◼Beautiful Soup
- HTML : 웹 페이지를 구성하는 마크업 언어
- html 태그 : 웹 페이지 표현
- head 태그 : 눈에 보이지 않지만 문서에 필요한 헤더 정보 보관
- body 태그 : 눈에 보이는 정보 보관
- Beautiful Soup 테스트를 위해 html 작성

Beautiful Soup : 태그로 이루어진 문서를 해석하는 기능을 가진 모듈
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
page = open('../data/03. bs4_test.html', 'r').read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(page, "html.parser")
print(soup.prettify())
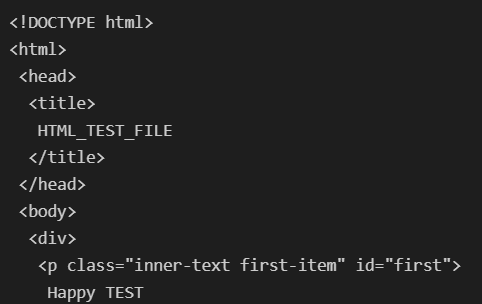
- 태그 키워드 활용
- 원하는 태그를 키워드로 선택할 수 있다. 처음 만나는 태그만을 선택한다.
head 키워드 : head 태그를 선택body 키워드 : body 태그를 선택p 키워드 : p 태그를 선택
soup.p
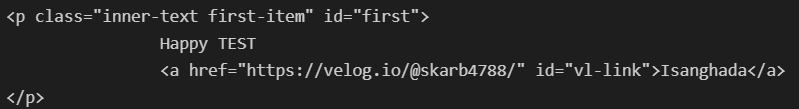
find, find_all
- 원하는 태그를 찾을 수 있다.
- 클래스를 이용할 수 있다.
- 아이디를 이용할 수 있다. 아이디는 중복이 없다.
- 조건은 다중으로 사용할 수 있다.
- 속성은 dict형으로 사용할 수 있다.
- {'class' : CLASS, 'id' : ID ...}
soup.find("p")
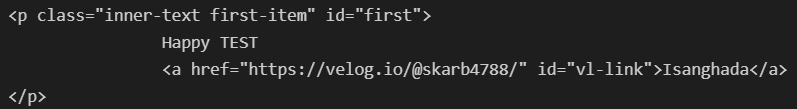
soup.find_all('p')
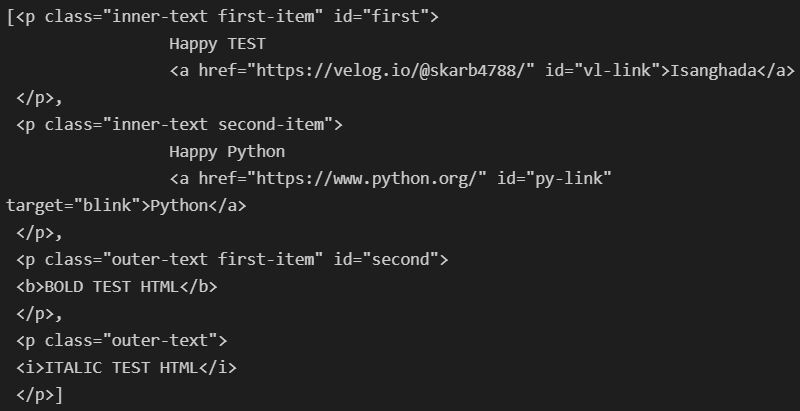
soup.find_all(class_= 'outer-text')
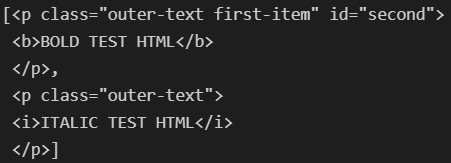
soup.find_all(id = 'first')
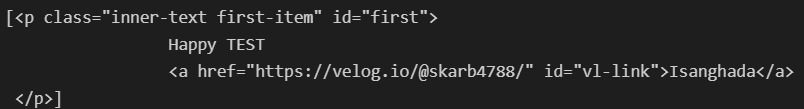
- 텍스트 키워드 : 태그에 포함된 텍스트 반환
text 키워드 : 태그에 포함된 텍스트를 반환string 키워드 : 태그에 포함된 텍스트를 반환(단, 단일 태그인 경우에만 동작)get_text() : 태그에 포함된 텍스트를 반환
- 텍스트가 여러 개 있다면 태그를 기준으로 개행되어 반환
'구분자' : 태그 사이의 구분자 설정strip 옵션 : 데이터의 양끝 공백 제거 설정(True / False)
stripped_strings 키워드 : for을 사용하여 리스트, 튜플 등의 형태로 반환할 수 있다.
for each_tag in soup.find_all('p'):
print('-'*40)
print('1.', each_tag.get_text())
print('2.', each_tag.text)
print('3.', each_tag.string)

- 외부로 연결되는 링크의 주소 알아내기
- find("a")로 링크 태그를 찾는다.
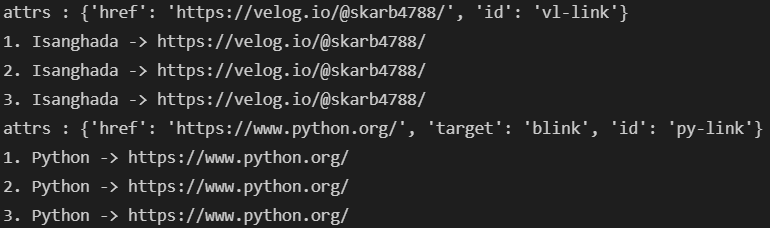
attrs 키워드 : 해당 태그의 속성 dcit형으로 반환태그[속성], 태그.get(속성) : 해당 태그의 속성 값 반환
links = soup.find_all('a')
for each in links:
print('attrs : {}'.format(each.attrs))
href = each["href"]
text = each.string
print('1. ' + text + " -> " + href)
text = each.get_text()
print('2. ' + text + " -> " + href)
text = each.text
print('3. ' + text + " -> " + href)
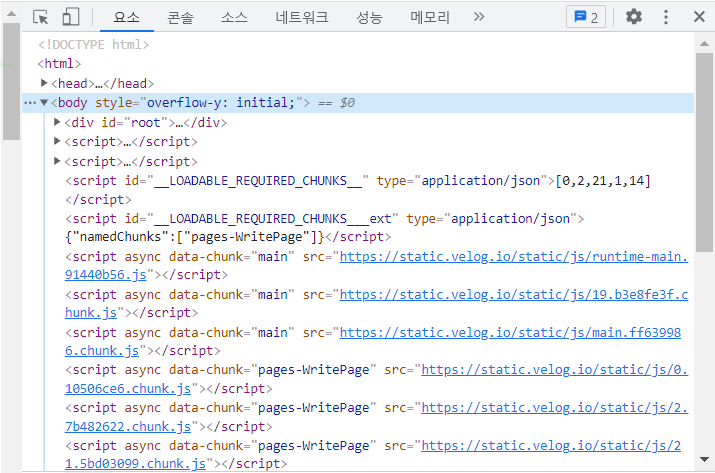
◼크롬 개발자 도구
- 크롬 개발자 도구를 활용해 찾고자 하는 데이터의 태그, 클래스, 아이디 등 정보 확인
- 소스 코드를 통해 확인할 수 있다.
urllib의 request 모듈 : 웹주소에 접근하기 위해 사용하는 모듈
urlopen() : url로 웹 페이지를 요청하는 함수status 키워드 : http 상태 코드로 200일 경우 정상적으로 정보를 받았다는 의미- http 상태 코드
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from urllib.request import urlopen
1. 네이버 금융 : 환율 확인
url = 'https://finance.naver.com/marketindex/'
page = urlopen(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(page, 'html.parser')
print(page.status)
print(soup.prettify())
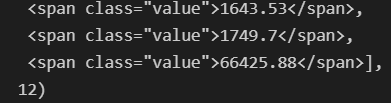
soup.find_all("span", class_="value"), len(soup.find_all("span", class_="value"))
soup.find_all("span", class_="value")[0].string

2. 네이버 금융 : 환전 고시 환율
requests 모듈 사용
get(), post() 모드가 있다.- 웹 페이지를 해당 명령으로 열게되면 http 상태 코드를 확인할 수 있다.
text 키워드 : 웹 페이지의 내용 반환
url = 'https://finance.naver.com/marketindex/'
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
print(soup.prettify())

- find,
select_one : 단일 선택
- find_all,
select : 다중 선택
exchangeList = soup.select("#exchangeList > li")
len(exchangeList), exchangeList
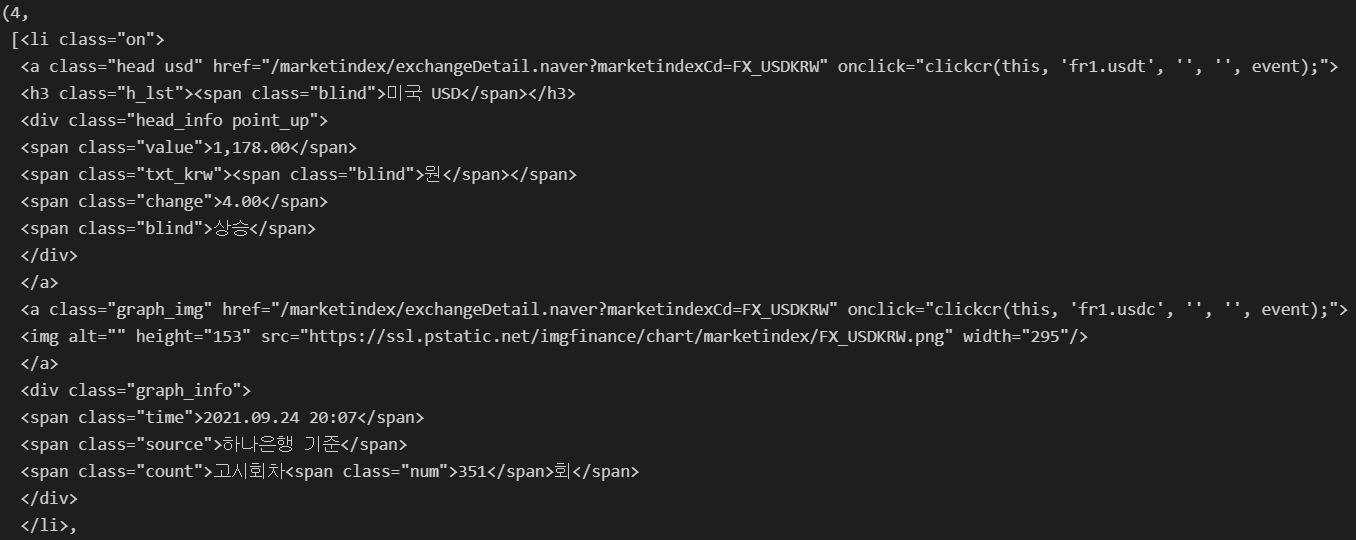
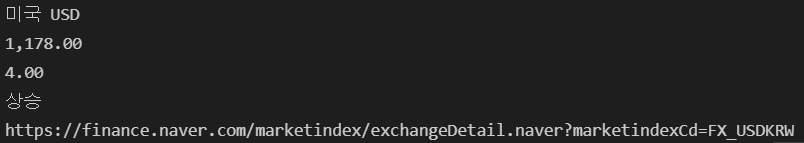
title = exchangeList[0].select_one('.h_lst').text
print(title)
exchange = exchangeList[0].select_one('.value').text
print(exchange)
change = exchangeList[0].select_one('.change').text
print(change)
updown = exchangeList[0].select_one('div.head_info > .blind').text
print(updown)
baseUrl = 'https://finance.naver.com'
link = baseUrl + exchangeList[0].select_one('a').get('href')
print(link)
exchangeDatas = []
baseUrl = 'https://finance.naver.com'
for item in exchangeList:
data = {
'title' : item.select_one('.h_lst').text,
'exchange' : item.select_one('.value').text,
'change' : item.select_one('.change').text,
'updown' : item.select_one('div.head_info > .blind').text,
'link' : baseUrl + item.select_one('a').get('href')
}
exchangeDatas.append(data)
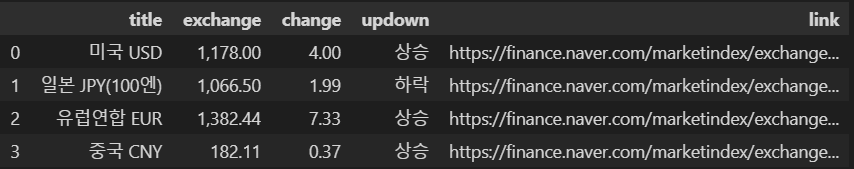
df = pd.DataFrame(exchangeDatas)
df.to_excel('./naverfinance.xlsx', encoding='utf-8')
df
◼위키백과 활용
import urllib
from urllib.request import urlopen, Requests
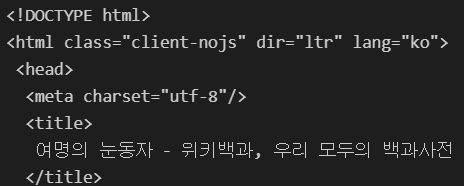
html = "https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/{search_words}"
req = Request(html.format(search_words=urllib.parse.quote("여명의_눈동자")))
response = urlopen(req)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response, "html.parser")
print(soup.prettify())
n = 0
for each in soup.find_all('ul'):
print('=>' + str(n)+"=================================")
print(each.get_text('|', strip=True))
n += 1

soup.find_all('ul')[15].text.replace('\xa0', '').replace('\n', ' ')





















