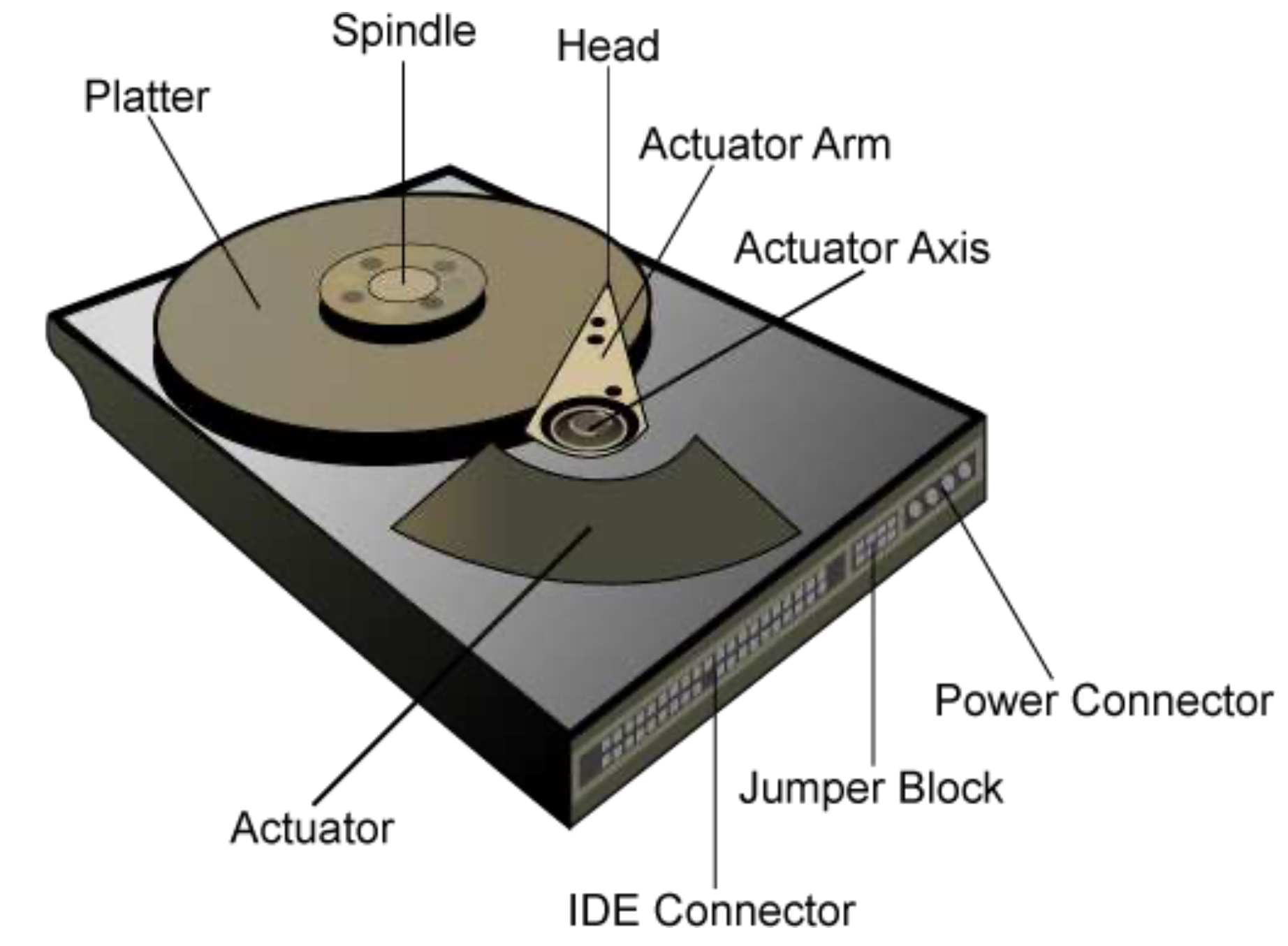
Hard Disk Drive
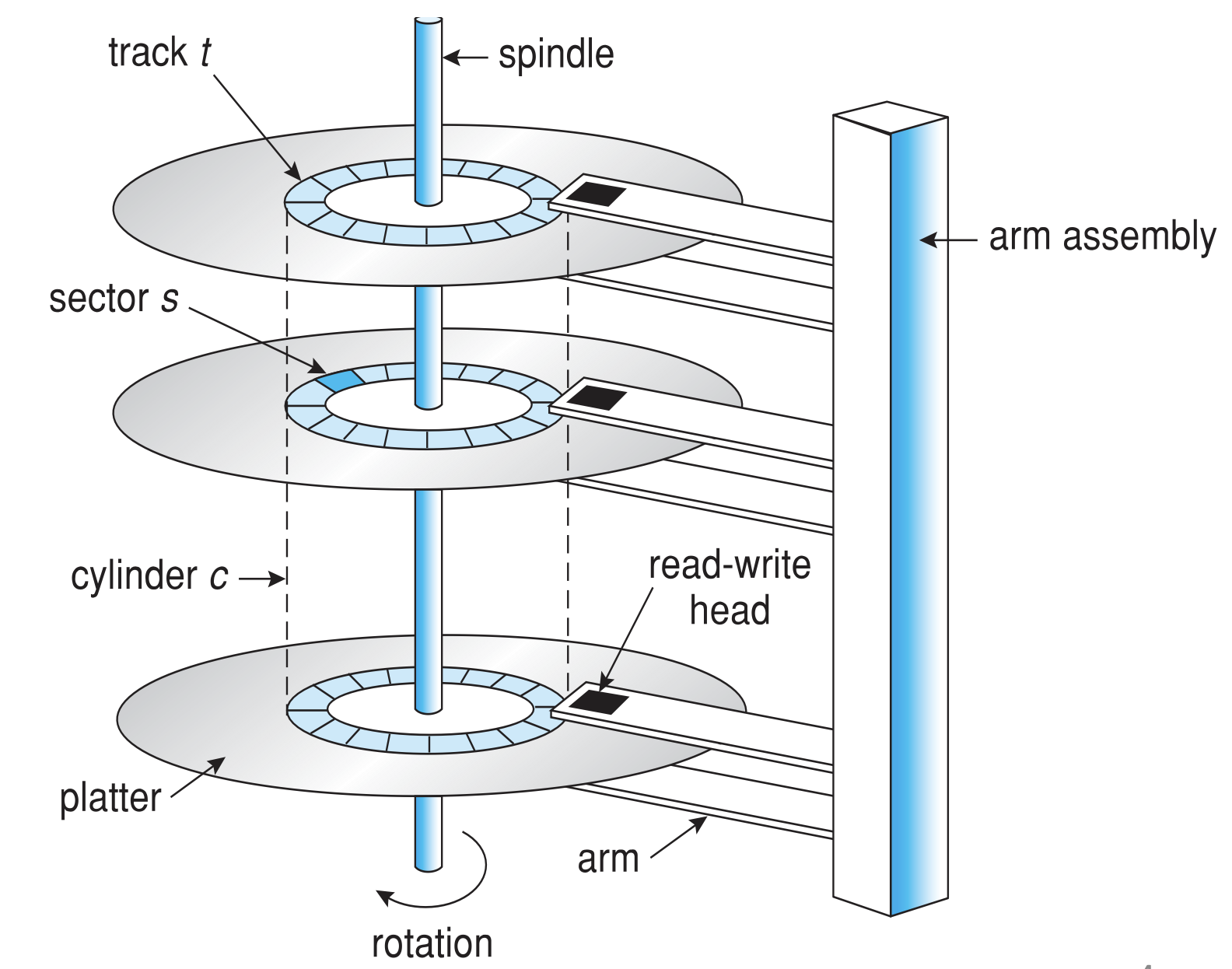
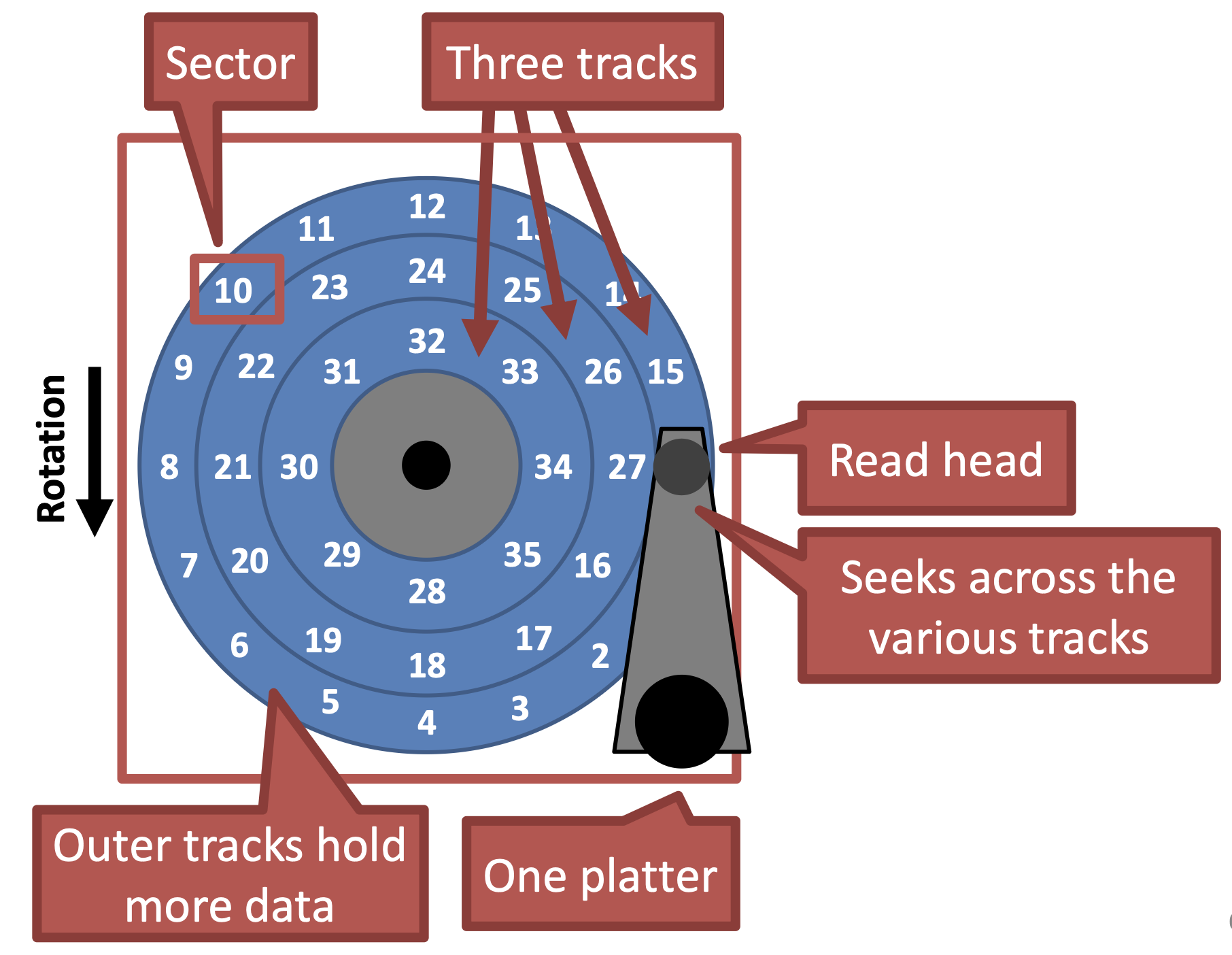
Geometry
- Hard drives expose a large number of sectors(blocks)
- Typically 512 or 4096 bytes(=page size -> easy to swap)
- Individual sector writes are atomic
- Multiple sectors writes may be interrupted
- Drive geometry
- Sectors arranged into tracks
- Cylinder is a particular track on multiple platters
- Tracks arranged in concentric circles on platters
- A disk may have double-sided platters
LBA: Logical Block Addresses
Types of Delay with Disks
Three types of delay
- Rotational delay
- Time to rotate the desired sector to the read head
- Related to RPM
- Seek delay
- Time to move the read head to a different track
- Transfer time
- Time to read or write bytes
- Track skew
- offset sectors so that sequential reads across tracks incorporate seek delay
= Consider movement of read head to a different track
- offset sectors so that sequential reads across tracks incorporate seek delay
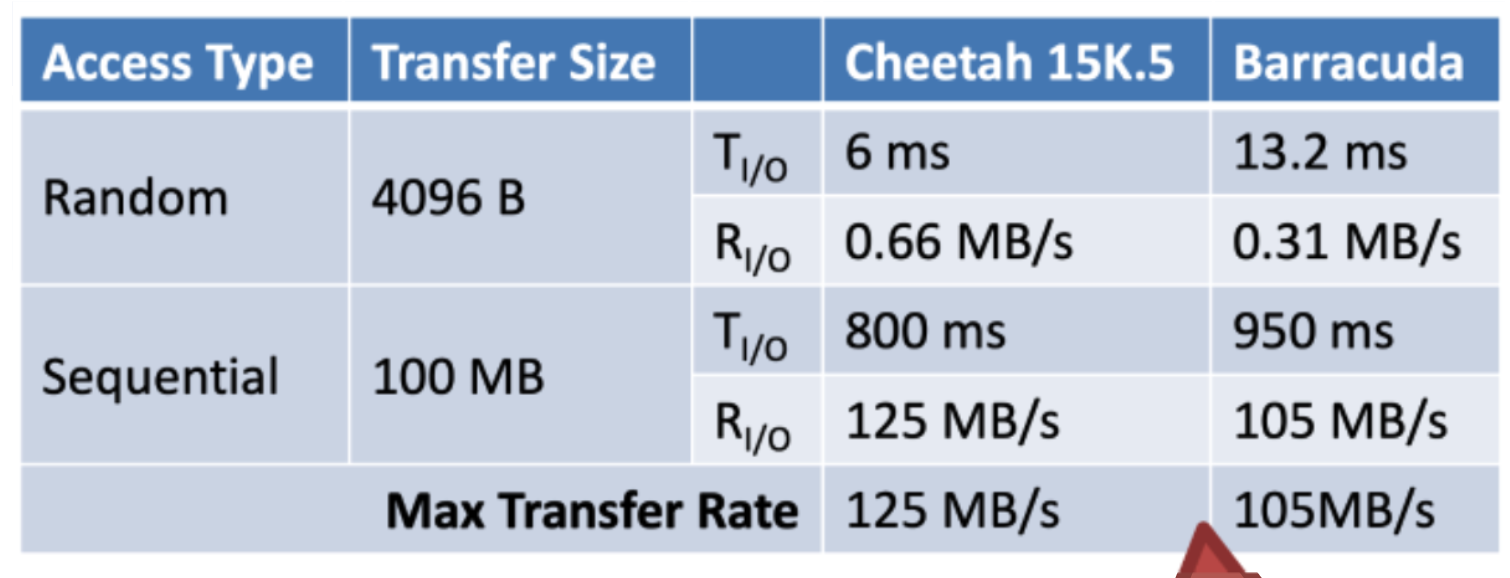
Caculating Transfer time
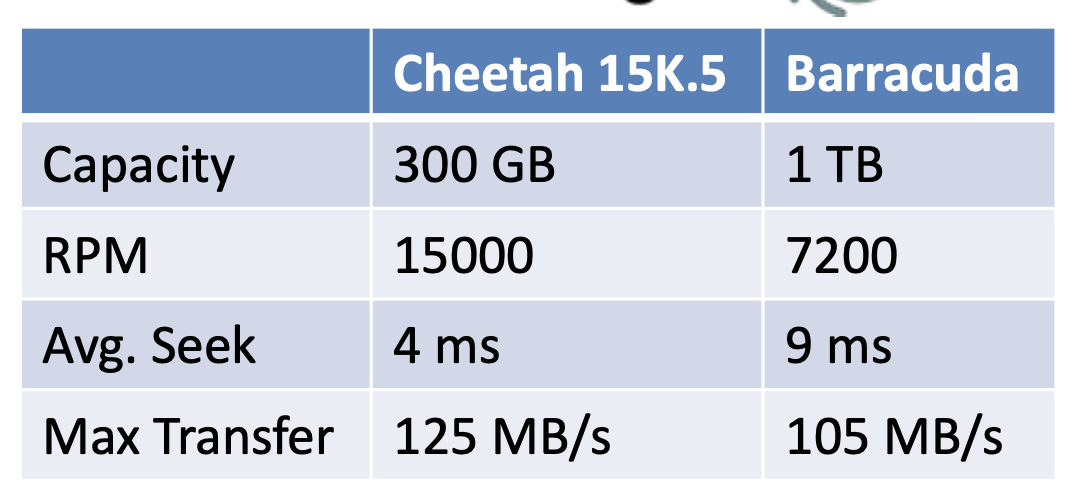
- Assume transffering 4096 bytes
- Cheetah
- Barracuda
Sequential vs Random Access
- Sequential Access
- Caculate rotational and seek time only once
Caching
- Many disks incorporate caches
- Read caching
- Reduces read delays
- Write caching
- Write back cache
- Write on only cache
- Possibly dangerous (Volatile -> power off -> cache doesn't exist)
- Write through cache
- Write on disk too
- Write back cache
- Some disks include flash memory for persistent caching
Disk Scheduling
- Caching can't make up for poor random access time
- A queue of requests to the disk, they can be reordered to improve performance
FCFS: First come, first serve
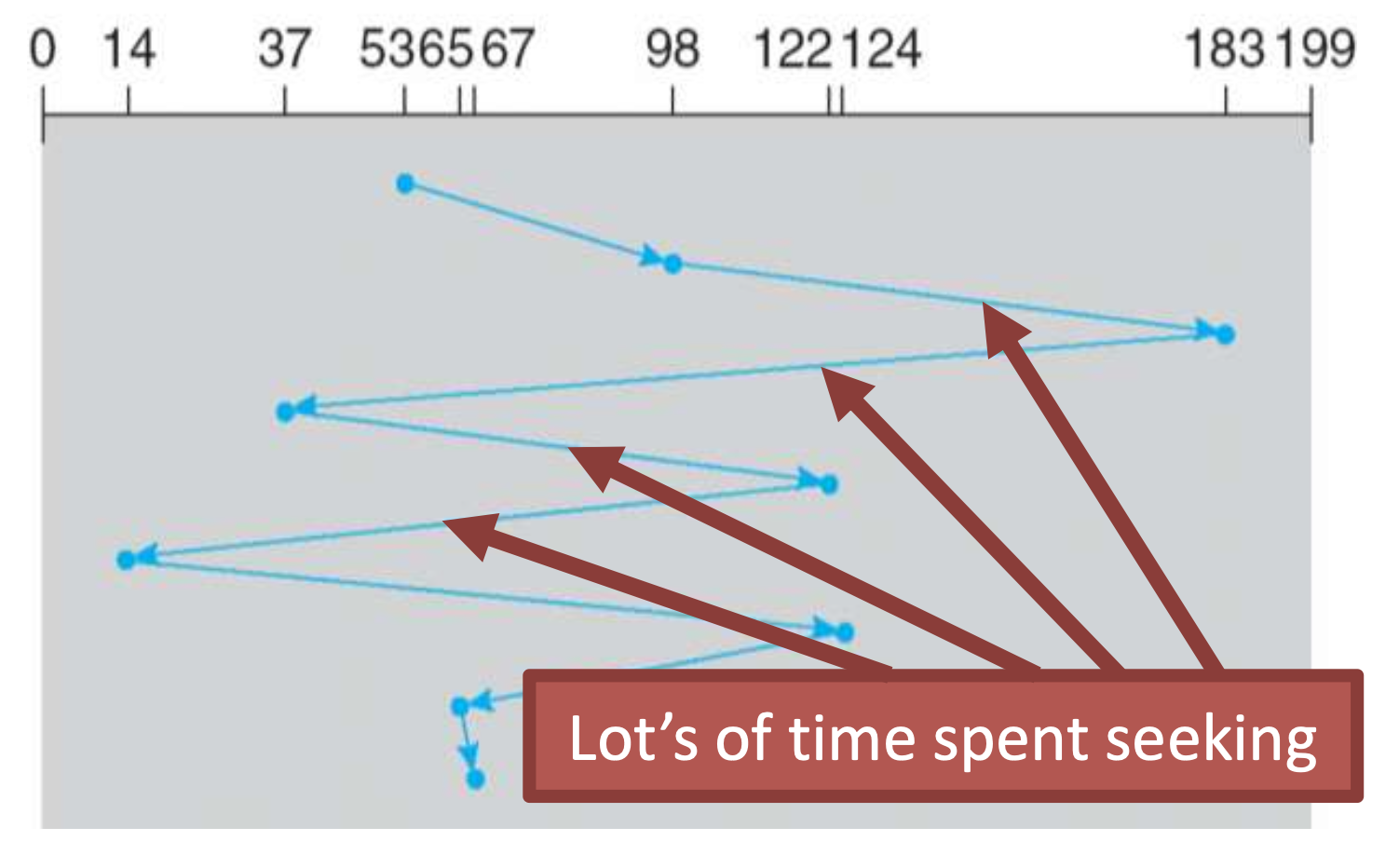
SSTF: Shortest seek time first
- Minimize seek time by always selecting the block with the shortest seek time
- Optimal
- Prone to starvation
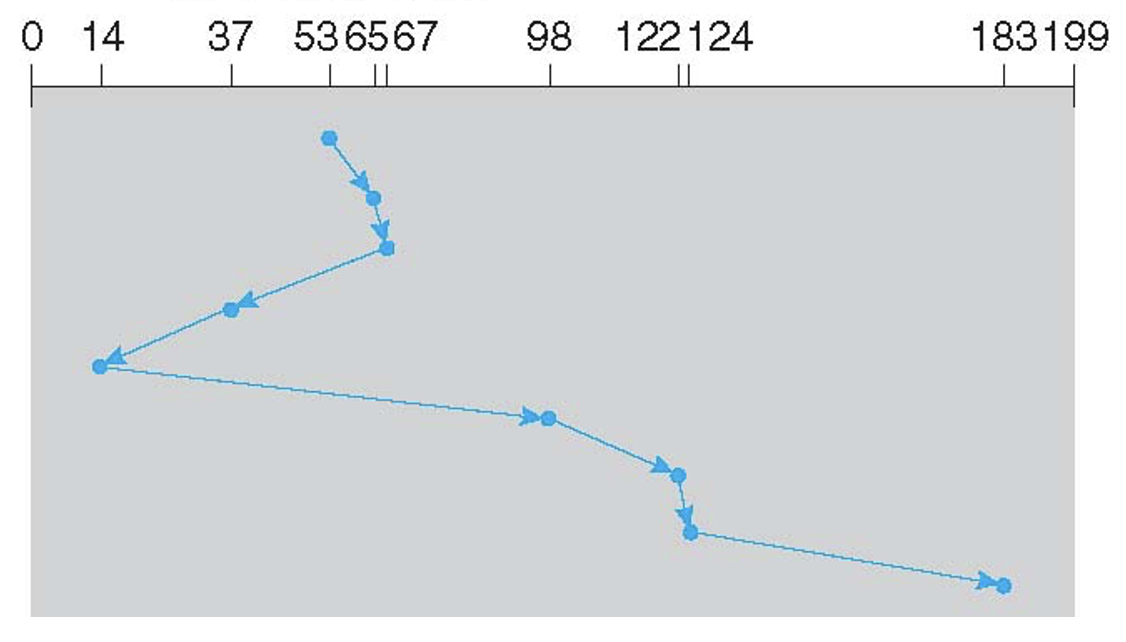
SCAN (Elevator)
- Sweeps across the disk servicing requests in order
- No starvation
- Average access times are less for requests at high and low addresses
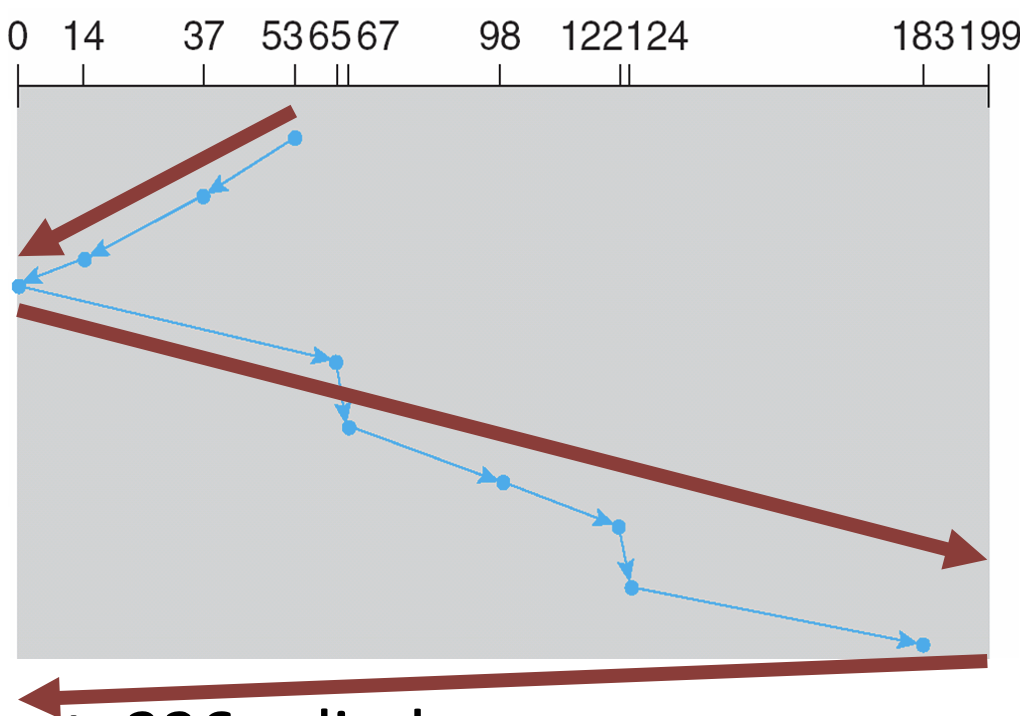
C-SCAN
- Service requests in one direction
- Fairer than SCAN
- Worse performance than SCAN
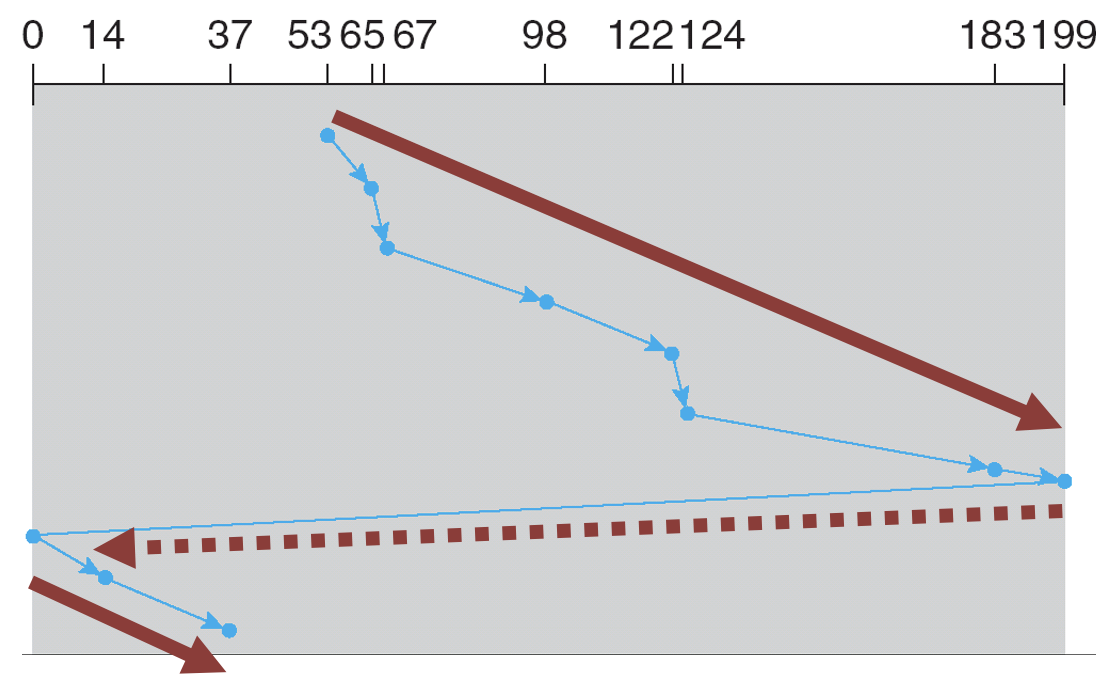
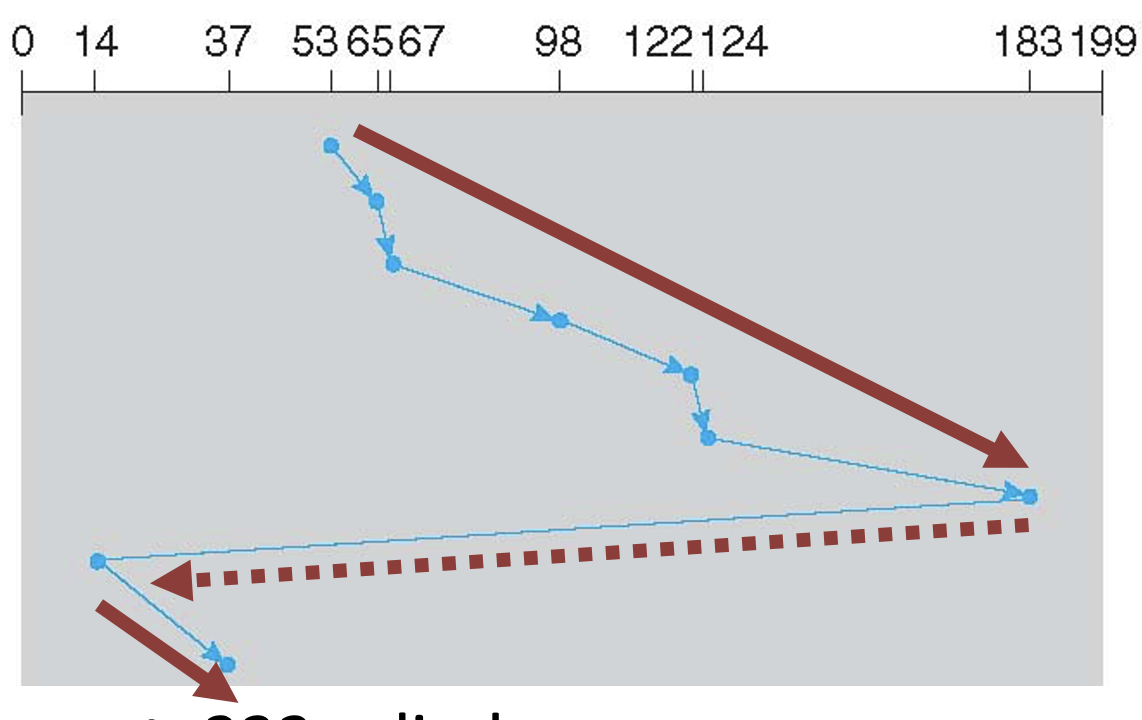
C-LOOK
- Only goes as far as the last request (not until the end)
Implementing Disk Scheduling
- Where should be implemented?
- OS Scheduling
- OS cannot account for rotation delay
Do not know where the head is (mechanically)
- OS cannot account for rotation delay
- On-disk Scheduling
- Disk knows the exact position of the head and platters
- But requires specialized hardware and drivers
- OS Scheduling
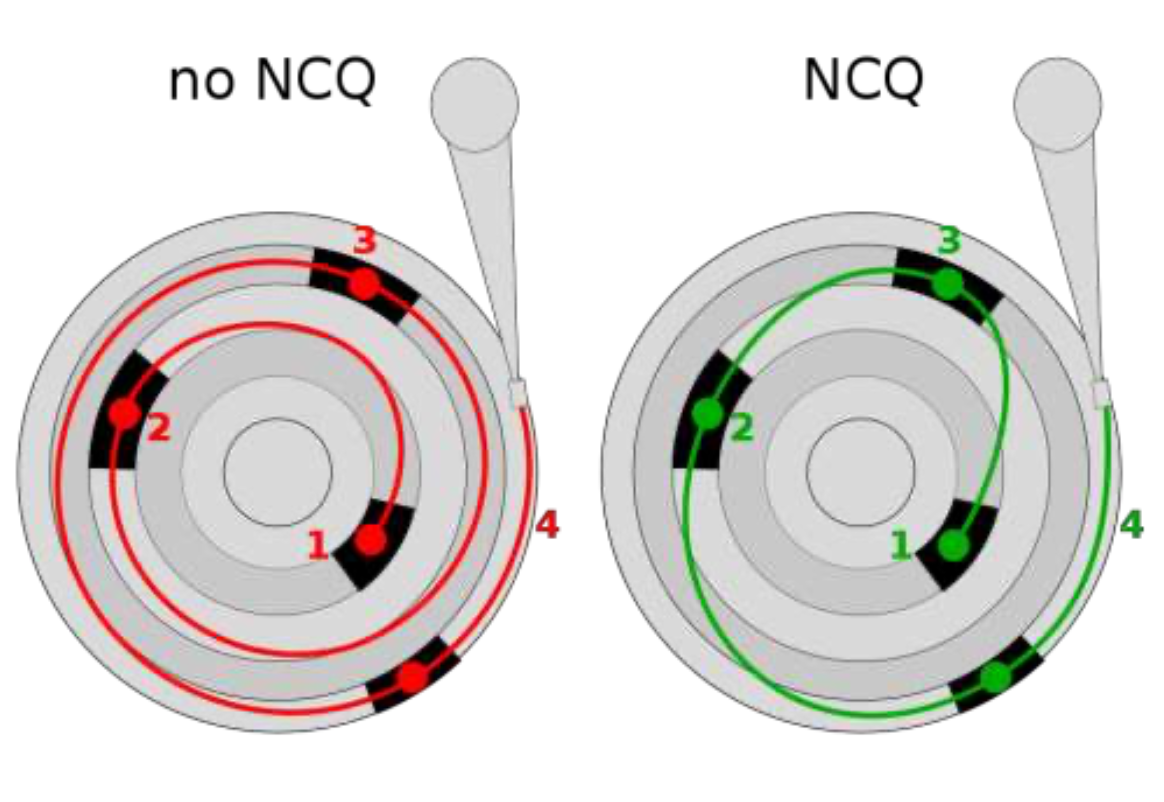
Command Queuing
- Feature where a disk stores of queue of pending read / write requests
- Called NCQ(Native Command Queuing) in SATA
- Disk may reorder items in the queue
- Tagged command queuing
- Allow the host to place constraints on command re-ordering