Numpy (Numerical Python)
- 과학계산에서 많이 사용하는 선형대수의 계산식을 파이썬으로 구현할 수 있도록 도와주는 라이브러리
- 파이썬의 고성능 과학 계산용 패키지
- Matrix와 Vector와 같은 Array연산의 사실상의 표준

 -> 가상환경 생성 후 numpy install
-> 가상환경 생성 후 numpy install
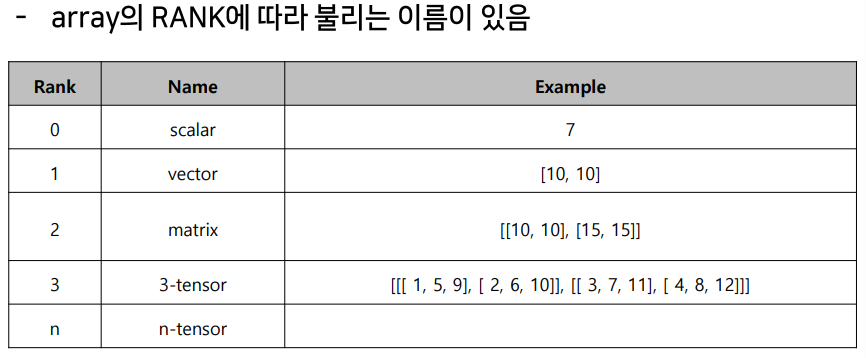
ndarray

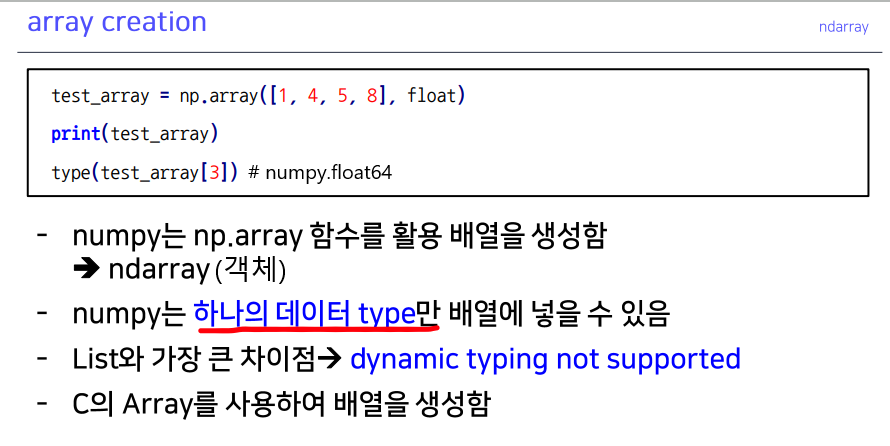

numpy와 array의 메모리 사용 차이
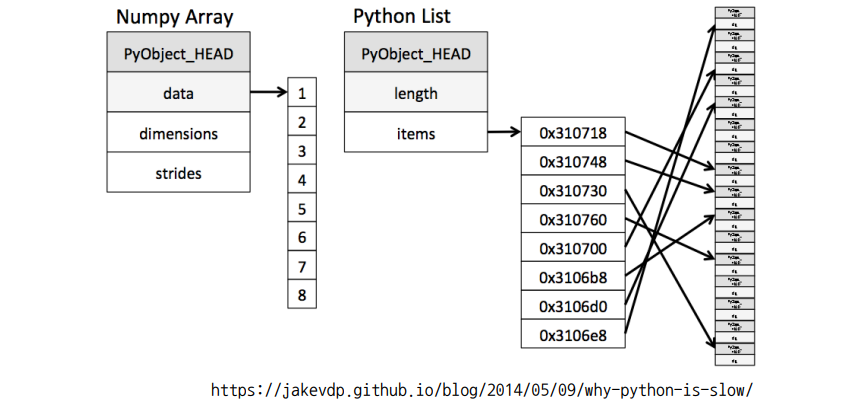
- Numpy array
- 데이터가 차례대로 메모리의 어떤 공간에 할당 -> 연산의 용이함, 메모리의 접근성 좋음
- 메모리의 크기가 일정해 데이터 저장 공간을 잡기 효율적
- Python List
- ~까지의 값이 메모리의 어떤 static한 공간에 존재
- 값 자체(ex. 7, 8, 9)가 아니라 값의 주소값(ex. 0x310718, 0x310748, 0x310730)이 List에 차례대로 저장된다.
- 주소값에서 한 번 더 들어가야 값을 찾을 수 있는 구조 (리스트의 변형이 쉽다.)
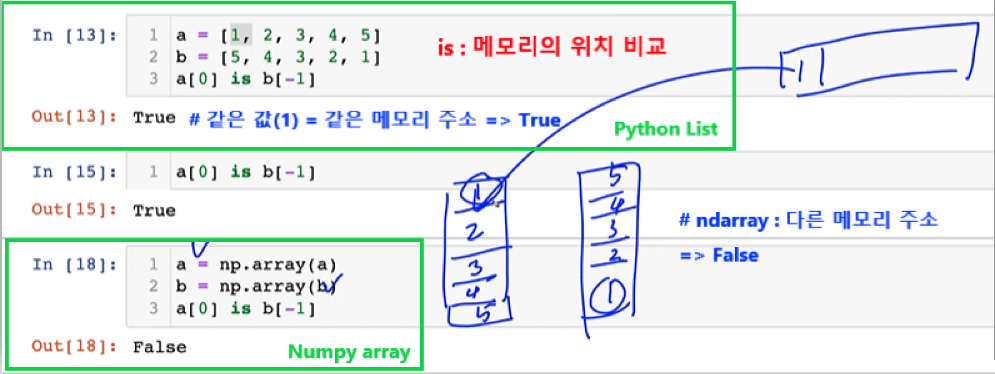
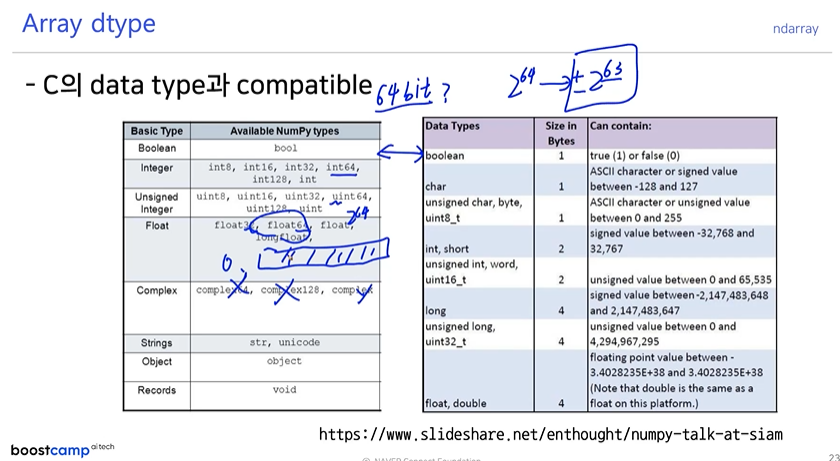
shape, dtype
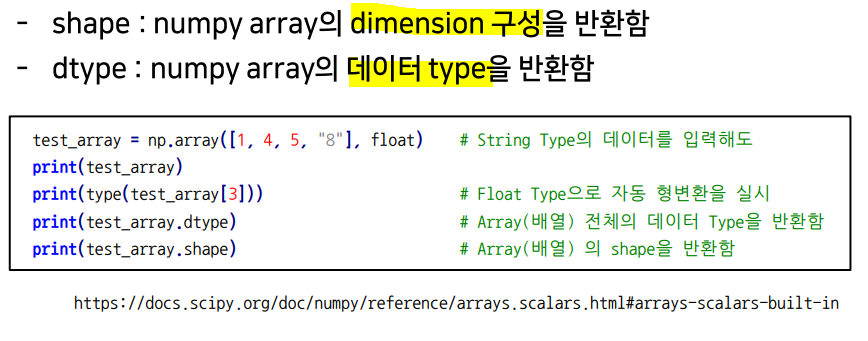
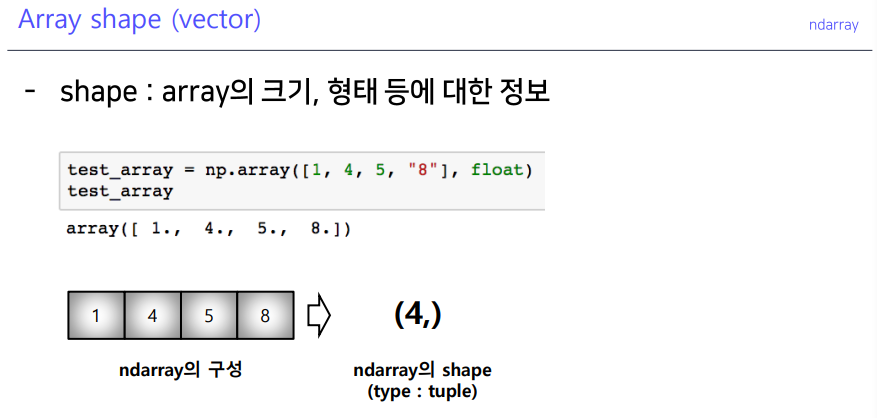
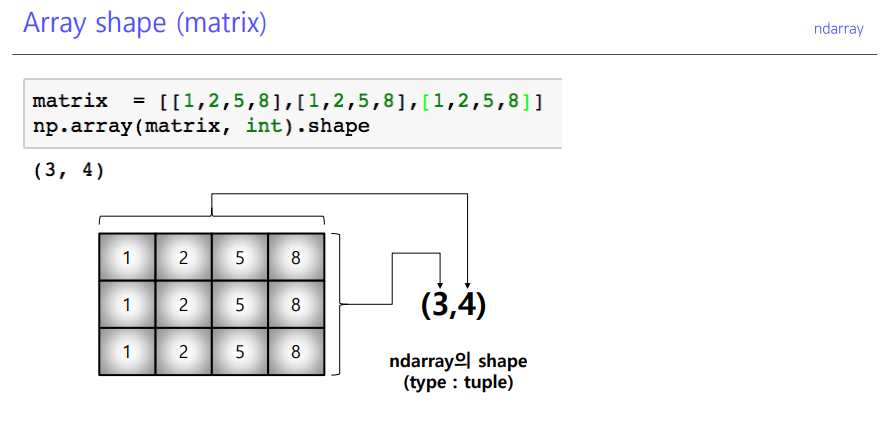
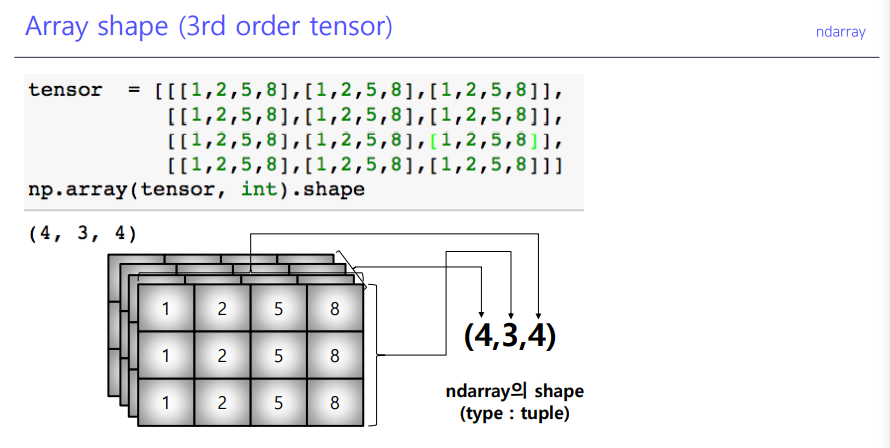
shape
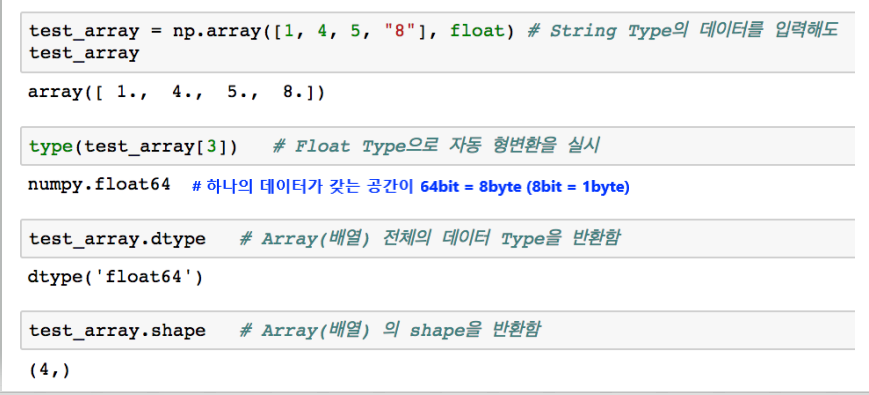

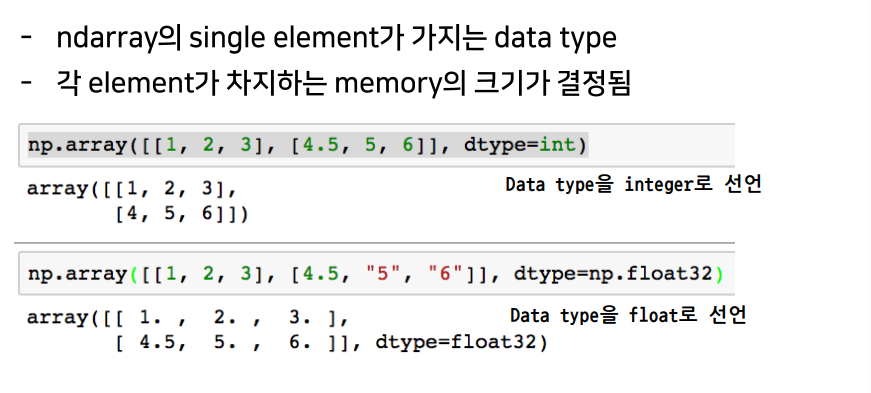
dtype


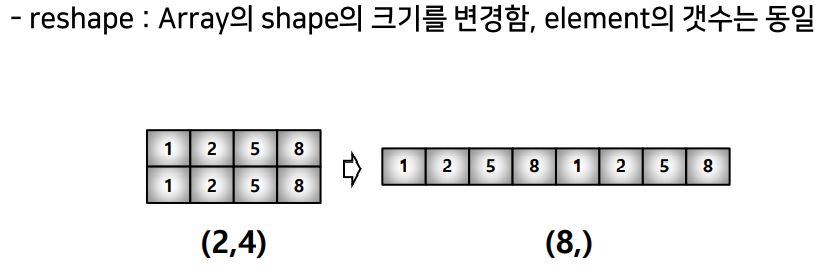
Handling shape
reshape



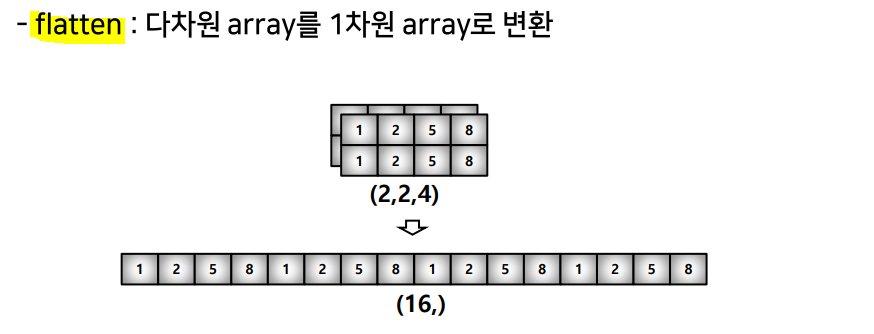
flat or flatten()

indexing & slicing
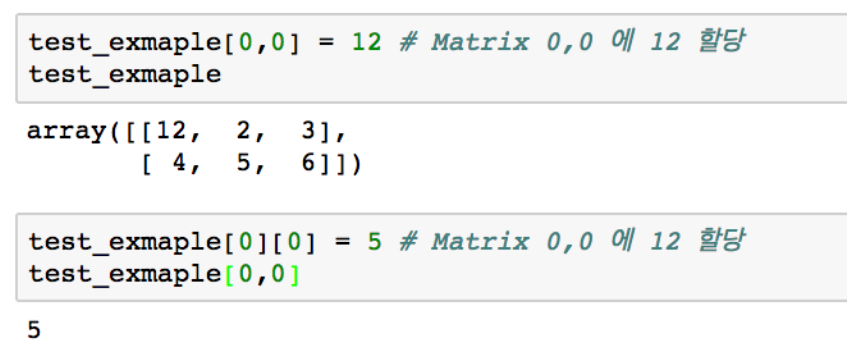
indexing


slicing
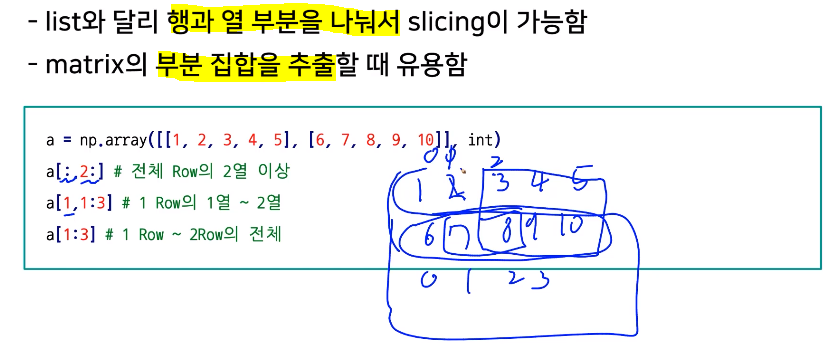
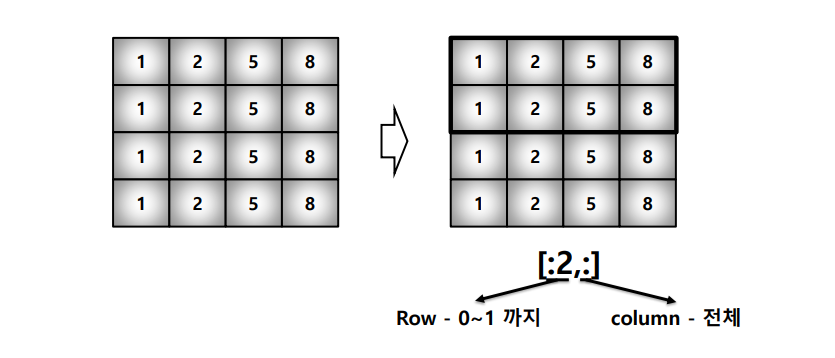

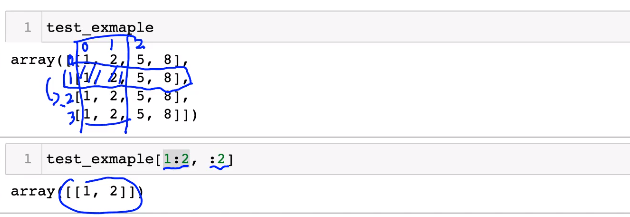
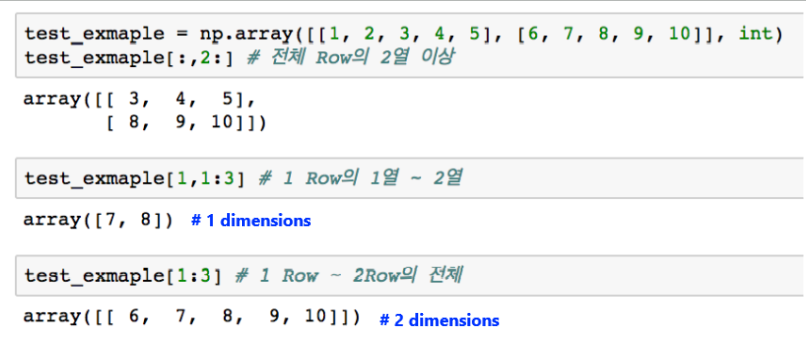

start : end : step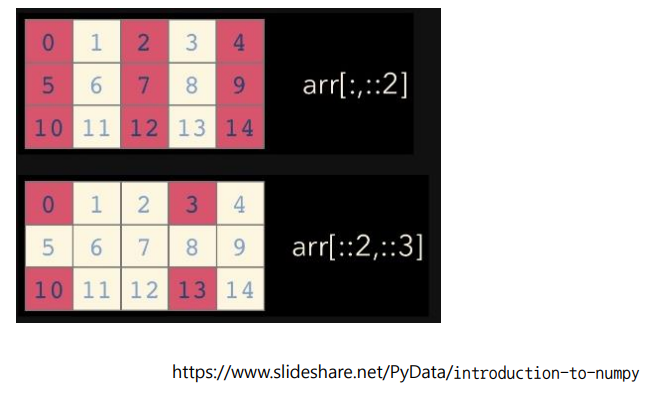
creation function
arange()

ones, zeros and empty
- shape는 항상 튜플(tuple)의 형태로 적어주어야 한다.


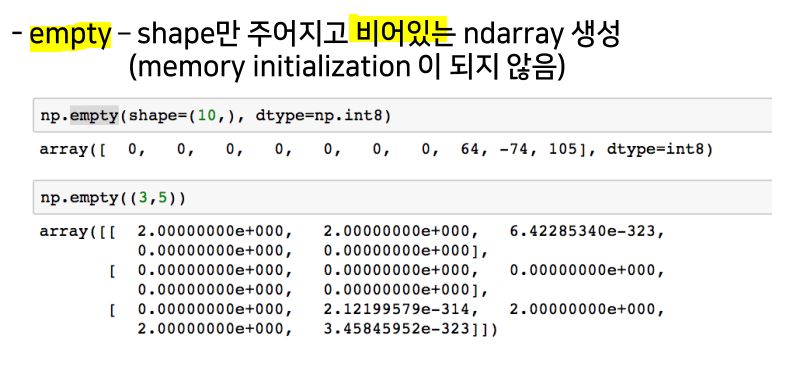 -> memory initialization 되지 않아 주소값만 잡게 되고 실행시킬 때마다 다른 값이 출력됨 (실행시킬 때마다 새로운 주소값을 잡는 것)
-> memory initialization 되지 않아 주소값만 잡게 되고 실행시킬 때마다 다른 값이 출력됨 (실행시킬 때마다 새로운 주소값을 잡는 것)
-> 이전 값들은 남아있다. (garbage collection)
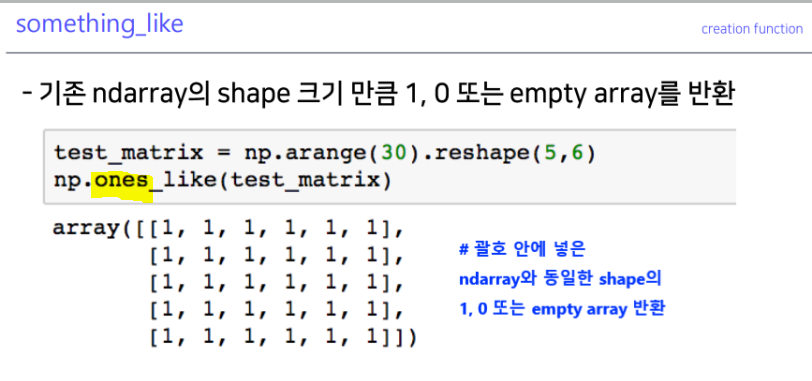
identity
n = a: a by a matrix 생성
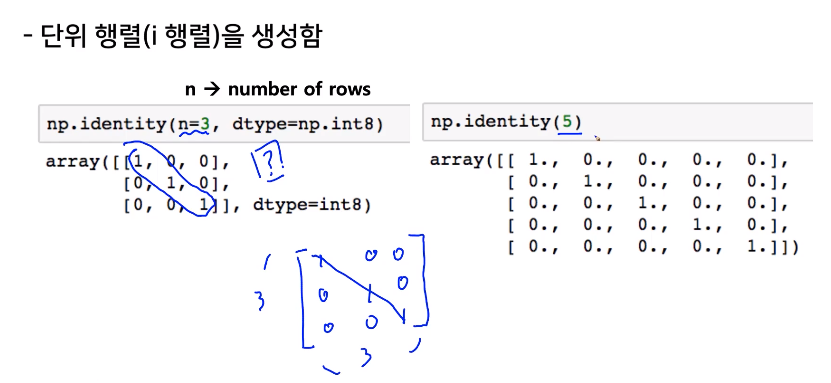
eye
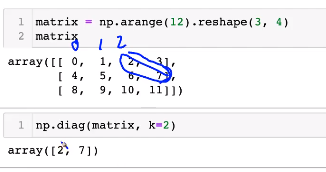
n: 행(row)m: 열(column)k: start index

diag


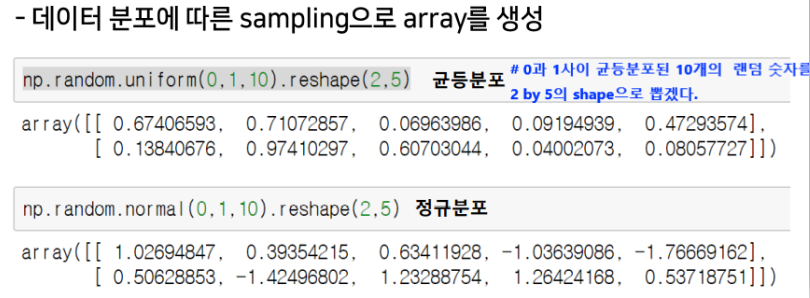
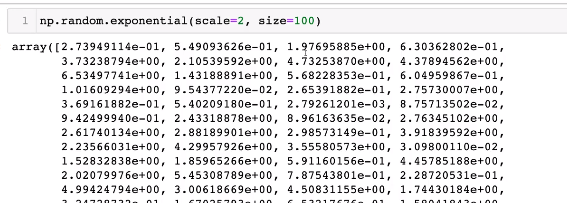
random
operation function
axis
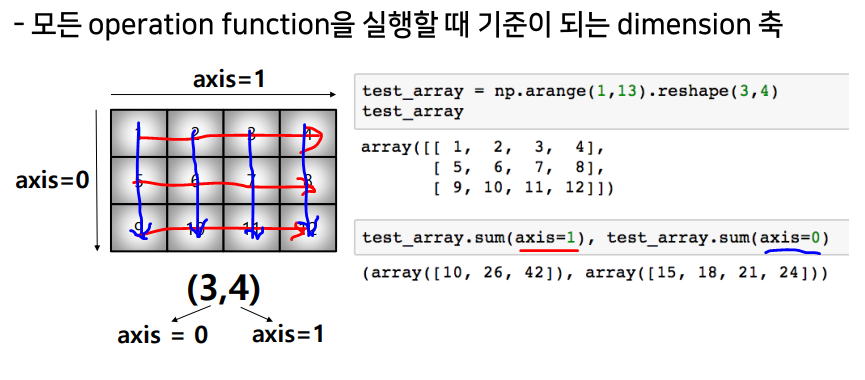
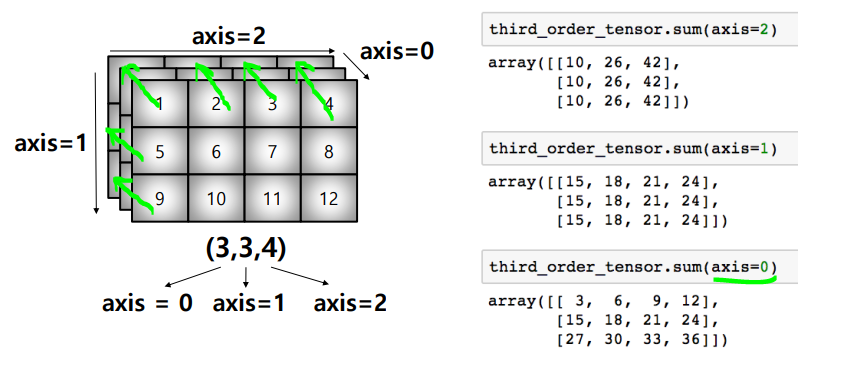 -> 항상 새롭게 생성된 축이
-> 항상 새롭게 생성된 축이 axis=0이 된다.
sum
 -> 연산이 가능하다는 것에 주목!
-> 연산이 가능하다는 것에 주목!
mean & std

etc


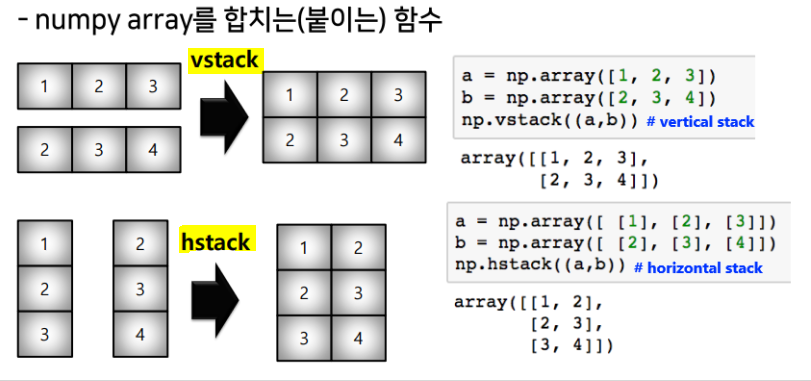
concatenate
stack
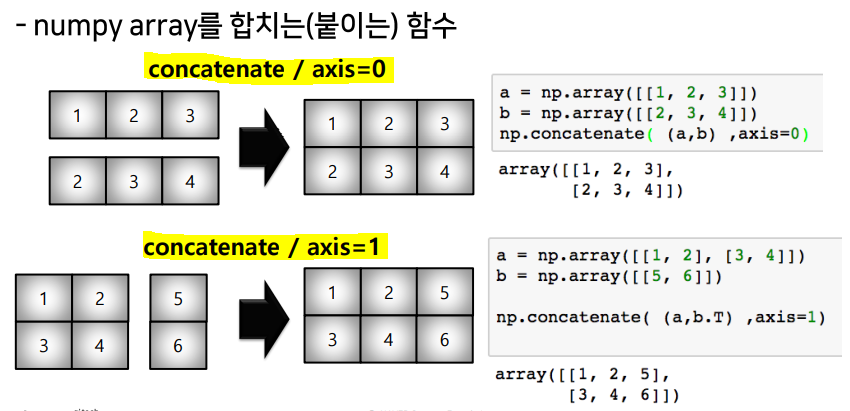
concatenate
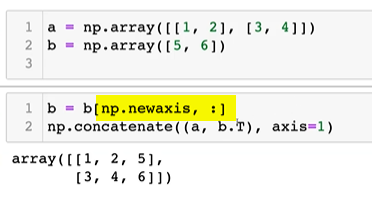
np.newaxis: 새로운 축을 하나 추가
array operation

Element-wise operations
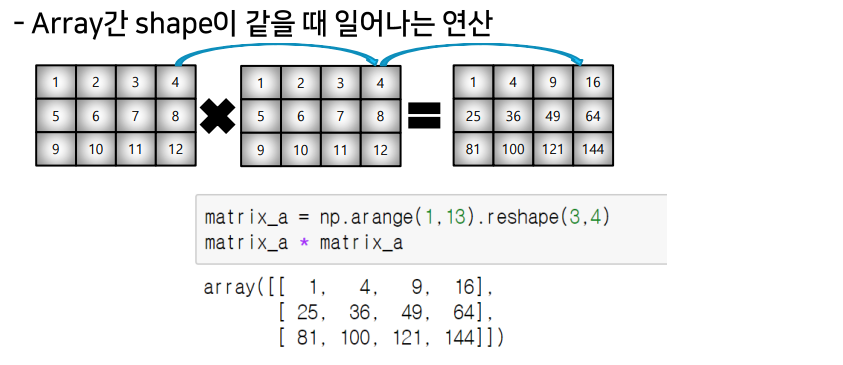
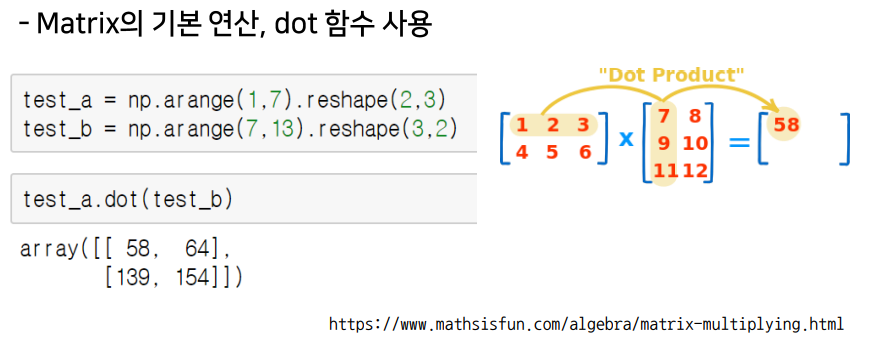
Dot product
transpose

broadcasting
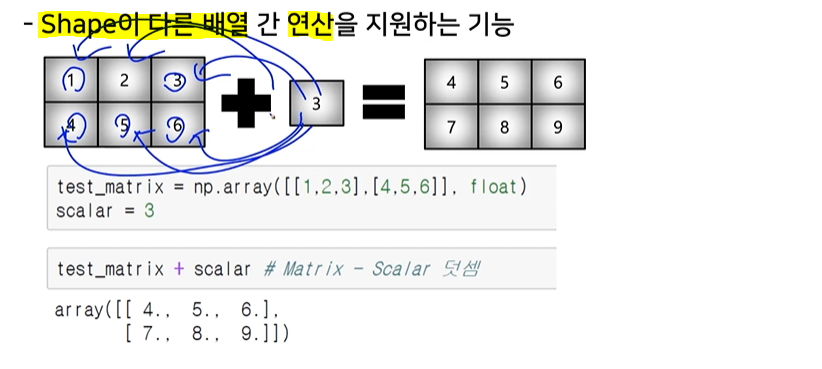
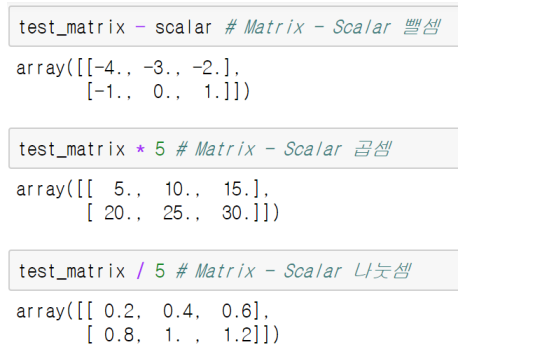
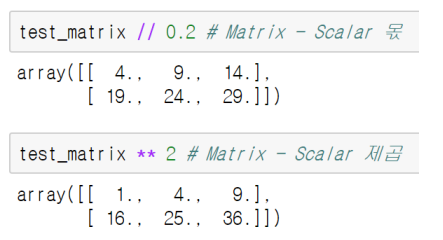
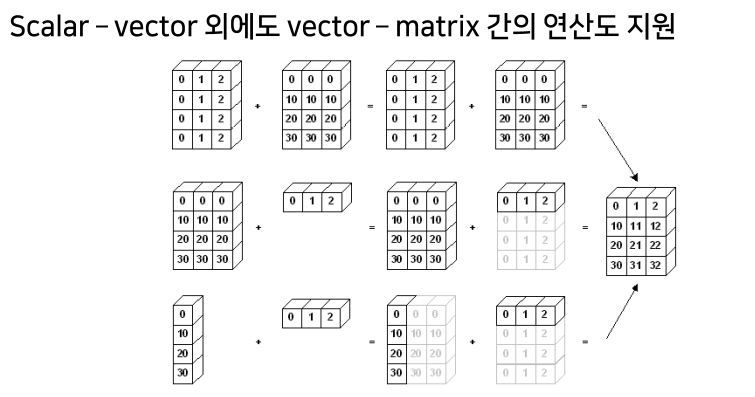 -> 연산시, 주의!
-> 연산시, 주의!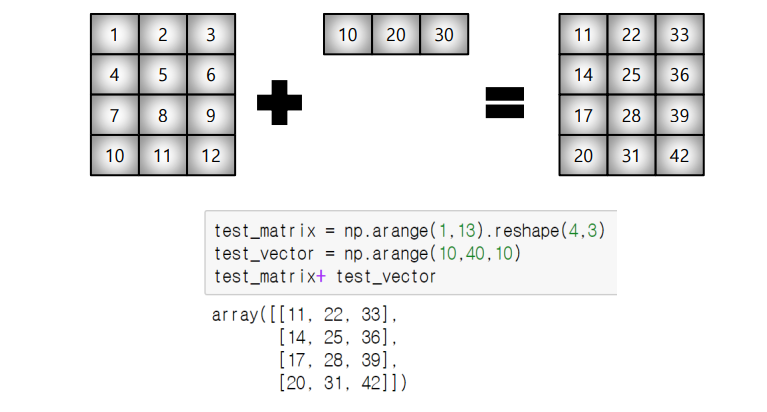
numpy performance


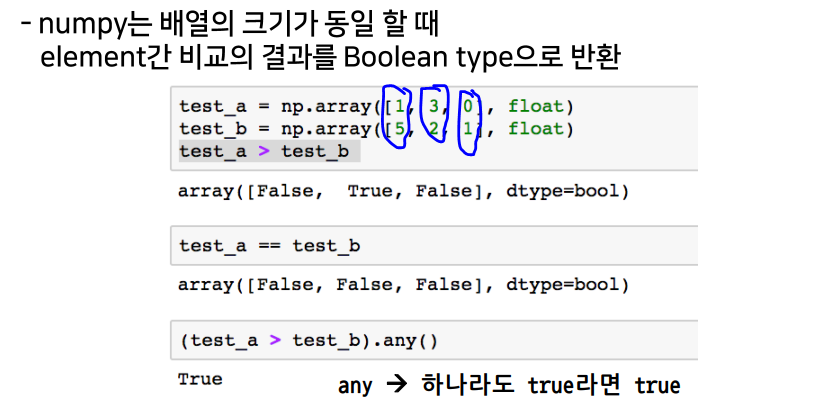
comparisons
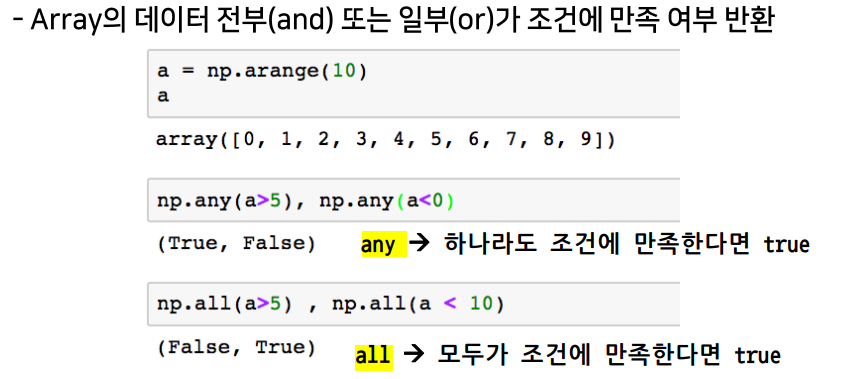
All & Any
comparison operation
broadcasting(shape이 다른 array 간 연산)Element-wise operations(shape이 같은 array의 연산)
-> 두가지 모두 발생

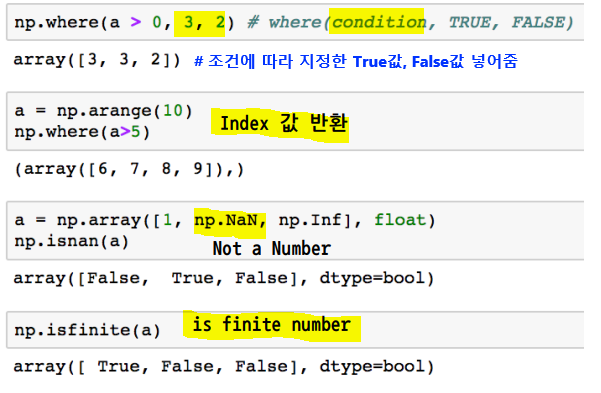
np.where
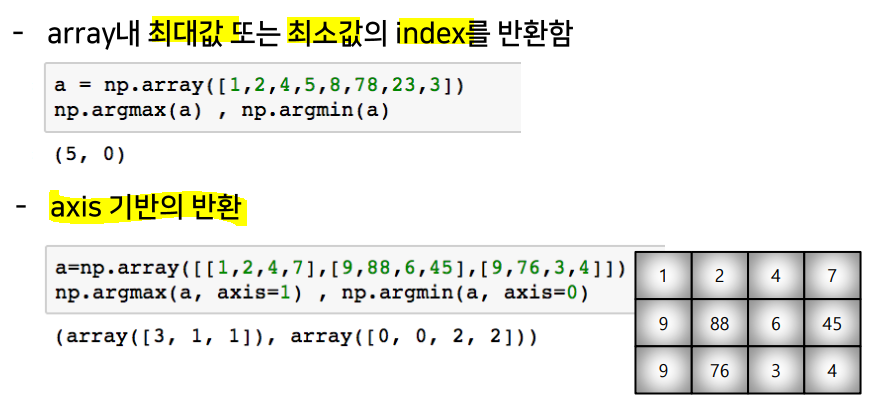
argmax & argmin


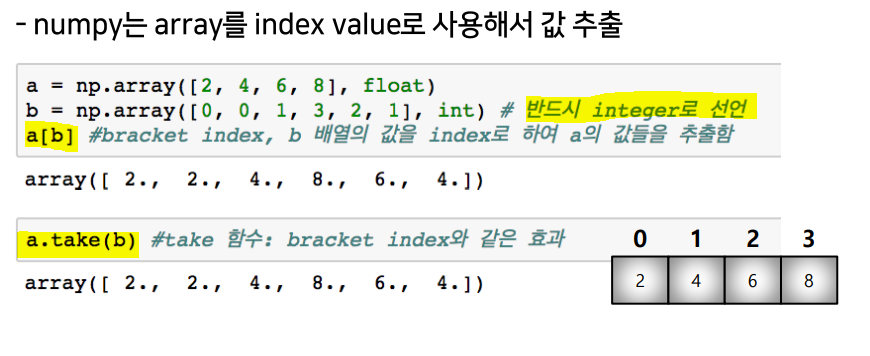
boolean & fancy index
boolean

fancy

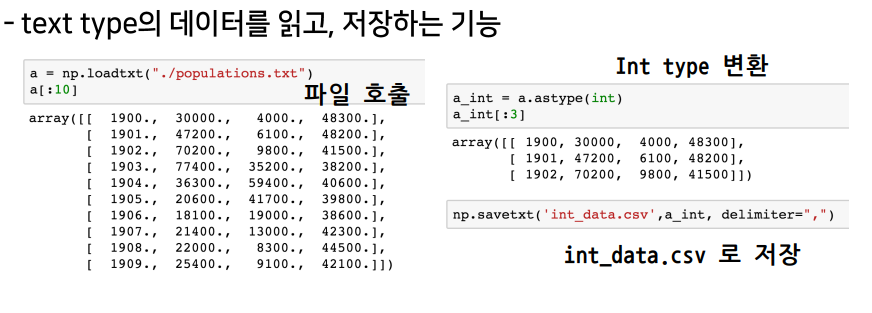
numpy data i/o(in and out)
loadtxt & savetxt
Review
-
numpy 모듈의 호출 :
import numpy as np -
array의 생성 :
np.array(a, int) -
array shape
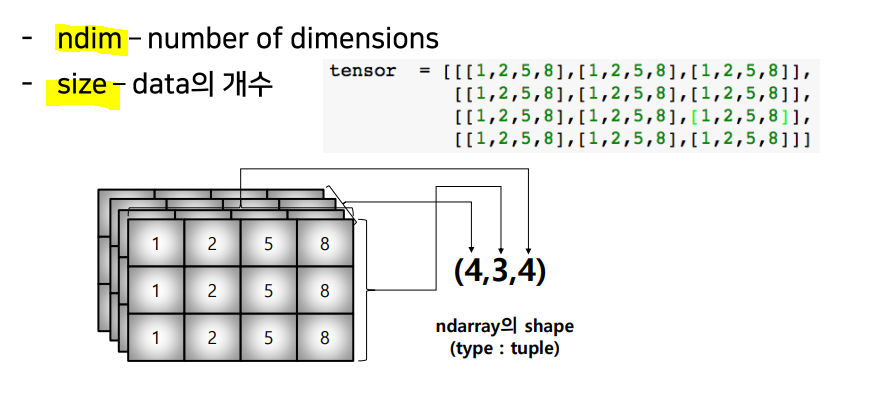
.shape: array(배열)의 크기, 형태 (tuple).ndim: dimensions(차원)의 개수.size: data의 개수
-
numpy dtype
.dtype: data type (이에 따라 memory의 크기가 결정됨).nbytes: 메모리 크기 반환
-
Handling shape
.reshape(): array shape 변경.flatten(): 다차원 -> 1차원indexing: [0,0] or [0][0]slicing: [row:column:step]
-
Creation function
np.arange(start, end, step): 범위 지정하여 값의 list 생성np.zeros(shape=(), dtype, order): 0으로 가득찬 ndarray 생성np.ones(shape=(), dtype, order): 1로 가득찬 ndarray 생성np.empty(shape=(), dtype, order): shape만 주어지고 비어있는 ndarray 생성np.something_like(array): 기존 ndarray의 shape 크기 만큼 1, 0 또는 empty array 반환np.identity(n, dtype): 단위 행렬 생성np.eye(n, m, k, dtype): 대각선이 1인 행렬, k값=시작 indexnp.diag(matrix, k): 대각 행렬의 값 추출np.random: 데이터 분포에 따른 sampling으로 array 생성
-
operation function
axis: 모든 operation function을 실행할 때 기준이 되는 dimension 축sum,mean,std: array의 합, 평균, 표준편차 연산vstack,hstack,concatenate: numpy array를 합치는(붙이는) 함수np.newaxis: array에 새로운 축 추가
-
array operation
+,-,*: array간의 사칙 연산 지원element-wise operations: array간 shape이 같을 때 일어나는 연산.dot(): Matrix의 기본 연산.transpose()/.T: array의 축 바꾸기 (전치행렬)broadcasting: Shape이 다른 배열 간 연산 지원 기능 (Scalar-vector, vector-matrix)%timeit: jupyter환경에서 코드의 퍼포먼스 체크하는 함수
-
Comparisons
np.all(),np.any: array의 데이터 전부(and) 또는 일부(or)의 조건 만족 여부 반환comparison operation: numpy는 배열의 크기가 동일할 때 element간 비교의 결과를 Boolean type으로 반환한다.np.where(condition, TRUE, FALSE): 조건에 따라 테스트한 후 결과는 지정값으로 채워진 array로 반환np.where(condition): Index 값 반환np.isnan(array): NAN인지 아닌지 테스트한 후 결과는 부울 array로 반환np.isfinite(array): 유한 요소 (무한이 아니거나 숫자가 아님)에 대해 요소별로 테스트한 후 결과는 부울 array로 반환np.argmax(),np.argmin(): array내 최대값 또는 최소값의 index 반환boolean index-test_array[test_array > 3]: 조건이 True인 index의 element만 추출fancy index-a[b]/a.take(b)/a[b,c]: array를 index value로 사용해서 값 추출(matrix 형태의 데이터도 가능)
-
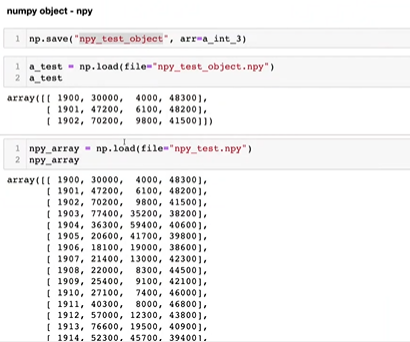
numpy data i/o
np.loadtxt()np.savetxt()np.save()np.oad()
