SJF (Shortest Job Fisrt)
- FCFS : 들어온 순서대로 작업을 처리
- SJF : 대기중인 작업들 중에 처리시간이 가장 짧은 작업을 먼저 처리
- FCFS에 비해 response time과 wait time이 줄어든다는 장점
- Non-preempitve : FCFS와 마찬가지로 voluntary yield 없이는 다른 작업들이 도중에 수행될 수 없다. starvation 야기
- Starvation
- 작업시간이 오래걸리는 프로그램은 후순위로 밀려 처리되는데까지 오래 걸린다.
- 오래 기다린 작업에게는 우선순위를 부여해주는 방식으로 해결가능.
SJF scheduling kucpu 구현
- jobTime을 고려해야 하기에 queue node에 jobTime을 추가해줌.
- FCFS와 대부분 비슷하나 queue에서 차이가 존재. 2가지 방식의 구현 가능
- 새로운 대기작업 enqueue시 오름차순이 유지되도록 waiting queue에 삽입
- enqueue는 요청 순서대로 하고, dequeue시 가장 짧은 처리 시간을 가지는 작업을 반환
- 장단점
- 삽입할 때마다 들어갈 자리를 찾아야 하므로 삽입 시 오래 걸림. 하지만 ku_pop 시에는 가장 앞의 작업을 반환하면 되기 때문에 빠름.
- enqueue 시에는 삽입만 하므로 시간이 짧게 걸림. 하지만 ku_pop 시마다 전체 queue를 검색해야 하므로 ku_pop시 오래걸림.
- 작업을 다 처리하고 다음 작업을 빠르게 반환 받는것이 중요하다 생각하기에, ku_pop이 빠른 첫 번째 구현방법으로 구현.
- FCFS는 ku_push를 통해 enqueue, SJF의 경우 ku_push_SJF를 통해 오름차순으로 삽입.
- enqueue하는 코드문장에서 scheduling에 따라 나머지 하나는 주석처리
- ku_push_SJF는 jobTime도 고려해야하기에 추가로 인자로 전달해줌.
/*2024 Fall COSE341 Operating System*/
/*Project 2*/
/*Kim JinHyeong*/
/* If FCFS, use ku_push(int) instead of ku_push_SJF(int, int) in main*/
/* If SJF, use ku_push_SJF(int, int) instead of ku_push(int) in main*/
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/linkage.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
# define IDLE -1
typedef struct _job_t {
int pid;
int jobTime;
} job_t;
int now = IDLE;
typedef struct _node{
int pid; // waiting process pid
int jobTime; // remaining jobTime
struct _node * next; // next node
} NODE; // queue elements
typedef struct header {
int num; // number of waiting queue elements
NODE* first; // first element
NODE* last; // last element
} HEADER;
HEADER waiting_header = {0, NULL, NULL};
int ku_pop(void); // dequeue
int check(int x); // check whether x is in waiting_queue
void ku_push(int pid);
void ku_push_SJF(int pid, int jobTime); // enqueue
SYSCALL_DEFINE2(os2024_ku_cpu, char*, name, int, jobTime) {
// store pid of current process as pid_t type
job_t newJob = {current->pid, jobTime};
// register the process if virtual CPU is idle
if (now == IDLE) now = newJob.pid;
// If the process that sent the request is currently using virtual CPU
if (now == newJob.pid) {
// If the job has finished
if (jobTime == 0) {
printk("Process Finished: %s\n", name);
// if queue is empty, virtual CPU becomes idle
if (waiting_header.num == 0) now = IDLE;
// if not, get next process from queue and load
else now = ku_pop();
}
else printk("Working: %s\n", name);
// request accepted
return 0;
}
else {
// if the request is not from currently handling process
// if (check(newJob.pid)) ku_push(newJob.pid); // enqueue pid b
y FCFS if process is not in waiting queue
if (check(newJob.pid)) ku_push_SJF(newJob.pid, jobTime);
// enqueue pid by SJF if process is not in waiting queue
printk("Working Denied:%s \n", name);
}
//request rejected
return 1;
}
int ku_pop() { // dequeue from waiting queue and return dequeue
d pid valud
NODE* temp = waiting_header.first;
int res = temp->pid;
waiting_header.first = waiting_header.first->next;
waiting_header.num--;
if (waiting_header.num == 0) waiting_header.last == NULL;
kfree(temp);
return res;
}
int check(int new_pid) { // check whether or not the pid of newJo
b is in waiting queue. If it doesn't exist, return 1.
NODE* temp;
int i;
if (waiting_header.num == 0) return 1;
temp = waiting_header.first;
for (i = waiting_header.num; i > 0; i--) {
if (temp->pid == new_pid) return 0;
temp = temp->next;
}
return 1;
}
void ku_push(int pid) { // enequeue the pid of newJob into waiti
ng queue
NODE* new_node = (NODE *)kmalloc(sizeof(NODE), GFP_KERNEL);
new_node->pid = pid;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (waiting_header.num == 0) {
waiting_header.first = new_node;
waiting_header.last = new_node;
waiting_header.num++;
return;
}
waiting_header.last->next = new_node;
waiting_header.last = new_node;
waiting_header.num++;
return;
}
void ku_push_SJF(int pid, int jobTime) { // enequeue the
pid of newJob into waiting queue by ascending order
NODE* pPre = NULL; // former location of ploc
NODE* pLoc; // searching location
NODE* new_node = (NODE *)kmalloc(sizeof(NODE), GFP_KERNEL);
new_node->pid = pid;
new_node->jobTime = jobTime;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (waiting_header.num == 0) {
waiting_header.first = new_node;
waiting_header.last = new_node;
waiting_header.num++;
return;
}
pLoc = waiting_header.first;
while (pLoc) {
if (pLoc->jobTime > new_node->jobTime) break;
pPre = pLoc;
pLoc = pLoc->next;
}
new_node->next = pLoc;
if (pLoc == NULL) waiting_header.last = new_node; // last
if (pPre == NULL) waiting_header.first = new_node; // first
else pPre->next = new_node;
waiting_header.num++;
return;
}run
run file
./kucpu_run 7 0 A & ./kucpu_run 5 1 B & ./kucpu_run 3 2 C &
console log
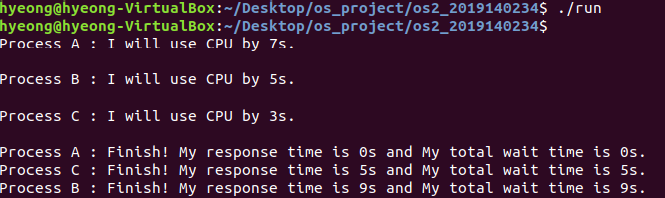
user process log
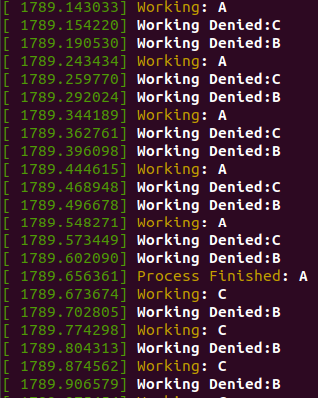
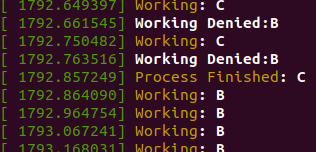
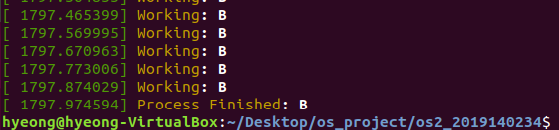
kernel process log

결론
- 원하는대로 가장 먼저 작업 요청한 A가 먼저 실행됨.
- B가 먼저 작업 요청을 했으나 작업시간이 더 짧았던 C가 먼저 실행됨.
- C가 끝나고 남은 B가 실행됨.
- average response time : (0 + 5 + 9) / 3 = 4.67
- FCFS보다 average response time이 짧음
구현 개선점
- check 함수의 개선
- queue가 오름차순으로 정렬되어 있기에 check 함수를 통해 해당 pid가 queue에 있는지를 확인함과 동시에 삽입되어야 할 위치를 알 수 있음.
- 그러므로 ku_push 없이 check 함수 내에서 push까지 이루어질 수 있고, queue의 순회를 2번에서 1번으로 줄이며 시간복잡도도 훨씬 줄일 수 있다.
- Header last
- enqueue의 위치가 맨 마지막이 아니므로 정렬된 queue에서의 삽입에는 last의 위치가 필요하지 않다.
