url : https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.06983
배경
- LLM이 언어를 이해하고 생성하는 성능이 좋아도, hallucination & 사실적으로 오답인 결과를 내놓는 경향이 있음
- 기존의 방법은 입력에 기반해 ‘한 번’ information을 retrieve 하고 끝(single-time RAG) → 긴 텍스트를 생성하는 경우, 이 방법은 제한적 → 생성하는 동안 지속적으로 정보를 수집해야 하는 것이 필수적
- 고정된 간격에서 context를 사용해서 추가적인 정보를 retrieve 하는 방법의 단점:
- 미래에 LM이 무엇을 생성하고 싶은지를 정확히 반영할 수 없을 수 있음
- 부적절한 포인트에서 정보를 retrieve 할 수 있음
- 생성 프로세스에서 ‘언제’, ‘무엇’을 검색할지 적극적으로 결정하고, 다양한 long-term 생성 task에 적용할 수 있는 간단하고 일반적인 검색 증강 LM을 만들 수 있을까?
의의
- 생성이 길어질 경우, ‘입력’에 대해서 추가된 정보만을 augmentation 해서 생성하는 것은 한계가 있다 → 생성 내내, ‘입력’과 ‘생성되는 것들’을 활용하여 계속 정보를 추가하여 생성에 도움을 줌
- Inference time에 추가적인 학습 없이, 아무 기존 LM에 적용할 수 있음
Related Works
- Single-time Retrieval Augmented Generation
- 방법: 사용자 입력을 직접적으로 retrieval의 query로 사용 → 완벽한 답변을 한 번에 생성
- 식:
- Active Retrieval Augmented Generation
- 배경: Long-form generation을 돕기 위해 만들어짐
- 방법: 생성 프로세스동안 ‘언제’, ‘어떤 것’을 retrieve 할지 active하게 결정하는 일반적인 framework → retrieval과 generation이 번갈아 수행됨
- 식:
- retrieval query (t시점에서)
- 식:
- 설명: 사용자 입력 와 t 시점 이전에 생성된 output 에 기반하여 query 생성. : query formulation function
- 전체적인 식
- 식:
- 설명: 각 시점에서의 retrieved documents 을 사용해서, next retrieval이 야기되거나 종료될 때까지 계속해서 답변 생성. 이전 retrieved docs는 버리고, 오직 현재 step에서의 retrieved docs만 사용해서 next generation 진행(LM의 입력 길이 제한에 걸리지 않게 하려고)
- retrieval query (t시점에서)
방법론
Retrieve information을 할 때, 중요시 여기는 2가지 측면:
- When: 언제 retrieve information
- 방법: LM이 낮은 확률의 토큰을 생성할 때, retrieval 진행
- What: 어떤 information을 Retrieve
- 방법: 임시 next sentence 생성 → 이 sentence를 query로 사용해서, relevant documents를 retrieving → 이 retrieved documents를 조건으로 next sentence를 다시 생성
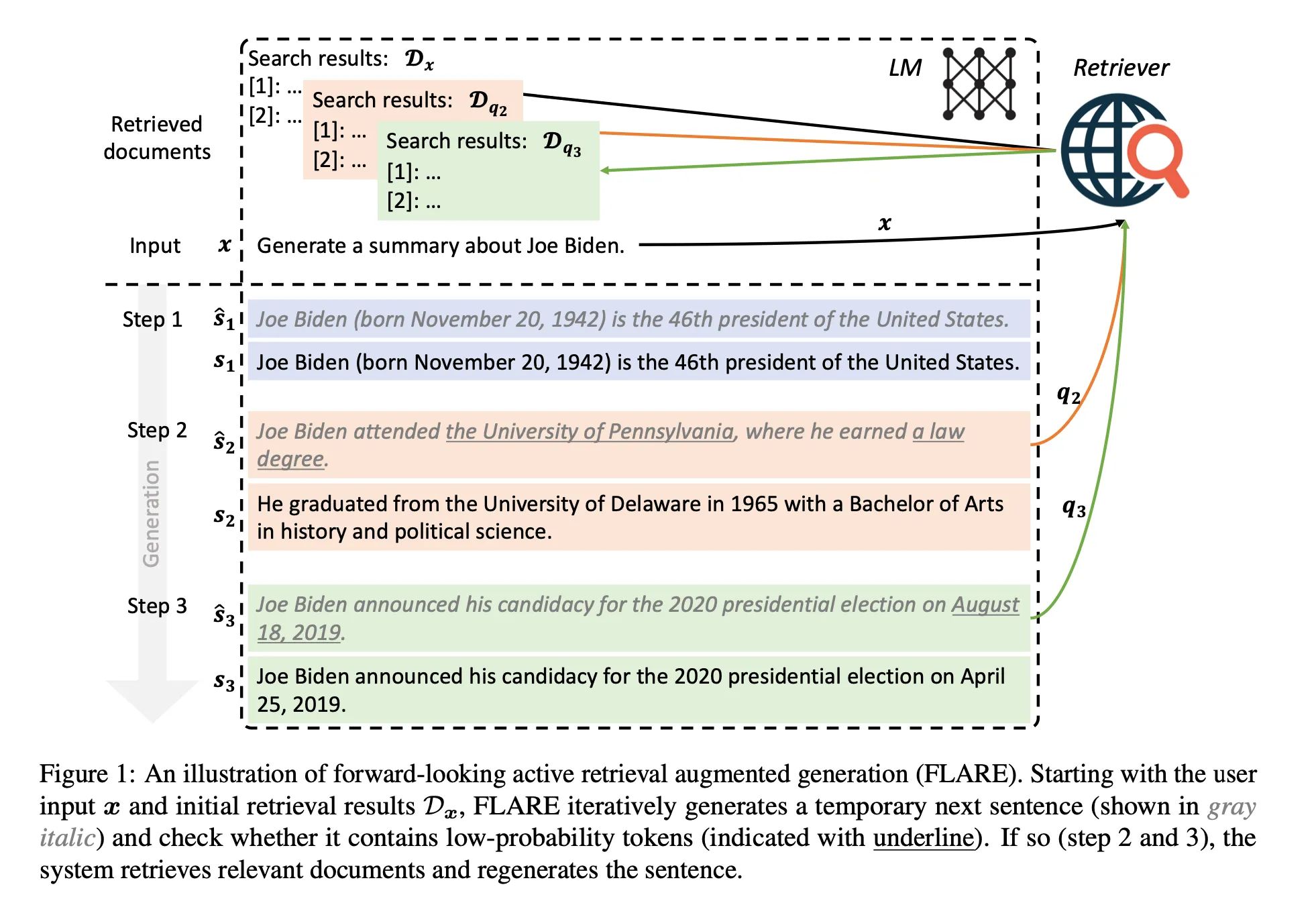
제시하는 방법론 이름: FLARE(Forward-Looking Active REtrieval Augmented Generation)
논문의 Intuitions:
- 필요한 지식이 없을 때만, retrieving information
- Retrieval query는 ‘미래 생성의 의도(intents of future generations)’를 반영해야 함
2가지 FLARE 방법론 제시
- LM이 retrieval-encouraging instructions를 사용하여 retrieval queries를 생성하게 프롬프팅 한다:
- Search queries로 LM의 생성을 직접적으로 사용:
- 미래 토픽에 대한 인사이트를 얻기 위해 다음 문장을 반복적으로(iteratively) 생성
- 만약 불확실한 토큰이 오면, 다시 다음 문장을 생성하기 위해 relevant docs를 retrieve.
1. FLARE with Retrieval Instructions
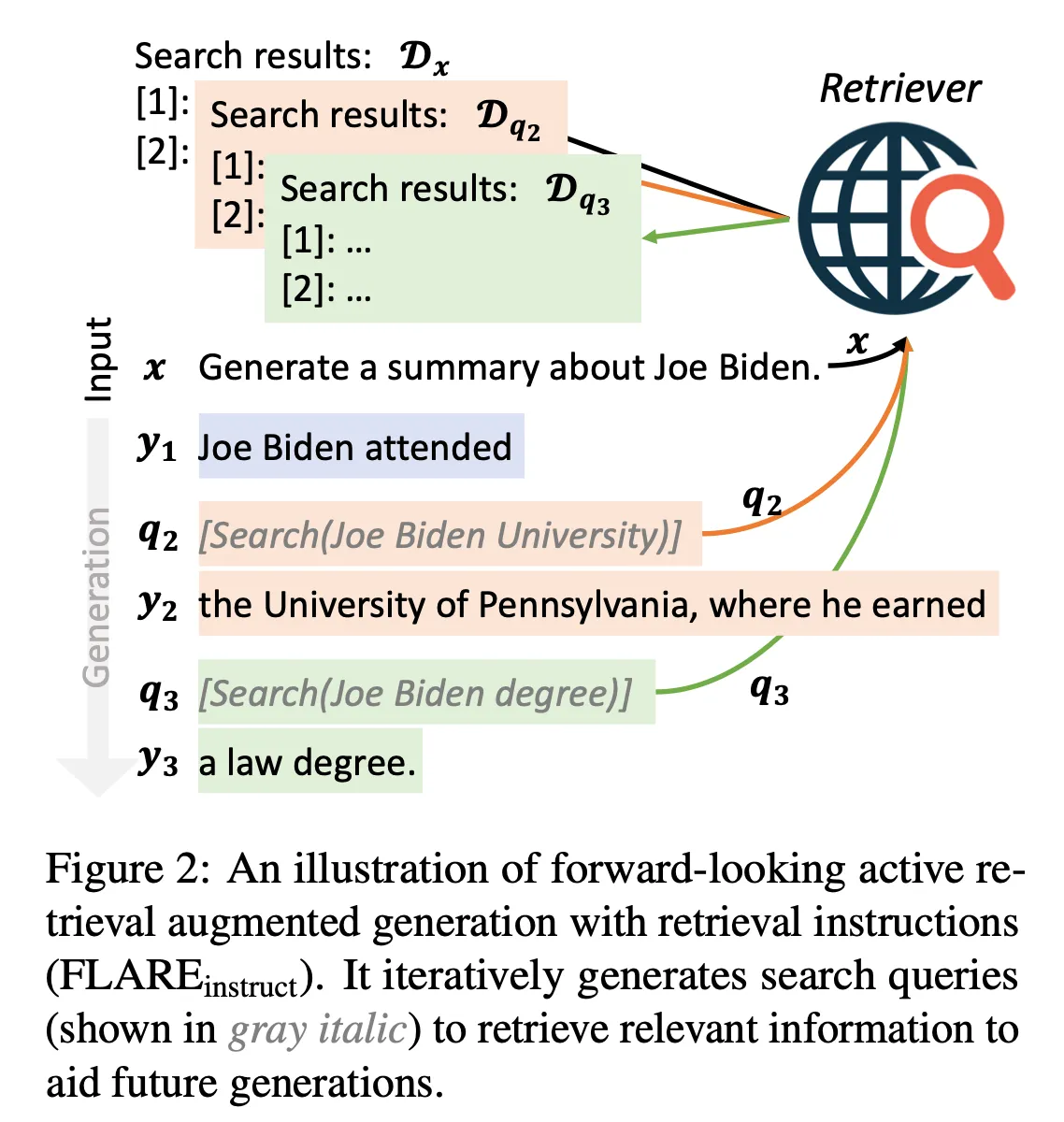
Retrieval을 위한 정보 요구(information needs)를 표현하는 간단한 방법: “[Search(query)]”를 사용
e.g. “The colors on the flag of Ghana have the following meanings. Red is for [Search(Ghana flag red meaning)] the blood of martyrs, ...”
구체적인 방법)
- Skill 1: Search 관련 instruction & exemplars를 시작 부분에 둠
- Skill 2: downstream task의 instruction & exemplars를 그 다음에 둠
- 주어진 test case에서는 LM에게 skill 1 & 2를 결합하여 task를 수행하는 동안 search queries를 생성하라고 요청
<Structure of Prompt>
<Details>
전체적인 설명:
- LM이 생성하다가, ‘search[query]’를 생성하면 생성을 멈춘다
- Search-query를 이용해서, relevant docs를 retrieval
- Relevant docs를 입력 앞에 붙이고 생성 계속해서 진행
- 다음 [search(query)]가 오면 기존의 relevant docs는 제거하고, 현재 [search(query)]를 통해 retrieved 된 docs를 앞에 붙이고 다시 생성 시작
Figure 2를 보면 이해하기 쉬울 것 같음 & 설명)
input = '''
Now, combine the aforementioned two skills. First, write out the reasoning steps, then draw the conclusion, where the reasoning steps should also utilize the Search API “[Search(term)]” whenever possible.
Question: Generate a summary about Joe Biden.
Answer(with step-by-step & Search):
'''위 input을 LM에 넣으면, 답변이 생성된다.
- “Joe Biden attended [Search(Joe Biden University)]”가 생성됨
- 그러면 [Search(query)] term이 나왔으니까, 생성을 멈추고 “Joe Biden University”를 search query로 retrieval 진행
- Retrieval로 relevant docs를 찾고, 이를 입력 앞에 붙임 & [Search(query)] term을 제거
- 아까 멈췄던 생성을 다시 이어간다.
- 그러면 “Joe Biden attended the University of Pennsylvania, where he earned [Search(Joe Biden degree)]”가 생성됨
- 또 [Search(query)] term이 나왔으니까, 생성을 멈추고 retrieval 진행.
- Search query인 “Joe Biden degree”를 사용해 retrieval 진행
- Relevant docs를 찾고, 기존의 relevant docs를 제거하고 지금 검색한 relevant docs를 입력 앞에 붙인다 & [Search(query)] term 제거
- 아까 멈췄던 생성을 다시 이어간다 → “Joe Biden attended the University of Pennsylvania, where he earned a law degree”
- 이런 식으로 생성이 진행되면 된다.
2. Direct FLARE
[배경] Black-box LM을 fine-tuning 할 수 없기 때문에, retrieval instruction을 통해 로 생성되는 queries는 믿을만하지 않음
2.1 Confidence-based Active Retrieval
Figure 1 참고)
- 먼저 step t에서 현재 next sentence 생성: (retrieved docs 없이)
- 그 다음 retrieval을 할지 결정하고, 에 기반하여 query를 공식화
- 여기서 갈림길
3-1. 만약 가 confident인 경우) → 추가 정보 retrieval 없이, next sentence 를 accept
3-2. 만약 가 not confident인 경우) → 를 사용해서 search queries 공식화 → relevant docs retrieval → next sentence 재생성
Probability가 threshold 보다 작은 경우, retrieval 사용
여기서 문장을 iteration의 기준으로 잡는 이유: 의미론적 단위로서 phrase처럼 짧지도 paragraph처럼 너무 길지도 않기 때문
그러나 ‘Phrases’ 또는 ‘paragraph’도 basis로 활용할 수 있다.
식)
궁금증)
- Black-box LM을 사용하는데, next sentence의 probability는 어떻게 구할 수 있을까? (logits을 공개하지 않는 경우..?)
- 재생성된 sentence의 confident도 threshold보다 낮으면 재생성? 아니면 그냥 그대로?
2.2 Confidence-based Query Formulation
Next sentence 를 query로 직접 사용
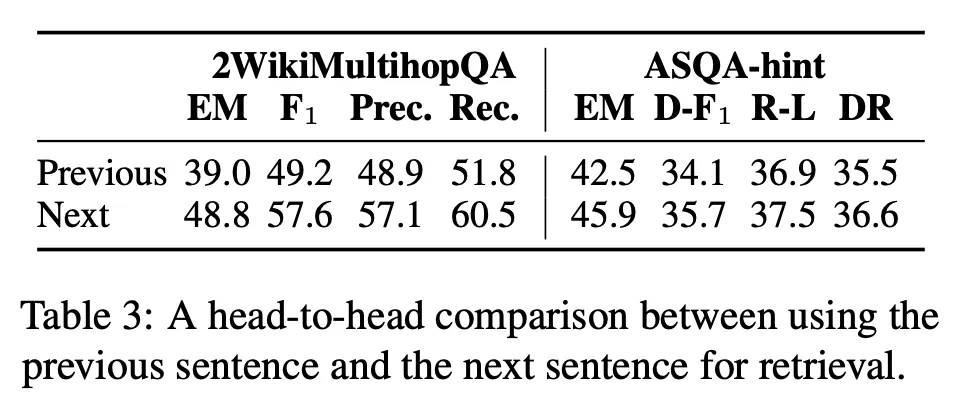
Past context를 사용해서 retrieval 하지 않고, next sentence를 가지고 retrieval 하는 이유:
이전 context 사용해서 retrieving 하는 것보다 next sentence를 가지고 retrieving 하는 것이 더 낫다는 결과가 있다 (Table 3)
[이 과정 속 발생할 수 있는 문제]
Next sentence 내의 perpetuating error에 대한 risk가 있다. 즉, 잘못된 정보를 LM이 next sentence로 생성하고 이를 retrieval에 사용하면, 잘못된 정보를 retrieval 해올 수 있다.
[문제를 해결할 수 있는 두 가지 방법 제시]
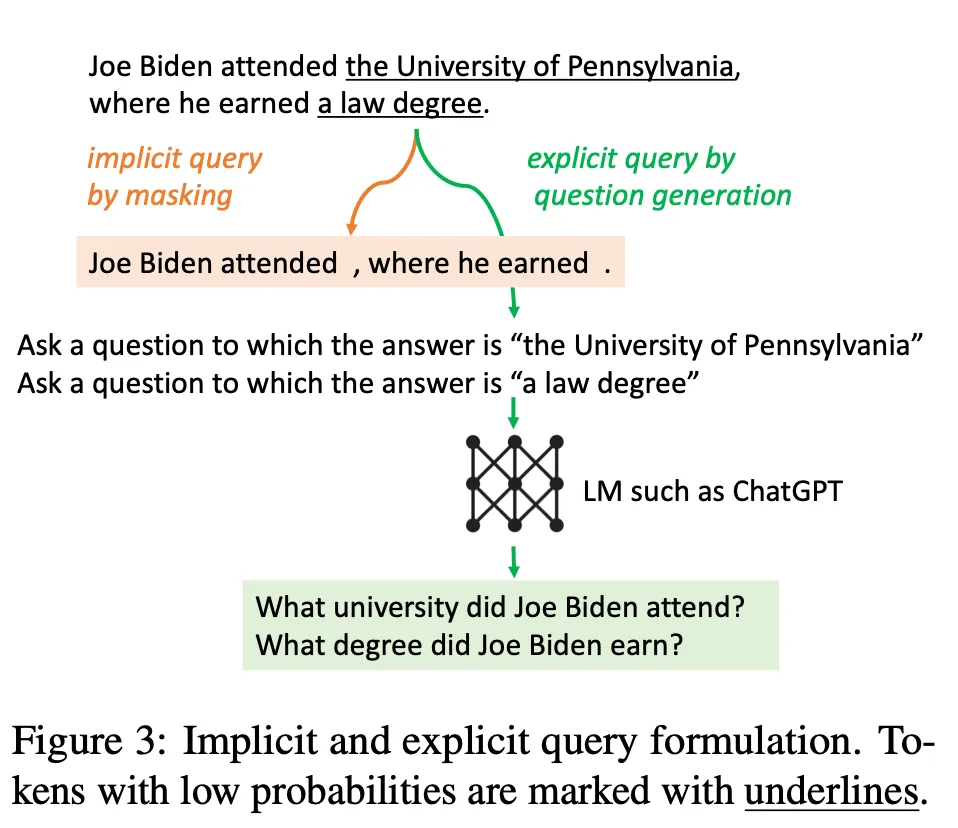
- Masked Sentences as implicit queries
[설명] Next sentence 에서 confident가 낮은 tokens는 masking. Threshold 를 이용해서 threshold보다 낮은 토큰들은 masking. 가 높을수록, 공격적인 masking 전략.
[결과] 문장에서 잠재적인 혼란을 제거 → Retrieval accuracy 증가
- Generated questions as explicit quries
[설명] Next sentence 에서 low-confident span을 타겟하는 명백한 질문 생성. e.g. “the University of Pennsylvania”가 uncertain이면, “Which university did Joe Biden attend?”와 같은 질문이 relevant information을 retrieve 하는데 도움을 줄 것 에서 probability가 보다 낮은 spans를 추출 → 각 추출된 span 에 대해, gpt-3.5-turbo를 사용하여 해당 span 를 가지고 답변할 수 있는 질문 를 생성:

각 생성된 questions를 사용해서 retrieve & 반환된 docs를 single ranking list에 끼워 넣어서 future generation을 도움.
기반 Query 식)
Multi-time Retrieval Baselines
본 논문의 방법론과 비교할 수 있는 baselines
‘언제’, ‘무엇’을 retrieval 할 지를 기준으로 3가지 baseline categories를 소개
- Previous-window
- 설명: 매 개의 토큰마다 retrieval 진행. 여기서 은 window-size. 이전 window에 생성된 토큰들이 query로 사용됨
- 방법론: RETRO, IC-RALM, KNN-LM, etc.
- Previous-sentence
- 설명: retrieval을 매 sentence마다 진행하며, 이전의 sentence를 query로 사용
- 방법론: IRCoT
- Question decomposition
- 설명: 수동적으로 task-specific exemplars를 annotation → Outputs를 생성하는 동안 LM이 decomposed sub-questions를 생성하도록 유도
- 방법론: Self-ask
위 3가지 방법론들의 장단점)
[장점]
- Generating 동안 추가적인 정보를 retrieve 할 수 있음
[단점]
- 이전에 생성된 토큰을 query로 사용하는 것은 LM이 미래에 생성하고자 하는 것을 반영하지 않을 수 있다.
- 고정된 구간에서 retrieving information 하는 것은 효율적이지 않을 수 있다 → 부적절한 시기에 retrieval이 일어날 수 있기 때문
- Question decomposition approaches는 task-specific prompt engineering이 필요하다 → 새로운 task에 대한 “일반화(generalizability)”가 제한된다
실험
Few-shot incontext learning을 사용하여 4가지 다양한 knowledge-intensive tasks에 대해 FLARE의 효과성 평가
- Multihop QA
- 설명: Information retrieval & reasoning을 통해 복잡한 문제에 대해 답하는 task
- 사용 데이터셋: 2WikiMultihopQA
- Commonsense reasoning
- 설명: 세상과 상식에 대한 지식이 필요한 Task
- 사용 데이터셋: StrategyQA
- Long-form QA
- 설명: 복잡한 정보를 찾는 질문에 포괄적인 답변을 생성하는 task
- 사용 데이터셋: ASQA, ASQA-hint
- Open-domain Summarization
- 설명: Open-web에서 정보를 수집하여 주제에 대한 포괄적인 요약을 생성하는 task
- 사용 데이터셋: WikiAsp
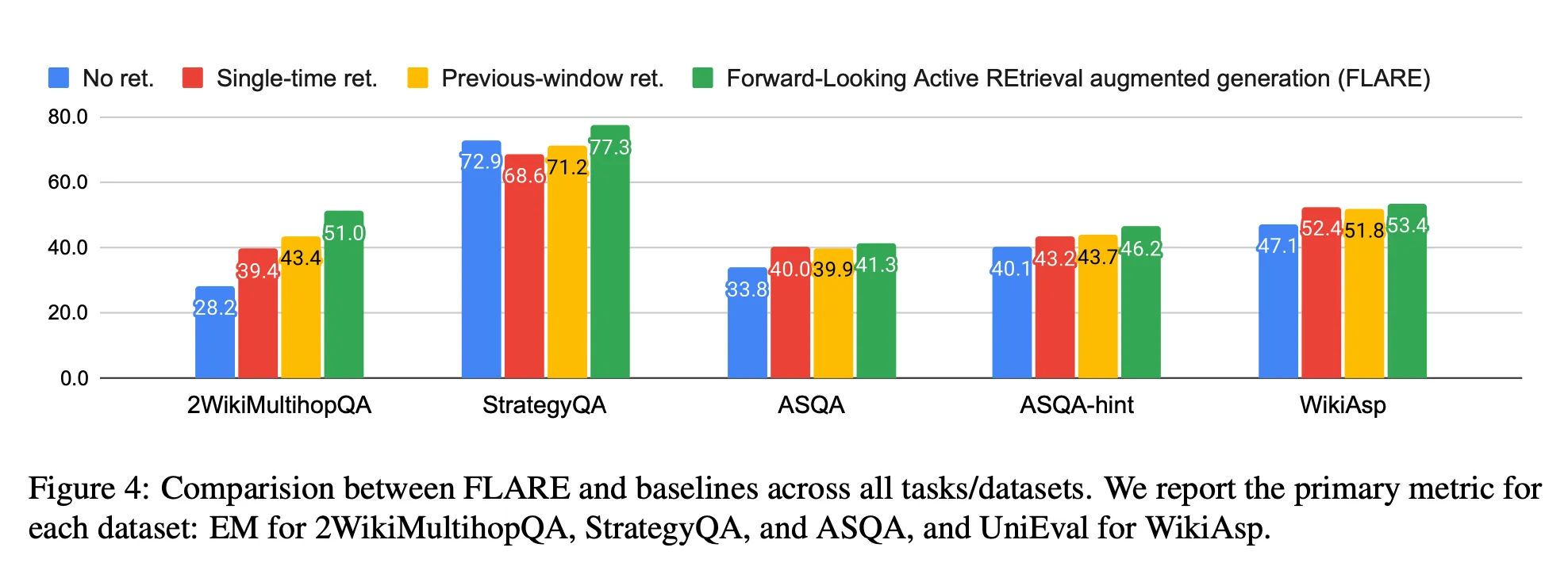
<Baseline과 비교한 전체적인 결과>
[결과 분석]
FLARE가 모든 tasks/datasets에서 모든 baselines 성능을 능가
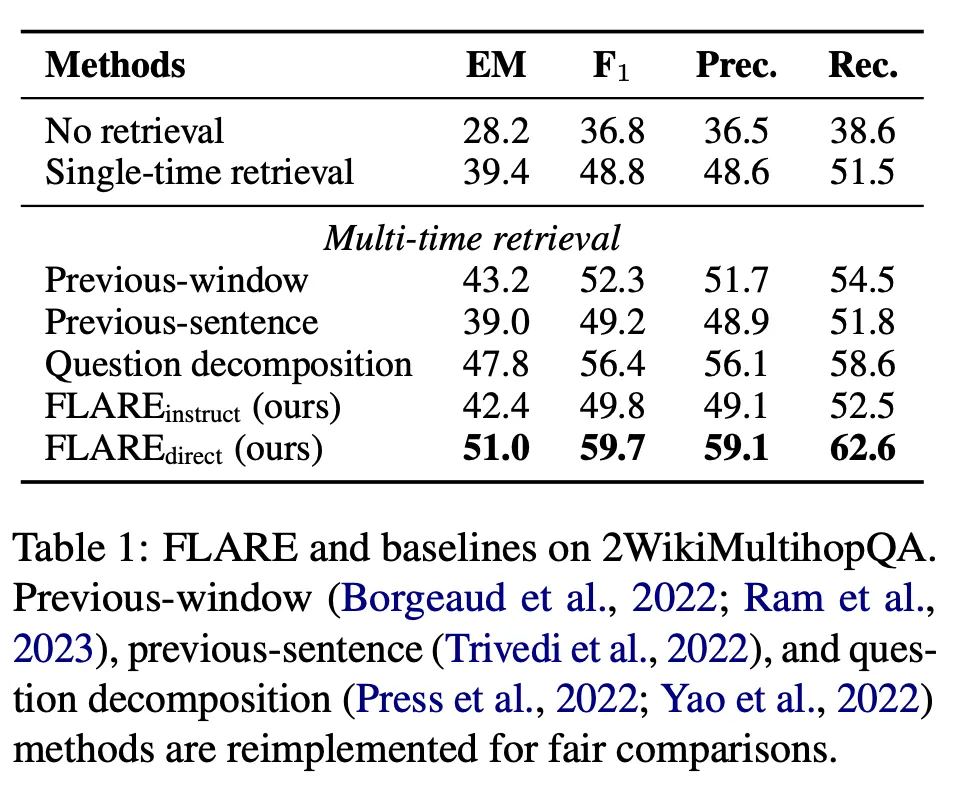
<Baseline과의 철저한 비교(2WikiMultihopQA)>
[결과 분석]
FLARE가 모든 baseline보다 성적이 좋았으며, 대부분의 multi-time retrieval augmented approaches가 single-time retrieval보다 좋은 성능을 보였다.
Question-decomposition의 성능이 좋았는데, 이유는 in-context exemplars가 “decomposed sub-questions를 가지고 수동으로 annotation되기에” 그런 것 같다.
Question decomposition과 FLARE-instruct를 비교하면, FLARE-instruct가 더 좋지 않은 성적을 보인다 → 이는 task-generic retrieval instructions & exemplars를 사용해서 LM에게 search queries를 생성하도록 가르치는 것이 어려운 일이라는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
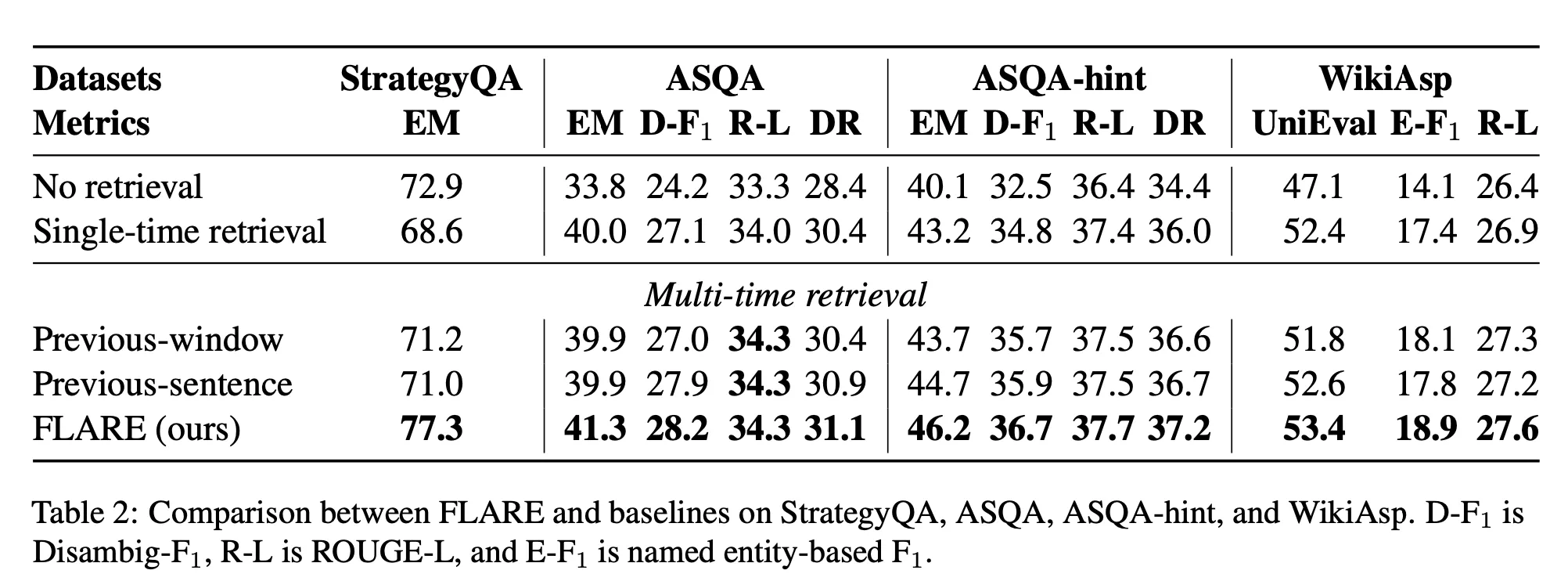
<다른 datasets들에 대한 모든 metric 결과>
결론(느낀점)
- External Information이 필요한 시기를 측정해서, 그 때 retrieval을 수행한다는 사실이 획기적이었다.
- Retrieval query를 만드는 여러 방법들을 봐서 신기했다.
- Black-box LM을 사용하기에 FLARE-direct를 사용한다고 했는데, black-box LM을 사용할 때 생성되는 토큰의 logits&probability를 반환할 수 없는 경우에는 confident를 측정할 수 있을지 모르겠다.
- 2WikiMultihopQA에서 FLARE-instruct보다 Question decomposition의 성능이 더 높았던 점은, 현재로서는 사람이 직접 설계한 어노테이션이 LLM의 자동화된 접근보다 더 효과적이라는 것을 알 수 있다.




