HSV 컬러 필터를 사용하여 마스크를 만든 다음 원하는 개체를 추적
(How to use an HSV Color Filter to Create a Mask and then Track our Desired Object
)
특정 색상 객체를 추적하고, 그 객체의 움직임을 시각적으로 표시하는 예제
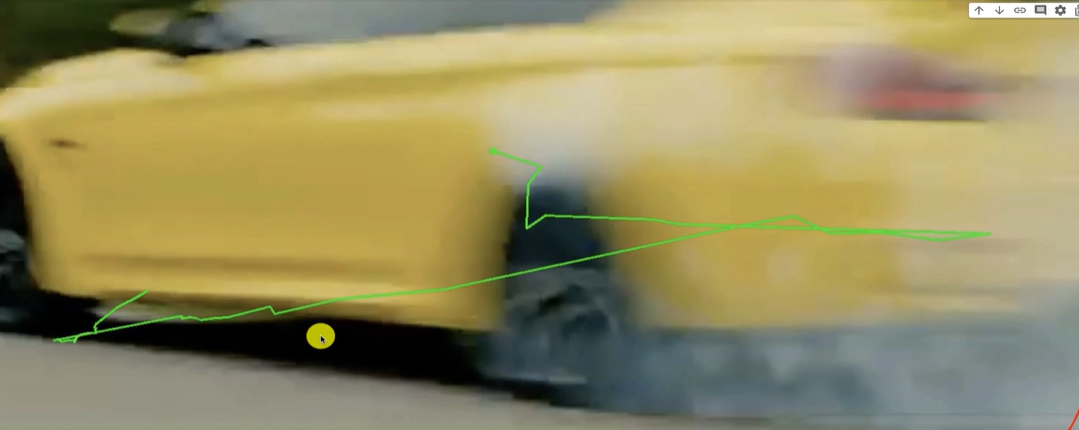
https://youtu.be/KJmd92nA5vo
A. 색상 범위 지정
lower = np.array([20,50,90])
upper = np.array([40,255,255])추적하려는 객체의 HSV 색상 범위를 지정
영상의 BMW는 노란색을 하고 있으므로 노란색 범위 내의 색상 HSV 를 지정해주면 된다.
B. 색상 임계값 처리
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower, upper)
HSV 이미지에서 색상 범위에 해당하는 부분을 찾아내는 마스크를 생성
C. 컨투어 및 중심 계산
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
마스크에서 외곽선을 찾고, 외곽선의 중심을 계산합
D. 객체 추적 및 시각화
cv2.circle(frame, (int(x), int(y)), int(radius),(0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.circle(frame, center, 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
찾은 객체의 외곽에 원을 그리고, 객체의 중심에 초록색 점을 표시
E. 움직임 시각화
for i in range(1, len(points)):
cv2.line(frame, points[i - 1], points[i], (0, 255, 0), 2)
객체의 움직임을 추적하고, 추적된 경로를 선으로 그려 시각화
#Object Tracking
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Initalize camera
#cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# define range of color in HSV
lower = np.array([20,50,90])
upper = np.array([40,255,255])
# Create empty points array
points = []
# Get default camera window size
# Load video stream, long clip
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('bmwm4.mp4')
# Get the height and width of the frame (required to be an interger)
width = int(cap.get(3))
height = int(cap.get(4))
# Define the codec and create VideoWriter object. The output is stored in '*.avi' file.
out = cv2.VideoWriter('bmwm4_output.avi', cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('M','J','P','G'), 30, (width, height))
ret, frame = cap.read()
Height, Width = frame.shape[:2]
frame_count = 0
radius = 0
while True:
# Capture webcame frame
ret, frame = cap.read()
if ret:
hsv_img = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# Threshold the HSV image to get only green colors
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower, upper)
#mask = cv2.morphologyEx(mask, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Create empty centre array to store centroid center of mass
center = int(Height/2), int(Width/2)
if len(contours) > 0:
# Get the largest contour and its center
c = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea)
(x, y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c)
M = cv2.moments(c)
# Sometimes small contours of a point will cause a divison by zero error
try:
center = (int(M["m10"] / M["m00"]), int(M["m01"] / M["m00"]))
except:
center = int(Height/2), int(Width/2)
# Allow only countors that have a larger than 25 pixel radius
if radius > 25:
# Draw cirlce and leave the last center creating a trail
cv2.circle(frame, (int(x), int(y)), int(radius),(0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.circle(frame, center, 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
# Log center points
points.append(center)
# If radius large enough, we use 25 pixels
if radius > 25:
# loop over the set of tracked points
for i in range(1, len(points)):
try:
cv2.line(frame, points[i - 1], points[i], (0, 255, 0), 2)
except:
pass
# Make frame count zero
frame_count = 0
out.write(frame)
else:
break
# Release camera and close any open windows
cap.release()
out.release()