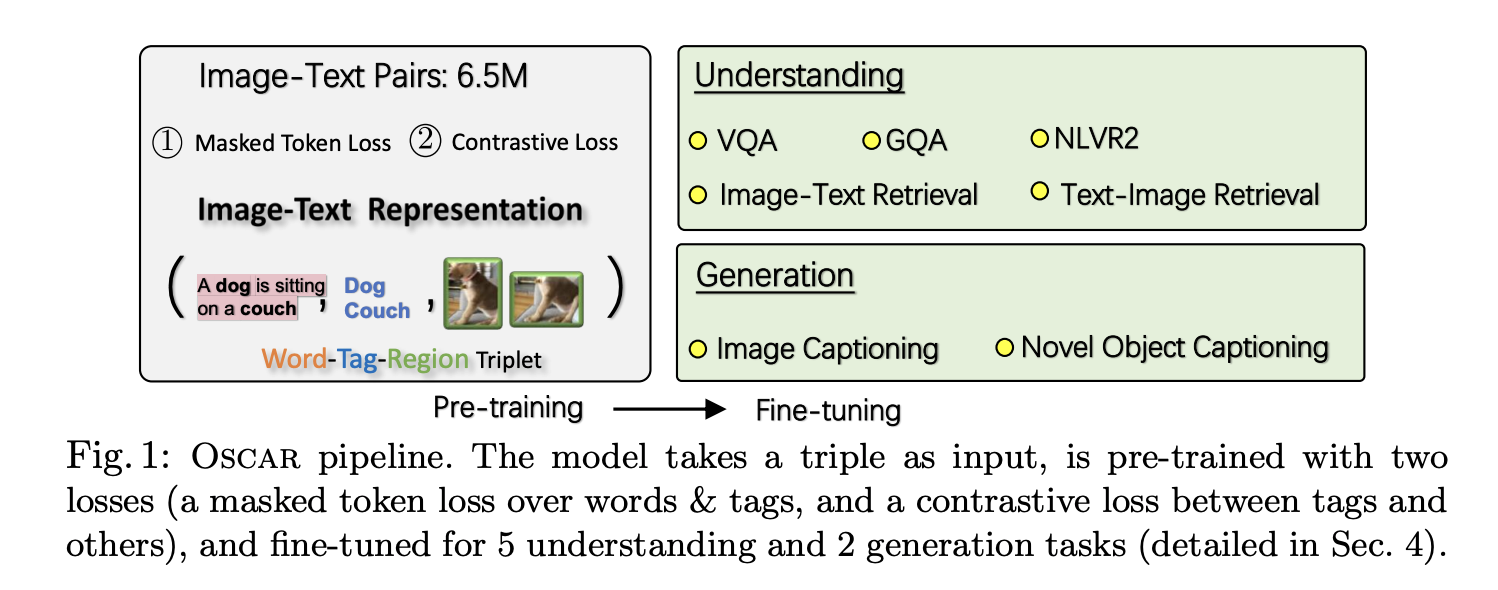
Abstract
- 많은 양의 데이터로 pre-training하는 것은 cross-modal representation을 학습 하는 것에서도 인기가 많다
- 거대한 양의 image-text pair로 pre-training
- 지금까지의 모델들은 단지, image region features와 text features를 단순히 concatenate해서 model의 input으로 넣었지만 Oscar에서는 이 뿐만 아니라 image에서 detected된 object의 tag를 anchor point로 사용하여 input에 넣는다
- 6가지의 vision-language understanding, generation task에서 SOTA를 차지
Introduction
- V+L dataset으로 pre-training + task specific fine-tuning → SOTA
- VLP → multi-layer transformer
- text+image region을 단순하게 input으로 넣는 것은 weakly-supervised learning task
- visual regions over sampled → image regions끼리 겹치는 부분이 생기니까
- 그래서 최근에는 다시 image region이 아닌, image 전체를 사용하는 방향으로 나아가는 경향이 있음
- ex) Pixel-Bert (CNN), VLMo (Vision Transformer)
- Oscar’s Architecture
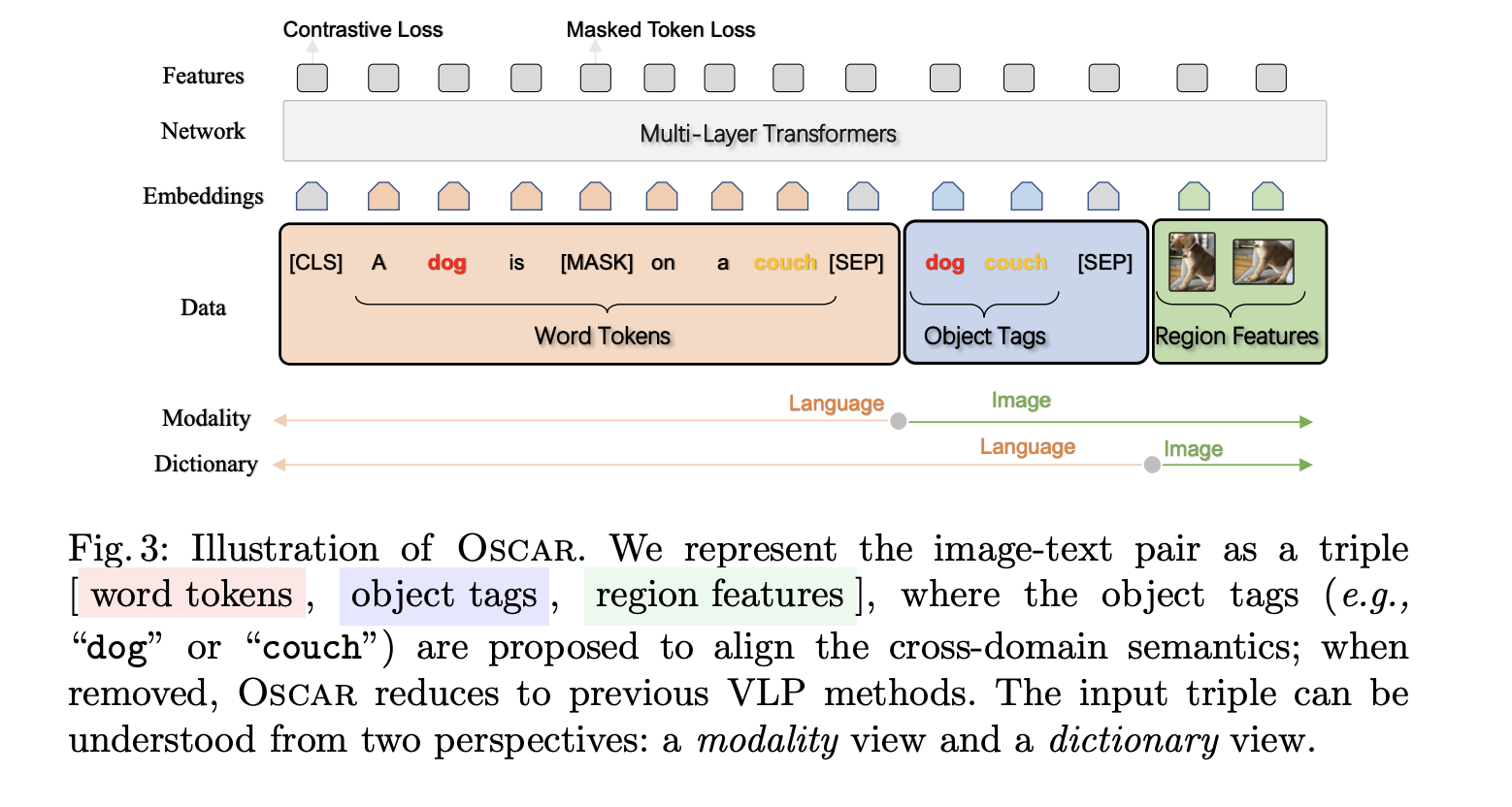
- image에서 detect된 object tag를 anchor points로 사용하는 것이 이 논문의 핵심
- input이 text+object tag+object image
- 이 전에도 object tag를 사용하는 경우가 있었지만, 그건 image regions의 feature representation을 강화하기 위한 목적으로 사용된 것이지, oscar처럼 image-text pair를 학습하기 위한 목적으로 사용된 것은 아님
- Unified vision-language pre-training for image captioning and VQA. AAAI (2020)에도 soft label로 prediction probability가 사용됨, 대응하는 region features에 concat 된 채로
- Contribution
- Oscar
- SOTA
- Object tag가 얼마나 유용한지 많은 실험을 수행했다
- object tag가 유용한 이유?
- 단순히 region image만 사용할 경우, region images끼리는 겹치는 경우가 많음
- 그래서 dog와 couch가 제대로 분리가 안되는 경우가 있는데
- 이를 word embedding space에서는 distinctive 하게 만들 수 있다
- 현재 존재하는 VLP methods의 두가지 이슈
- 우선 VLP는 image-text input을 받아서 multi-layer transformer를 지나는데 이때, cross-modal contextual representation을 만들게 된다
- ambiguity
- faster r-cnn을 사용해서 image region을 추출하는데, 이때 겹치는 구간이 생김
- 이것은 visual embedding을 추출하는데 모호함을 준다
- Lack of grounding
- VLP는 근본적으로 weakly-supervised
- 왜냐하면, image feature와 text feature 사이에, 어떤 explicitly labeled된 alignments가 없음
- 따라서 학습할 때 조금 문제가 될 수 있음
- Oscar에서는 object tag를 anchor points로 사용해서, image-text 사이의 semantic alignments를 학습할 수 있도록 한다
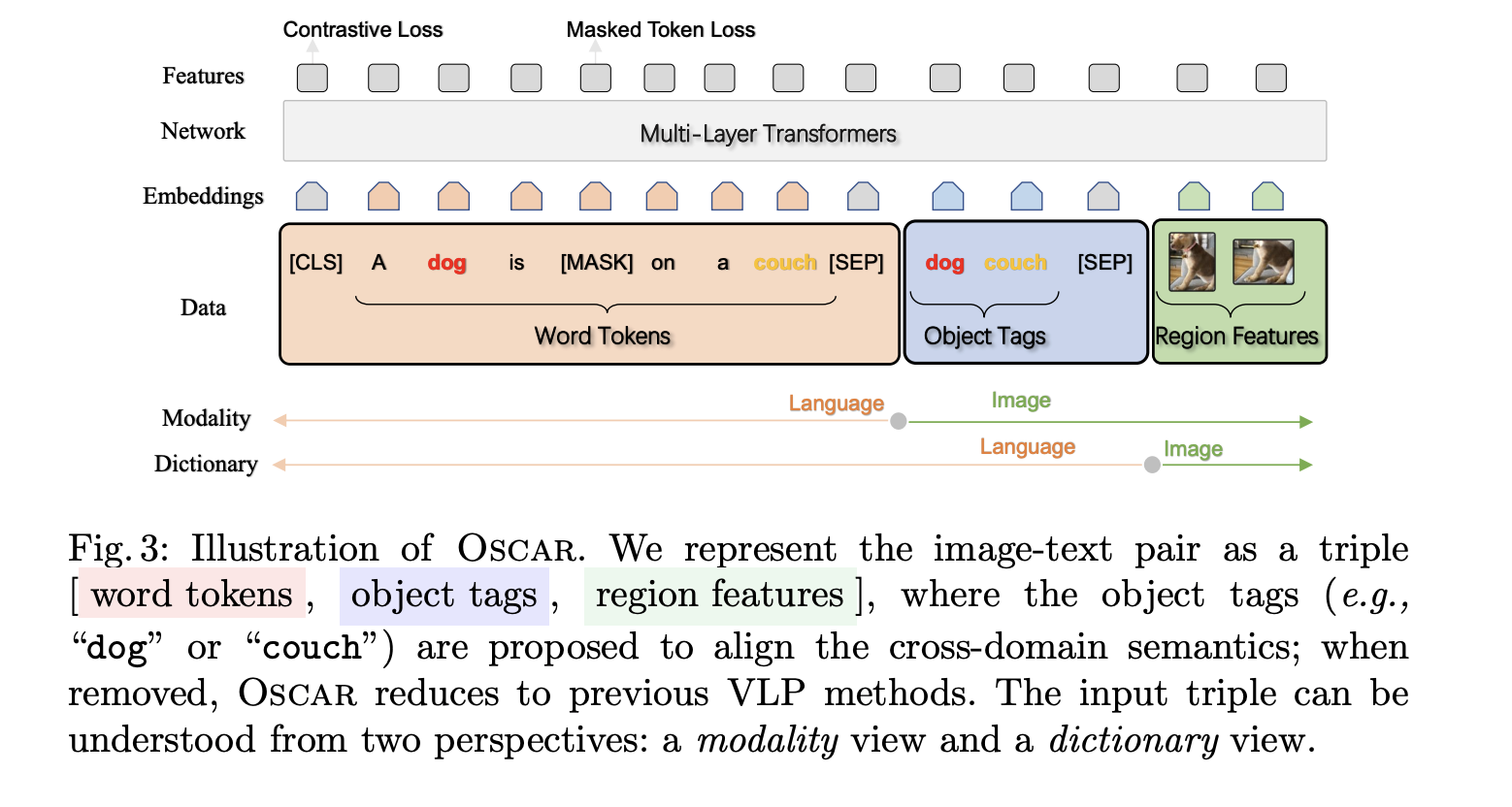
Oscar Pre-training
- Inputs
- (w, q, v)
- w → sequence of word embeddings of the text
- q → anchor points (object tag)
- q, w는 모두 text, pre-trained bert를 사용해서 상대적으로 identified하기가 쉬움
- v, q는 주어진 image에서 K regions의 object가 사용됨
- 추출하는데 Faster R-CNN이 사용됨
- 각각의 region을 (v’, z)로 추출함
- region featuer v’은 p dimensional vector (p=2048)
- region position z는 R dimensional vector (r=4, 6)^3
- v’과 z를 concat해서 position-sensitive region feature vector를 만든다
- 이거를 v로 linear projection해서 word embedding과 같은 vector dimension을 가지도록 한다
- q는 object tag의 sequence of word embedding
- v를 추출했던 것과 같은 Faster R-CNN으로 추출
- Pre-Traning Objective
- modality view → [w, (q,v)] → distinguish representation between a text and image
- dictionary view → [(w,q), v] → distinguish two different semantic spaces
- dictionary view → Masked Token Loss을 사용
- object tag와 word tokens은 같은 linguistic semantic space를 공유, 반면에 image region features는 visual semantic space에 놓여 있다
- pre-training시에, discrete token sequence h = [w,q]의 일부를 mask token으로 대체, all image feature, tokens h를 가지고 mask를 예측 → BERT와 비슷
- modality view → Contrastive Loss
- h’ = [q,v]
- q의 절반을 dataset D에서 임의로 샘플링한 다른 tag seq로 대체
- special token [CLS]에서의 encoder output이 (h’, w) fused vision-language representation이 되고, 우리는 binary classifier로 FC layer를 적용을 함
- (h’, w)가 원래 image representation을 가지면 1 아니면 0으로 loss를 계산
- 그래서 cross-modal pre-training 동안, object tag를 BERT의 word embedding space를 이것과 paired된 image와 비슷해지게 조절하는 image와의 proxy역할을 하도록 한다
- polluted된 것 과는 멀리 떨어지도록 한다
- full pre-training objective of Oscar
- L(Pre-training) = L(MTL) + L(C)
- 두가지 이유로 두개의 loss를 사용함
- 각각의 loss는 이것 자신의 관점에서 representative learning signal을 제공함
- 비록 전체적인 loss가 기존의 VLP보다 훨씬 간단함에도 불구하고, 훨씬 더 좋은 성능을 낸다
Adapting to V+L Tasks
- Image-Text Retrieval
- image retrieval
- text retrieval
- training
- binary classification problem
- image-text pair가 주어졌을 때
- 랜덤하게 image, text 하나만 주어지고, 나머지 하나를 만들어 내는 것으로 학습을 진행
- CLS 토큰의 마지막 representation이 classifier의 input으로 들어가서, pair가 맞는 지 확인
- Testing
- query로 들어간 image-text pair를 rank하는데 probability score가 사용
- top-k개의 결과가 나오도록
- Image Captioning
- training
- seq2seq objective를 사용해서 fine-tuning
- inputs은 triples
- caption의 15%를 랜덤하게 masking, mask된 token을 예측하는 것으로 학습
- VLP와 비슷하게 self-attention mask는 caption token이 오직 이전의 tokens에게만 attend하도록, uni-directional generation process를 가지도록 함
- testing
- image regions, object tags, CLS token을 encoding
- mask를 씌우고, likelihood 기반의 vocabulary로부터 token을 sampling
- 그 후, 이전 input의 mask token을 sampling한 vocab으로 대체, 다시 일부를 mask token으로 씌움
- model이 stop token을 output으로 내뱉을 때, generation termination
- Novel Object Captioning (NoCaps)
- Extension of image captioning task
- detection annotations는 가지지만, caption corpora에서 나타나지는 않는 objects를 novel objects라고 부르고, 이것이 포함된 image의 caption을 다는 task를 novel object captioning이라고 부름
- image captioning model의 in the wild generality performance를 측정할 수 있다
- open image dataset으로부터 image에 대한 benchmark를 제공
- training corpus에서 보지 못한 novel objects를 기술하는 것의 model capacity를 test함
- VQA
- image에 기반한 natural language questions에 답을 하는 task
- input으로 question, object tags, region features를 concat
- CLS output이 task-specific linear classifier for answer prediction으로 들어간다
- 그 후 사람의 대답과 비교해서 soft target score를 낸다
- 이것을 통해, cross-entropy loss를 계산한다
- GQA
- VQA와 비슷한 task인데, visual reasoning을 좀 더 강조하는 task
- NLVR2
- image-natural language pair에 대해서, natural language가 정말로 image를 잘 표현하고 있는지 결정하는 task
- 두개의 input을 만들어냄, 각각은 주어진 sentence와 image
- 두 개의 CLS output은 concat되어 binary classifier의 joint input으로 들어감
- object tags의 효과
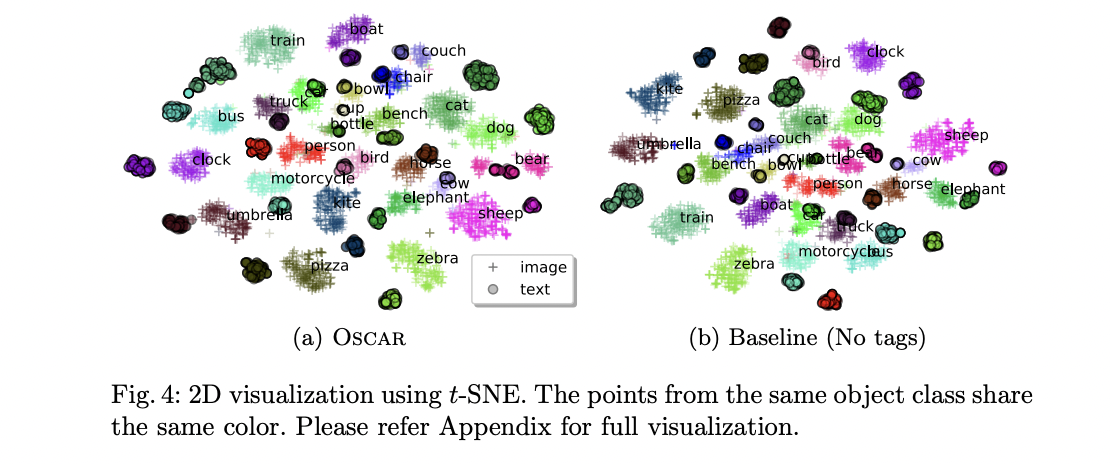
- tag를 쓰지않을 때, object detector로 뽑은 tag를 사용할 때, ground truth tag를 사용할 때 세 가지 경우로 실험을 진행했을 때, 확실히 tag를 썼을 때, 그 중에서도 ground truth tag를 사용했을 때 성능 향상을 보였다
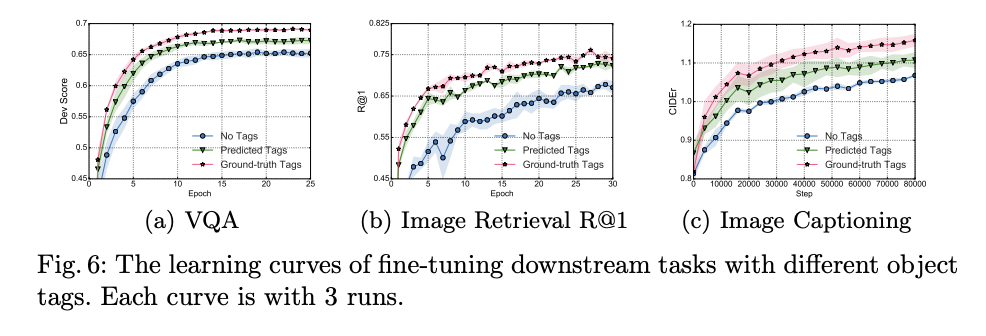
- 단 feature 자체로 사용되었을 때, 약간의 성능 향상을 보였다. 이로 알 수 있는 사실은, object tag는 두 modality 사이의 어떤 이질성을 서로 연결해주는 anchor point의 역할을 하는데 더 큰 의의가 있다고 할 수 있다.
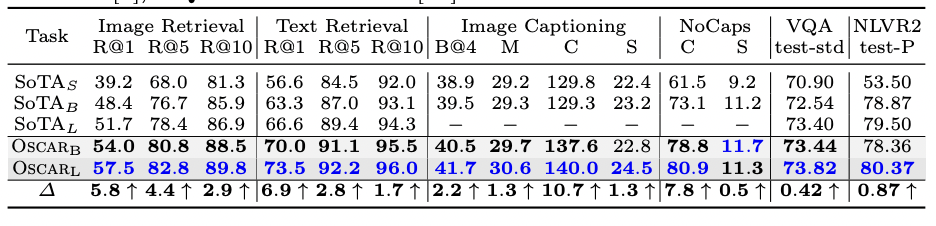
- visual genome dataset이 Open image dataset에 비해 더 다양한 object를 가지고 있기 때문에, 학습을 통한 성능이 더 높게 나타났다
Conclusion
- object tags를 anchor points로 사용하여 natural language와 image 사이의 다른 modality를 같은 semantic space에 두어 모델 성능을 향상하려는 시도를 보여준 Oscar를 소개함
- Oscar는 다양한 V+L task에서 SOTA를 차지






