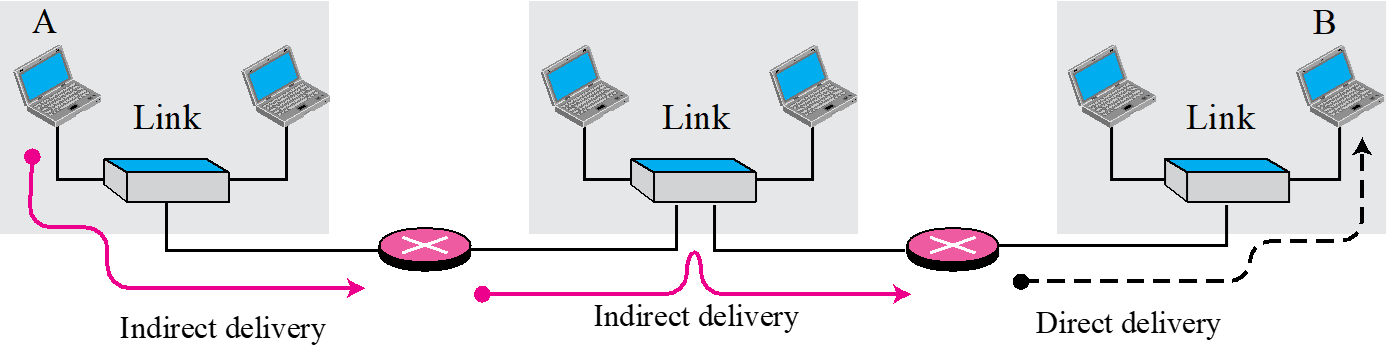
Indirect delivery
- 다른 네트워크로 전달할 때 사용
- 여러개의 Direct delivery로 구성
Forwarding
Forwarding: Packet을 다음 목적지(홉)으로 전달하는 것. (몇 번 포트로 forwarding 할 것인지)
- Indirect delivery의 경우, 처음 부터 최종 목적지로 전달하는 것이 아니기 때문에 Packet이 최종 목적지로 잘 전달해 주는 과정이 필요하다.
Connection oriented protocol(TCP)
Connection setup(연결 설정) -> 데이터 전송 -> Lilis(연결 해제)
전화 받기 -> 통화 -> 전화 끊기
Connectionless protocol(IP)
자동적으로 이루어짐
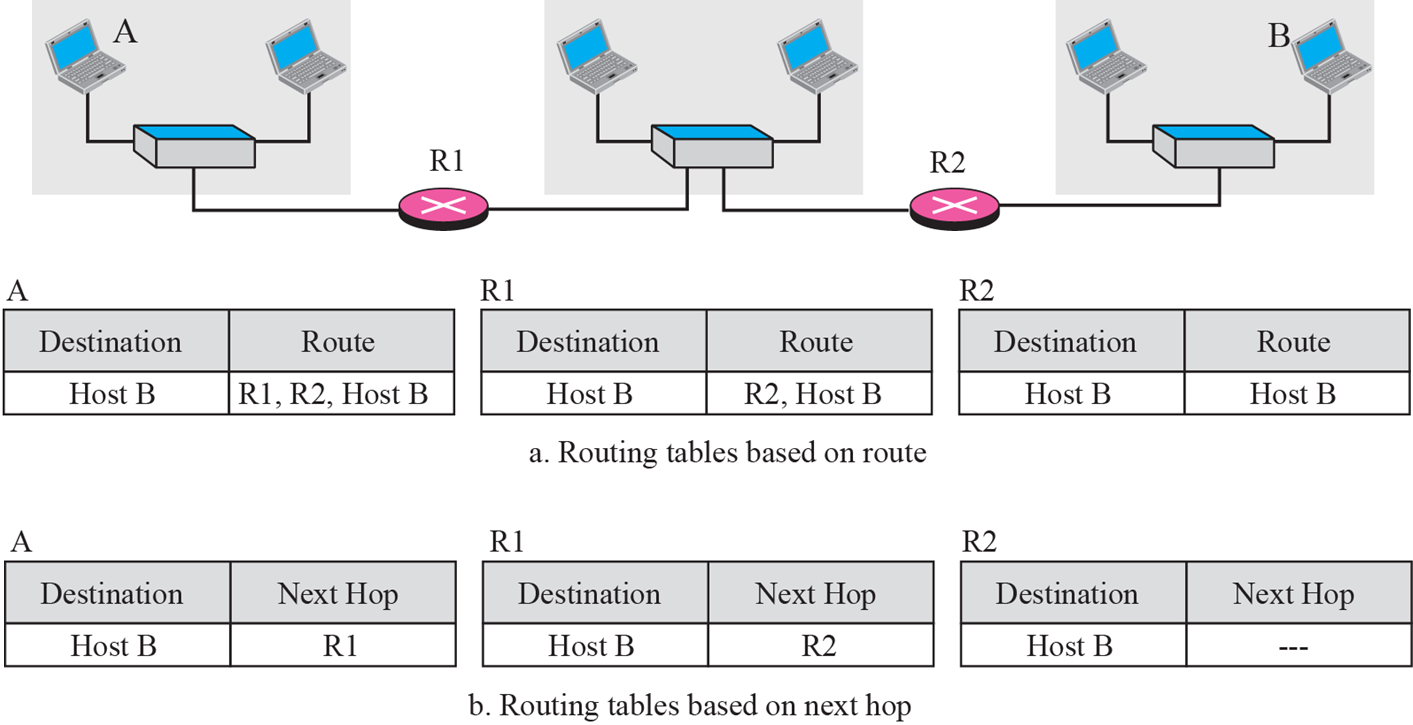
Next-hop method
Forwading의 2가지 방식
1) Routing tables based on route
- 길을 다 적음
2) Routing tables based on next hop - 다음 목적지만 적음
- 오늘날은 next hop method 사용
Network-specific routing
- 각 host 별로 Routing table을 작성하면 길이가 너무 길다
-> Network 별로 Routing table 작성
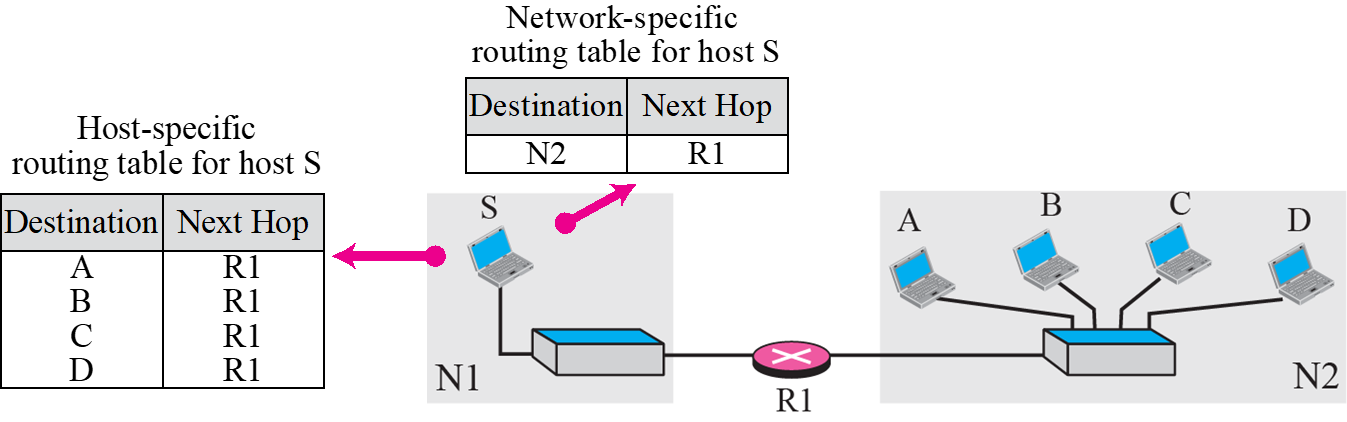
Host-specific routing
Host-specific routing table은 특별히 길을 지정해야 할 때 사용
- Routing table을 만들 땐, Host-specific method를 우선 기입
-> 그렇지 않으면 Network주소를 먼저 보고 Network-specific method로 전달됨.
Default routing
- Host-specific routing과 Network-specific routing에 언급되지 않은 address가 들어오면 Default routing이 된 곳으로 전송
- Routing table의 맨 마지막에 작성
Classful 방식의 forwarding 과정
-
과거 Classful방식을 사용할 때이다
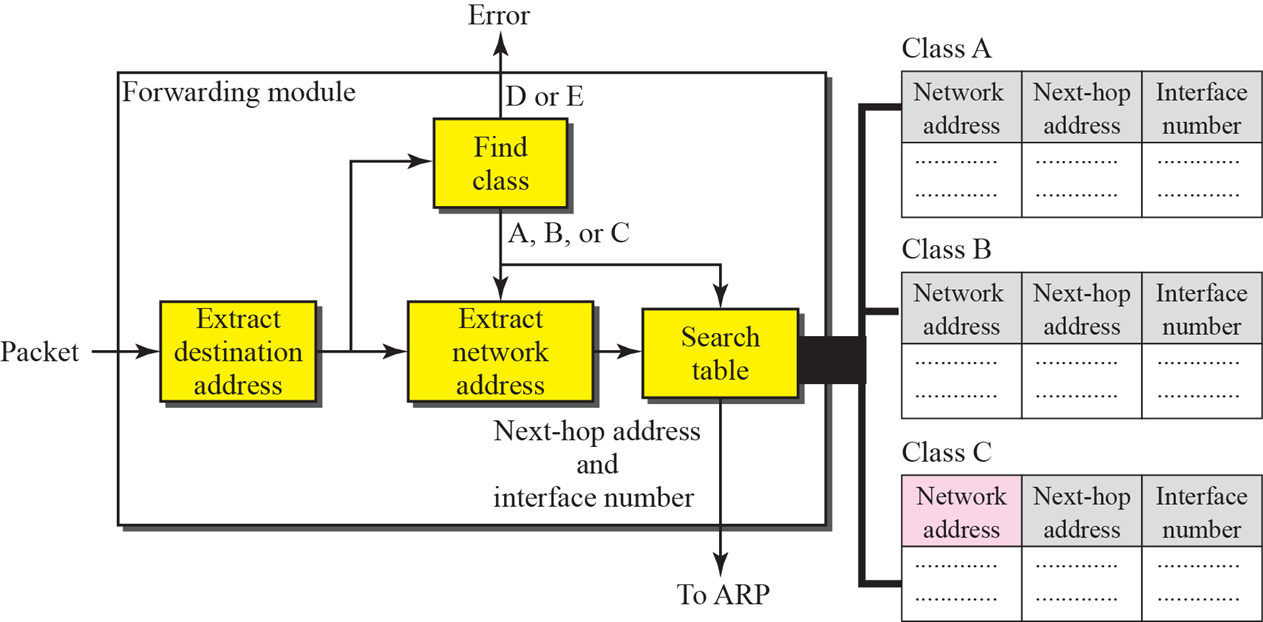
1) 패킷 받고 subnet mask를 통해 네트워크 주소 확인
2) Class별로 분류된 Search table에서 Next-hop address 획득
3) Next-hop address(IP)를 통해 ARP 진행 -> MAC address 획득
4) MAC address 적어서 broadcast -
subnetting의 경우 subnet mask로 Network addresss를 찾을 수 있다.
ex6.1
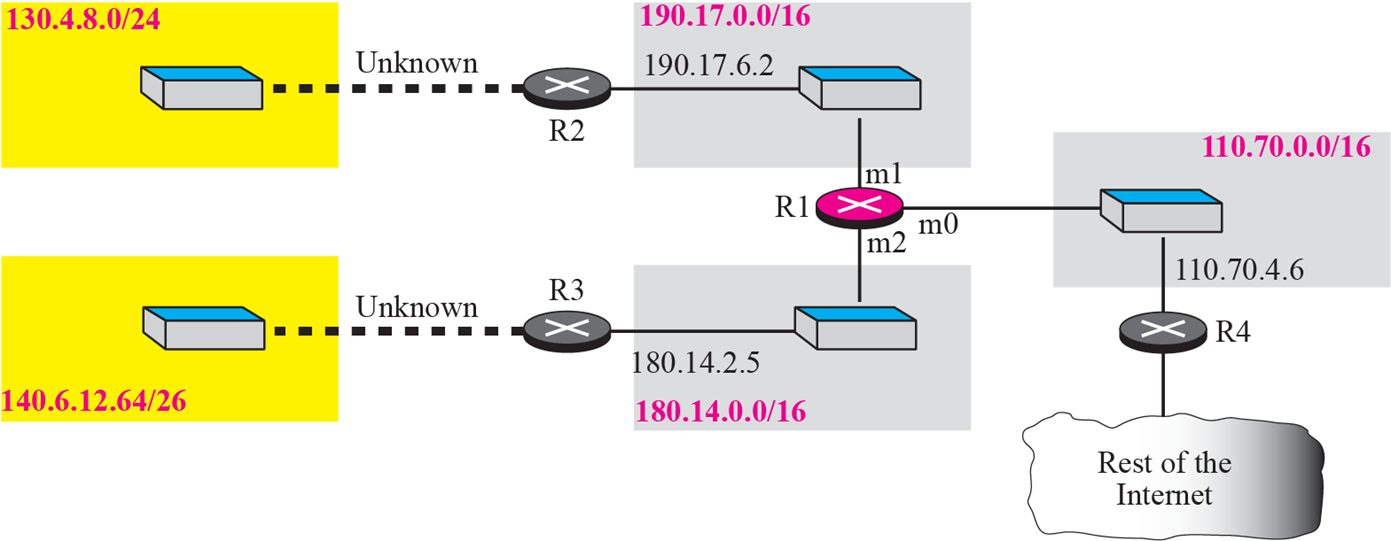
Figure 6.8 shows and imaginary part of the Internet. Show the routing tables for router R1.
(그림 6.8의 R1의 routing table은?)
:
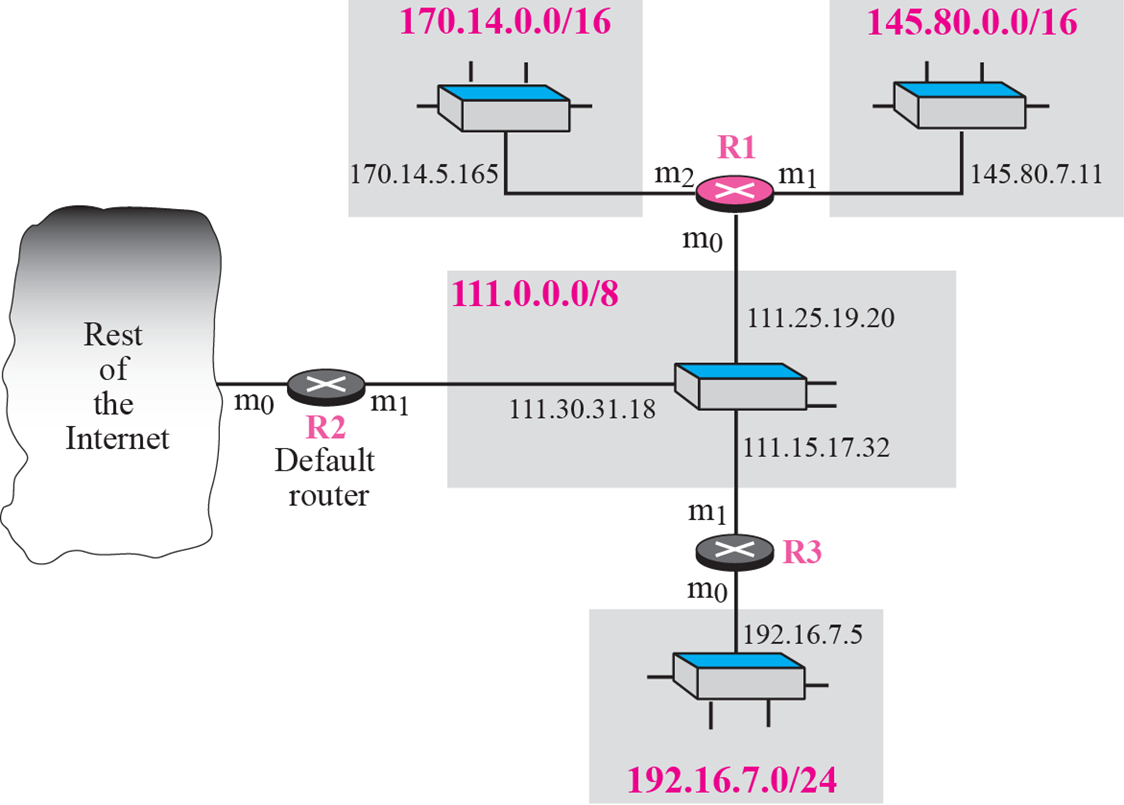
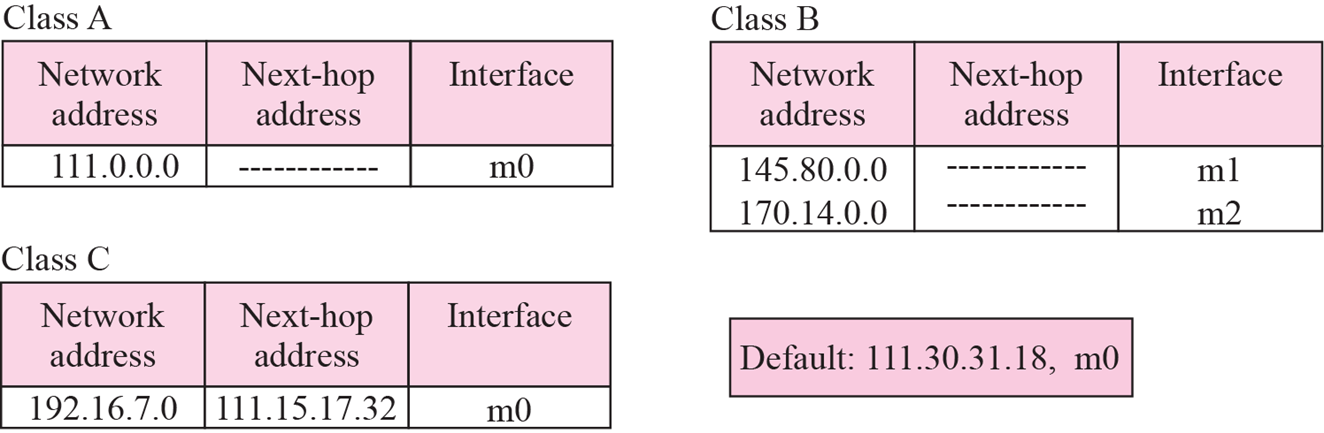
ex6.2
Router R1 in Figure 6.8 receives a packet with destination address 192.16.7.14. Show how the packet is forwarded.
(목적지 주소가 192.16.7.14인 packet의 forwarding 과정은?)
:
- 192.16.7.14는 class C.
- Network address는 192.16.7.0. (컴퓨터는 28bit >>하면 알 수 있음)
- C table. m0를 활용해 111.15.17.32 ARP
- R3 전달
- R3의 table을 활용하여 destination address로 direct delivery됨
ex6.3
Router R1 in Figure 6.8 receives a packet with destination addres 167.24.160.5. Show how the packet is forwarded.
(목적지 주소가 167.24.160.5인 packet의 forwarding 과정은?)
:
- Class B -> Network address: 167.24.0.0
- R1 Rable에 의해 Default router로 전달
ex6.4
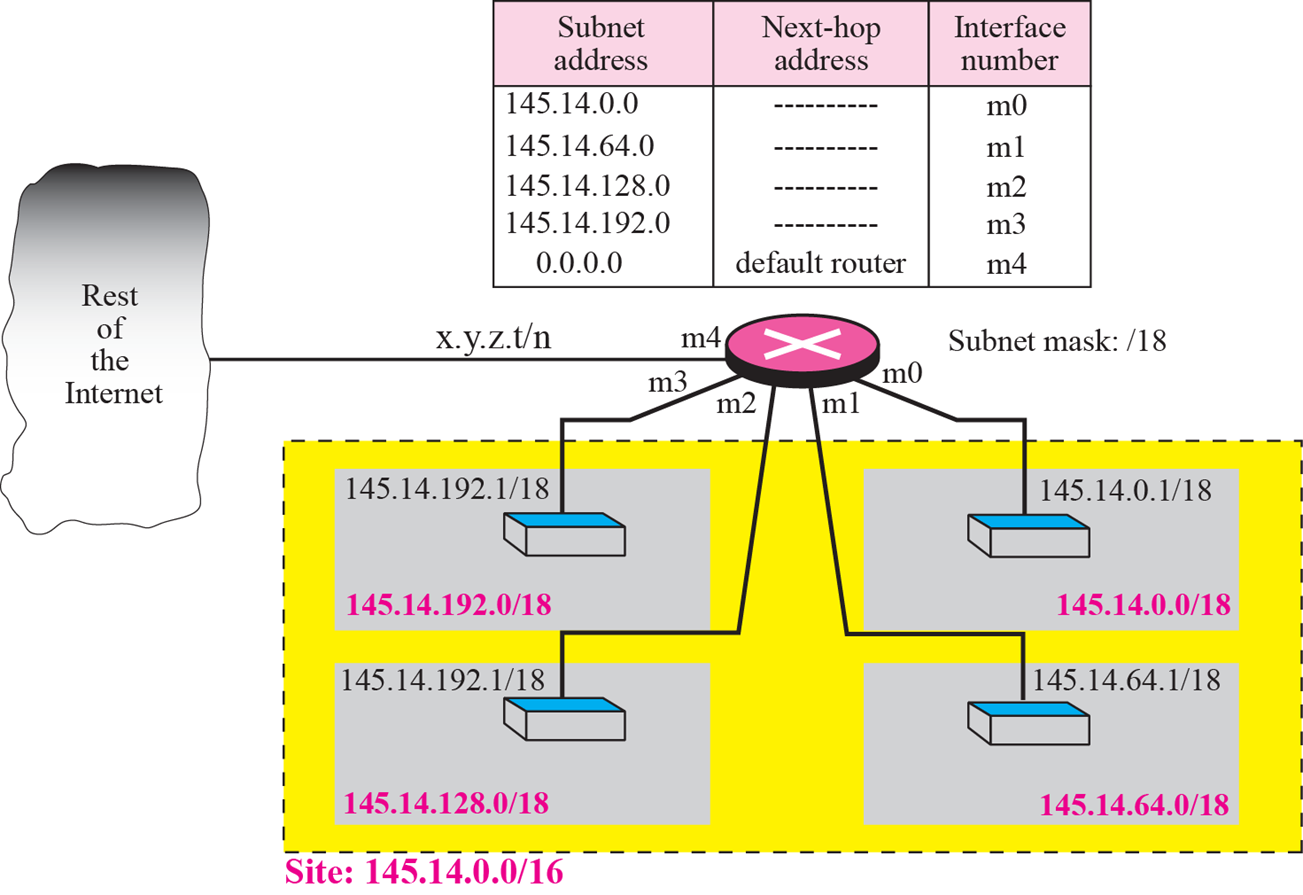 - Network address가 0.0.0.0이라면 이는 Default router이다.
- /18(subnet mask)적용
-> Classless는 Routing table에 subnet mask도 포함됨
- 나머지 과정은 Classful과 동일하다
- Network address가 0.0.0.0이라면 이는 Default router이다.
- /18(subnet mask)적용
-> Classless는 Routing table에 subnet mask도 포함됨
- 나머지 과정은 Classful과 동일하다
ex6.7
Network로 Table 찾기
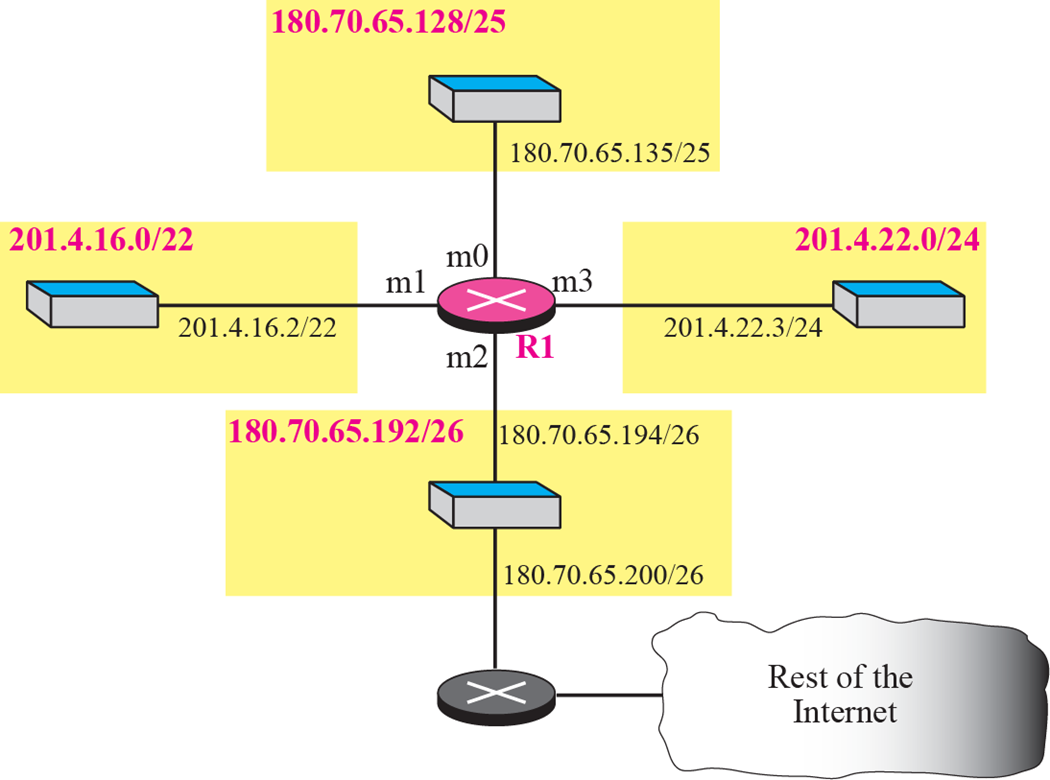
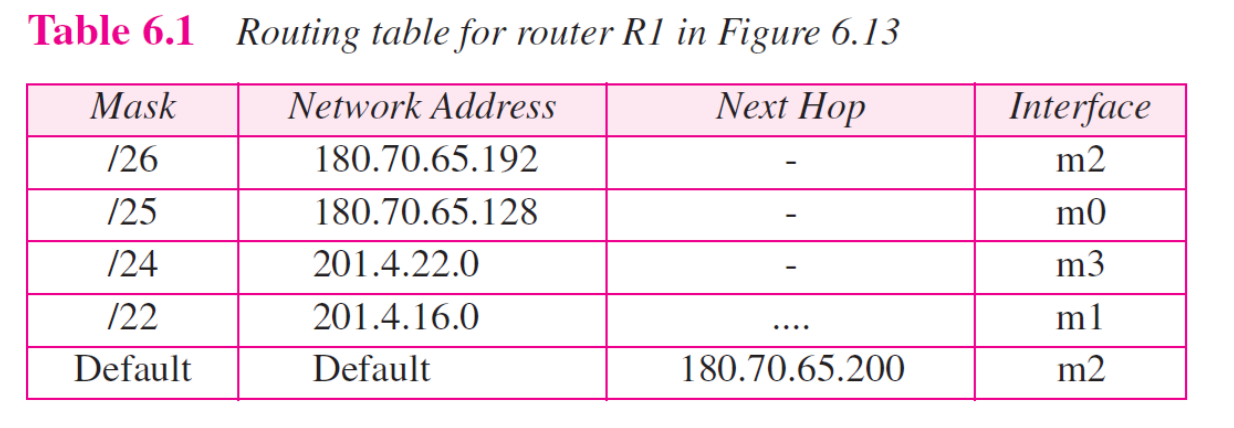 - longgest mask first
- Classless의 경우 Network address를 찾기 위해 subnet mask를 하나씩 적용해보고 Table에 일치하는 Network address가 있는지를 확인한다.
- longgest mask first
- Classless의 경우 Network address를 찾기 위해 subnet mask를 하나씩 적용해보고 Table에 일치하는 Network address가 있는지를 확인한다.
ex6.11
Table로 Network 그리기
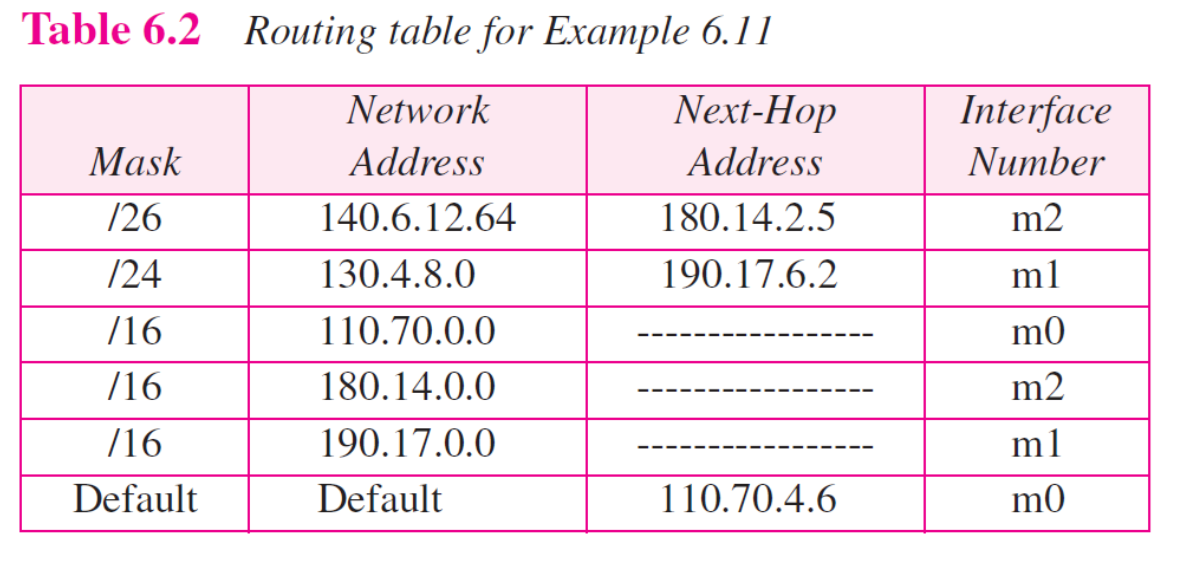
Address aggregation
- 주소 모음
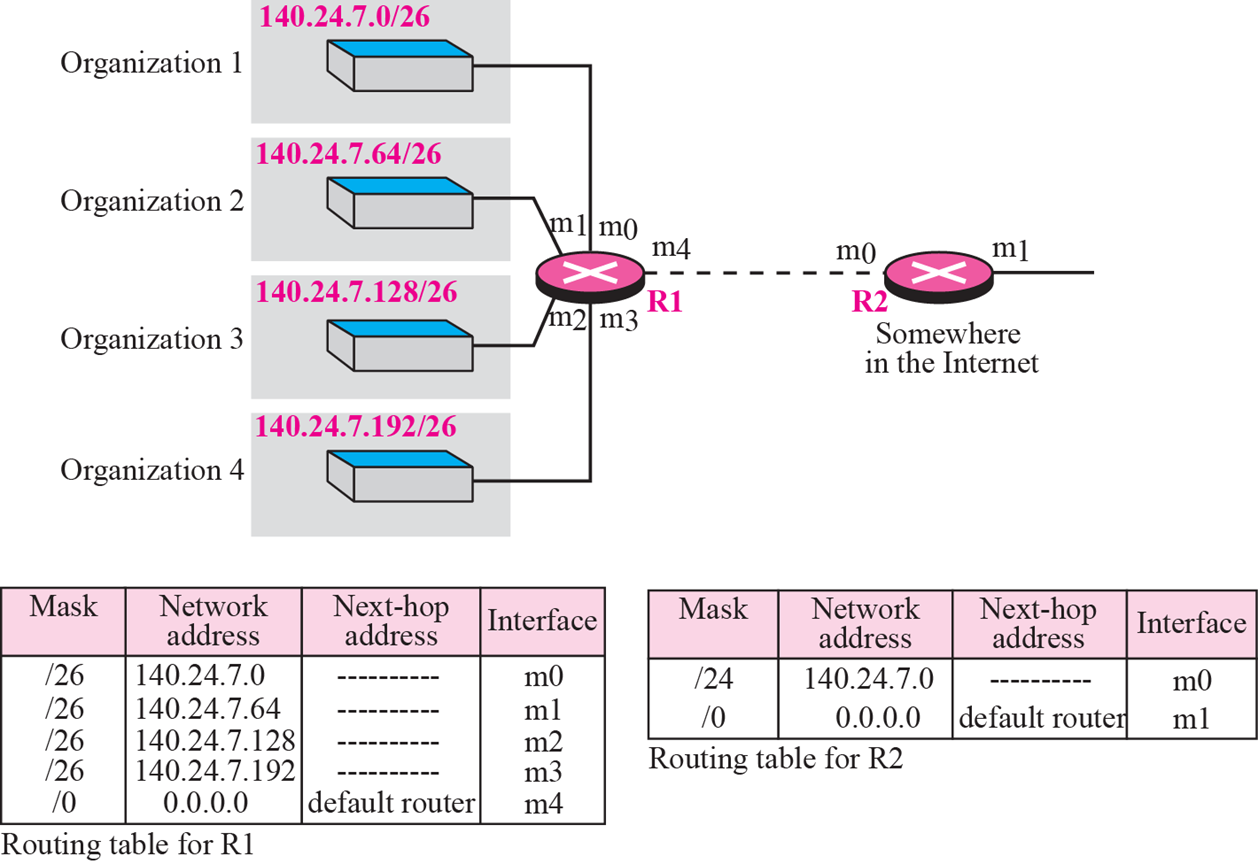
- R2는 각각에 대한 Table을 만들 필요 없이 140.24.7.0이라는 subnetting 전의 Network address만 기입하면 된다.
- 동일하게 Longgest mask first 적용
Label
-
Subnet mask를 하나씩 확인해 나가는 과정은 많은 delay가 발생한다.
Label: table의 index값을 나타내 필요한 정보를 바로 뽑아 쓸 수 있다. -
기존의 packet에 MPLS(Multi Protocol Label Switch) Header를 씌운다(label값)
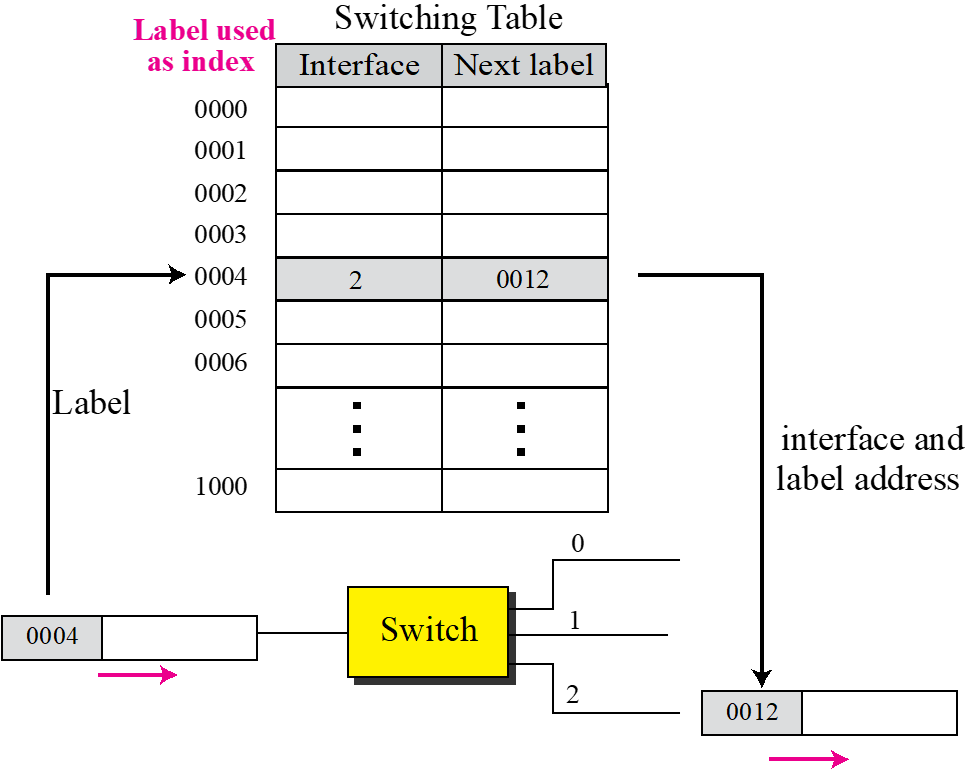
-
label 004는 index이기 때문에 바로 004로 이동
-
2번 포트로 전송 및 label을 0012로 변경
-
Next hop에서 0012로 바로 이동
Structure of a Router
- Routing과 Forwarding은 같은 개념이다.
Router의 내부
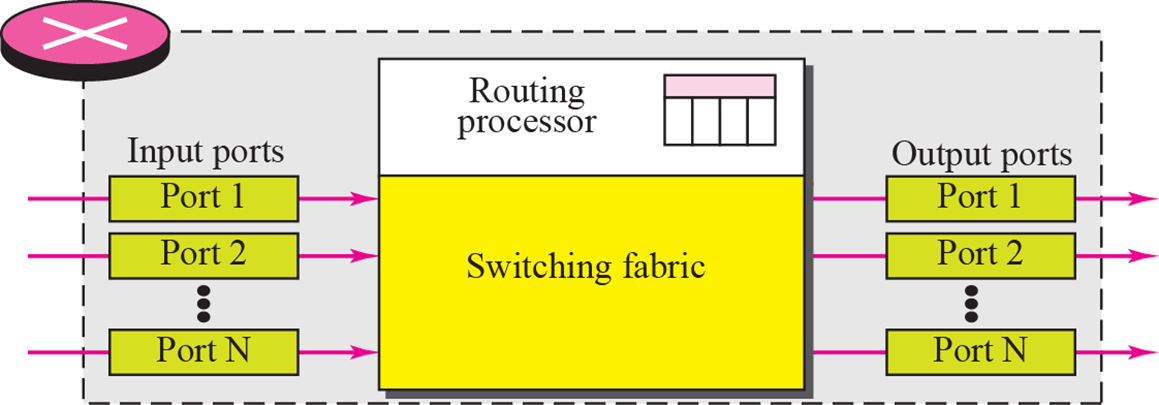
Switching fabric: port 1으로 들어온 packet을 port 2로 돌려주는 역할을 함- Input port와 Output port는 각각 Queue를 통해 순차적으로 처리한다.
Crossbar switch
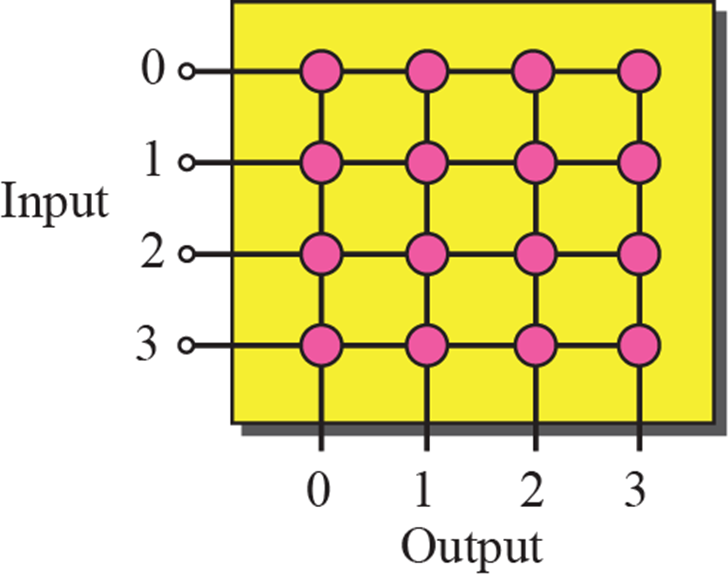 - 단점: 입력이 n, 출력이 n이면 n * n개의 switch가 필요함
- 단점: 입력이 n, 출력이 n이면 n * n개의 switch가 필요함
A banyan switch
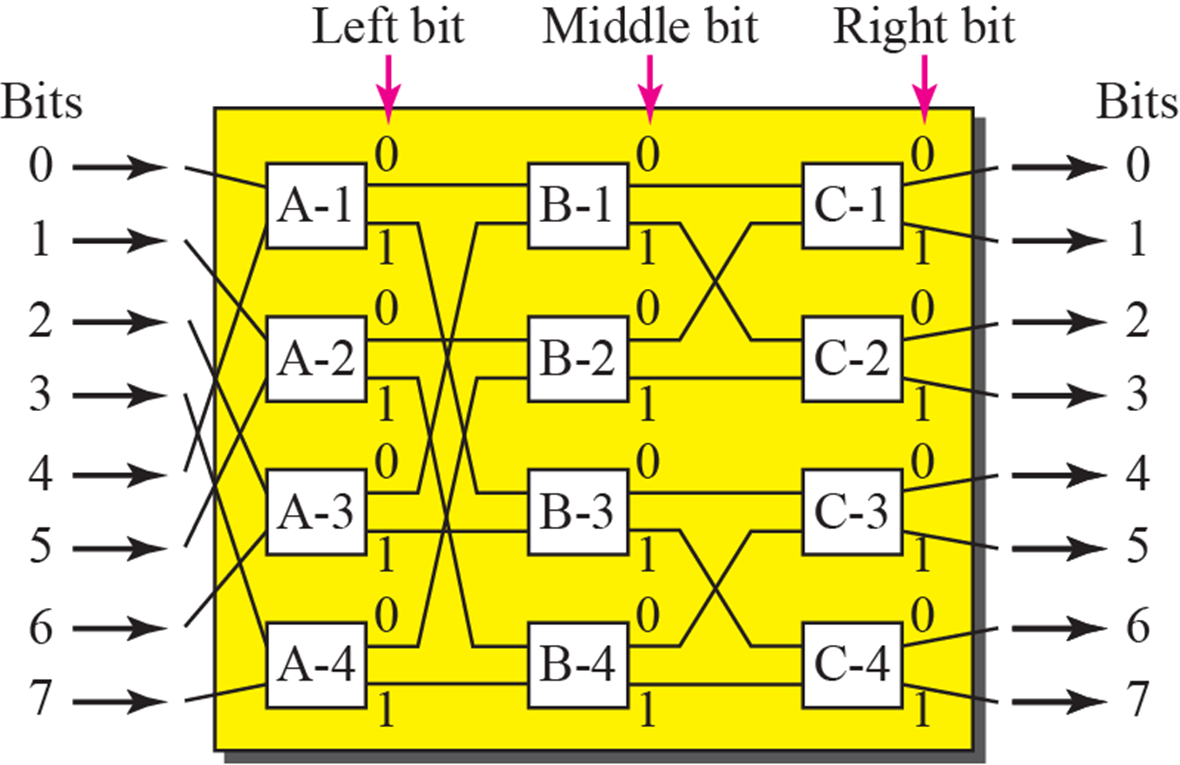 - multi stage로 구성되어 있다.
- 장점: 적은 Switch 사용
- 단점: 같은 목적지를 가진 packet이 오면 도중에 내부 블로킹이 일어날 수 있다.
- multi stage로 구성되어 있다.
- 장점: 적은 Switch 사용
- 단점: 같은 목적지를 가진 packet이 오면 도중에 내부 블로킹이 일어날 수 있다.
Batcher-banyan switch
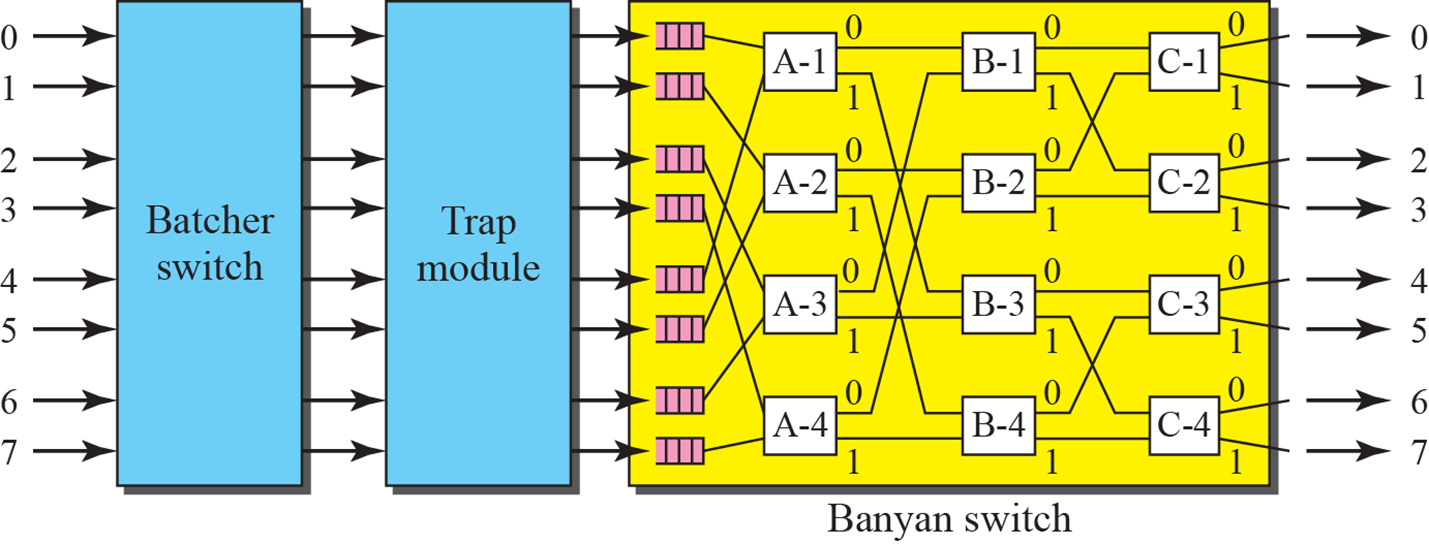
Batcher switch: 내부 블로킹이 일어나지 않도록 패킷을 정렬Trap module: 같은 목적지로 가지 않도록 조정
-> 블로킹 확률을 줄일 수 있다