FCFS
- FIFO처럼 먼저 온 순서대로 일을 처리.
- non-preemptive 방식으로 한 번 cpu가 process를 처리하면 voluntary-yield를 하지 않는 이상 cpu를 다시 내놓지 않는다.
- voluntary yield : I/O task를 처리하는 것과 같이 cpu를 사용하고 있던 프로세스가 cpu를 내놓는 상황.
User Program 구현
- kucpu의 작업을 요청하는 user program 구현.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define KU_CPU 337 // define syscall number
int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
int jobTime;
int delayTime;
char name[4];
int wait = 0;
int response = 0;
if (argc < 4) {
printf("\nInsufficient Arguments..\n");
return 1;
}
/* first argument : job time (second)
second argument : delay time before execution (second)
third arument : process name
*/
jobTime = atoi(argv[1]);
delayTime = atoi(argv[2]);
strcpy(name, argv[3]);
// wait for 'delayTime' seconds before execution
sleep(delayTime);
printf("\nProcess %s : I will use CPU by %ds.\n", name, jobTime);
jobTime *= 10; // execute system call in every 0.1 second
// continue requesting the system call as long as the jobTime remains
while(jobTime) {
// if request is rejected, increase wait time
if (!syscall(KU_CPU, name, jobTime)) jobTime--;
else {
wait ++;
response ++;
}
usleep(100000); // delay 0.1 second
}
syscall(KU_CPU, name, 0);
printf("\nProcess %s : Finish! My response time is %ds and My total wait time is %ds. ", name, (response+5)/10, (wait+5)/10);
return 0;
}System call 구현
- FCFS scheduling으로 돌아가는 kucpu 구현
- cpu의 현재 작업 상태를 now로 저장. IDLE 상태일 경우 -1.
- 작업 대기열은 waiting queue에 순서대로 저장. queue는 linked list로 연결, queue의 metadata는 waiting_header에 저장.
- cpu 처리 알고리즘
- cpu가 IDLE하다면 요청받은 작업 처리
- cpu가 요청받은 작업과 동일한 작업 처리중이라면
1) jobTime이 0이면, "완료" 출력. 다음 작업 처리
2) jobTime이 0이 아니면, "처리중" 출력. - cpu가 요청받은 작업과 다른 작업을 처리중이라면
1) 대기열에 존재하지 않는 작업이라면 대기열에 추가
2) 대기열에 존재하면 넘어감
3) "처리 거절" 출력 - 요청한 작업을 처리했다면 0을 그렇지 않다면 1을 반환.
/*2024 Fall COSE341 Operating System*/
/*Project 2*/
/*Kim JinHyeong*/
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/linkage.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
# define IDLE -1
typedef struct _job_t {
int pid;
int jobTime;
} job_t;
int now = IDLE;
typedef struct _node{
int pid; // waiting process pid
struct _node * next; // next node
} NODE; // queue elements
typedef struct header {
int num; // number of waiting queue elements
NODE* first; // first element
NODE* last; // last element
} HEADER;
HEADER waiting_header = {0, NULL, NULL};
int ku_pop(void); // dequeue
int check(int x); // check whether x is in waiting_queue
void ku_push(int pid); // enqueue
SYSCALL_DEFINE2(os2024_ku_cpu, char*, name, int, jobTime) {
// store pid of current process as pid_t type
job_t newJob = {current->pid, jobTime};
// register the process if virtual CPU is idle
if (now == IDLE) now = newJob.pid;
// If the process that sent the request is currently using virtual CPU
if (now == newJob.pid) {
// If the job has finished
if (jobTime == 0) {
printk("Process Finished: %s\n", name);
// if queue is empty, virtual CPU becomes idle
if (waiting_header.num == 0) now = IDLE;
// if not, get next process from queue and load
else now = ku_pop();
}
else printk("Working: %s\n", name);
// request accepted
return 0;
}
else {
// if the request is not from currently handling process
if (check(newJob.pid)) ku_push(newJob.pid); // enqueue pid i
f process is not in waiting queue
printk("Working Denied:%s \n", name);
}
//request rejected
return 1;
}
int ku_pop() { // dequeue from waiting queue and return dequeue
d pid valud
NODE* temp = waiting_header.first;
int res = temp->pid;
waiting_header.first = waiting_header.first->next;
waiting_header.num--;
if (waiting_header.num == 0) waiting_header.last == NULL;
kfree(temp);
return res;
}
int check(int new_pid) { // check whether or not the pid of newJo
b is in waiting queue. If it doesn't exist, return 1.
NODE* temp;
int i;
if (waiting_header.num == 0) return 1;
temp = waiting_header.first;
for (i = waiting_header.num; i > 0; i--) {
if (temp->pid == new_pid) return 0;
temp = temp->next;
}
return 1;
}
void ku_push(int pid) { // enequeue the pid of newJob into waiti
ng queue
NODE* new_node = (NODE *)kmalloc(sizeof(NODE), GFP_KERNEL);
new_node->pid = pid;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (waiting_header.num == 0) {
waiting_header.first = new_node;
waiting_header.last = new_node;
waiting_header.num++;
return;
}
waiting_header.last->next = new_node;
waiting_header.last = new_node;
waiting_header.num++;
return;
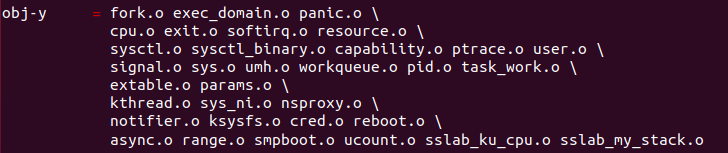
}Makefile
Syscall header
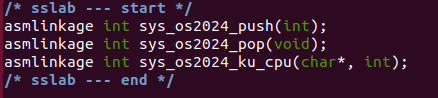
System Call table
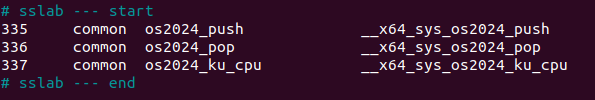
run
run file
./kucpu_run 7 0 A & ./kucpu_run 5 1 B & ./kucpu_run 3 2 C &
- 위와 같은 command로 run file을 생성.
chmod 777 run명령어를 통해 read, write, execute 권한 부여- ./run을 통해 kucpu_run프로그램 3개 concurrently하게 실행
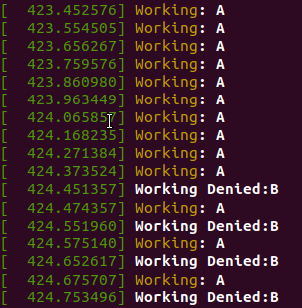
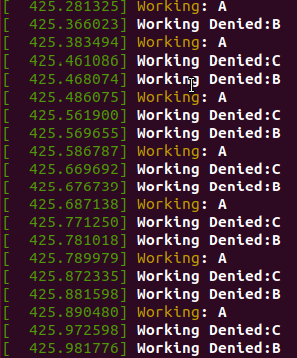
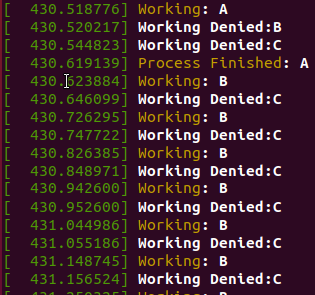
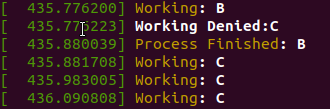
Result
user process console log
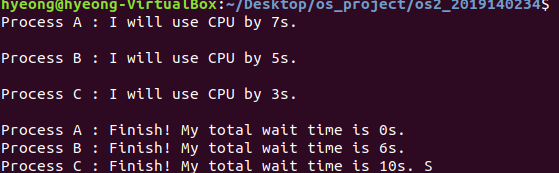
kernel process console log
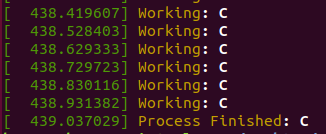
결론
- kucpu 작업을 요청한 순서인 A, B, C 순서대로 실행됨
- average response time : (0 + 6 + 10) / 3 = 5.33
