★ Contours 2 -Moments, Sorting, Approximating and Matching Contours
Modern Computer Vision
목표
1. 영역별 윤곽 정렬
2. 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 정렬(OCR에 적합)
3. 근사 윤곽선
4. 볼록한 선체
5. Matching Contours
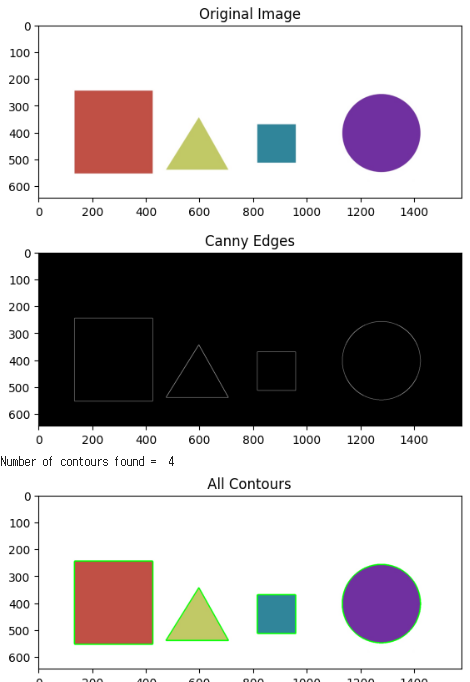
저번 시간에 이어서 이미지의 윤곽을 추출하고 색을 칠해준다.
grayscale > canny edge를 사용해서 윤곽을 추출하고 색을 입혀줬다.
# Load our image
image = cv2.imread('images/bunchofshapes.jpg')
imshow('Original Image', image)
# Grayscale our image
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Find Canny edges
edged = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 200)
imshow('Canny Edges', edged)
# Find contours and print how many were found
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
print("Number of contours found = ", len(contours))
# Draw all contours over blank image
cv2.drawContours(image, contours, -1, (0,255,0), 3)
imshow('All Contours', image)윤곽을 찾을 때 사용된 인자는 cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL 으로 가장 외각의 윤곽만 찾을때 사용되는 인자를 사용했다.
여기서 윤곽별로 구별을 어떻게 할까?
같은말로 도형을 어떻게 분리할까?
1. 영역별 윤곽 정렬(Sort Contours by Area)
그러기 위해선 OpenCV 내부의 기능을 사용해야한다.
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Function we'll use to display contour area
def get_contour_areas(contours):
"""returns the areas of all contours as list"""
all_areas = []
for cnt in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
all_areas.append(area)
return all_areas
# Load our image
image = cv2.imread('images/bunchofshapes.jpg')
# Let's print the areas of the contours before sorting
print("Contor Areas before sorting...")
print(get_contour_areas(contours))
# Sort contours large to small by area
sorted_contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
print("Contor Areas after sorting...")
print(get_contour_areas(sorted_contours))
# Iterate over our contours and draw one at a time
for (i,c) in enumerate(sorted_contours):
M = cv2.moments(c)
cx = int(M['m10'] / M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01'] / M['m00'])
cv2.putText(image, str(i+1), (cx, cy), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.drawContours(image, [c], -1, (255,0,0), 3)
imshow('Contours by area', image)def get_contour_areas(contours):
"""returns the areas of all contours as list"""
all_areas = []
for cnt in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
all_areas.append(area)
return all_areas위 함수는 주어진 윤곽선 목록(contours)의 각 윤곽선에 대한 면적을 계산하고, 이를 리스트로 반환하는것.
print("Contor Areas before sorting...")
print(get_contour_areas(contours))이미지를 불러온 후, 초기 윤곽선의 면적을 출력
# Sort contours large to small by area
sorted_contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
윤곽선을 면적이 큰 순서대로 정렬하는 코드
key=cv2.contourArea 인자를 통해 윤곽선을 면적에 따라 정렬
reverse=True 옵션을 통해 큰 값부터 정렬
print("Contor Areas after sorting...")
print(get_contour_areas(sorted_contours))
가장 왼쪽에 면적이 가장 큰 윤곽
for (i,c) in enumerate(sorted_contours):
M = cv2.moments(c)
cx = int(M['m10'] / M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01'] / M['m00'])
cv2.putText(image, str(i+1), (cx, cy), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.drawContours(image, [c], -1, (255,0,0), 3)
imshow('Contours by area', image)정렬된 윤곽선을 순회하면서 각 윤곽선의 중심점을 계산하고, 윤곽선 주위에 해당 윤곽선의 인덱스 번호를 표시하고
중심점은 윤곽선의 모멘트(moment)를 계산하여 구한다.
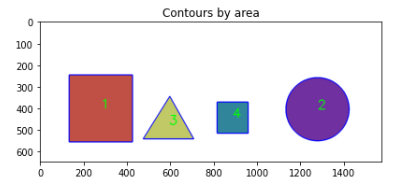
정렬된 윤곽선을 순회하는 코드를 자세하게 보면
-
윤곽선의 중심점 계산:
cv2.moments() 함수를 사용하여 윤곽선의 모멘트(moments)를 계산합니다.
모멘트는 윤곽선의 특징을 나타내는 값으로, 이를 통해 중심점을 계산할 수 있습니다.
모멘트를 계산하면, 중심점의 x좌표와 y좌표를 구할 수 있습니다. 이를 각각 cx와 cy 변수에 저장합니다. -
인덱스 번호 표시:
cv2.putText() 함수를 사용하여 이미지에 텍스트를 그립니다.
이때, 텍스트는 윤곽선의 중심점 주변에 위치하도록 설정합니다.
그래서 결과는 윤곽선의 면적 크기 순서대로 인덱스 번호를 윤곽의 중심점에 입력하는 결과가 나온다.
2. 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 정렬(OCR에 적합) [Sort by Left to Right (Great for OCR)]
본 코드로 들어가기전에 먼저 두개 함수에 대해서 선언했다.
# Functions we'll use for sorting by position
def x_cord_contour(contours):
"""Returns the X cordinate for the contour centroid"""
if cv2.contourArea(contours) > 10:
M = cv2.moments(contours)
return (int(M['m10']/M['m00']))
else:
pass
def label_contour_center(image, c):
"""Places a red circle on the centers of contours"""
M = cv2.moments(c)
cx = int(M['m10'] / M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01'] / M['m00'])
# Draw the countour number on the image
cv2.circle(image,(cx,cy), 10, (0,0,255), -1)
return image-
x_cord_contour 함수: 이 함수는 윤곽선의 x 좌표를 기준으로 정렬하기 위해 사용됩니다.

-
label_contour_center 함수: 이 함수는 이미지 상에 윤곽선의 중심점 주변에 빨간색 원을 그리는 역할을 합니다.
이 코드는 윤곽선을 좌측에서 우측으로 정렬하여 순서대로 번호를 매기는 작업을 수행
# Load our image
image = cv2.imread('images/bunchofshapes.jpg')
orginal_image = image.copy()
# Computer Center of Mass or centroids and draw them on our image
for (i, c) in enumerate(contours):
orig = label_contour_center(image, c)
# Showing the Contour centers
imshow("Sorting Left to Right", image)
# Sort by left to right using our x_cord_contour function
contours_left_to_right = sorted(contours, key = x_cord_contour, reverse = False)
# Labeling Contours left to right
for (i,c) in enumerate(contours_left_to_right):
cv2.drawContours(orginal_image, [c], -1, (0,0,255), 3)
M = cv2.moments(c)
cx = int(M['m10'] / M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01'] / M['m00'])
cv2.putText(orginal_image, str(i+1), (cx, cy), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, (0, 255, 0), 3)
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
imshow('Sorting Left to Right', orginal_image)위 코드의 결과부터 보면
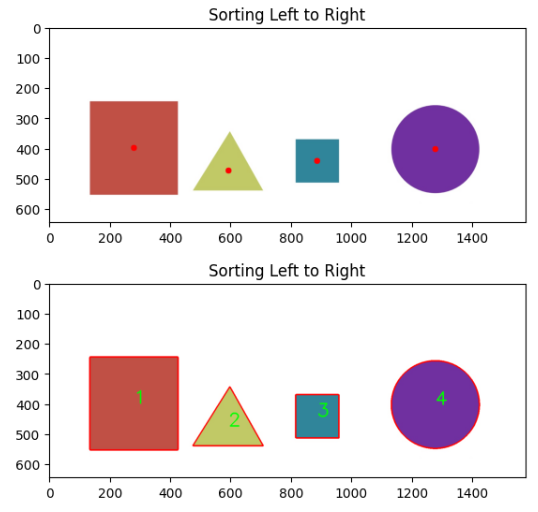
1. x_cord_contour 함수를 이용하여 만든 결과를 출력.
2. 번호가 매겨진 윤곽선과 중심점이 표시된 이미지를 출력
3. 근사 윤곽선(Approximate Contours)
윤곽을 잡고 모양을 잡을 수 있다.
import numpy as np
import cv2
# Load image and keep a copy
image = cv2.imread('images/house.jpg')
orig_image = image.copy()
imshow('Original Image', orig_image)
# Grayscale and binarize
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
# Find contours
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
copy = image.copy()
# Iterate through each contour
for c in contours:
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
cv2.rectangle(orig_image,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,0,255),2)
cv2.drawContours(image, [c], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
imshow('Drawing of Contours', image)
imshow('Bounding Rectangles', orig_image)
# Iterate through each contour and compute the approx contour
for c in contours:
# Calculate accuracy as a percent of the contour perimeter
accuracy = 0.03 * cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, accuracy, True)
cv2.drawContours(copy, [approx], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
imshow('Approx Poly DP', copy)정리하자면
- 원본 이미지를 로드하고 복사본을 유지합니다.
- 그레이스케일 이미지로 변환하고 이진화합니다.
- 이진화된 이미지에서 윤곽을 찾습니다.
- 찾은 윤곽을 이용하여 원본 이미지에 바운딩 박스를 그리고 윤곽선을 그립니다.
- 찾은 윤곽에 대해 다각형 근사를 수행하고 이를 시각화합니다.
따라서 결과적으로 세 가지 이미지가 생성됩니다:
- 윤곽선이 그려진 원본 이미지
- 바운딩 박스가 그려진 원본 이미지
- 다각형 근사가 그려진 이미지
출력 결과
Original image
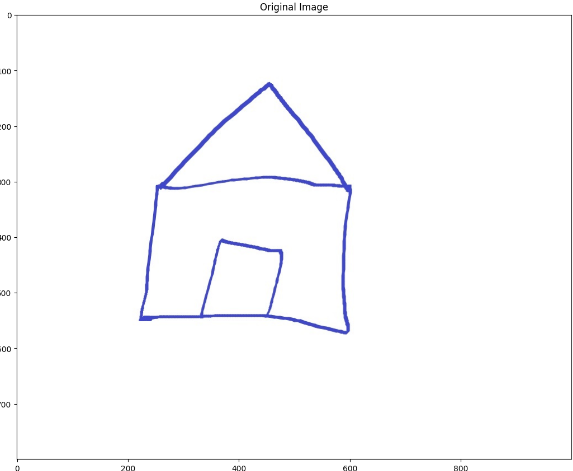

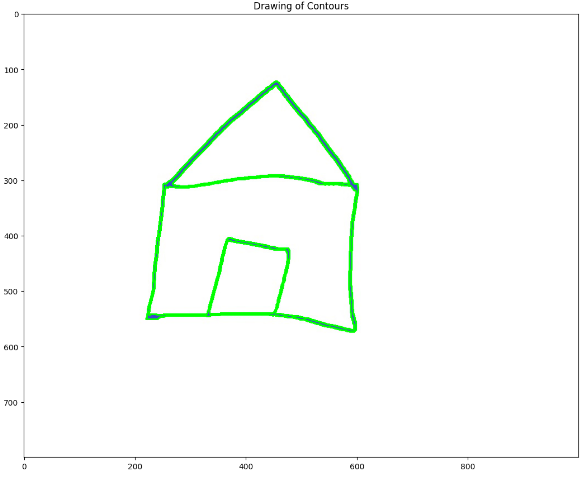
Drawing of Contours
윤곽 따라그리기
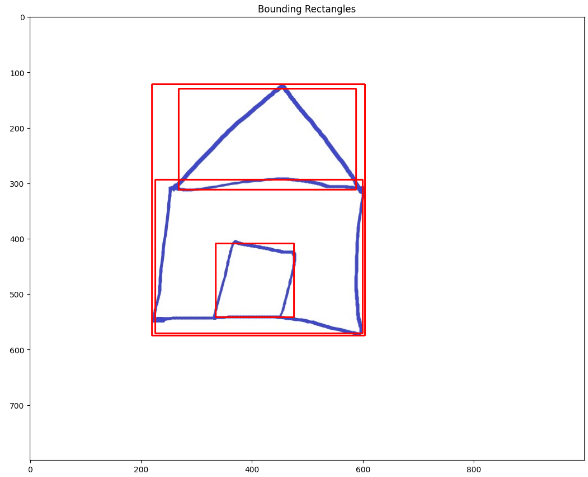
Boundiong Rectangles
윤곽을 둘러싼 다각형
Approx Poly DP
이미지를 윤각화, 다듬을때 사용
# Iterate through each contour and compute the approx contour
for c in contours:
# Calculate accuracy as a percent of the contour perimeter
accuracy = 0.03 * cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, accuracy, True)
cv2.drawContours(copy, [approx], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
imshow('Approx Poly DP', copy)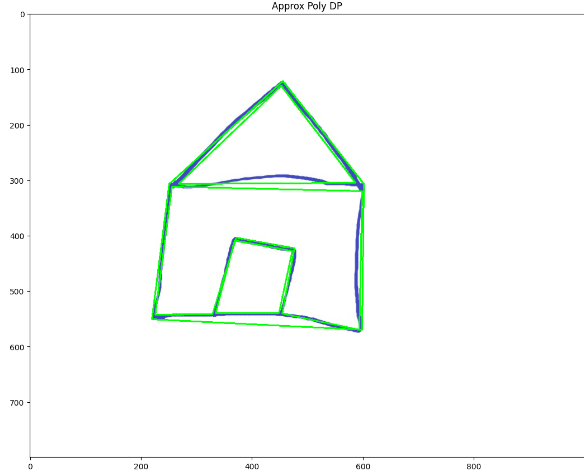
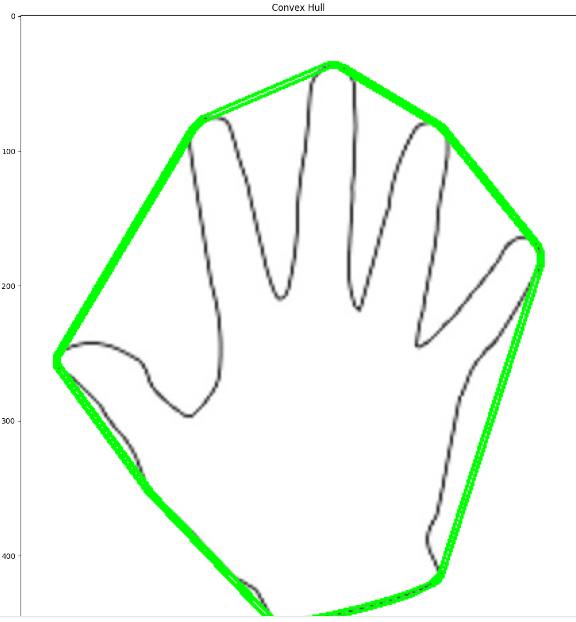
4. 볼록한 선체(Convex Hull)
윤곽선과 같은 결과를 내기도 하며 윤곽선과 비슷해 보이지만 실제로는 그렇지 않다.
import numpy as np
import cv2
image = cv2.imread('images/hand.jpg')
orginal_image = image.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imshow('Original Image', image)
# Threshold the image
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 176, 255, 0)
# Find contours
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cv2.drawContours(image, contours, 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
imshow('Contours of Hand', image)
# Sort Contors by area and then remove the largest frame contour
n = len(contours) - 1
contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=False)[:n]
# Iterate through contours and draw the convex hull
for c in contours:
hull = cv2.convexHull(c)
cv2.drawContours(orginal_image, [hull], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
imshow('Convex Hull', orginal_image)- 이미지를 로드하고 원본 이미지를 복사합니다.
- 그레이스케일로 이미지를 변환합니다.
- 이미지를 이진화합니다.
- 이진화된 이미지에서 윤곽을 찾습니다.
찾은 윤곽을 그려줍니다. - 윤곽을 면적에 따라 정렬하고 가장 큰 프레임 윤곽을 제거합니다.
- 각 윤곽에 대해 볼록 다각형을 그리고 이를 원본 이미지에 표시합니다.
결과적으로 세 가지 이미지가 생성됩니다:
- 원본 이미지 위에 윤곽이 그려진 이미지
- 볼록 다각형이 그려진 이미지
- 원본 이미지 위에 볼록 다각형이 그려진 이미지
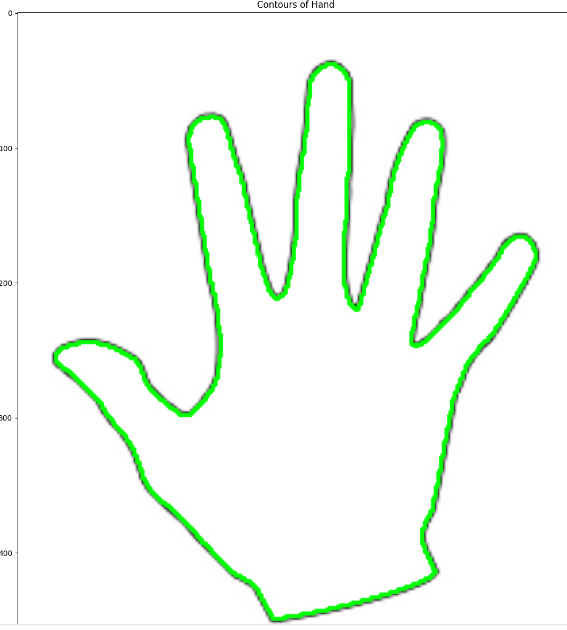
Original Imgae

Contours of Hand

Convex Hull
# Sort Contors by area and then remove the largest frame contour
n = len(contours) - 1
contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=False)[:n]
# Iterate through contours and draw the convex hull
for c in contours:
hull = cv2.convexHull(c)
cv2.drawContours(orginal_image, [hull], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
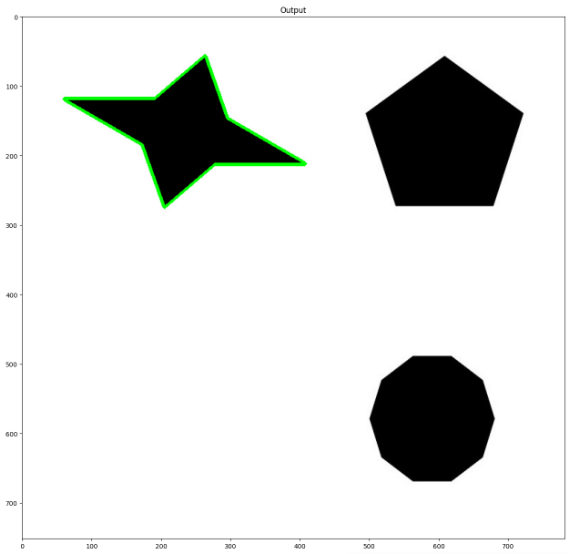
5. 일치 윤곽(Matching Contours)
cv2.matchShapes(contour template, contour, method, method parameter)
주어진 형태 템플릿과 대상 이미지에서 유사한 형태를 찾는 데 사용된다.
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Load the shape template or reference image
template = cv2.imread('images/4star.jpg',0)
imshow('Template', template)
# Load the target image with the shapes we're trying to match
target = cv2.imread('images/shapestomatch.jpg')
target_gray = cv2.cvtColor(target,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Threshold both images first before using cv2.findContours
ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(template, 127, 255, 0)
ret, thresh2 = cv2.threshold(target_gray, 127, 255, 0)
# Find contours in template
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh1, cv2.RETR_CCOMP, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# We need to sort the contours by area so that we can remove the largest
# contour which is the image outline
sorted_contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
# We extract the second largest contour which will be our template contour
template_contour = contours[1]
# Extract contours from second target image
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh2, cv2.RETR_CCOMP, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for c in contours:
# Iterate through each contour in the target image and
# use cv2.matchShapes to compare contour shapes
match = cv2.matchShapes(template_contour, c, 3, 0.0)
print(match)
# If the match value is less than 0.15 we
if match < 0.15:
closest_contour = c
else:
closest_contour = []
cv2.drawContours(target, [closest_contour], -1, (0,255,0), 3)
imshow('Output', target)- 형태 템플릿 이미지와 대상 이미지를 로드
- 템플릿 이미지와 대상 이미지를 그레이스케일로 변환하고 임계값을 적용하여 이진화
- 템플릿 이미지에서 윤곽을 찾는데, 가장 큰 윤곽은 이미지의 외곽을 나타내므로 제외
- 템플릿으로 사용할 윤곽을 선택, 이 코드에서는 두 번째로 큰 윤곽을 선택
- 대상 이미지에서 윤곽을 찾고, 각 윤곽과 템플릿 윤곽 사이의 모양 유사성을 비교.
- 모양이 일치하는 윤곽을 찾으면 해당 윤곽을 대상 이미지에 매칭
탬플릿 로드

임계값 이진화
유사한 윤곽을 찾는 것을 목적으로 임계값을 이진화하는것으로 템플릿 이미지의 윤곽을 수치화 시킴
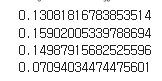
결과
각 윤곽과 템플릿 윤곽 사이의 모양 유사성을 비교,
수치화 한 템플릿 윤곽값과 이미지 내의 윤곽값들을 비교해서
일치하는 윤곽을 찾으면 해당 윤곽을 대상 이미지에 그린다.