url: https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.11511
code & trained models are available at https://selfrag.github.io/
배경
- LLM 성능 향상에도 불구, 부정확한 사실을 답변으로 생성하기도 함 → RAG 사용
- RAG를 할 때, 검색 필요성 & 관련성 여부에 관계 없이 일정 수의 passages retrieving 하는 경우 → LM의 범용성을 낮추거나 도움이 되지 않는 응답을 생성을 초래할 수 있음
의의
- New framework 제안: “Self-Reflective Retrieval-Augmented Generation(SELF-RAG)” → retrieval & self-reflection을 통해 LM quality & factuality 향상(LLM의 원래의 창의성과 다재다능함을 잃지 않으며)
- Reflection token이라는 special token 사용
- 의의: Reflection token은 Inference phase에서 LM을 controllable하게 만듦(controllable generation) ↔ RLHF는 학습 시 인간 선호도에 일치시키는 것에 초점을 둠
- 역할
- Retrieval이 필요한지 결정
- 생성 퀄리티를 self-evaluation(factuality 포함 여러가지 측면)
- Retrieved passages를 병렬적으로 처리 & self-reflection을 통해 관계 없는 passages를 필터링(추론시 외부 모델에 의존 X)
- Critic model offline으로부터 나온 reflection tokens를 가지고 증강된 task examples에 대해 target LM을 학습 시킴 → RLHF보다 학습 비용이 매우 저렴함 (retrieval & generation에 대한 fine-grained critique에 대해서도 연구를 해봤음)
Related Works
- RAG
- 설명: 입력을 retrieved passages로 증강해서 language modeling 성능을 향상시키는 방법
- 기존의 한계: runtime efficiency 저하, irrelevant context, lack of attributions(출처 부족)
- Concurrent RAG (RAG에 대한 현재 연구들 설명)
- RA-DIT(Retrieval-augmented dual instruction tuning): Instruction tuning dataset에 대해 retriever과 LM finetuning을 두 단계로 진행
- Making Retrieval-Augmented Language Models Robust to Irrelevant Context: 자연어 추론 모델을 사용해서 retrieved passages를 필터링 하거나 압축 시켜서 prompt에 사용
- Recomp(Improving retrieval-augmented LMs with compression and selective augmentation): 요약 모델을 사용해서 retrieved passages를 필터링 하거나 압축시켜서 prompt에 사용
- Training and generating with critics
- PPO(Proximal Policy Optimization): Human feedback으로부터의 강화 학습을 통해 LLM 학습 방법 → LLM을 사람의 선호와 일치시키는데 효과적
방법론
End-to-End 학습:
- 필요한 경우 LM 이 retrieved passages를 참고하여 텍스트 생성
- Special token 생성하는 것을 배움으로써 output 비판
Reflection tokens의 역할(아래 Table 1 참고)
- Retrieval 필요성 신호
- 출력의 relevance, support, completeness 확인
1. Problem Formulation and Overview
입력 가 주어지면, 을 학습시킴 → 여러 개의 segments들로 구성되어 있는 텍스트 출력 를 순차적으로 생성하도록 (여기서 는 번째 segment에 대한 토큰의 시퀀스)
내 생성된 토큰들은 original vocabulary와 reflection token을 포함
실험에서는 segment 단위를 sentence 1개로 함 그러나 self-rag framework는 아무 segment unit에도 적용 가능함
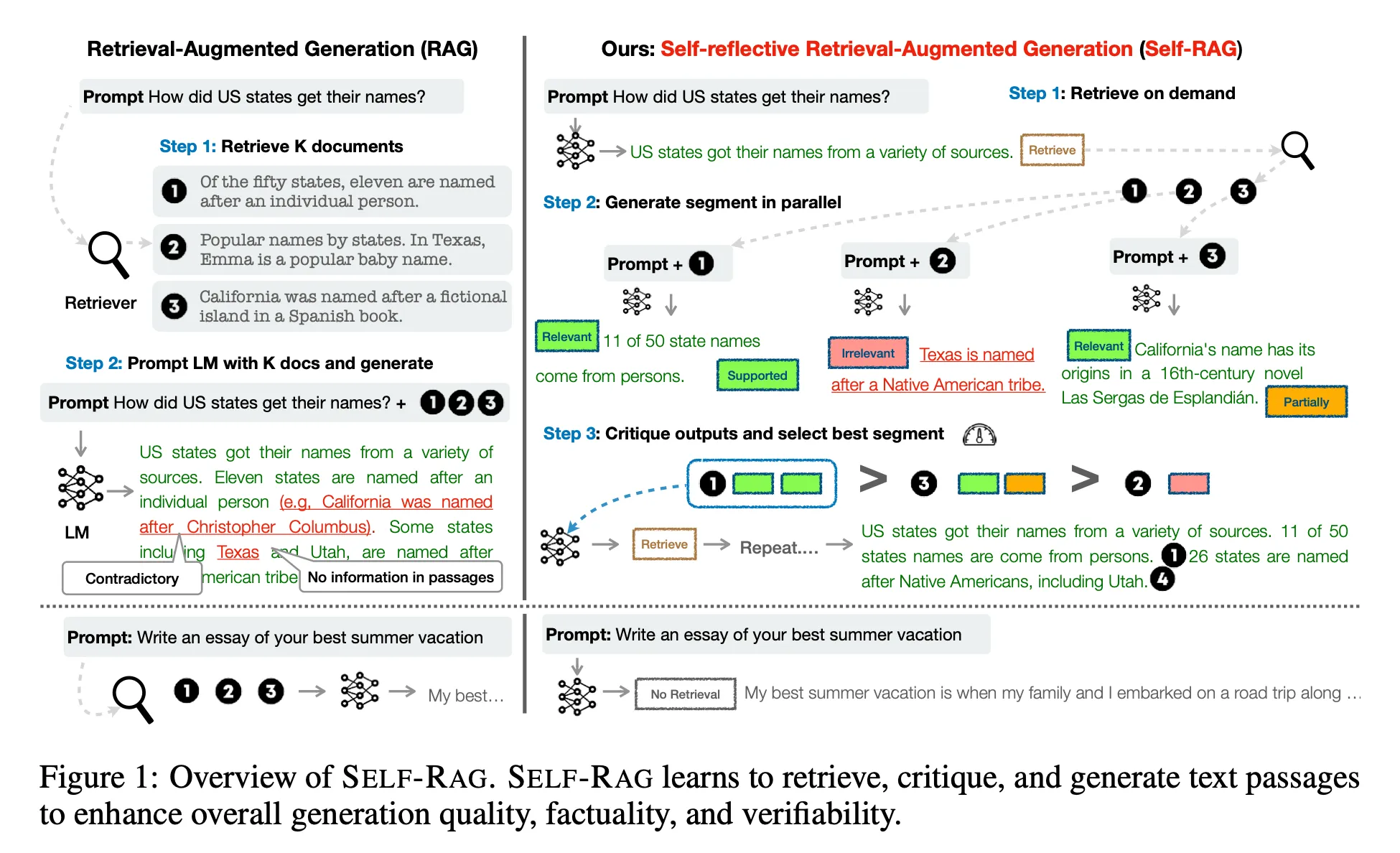
Inference Overview
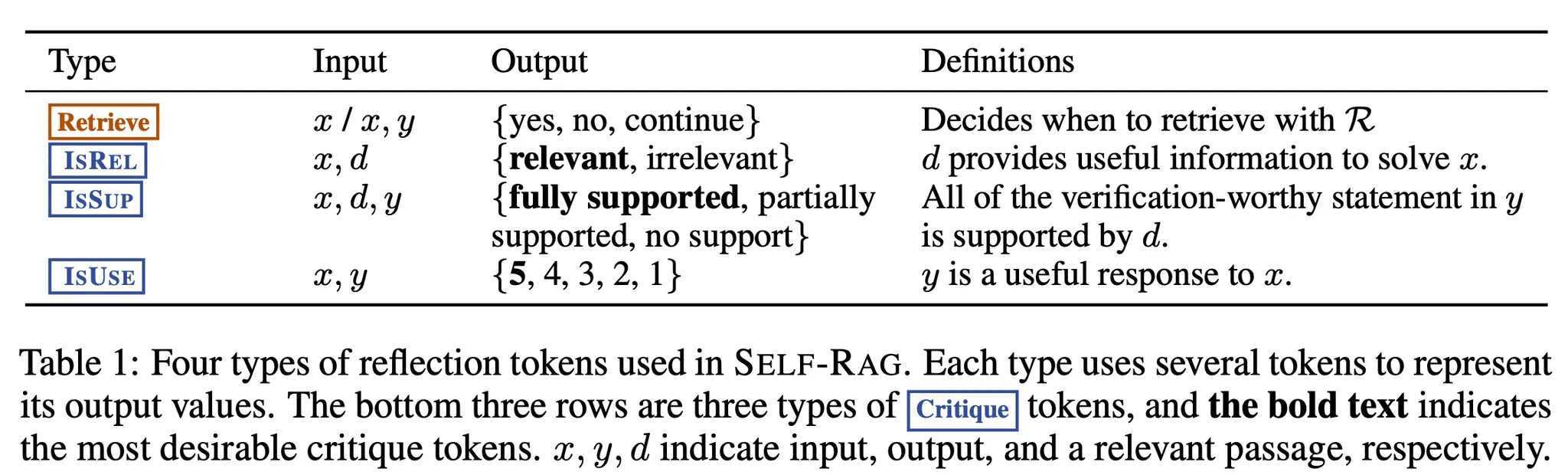
Fig 1 & Algorithm 1이 추론시 self-rag의 overview를 보여줌.
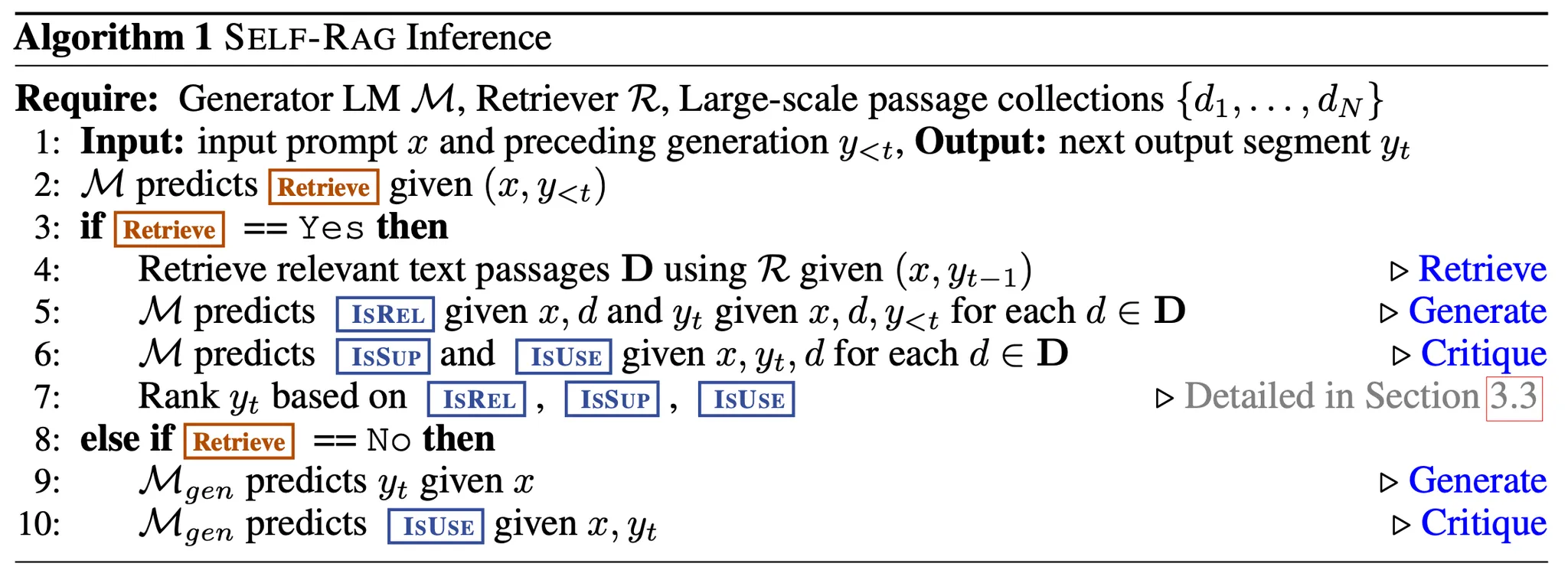
- 를 가지고
Retrieve token을 예측- ‘Yes’로 예측하면, retrieval 진행
- [Retrieve 단계] Relevant text passages retrieval 진행(주어진 을 가지고)
- [Generate 단계]
IsREL토큰 예측 ← 를 이용 / 예측 ← 를 이용(각 에 대해) - [Critique 단계]
IsSUP토큰,IsUSE토큰 예측 ← 를 이용(각 에 대해) IsREL,IsSUP,IsUSE을 기반으로 의 순위를 매김
- ‘No’로 예측하면, retrieval 진행하지 않고, 생성 진행 (Standard LM)
- [Generate 단계] 예측 ← 를 이용
- [Critique 단계]
IsUSE토큰 예측 ← 를 이용
- ‘Yes’로 예측하면, retrieval 진행
[설명]
- 모든 입력 와 preceding generation 에 대해, 모델은 retrieval token을 decoding → Retrieval의 유용성 평가(해야 하는지)
- Retrieval이 필요하지 않다면, 생성하는 것: next output segment (Standard LM과 같음)
- Retrieval이 필요하다면, 생성하는 것들:
IsREL(critique token; retrieved passage의 relevance 평가), next output segment,IsSUP(critique token; passage가 reponse segment 내 정보에 도움이 되는지 평가)
- 최종적으로
IsUSE(critique token; response의 전체적인 유용성 평가) 토큰 생성
각 segment 생성에서 본 논문에서는 다음을 적용:
- Passages 병렬 처리
- 자체적으로 생성된 reflection tokens을 사용하여 생성된 task output에 대해 soft constraints 또는 hard control 적용
[적용 예시]
Fig 1을 보면, 이 선택되었다.
그 이유:
- 는 직접적인 증거를 제공하지 않음(
IsREL= Irrelevant) - 는 의 output에 부분적으로 도움을 주기에(
IsSUP= Partially supported) ↔ 은 fully supported
Training Overview
아무 LM을 사용할 수 있음: Text & Reflection token generation (기존의 Vocabulary + reflection token 인 expanded vacabulary를 이용한 Next Token Prediction 방식으로)
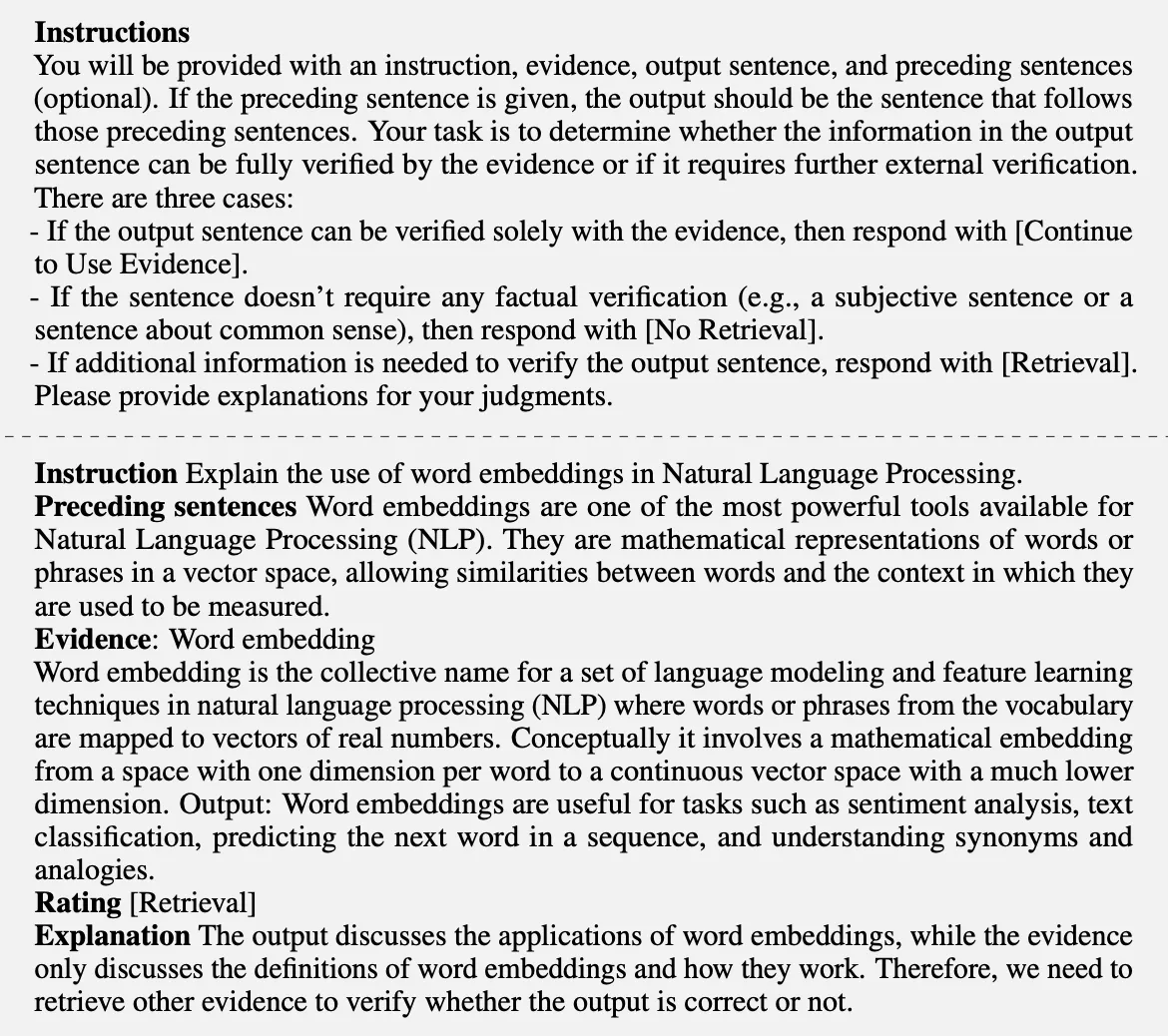
Generator model 학습을 시키려면, reflection token과 retrieved passages가 포함된 데이터셋이 필요하다. 그러나 이러한 데이터를 annotation 만으로 생성하기는 비용이 많이 듦.
따라서 critic model을 학습 시켜, 해당 데이터셋 생성에 도움을 줌
- [Critic model 학습]
Critic model이 ‘retrieved passages’와 ‘주어진 task output의 퀄리티’를 평가하는 reflection token을 생성하도록 학습
- [Generator model 학습]
SELF-RAG의 inference를 생각해보면, 중간에 retrieved passages와 여러 critiques가 있을 것(e..g, retrieval이 필요한 타이밍인지, retrieved passage가 relevant한지 등)
따라서 “이러한 부분을 generator model 학습 데이터에 추가해 주어야 함” ⇒ 새로운 데이터: Retriever 이 retrieving 한 passages와 critic model 이 예측한 reflection tokens로 기존의 데이터(input-output pair) 증강
위 새로운 데이터를 offline에서 미리 생성 → 생성된 데이터를 이용해서 generator model 학습(conventional LM objective를 이용해서; Next Token Prediction)
2. Self-RAG Training
2.1 Trainig the critic model
[Data Collection for critic model]
배경)
- 각 segment에 대해 reflection tokens을 수동적으로 생성하는 것은 비용이 너무 비쌈.
- SOTA LLM(e.g. GPT-4)을 사용하여 reflection token을 생성하는 것이 효과적일 수 있으나, 하지만 이에 의존한다면 API 비용이 많이 들고 재현성이 저하될 수 있다. (Critic model로 SOTA LLM API를 사용하는 방법)
방법)
- GPT-4를 이용해서 upervised data 생성(GPT-4에게 reflection token을 생성하라는 prompting을 통해) → GPT 4의 지식을 critic model 로 distillation
- 각 Reflection token은 자신의 정의와 입력을 가지고 있음(Table 1) → 각각에 맞는 instruction prompt를 사용해서 reflection token group 생성 (instruction and demonstrations는 아래에 정리)
- 각 Reflection token에 대한 학습 데이터를 만들기 위해 사용되는 데이터는 original training data(original task input and output )에서 random sampling:
- 각 타입마다 4k - 20k 개의 supervised 학습 데이터 수집 → 그리고 통합
Retrieve: 12,594개IsSUP: 11,181개IsREL: 19,317개IsUSE: 3,831개
GPT-4가 reflection token을 수집하게 하는데 사용한 “Instructions and demonstrations”
- Table 8: Instructions and demonstrations for
Retrieveaspect given input only → Initial retrieval token
- Table 9: Instructions and demonstrations for
Retrieveaspect given the input, preceding generations, and retrieved passages
- Table 10: Instructions and demonstrations for
IsRELaspect given the input only.
- Table 11: Instructions and demonstrations for
IsSUPtokens.
- Table 12: Instructions and demonstrations for
IsUSEtokens.
[Critic Learning]
-
Pretrained LM으로 critic model 를 초기화 (아무 LM이나 사용할 수 있지만, generator LM이랑 같은 것을 사용)
-
표준 조건부 언어 모델링 objective를 사용하고, likelihood를 maximizing:
여기서 은 reflection tokens
결과적으로 Critic model은 대부분 reflection token 종류에서 gpt-4 기반 예측 결과와 90% 이상 일치했다 → GPT-4의 성능 distillation이 성공적으로 이루어짐
2.2 Training the Generator model
[Data Collection for generator model]
주어진 input-output pair를 Self-RAG의 inference-time process와 동일하게 하기 위해, retrieval 모델과 critic 모델을 사용해 output 를 증강하여 supervised data를 생성
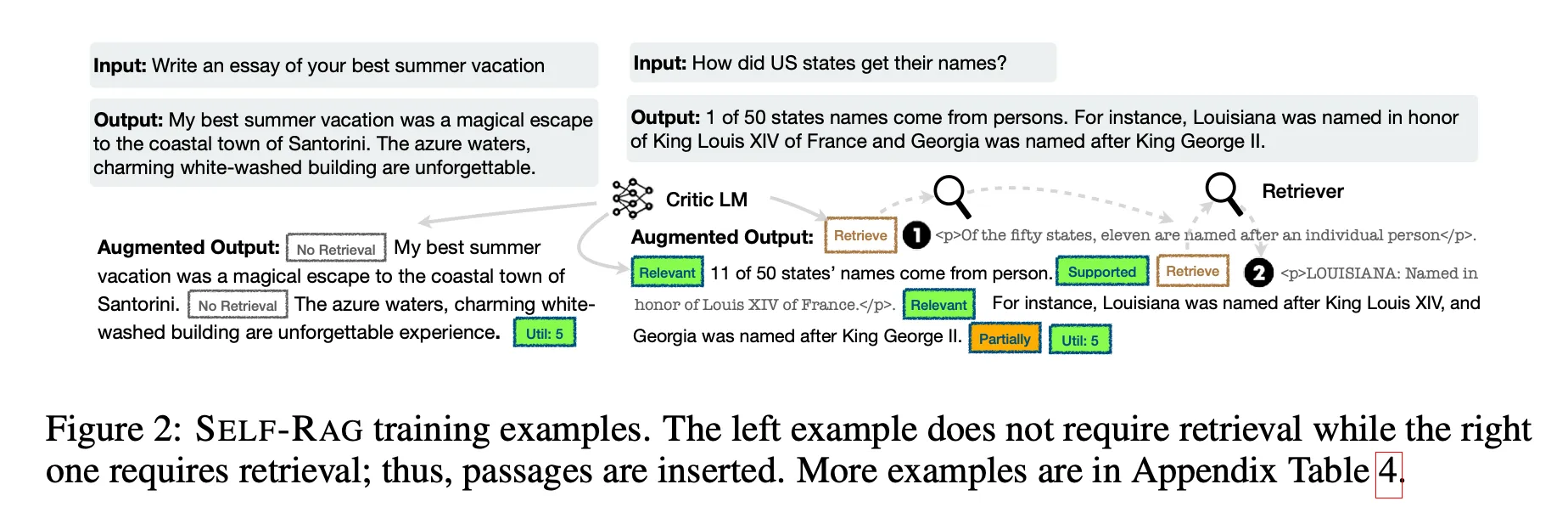
데이터 생성 방법)
우선 각 segment 에 대해, retrieval이 필요한지 체크
Retrieve=Yes인 경우- Retriever model 을 이용하여 top K passages retrieval ()
- 각 passage에 대해, critic model이 passage가 relevant 한지 평가하고
IsREL예측 - 만약 passage가 relevant 하다면, critic model이 passage가 generation을 support하는지 평가하고
IsSUP예측 - Retrieved passage 또는 generation 뒤에
IsREL,IsSUP토큰을 붙인다 - Output 끝에, critic model은
IsUSE예측 - Reflection token을 가지고 증강된(Augmented) output과 original input pair이 에 추가됨: (input , output ) → (input , augmented output ) 변환 & 새로운 데이터셋 생성
위 Figure 2에서 학습 데이터 예시를 확인할 수 있음
[Generator model learning]
학습 데이터: “기존의 curated corpus” + “reflection token이 추가되어 새로 생성된 데이터셋()”
표준 next token objective를 사용:
특징)
- 학습 중, retrieved text chunks에 대한 loss는 제외(<p> & </p> 태그로 감싸서)
- 기존 Vocabulary 확장: Reflection tokens 추가
[Connections to prior work on learning with critique]
최근 다른 연구에서도 학습 중 추가적인 critique(feedback)을 사용한다. e.g., RLHF(PPO를 통해)
PPO와 SELF-RAG 비교)
- PPO: 학습 중 별도의 reward model을 사용 & 해당 reward를 학습에 사용 → Reward 계산이 학습 중에 이뤄짐
- SELF-RAG: critic model의 response와 retrieval docs를 사용한 augmented output y를 offline에서 미리 계산한 후(미리 데이터셋 생성), 학습에 사용
따라서 SELF-RAG은 offline 계산을 통해 PPO에 비해 학습 비용을 절감할 수 있다.
3. SELF-RAG INFERENCE
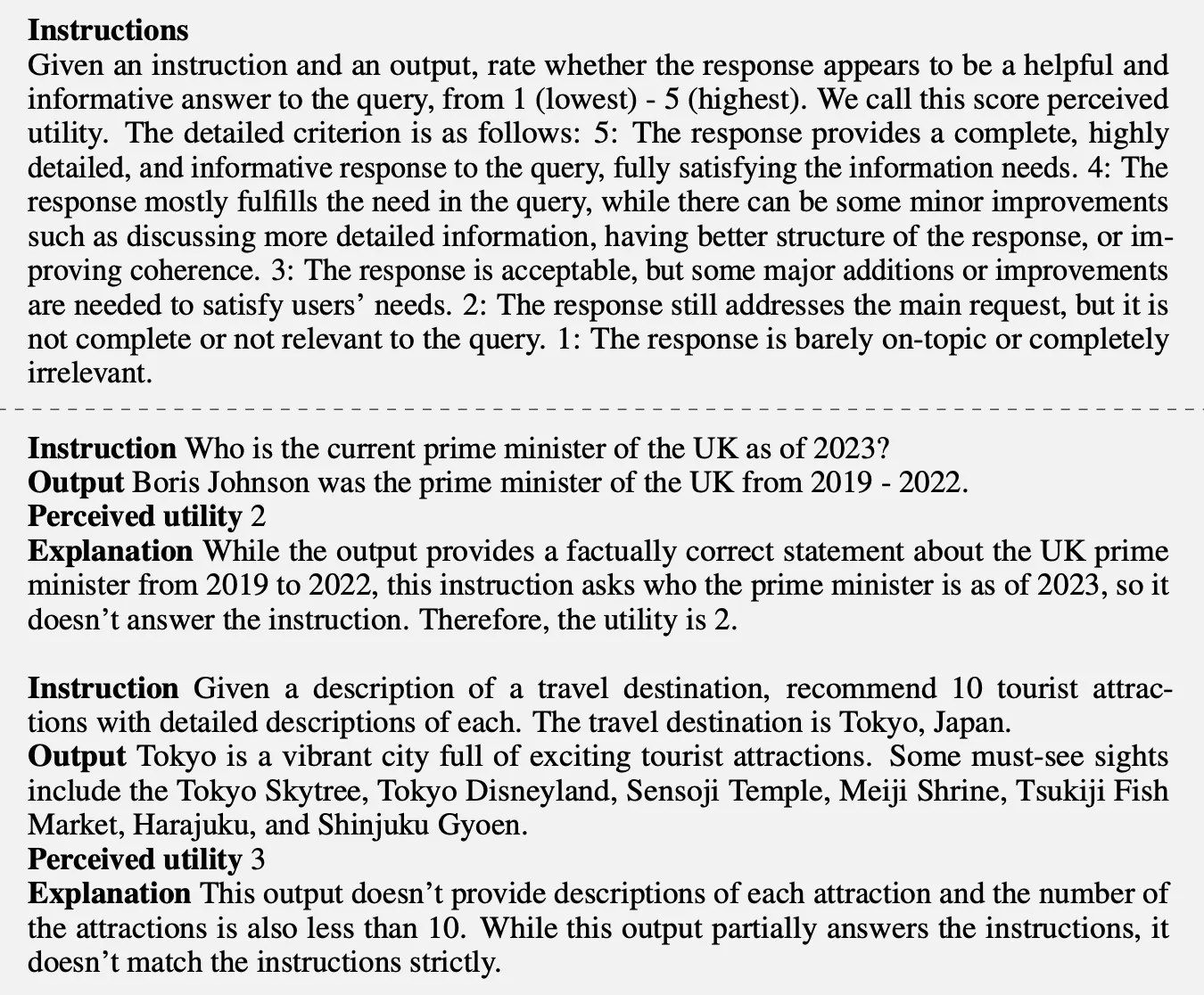
Reflection token을 사용해 output을 self-evaluate 한다면, 다양한 Task의 요구사항에 맞게 작업을 조절할 수 있음
ex) 사실적 정확성이 요구되는 task: Retrieval을 자주하여, 이를 활용해 사실적 정확성을 높인다 / open ended task (e.g., 개인적 경험을 작성하는 essay task): retrieval을 줄이고, 창의성과 유용성 점수에 우선 순위를 둔다
이 섹션에선 추론 과정에서 이렇게 서로 다른 목표에 대해 어떻게 control을 강화하는지를 다룸
Adaptive retrieval with threshold
SELF-RAG는 동적으로 retrieve가 필요한 때를 찾는다: Retrieve token을 예측하면서..
하지만 Threshold를 사용하는 방식도 가능.
[방식 설명]
- 모델이
Retrievetoken을 Yes로 생성할 logit을 구함 Retrievetoken에서 나올 수 있는 모든 출력 토큰에 대해 정규화- 모델이
Retrievetoken을 Yes로 생성할 확률이 나옴 - 해당 확률이 미리 설정한 threshold를 넘으면, retrieval 진행

Tree-decoding with critique tokens
[Retrieval이 필요한 경우]
hard or soft 조건에 기반하여 Retrieval을 해오고, K개의 passages를 병렬적으로 처리 & K개의 continuation candidates를 출력
[새로운 방법 제시]
여기서 segment-level beam search(Beam size=B) 설계 → t timestamp에서 top-B segment continuations를 얻고, 최종적으로(end of generation) best sequence 반환
[방법 설명]
Beam search를 하려면 candidate를 비교하기 위한 점수가 있어야 함
passage 에 대한 각 segment 의 점수: critic score (Normalized probability of Critique token type의 weighted sum)
예) critique token group (IsREL)의 경우, t 시점에서 점수를 라고 표현 & 다음과 같이 계산:
[식 추가 세부 설명]
-
의 경우 soft reward function.
-
여기서 : 해당 reflection token에서 바람직한 답변, 는 해당 reflection token 에서 표현할 수 있는 서로 다른 토큰 수. 그래서 은 reflection token 가 표현할 수 있는 답변들이 됨.
예) 가
IsREL이면, : relevant가 될 것. 또한, 의 경우 relevant, irrelevant가 될 것
-
즉, “해당 reflection에서 좋은 답변 토큰의 확률” / “해당 reflection token에서 나올 수 있는 토큰들의 확률 합”
-
: 특정 reflection 토큰의 중요도를 조절할 수 있는 hyperparameter(어떤 reflection token이 출력에 영향을 더 많이 줄지 조절할 수 있는 hyperparameter)
예) 결과 가 증거에 뒷받침 되는 결과였으면 좋겠다 →
IsSUPreflection token의 중요도를 높게 설정 & 다른 reflection token의 중요도를 상대적으로 낮게 설정
[강한 제약을 걸 수도 있음]
과 같은 soft reward function을 사용하는 대신, undesirable critique token이 나오는 경우 해당 segment continuation을 필터링을 할 수도 있음.
ex) IsSUP = No Support → 필터링
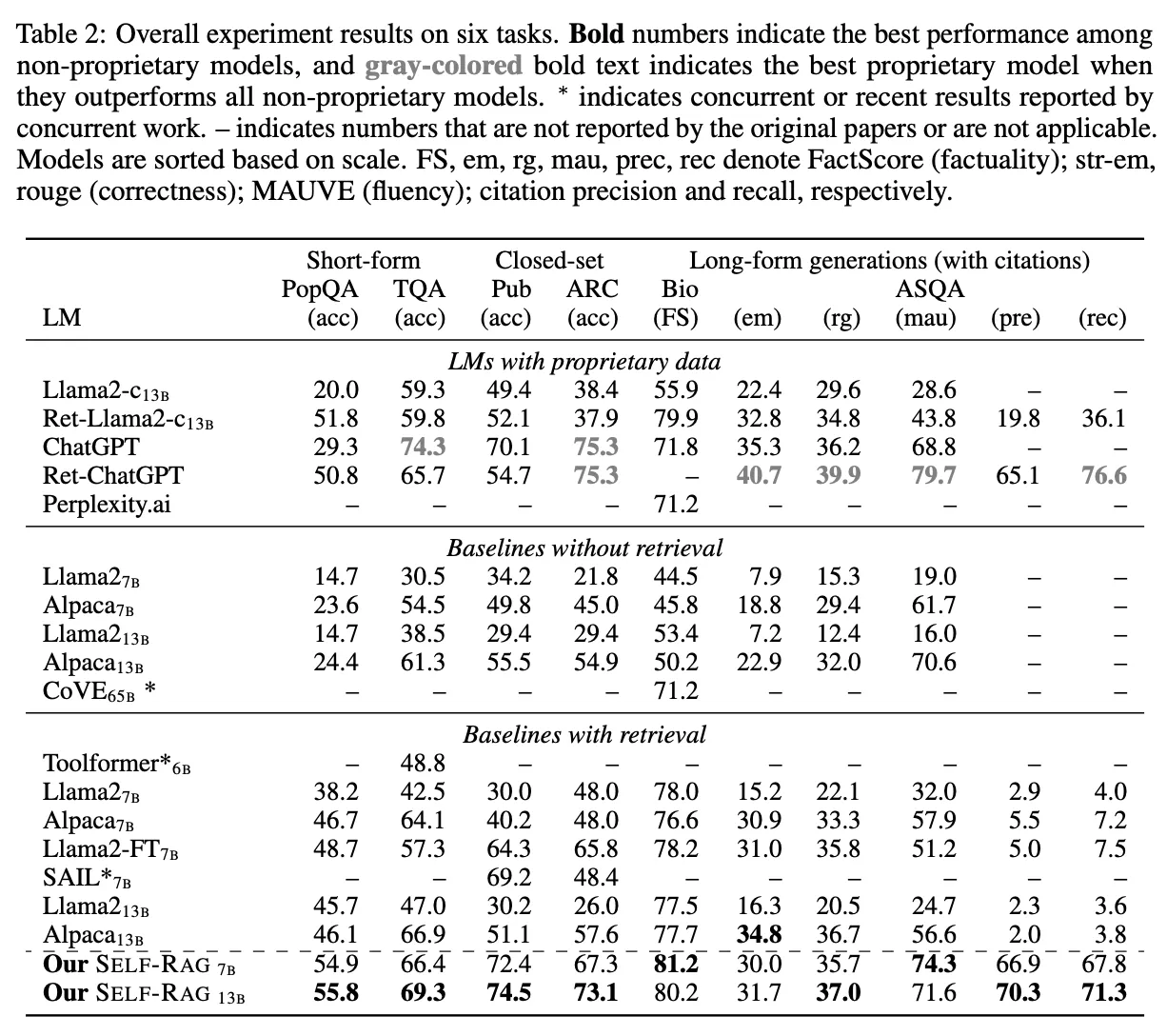
실험
- Baseline with Retrieval
- 사용 모델: Pretrained LLM(LLaMA2), Instruction-tuned model(Alpaca), Private data로 학습한 모델(Chat-GPT, LLaMA2-chat), iterative prompt engineering 적용 모델(CoVE; cocurrent work)
- 실험 방법: 공식적인 system prompt 또는 instruction format이 있는 모델의 경우(학습 중 특정 프롬프트 포맷을 사용한 모델), 해당 프롬프트 이용
- Baseline without Retrieval
- 실험 방법
- Standard RAG baseline: query 앞에 retrieval docs를 붙이는 형식으로 진행
- Cocurrent method: retrieved passage를 가지고 학습된 모델을 사용(SAIL, Toolformer)
- 실험 방법