이번 내용의 목적은
CNN이 특정 클래스를 예측할 때 어디를 주목하는지 시각화 하는것으로,
이는 모델의 작동 방식을 더 잘 이해하고, 모델의 신뢰성을 높이며, 디버깅을 도울 수 있다.
너무 깊게 이해하지말고, 간단하게 3가지 방식을 사용해서 무슨 말인지 이해하자.
Grad-CAM

GradCAM++

ScoreCAM
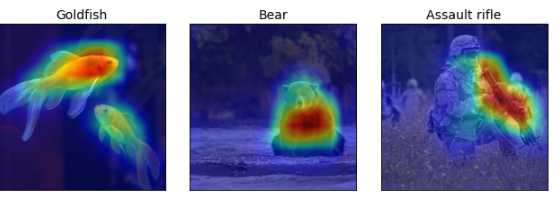
Grad-CAM 알고리즘 요약

GradCAM의 결과는 위와 같다
이 알고리즘은 Gradient Ascent 기반의 로컬라이즈드 기법을 사용하여 이미지의 특정 부분을 강조하고,
CNN이 특정 클래스를 출력하도록 한다.
즉, CNN이 특정 클래스를 출력하게 만든 이미지의 부분들을 하이라이트한다.
Grad-CAM의 동작 원리
Grad-CAM은 CNN에서 보존된 공간 정보를 활용
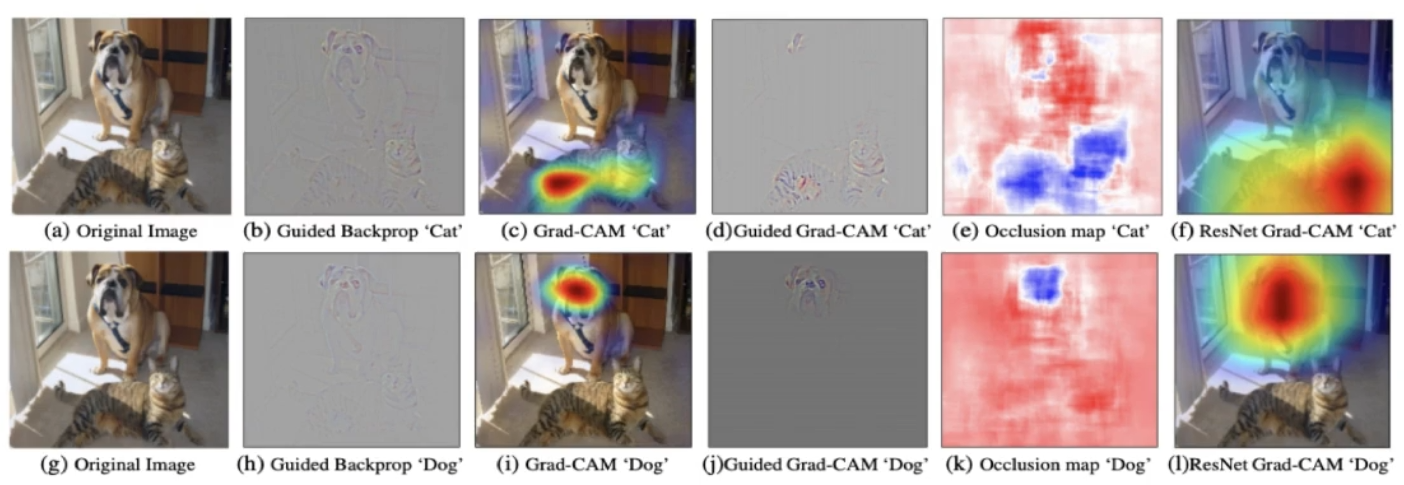

Grad-CAM의 예시로는 고양이 이미지에서 모델이 고양이의 눈과 귀 같은 특징에 집중하여 고양이로 예측하는 모습을 보여준다.
같은 방식으로, 개 이미지에서는 개의 얼굴에 집중하여 개로 예측하는 모습
Grad-CAM의 중요성
Grad-CAM은 모델이 결정을 내리는 데 사용한 이미지의 영역을 보여주기 때문에, 모델의 작동 방식을 더 잘 이해할 수 있게 도와준다.
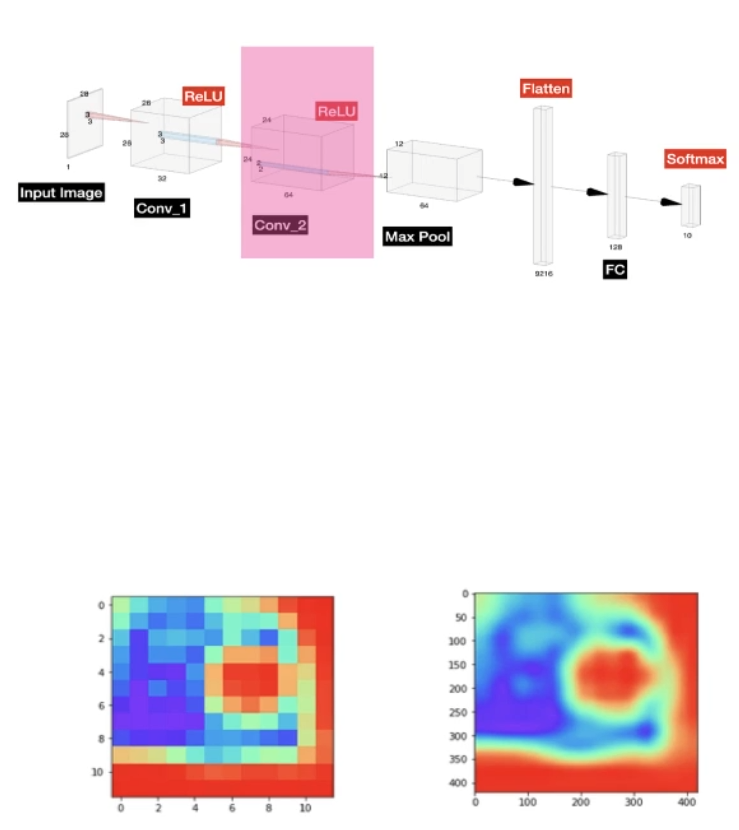
기본 Grad-CAM
기본 Grad-CAM은 특정 클래스에 대한 소프트맥스 출력 값을 반환하는 손실 함수를 만들어 사용
1. 라이브러리 설치 및 로드:
!pip install --upgrade tf-keras-vis tensorflow
2.Grad-CAM 구현:
모델 수정 함수를 사용하여 모델의 활성화를 선형 활성화로 설정
Grad-CAM 객체를 생성하고 손실 함수와 함께 사용
생성된 히트맵을 시각화

%%time
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from tf_keras_vis.utils import normalize
from matplotlib import cm
from tf_keras_vis.gradcam import Gradcam
# Create Gradcam object
gradcam = Gradcam(model,
model_modifier=model_modifier,
clone=False)
# Generate heatmap with GradCAM
cam = gradcam(loss,
X,
penultimate_layer=-1, # model.layers number
)
cam = normalize(cam)
f, ax = plt.subplots(**subplot_args)
for i, title in enumerate(image_titles):
heatmap = np.uint8(cm.jet(cam[i])[..., :3] * 255)
ax[i].set_title(title, fontsize=14)
ax[i].imshow(images[i])
ax[i].imshow(heatmap, cmap='jet', alpha=0.5) # overlay
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Grad-CAM++ 및 Score-CAM
Grad-CAM++은 Grad-CAM의 개선된 버전
Score-CAM은 그래디언트 없는 방법을 사용하여 클래스 활성화 맵을 생성
1. Grad-CAM++ 구현:
%%time
from tf_keras_vis.gradcam import GradcamPlusPlus
# Create GradCAM++ object, Just only repalce class name to "GradcamPlusPlus"
# gradcam = Gradcam(model, model_modifier, clone=False)
gradcam = GradcamPlusPlus(model,
model_modifier,
clone=False)
# Generate heatmap with GradCAM++
cam = gradcam(loss,
X,
penultimate_layer=-1, # model.layers number
)
cam = normalize(cam)
f, ax = plt.subplots(**subplot_args)
for i, title in enumerate(image_titles):
heatmap = np.uint8(cm.jet(cam[i])[..., :3] * 255)
ax[i].set_title(title, fontsize=14)
ax[i].imshow(images[i])
ax[i].imshow(heatmap, cmap='jet', alpha=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
2. Score-CAM 구현:
%%time
from tf_keras_vis.scorecam import ScoreCAM
# Create ScoreCAM object
scorecam = ScoreCAM(model, model_modifier, clone=False)
# This cell takes toooooooo much time, so only doing with GPU.
if gpus > 0:
# Generate heatmap with ScoreCAM
cam = scorecam(loss,
X,
penultimate_layer=-1, # model.layers number
)
cam = normalize(cam)
f, ax = plt.subplots(**subplot_args)
for i, title in enumerate(image_titles):
heatmap = np.uint8(cm.jet(cam[i])[..., :3] * 255)
ax[i].set_title(title, fontsize=14)
ax[i].imshow(images[i])
ax[i].imshow(heatmap, cmap='jet', alpha=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
else:
print("NOTE: Change to GPU to see visual output\n")

3. 빠른 Score-CAM 구현:
%%time
# Create ScoreCAM object
scorecam = ScoreCAM(model, model_modifier, clone=False)
# Generate heatmap with Faster-ScoreCAM
cam = scorecam(loss,
X,
penultimate_layer=-1, # model.layers number
max_N=10
)
cam = normalize(cam)
f, ax = plt.subplots(**subplot_args)
for i, title in enumerate(image_titles):
heatmap = np.uint8(cm.jet(cam[i])[..., :3] * 255)
ax[i].set_title(title, fontsize=14)
ax[i].imshow(images[i])
ax[i].imshow(heatmap, cmap='jet', alpha=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
