Operating Systems
1.Introduction: Hardware and Operating System

Introduction Operating System A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware Operating system goals Ex
2.Booting

Firmware $$\\rightarrow$$ Bootloader $$\\rightarrow$$ OS kernelxv6: BIOS $$\\rightarrow$$ bootblock $$\\rightarrow$$ kernelLinux: BIOS/UEFI $$\\righta
3.Lec 2-Processes

Processes Running Dynamic Code Basic function of OS is to execute and manage code dynamically Command line terminal Icon double click Jobs/tasks run a
4.Lec 2-Threads

A server with many clientsA computer with many CPU coresSpace must be allocated for the new processfork() copies all state of the parentEach message h
5.Lec 3-Scheduling(1)

N CPUs, P process/threadsIn what order should the process be run?On what CPU should each process run?Focus on scheduling in case of 1 CPUI/O bound or
6.Lec 3-Scheduling(2)

Priority is CPU burst timeFCFS's priority is arrival timeRR's priority is dynamicalStarvationHigh priority tasks can dominate the CPU$$\\Rightarrow$$
7.Lec 3-Scheduling(3)

Fair Share Scheduling New goal: Fairness From now on, schedulers are designed to optimize performance Minimize response time, turnaround time MLFQ achieves these goals, but complicated Non-trivial ...
8.Lec 4-Virtual Memory(1)

Evil process can ruin other process or access kernel memoryCompiled programs include fixed pointer addressesEx) two copies of the same programProgram
9.Lec 4-Virtual Memory(2)
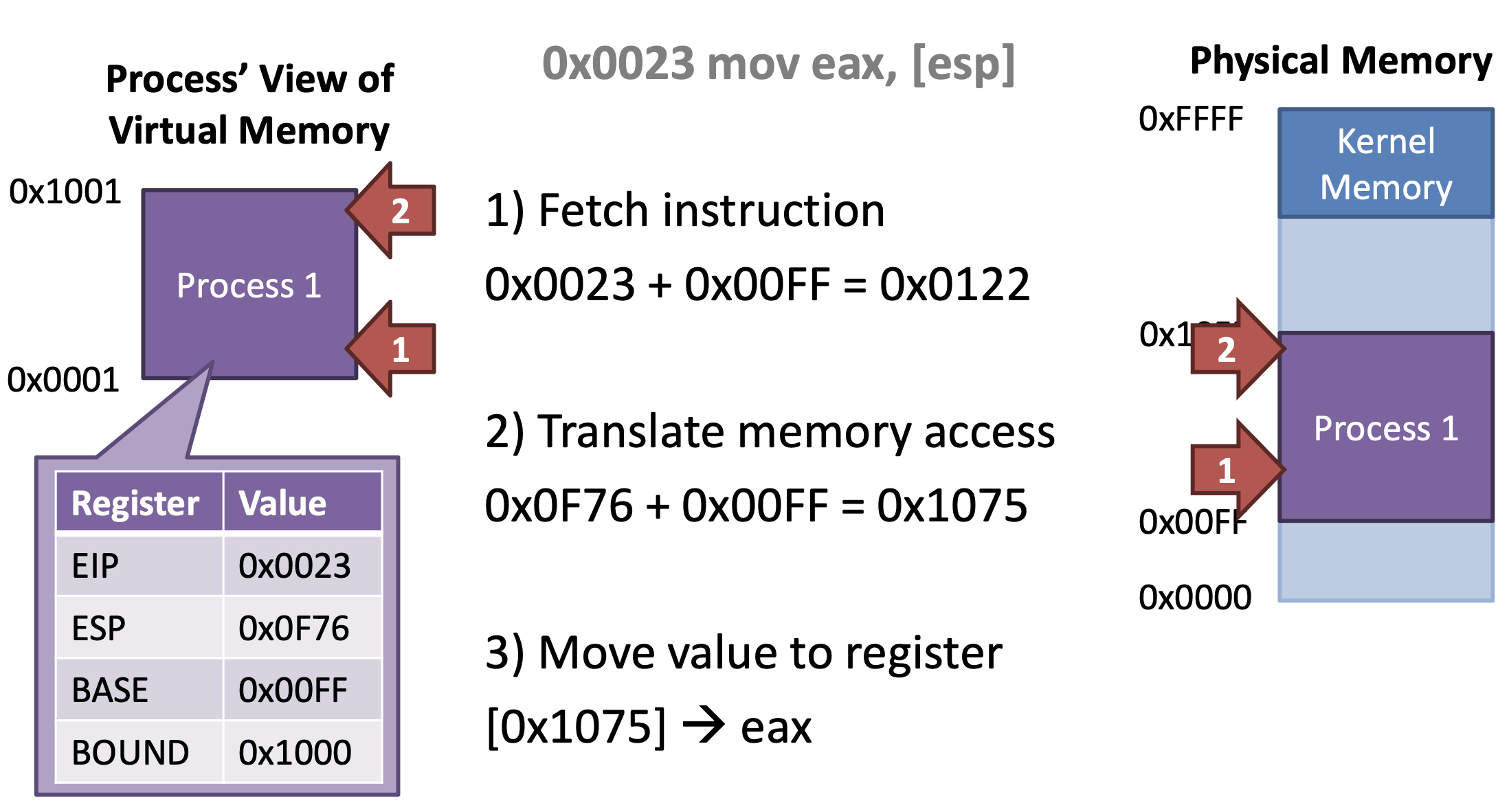
Add BASE value to virtual addressIf translated address is bigger than BASE + BOUND,then Raise Protection ExceptionBASE and BOUND are protectedOnly cod
10.Lec 4-Virtual Memory(3)

TLB
11.Lec 4-Virtual Memory(4)

Swap frames between physical memory and diskLoad data from swap back into memory on-demandIf a process access a page that has been swapped out,page fa
12.Lec 4-Free Memory Management

Basics Dynamic allocation of pages Page table allows the OS to dynamically assign physical frames to process on-demand On Linux, processes use sbrk(), brk(), mmap() to request additional heap pages ...
13.Lec 5-Concurrency (1)

Concurrency Concurrency vs Parallelism Concurrency Whether processes can access resources (CPU) simultaneously Parallelism Whether actually do multip
14.Lec 5-Concurrency (2)

Construct for managing control flowCondition variables are not locksEach condition variable is associated with a mutexThreads that can't run yet wait(
15.Lec 5-Concurrency (3)

Non-Deadlock Bugs Atomicity violation Desired serializability among multiple memory accesses is violated Two different threads access the field proc
16.Lec 6-Storage Devices (1)

Hard Disk Drive Geometry Hard drives expose a large number of sectors(blocks) Typically 512 or 4096 bytes(=page size -> easy to swap) Individual sector writes are atomic Multiple sectors writes...
17.Lec 6-Storage Devices (2)

How to cope with disk failureMechanical parts break over timeSectors may become silently corruptedCapacity is limitedManaging files across multiple ph
18.Lec 6-Storage Devices (3)

The cheapest way to store large amounts of dataSlowest component in most computersFragile mechanical components can breakDisk motor is extremely power