

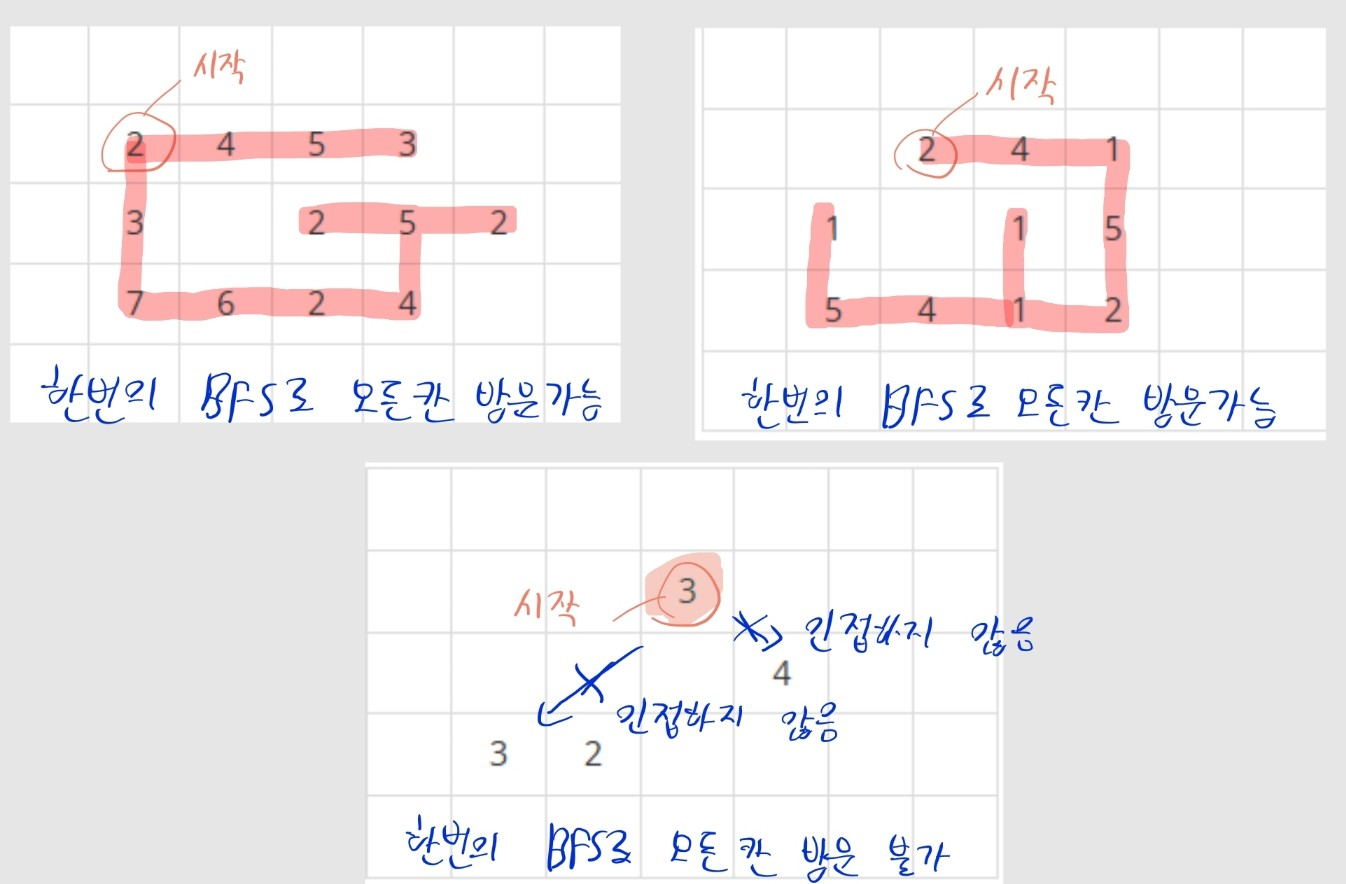
생각해봅시다!
- 남아있는 빙산이 두 덩어리로 분리되어 있는지 어떻게 확인할 수 있을까요?
- 일단 좌표 문제니까, 각 칸을 노드, 각 칸 사이사이를 간선이라고 생각해야 합니다.
- 빙산의 각 칸을 순회하면서, 방문하지 않은 칸인 경우 DFS / BFS를 시도합니다.
- 본 풀이에선 BFS를 사용하겠습니다.
- 한 번의 BFS로 남아 있는 빙산 칸 전체를 방문할 수 있으면, 빙산은 한 덩어리만 존재합니다.
- 한 번의 BFS로 방문이 불가능하면, 빙산이 둘 이상으로 분리되었다는 뜻입니다.
- 정직하게 BFS 하면서 빙산의 높이를 줄이는 과정을 반복하면 됩니다. 정직한 빡구현 문제입니다.
입력 받기
from collections import deque, defaultdict
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
N, M = map(int, input().split())
grid = []
# 2차원배열 입력받기
for _ in range(N):
grid.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
dy = [0, -1, 0, 1]- 이제는 꽤나 익숙해졌을 2차원 배열 문제입니다. 잘 입력받아 줍시다.
grid[x][y]는x행y열의 빙산 높이 정보를 저장합니다.
BFS
def bfs(sx, sy, visited, memo):
queue = deque([(sx, sy)])
visited[sx][sy] = True
while queue:
x, y = queue.popleft()
for i in range(4):
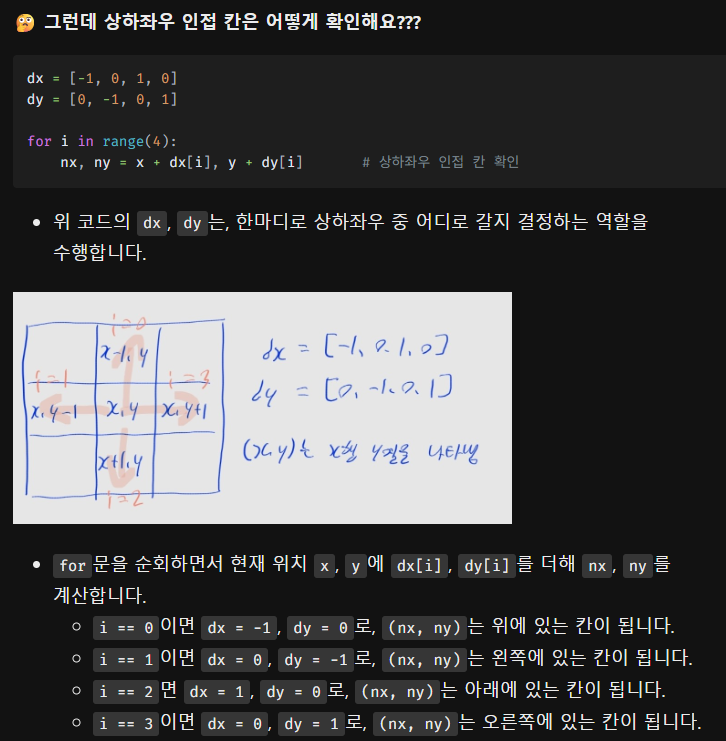
# 상, 하, 좌, 우 인접 칸
nx, ny = x + dx[i], y + dy[i]
# 범위를 안 벗어나는지
if 0 <= nx < N and 0 <= ny < M:
# 빙산이 아직 안 녹았는지
# + 아직 미방문했는지 확인
if grid[nx][ny] >= 1 and not visited[nx][ny]:
visited[nx][ny] = True
queue.append((nx, ny))
# 인접 칸에 바다가 있으면 체크
elif grid[nx][ny] == 0:
memo[(x, y)] += 1- BFS를 수행하는
bfs함수를 작성해봅시다. 단 이 문제에 맞게 약간 수정을 해야 합니다.
매개변수
sx,sy는 BFS의 시작점입니다.visited는 2차원 리스트로,visited[x][y]로 각 칸의 방문 여부를TrueorFalse로 저장합니다.- 그리고 이 문제에선, 각 빙산 칸의 높이는 바다(
0)와 인접한 방향 수만큼 줄어듭니다.- BFS를 하는 과정에서, 각 빙산 칸이 바다와 접한 횟수도 카운트해야 합니다.
- 이 역할을 하는
memo는 딕셔너리로, 키는(x좌표, y좌표), 값은인접한 '0'이 저장된 칸의 수입니다. 즉 줄어들 높이를 저장하는 겁니다. memo는defaultdict(int)로 지정했습니다.defaultdict는 키가 없을 때 자동으로 0의 값을 부여해 줘서 편합니다.
함수 구현
- 일단 인접 노드를 체크하는 대신 인접 칸을 체크해야 합니다.
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0], dy = [0, -1, 0, 1]의 각 원소를 순회하며- 원래 위치인
x행y열에 값을 더해주는 식으로 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 좌표 범위를 안 벗어났는지, 아직 미방문한 칸인지 체크하는 건 기본이고
- 여기선 추가로 빙산이 아직 안 녹아 존재하는 칸인지도 확인합니다.
- 빙산의 높이 정보가 저장된
grid[nx][ny] >= 1인지 체크하면 됩니다.
- 그리고 인접한 칸에
0이 저장된 칸이 있다면- 키가
(현재 칸 x좌표, 현재 칸 y좌표)인 값에 1을 더해 줍니다.
- 키가
정답 구하기
def get_answer():
# 현재 경과한 시간
time = 0
while True:
# 빙산 덩어리 수
count = 0
# bfs 함수에 매개변수로 보낼 visited, memo
visited = [[False] * M for _ in range(N)]
memo = defaultdict(int)
# 각 칸을 순회하며
# 빙산이 남아 있는데 미방문한 칸이 있으면 BFS 수행
for x in range(N):
for y in range(M):
if grid[x][y] >= 1 and not visited[x][y]:
count += 1
# BFS를 한 번 수행했는데 남은 칸이 있는 경우
# 덩어리가 2개 이상 -> 정답 반환
if count >= 2:
return time
bfs(x, y, visited, memo)
# 모든 얼음이 녹아 BFS가 실행되지 않은 경우, 정답 0 반환
if count == 0:
return 0
# memo에 저장한 대로, 각 칸의 높이를 줄이기
# 단 0보다 줄어들을 순 없음
for x, y in memo:
grid[x][y] = max(grid[x][y] - memo[(x, y)], 0)
# 시간을 1 증가
time += 1
print(get_answer()) - 이제 BFS 코드를 구현했으니, 실제로 매 초 빙산을 녹이면서 몇 덩어리인지 확인할 수 있습니다. 이 역할을 하는
get_answer함수를 작성해봅시다. - 우린 몇 초에 빙산이 2개 이상으로 나눠지는지 구해야 합니다. 이를 저장할
time변수를 0으로 초기화해 줍니다.while True문으로 BFS 수행 -> 얼음 높이 줄이기 -> 1초 늘리기를 반복합니다.
- 각 칸을 순회하며, 미방문했으면서 빙산이 남아 있는(
grid[x][y] >= 1) 칸을 만나면 BFS를 수행합니다.- 이때
count로 BFS 실행 횟수를 계산합니다. - 만약 BFS가 2번 이상 발생하면, 덩어리가 2개 이상 존재한다는 뜻이니 바로 정답인
time을 반환합니다.
- 이때
- 문제에서 빙산의 모든 칸이 녹은 경우
0을 반환하라고 지시했습니다.- 이 경우 BFS가 한 번도 실행되지 않아
count가0이 되는데, 이 때는0을 반환합니다.
- 이 경우 BFS가 한 번도 실행되지 않아
- BFS 수행 이후엔,
memo에 저장한 대로 각 칸의 높이를 줄입니다.- 단
0보다 더 낮게 줄일 순 없게 합니다.
- 단
- 이 과정이 종료되면, 시간을 1 증가시키고, 반환할 때까지 무한반복하면 됩니다.
풀이
from collections import deque, defaultdict
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
N, M = map(int, input().split())
grid = []
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
dy = [0, -1, 0, 1]
for _ in range(N):
grid.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
def bfs(sx, sy, visited, memo):
queue = deque([(sx, sy)])
visited[sx][sy] = True
while queue:
x, y = queue.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx, ny = x + dx[i], y + dy[i]
if 0 <= nx < N and 0 <= ny < M:
if grid[nx][ny] >= 1 and not visited[nx][ny]:
visited[nx][ny] = True
queue.append((nx, ny))
elif grid[nx][ny] == 0:
memo[(x, y)] += 1
def get_answer():
time = 0
while True:
count = 0
visited = [[False] * M for _ in range(N)]
memo = defaultdict(int)
for x in range(N):
for y in range(M):
if grid[x][y] >= 1 and not visited[x][y]:
count += 1
if count >= 2:
return time
bfs(x, y, visited, memo)
if count == 0:
return 0
for x, y in memo:
grid[x][y] = max(grid[x][y] - memo[(x, y)], 0)
time += 1
print(get_answer()) 시간 복잡도
- 매 초마다 빙산의 모든 칸을 1번씩 들리므로,
- 빙산이 모두 녹을 때까지 초가 소요되므로, 최종 .
- 사실 빙산이 언제 다 녹을 지 모르니까... 실제로 몇 번 반복할 진 알 수 없음.
- 하지만 이 풀이가 정답 처리됐으니 문제 없겠지.
기억할 점
- 빡구현 문제는 끈기가 필요하다.
