강의 복습 내용
[DAY 17]
(3강) Recurrent Neural Network and Language Modeling
1. Basics of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
- Basic structure
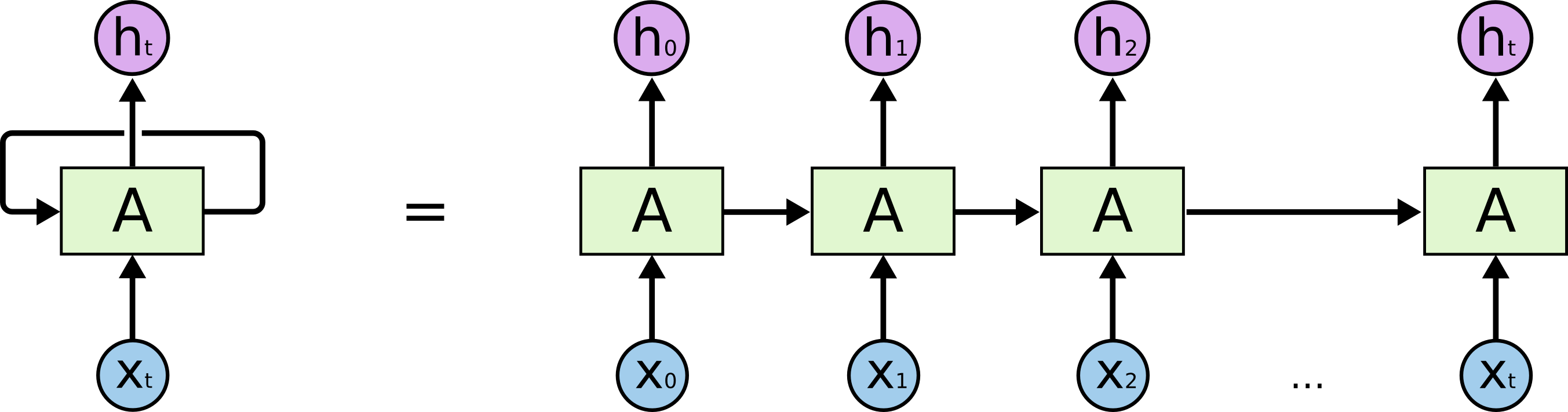
- Inputs and outputs of RNNs (rolled version)
- We usually want to predict a vector at some time steps
- How to calculate the hidden state of RNNs
- We can process a sequence of vectors by applying a recurrence formula at every time step

- Notice: The same function and the same set of parameters are used at every time step
- The state consists of a single “hidden” vector h
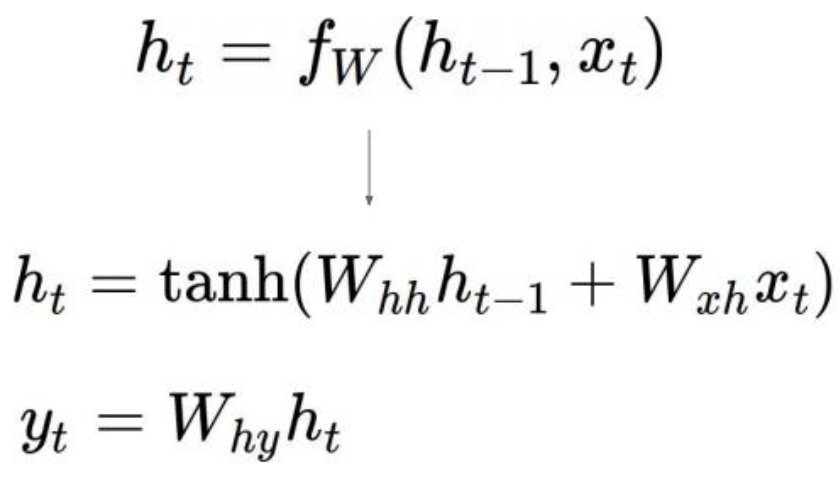
- We can process a sequence of vectors by applying a recurrence formula at every time step
2. Types of RNNs
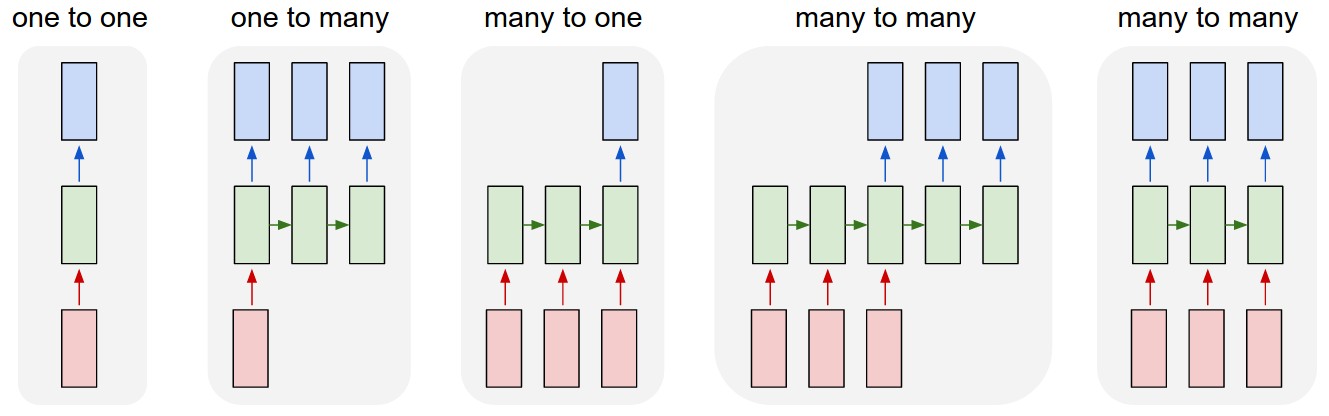
- One-to-one : Standard Neural Networks
- One-to-many : Image Captioning
- Many-to-one : Sentiment Classification
- Sequence-to-sequence : Machine Translation, Video classification on frame level
3. Character-level Language Model
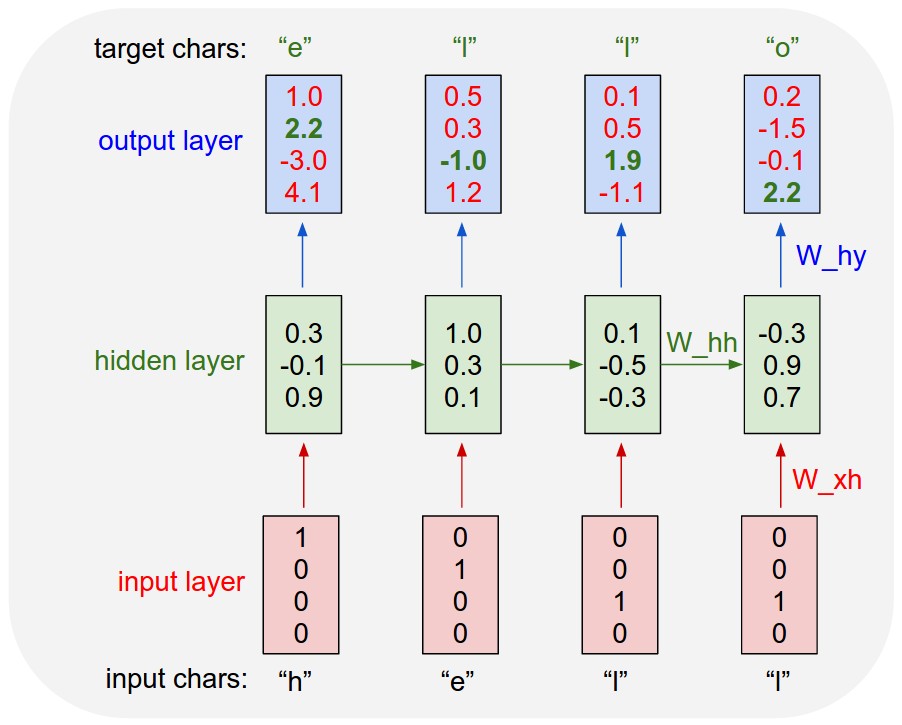
-
Backpropagation through time (BPTT)
- Forward through entire sequence to compute loss, then backward through entire sequence to comput gradient
- Run forward and backward through chunks of the sequence instead of whole sequence
- Carry hidden states forward in time forever, but only backpropagate for some smaller number of steps
-
Searching for Interpretable Cells
-
How RNN works
- Quote detection cell
- If statement cell
-
Vanishing/Exploding Gradient Problem in RNN
- RNN is excellent, but...
- Multiplying the same matrix at each time step during backpropagation causes gradient vanishing or exploding
- The reason why the vanishing gradient problem is important
- RNN is excellent, but...
(4강) LSTM and GRU
4. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
-
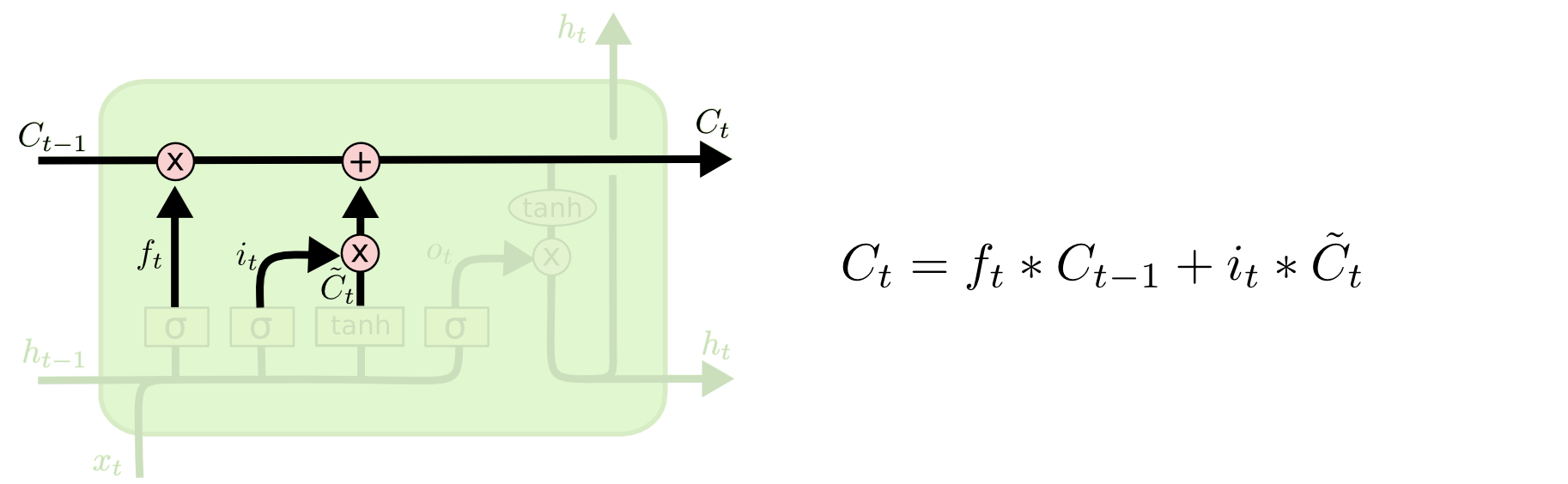
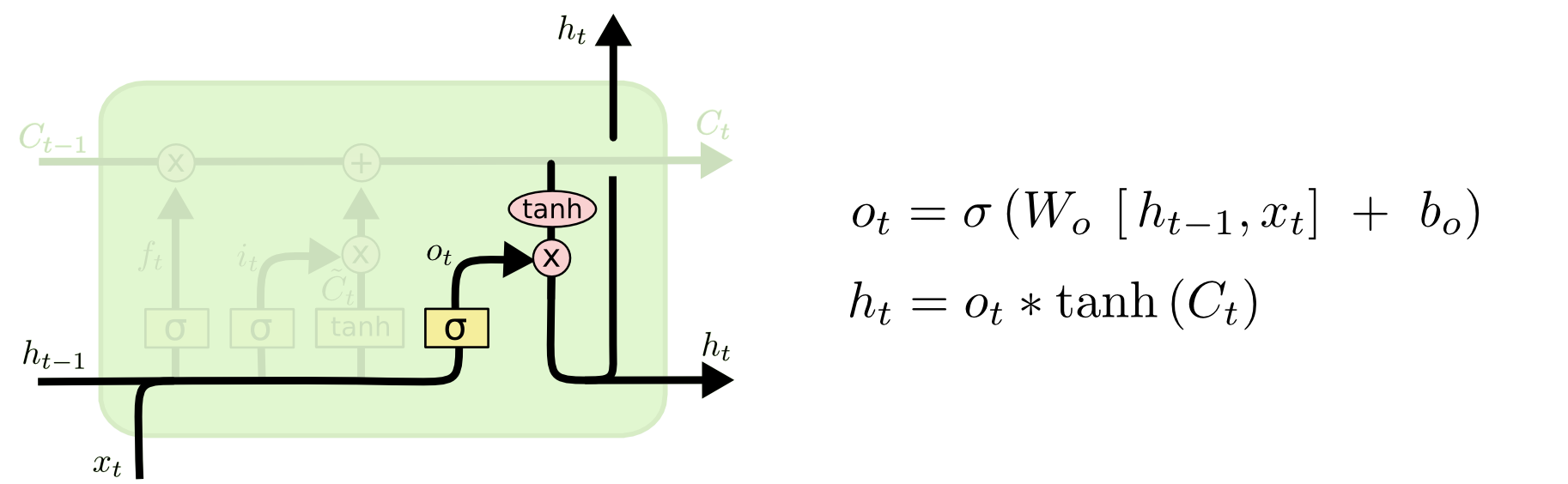
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
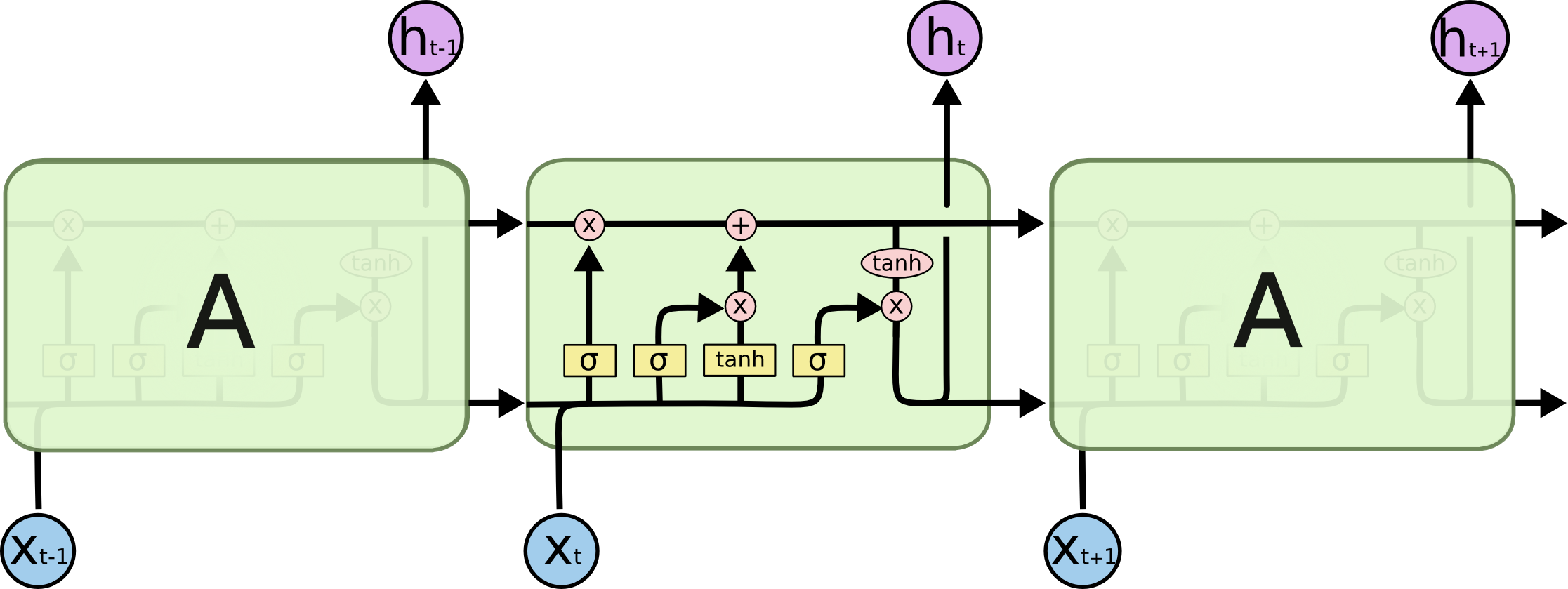
- Core Idea: pass cell state information straightly without any transformation
- Solving long-term dependency problem
- i : Input gate, Whether to write to cell
- f : Forget gate, Whether to erase cell
- o : Output gate, How much to reveal cell
- g : Gate gate, How much to write to cell
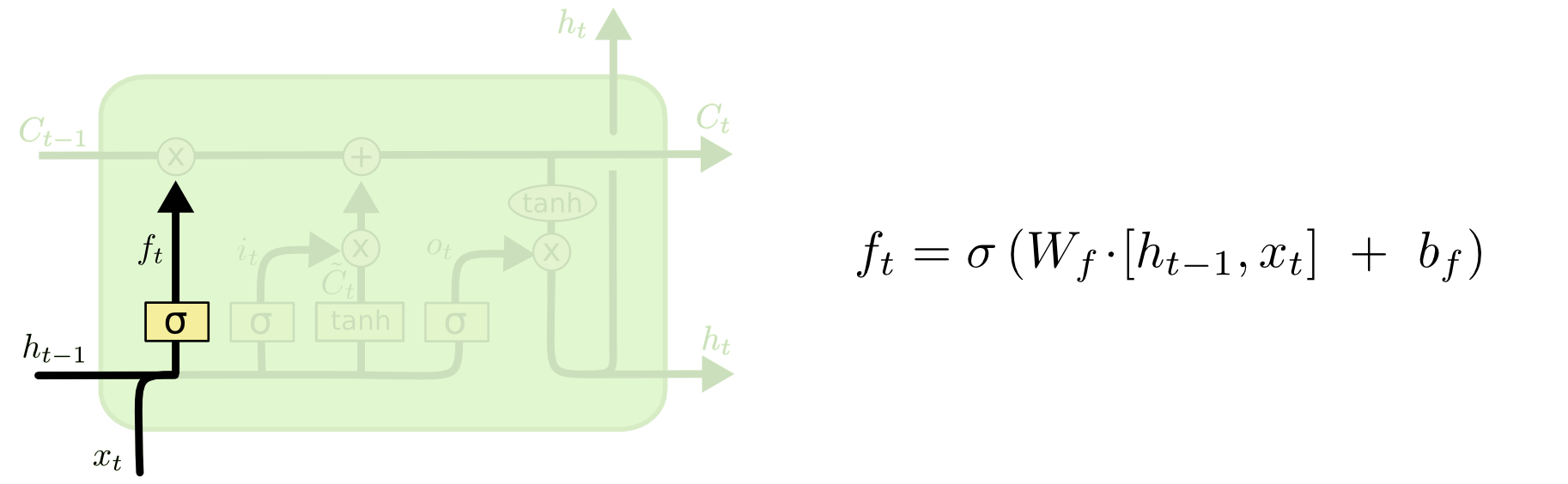
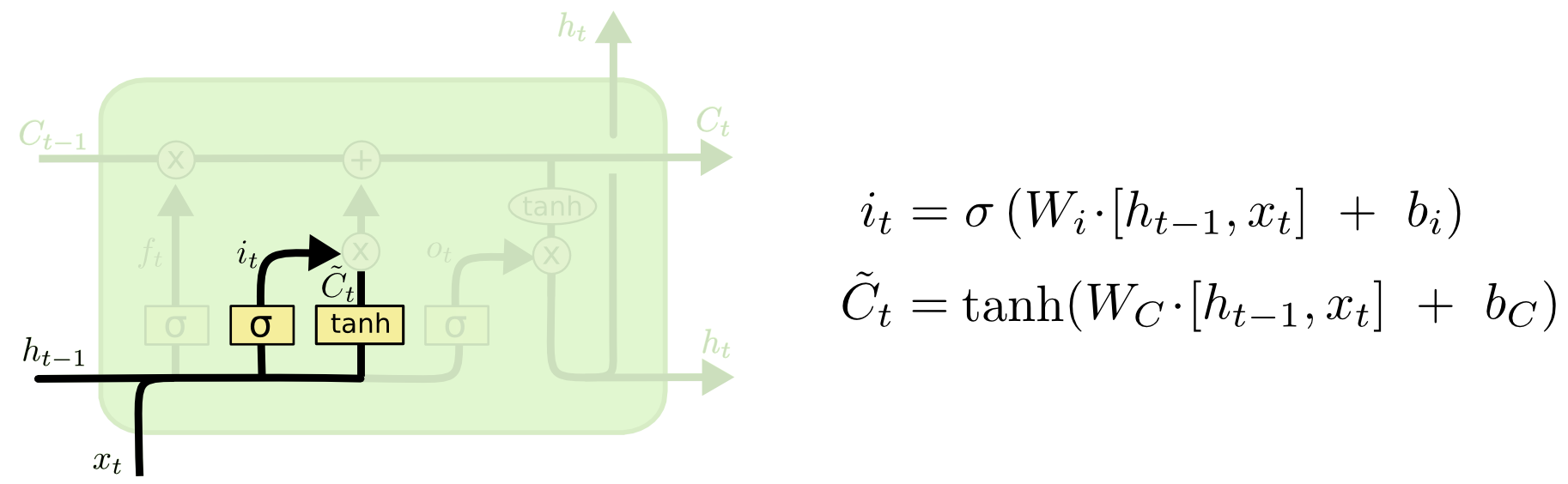
- Core Idea: pass cell state information straightly without any transformation
-
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)

-
Backpropagation in LSTM?GRU
- Uninterrupted gradient flow!
-
Summary on RNN/LSTM/GRU
- RNNs allow a lot of flexibility in architecture design
- Vanilla RNNs are simple but don’t work very well
- Backward flow of gradients in RNN can explode or vanish
- Common to use LSTM or GRU: their additive interactions improve gradient flow
Further Question
BPTT 이외에 RNN/LSTM/GRU의 구조를 유지하면서 gradient vanishing/exploding 문제를 완화할 수 있는 방법이 있을까요?
- ReLU와 ReLU의 변형들
- 그래디언트 클리핑(Gradient Clipping)
- 가중치 초기화(Weight initialization)
1) 세이비어 초기화(Xavier Initialization)
2) He 초기화(He initialization) - 배치 정규화(Batch Normalization)
1) 내부 공변량 변화(Internal Covariate Shift)
2) 배치 정규화(Batch Normalization)
3) 배치 정규화의 한계- 미니 배치 크기에 의존적이다.
- RNN에 적용하기 어렵다.
- 층 정규화(Layer Normalization)
RNN/LSTM/GRU 기반의 Language Model에서 초반 time step의 정보를 전달하기 어려운 점을 완화할 수 있는 방법이 있을까요?
- Bidirectional
- Attention
피어 세션 정리
강의 리뷰 및 Q&A
- (3강) Recurrent Neural Network and Language Modeling
- (4강) LSTM and GRU
[개인] pack_padded_sequence
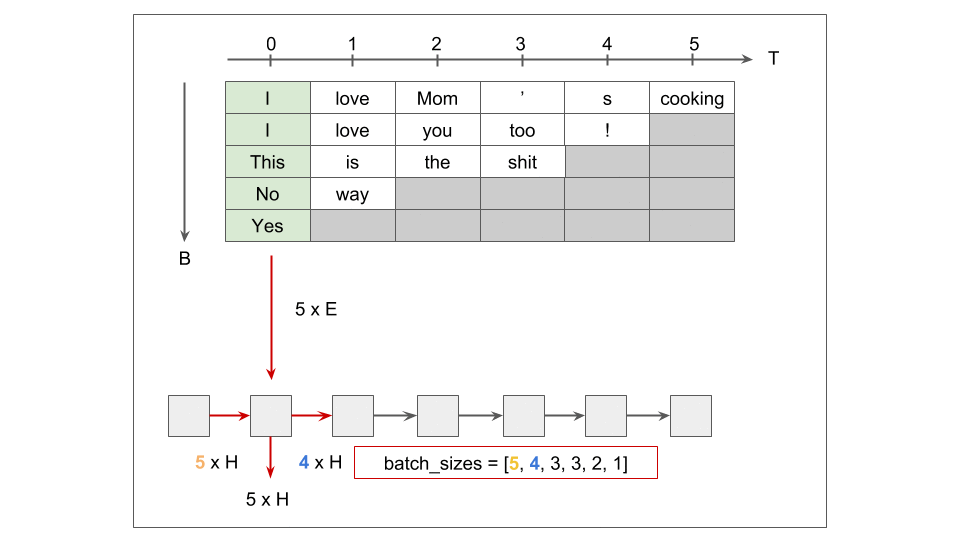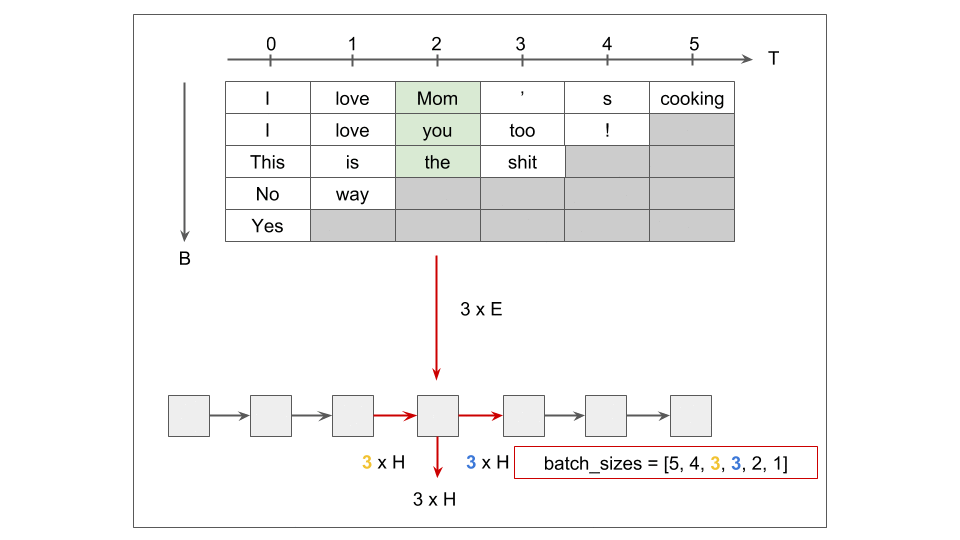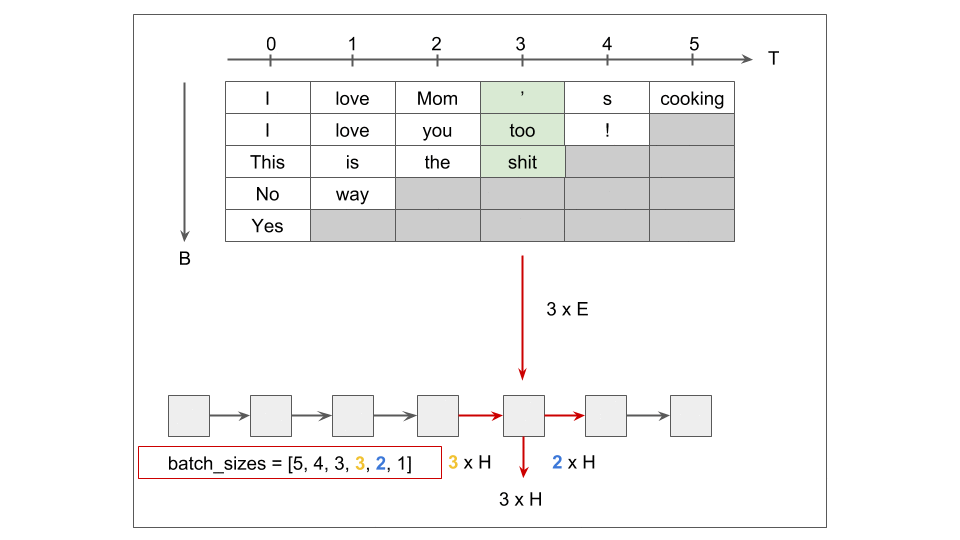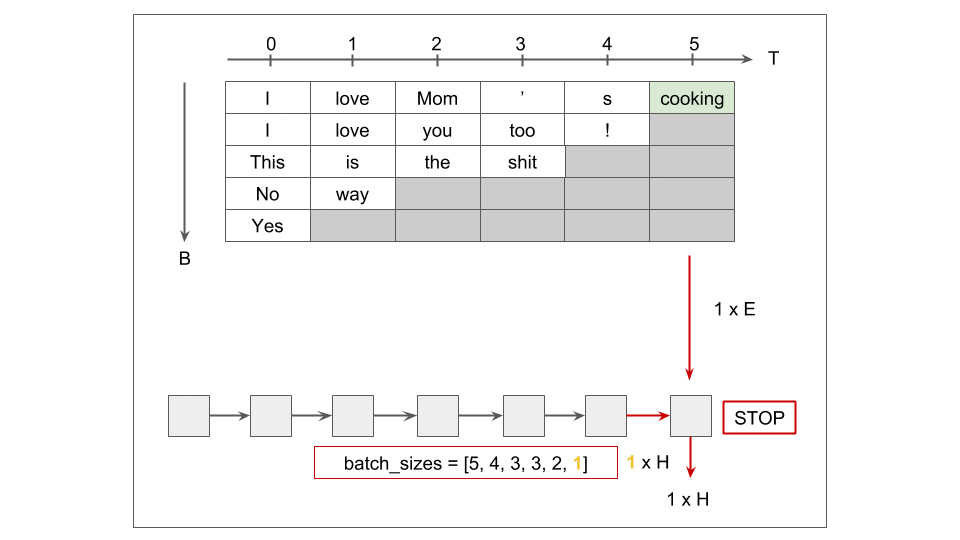
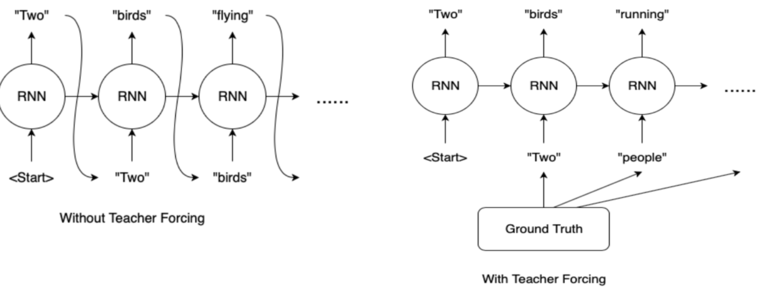
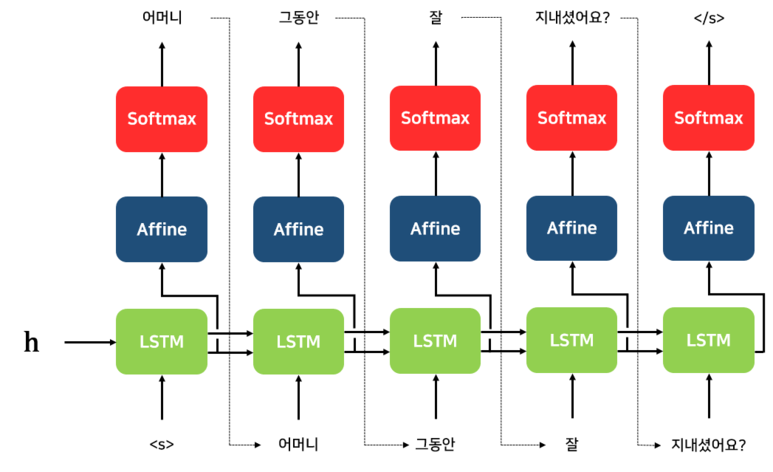
[개인] Teacher Forcing
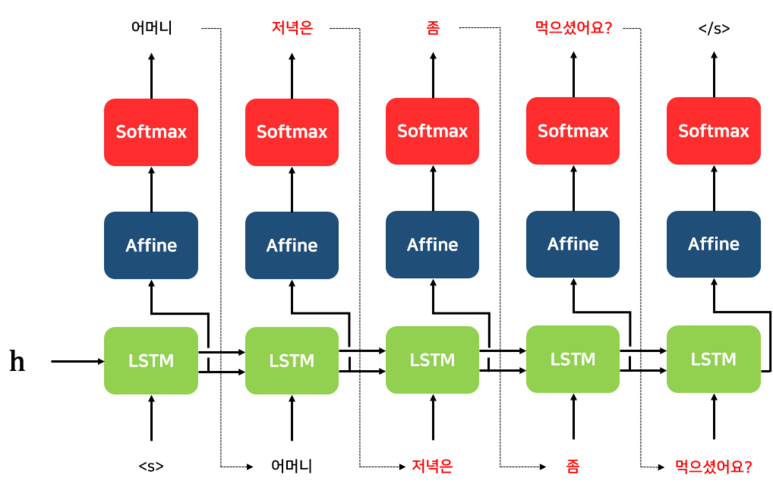
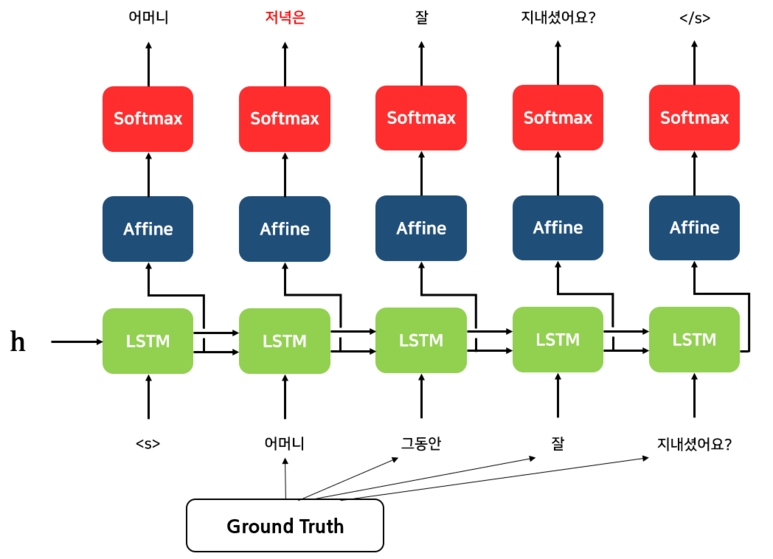
과제 진행 상황 정리 & 과제 결과물에 대한 정리
[과제] Pre-processing for NMT Model
Pre-processing for NMT Model에 대한 것으로, max_len을 계산하는 것에 있어서 SOS, EOS를 포함해야 한다는 것을 제외하고는 어렵지 않게 해결했습니다.
총평
RNN/LSTM/GRU에 대해서는 어느 정도 알고 있다고 생각했었는데, 실습과 Further Question 덕분에 부족한 부분을 학습할 수 있었습니다.
특히, 실습을 통해서 몰랐던 pack_padded_sequence와 Teacher Forcing을 학습할 수 있어서 좋았습니다.
그리고 Further Question을 통해서 RNN/LSTM/GRU에 대해 더욱 깊이 있게 생각해볼 수 있어서 좋았습니다.
모든 학문이 그렇겠지만, 정말 배움에는 끝이 없는 것 같습니다.
또, 생각해보면 그래서 재미있는 것 같기도 합니다.
오늘보다 더 성장한 내일의 저를 기대하며, 내일 뵙도록 하겠습니다.
읽어주셔서 감사합니다!
