프로토타입과 클래스
JavaScript는 프로토타입 기반 언어
프로토타입: 원형객체
class Human {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
sleep() {
console.log(`${this.name}은 잠에 들었습니다`);
}
}
let kimcoding = new Human('김코딩', 30);
Human.prototype.constructor === Human; // true
Human.prototype === kimcoding.__proto__; // true
Human.prototype.sleep === kimcoding.sleep; // trueHuman 이라는 클래스와 인스턴스, 그리고 프로토타입의 관계
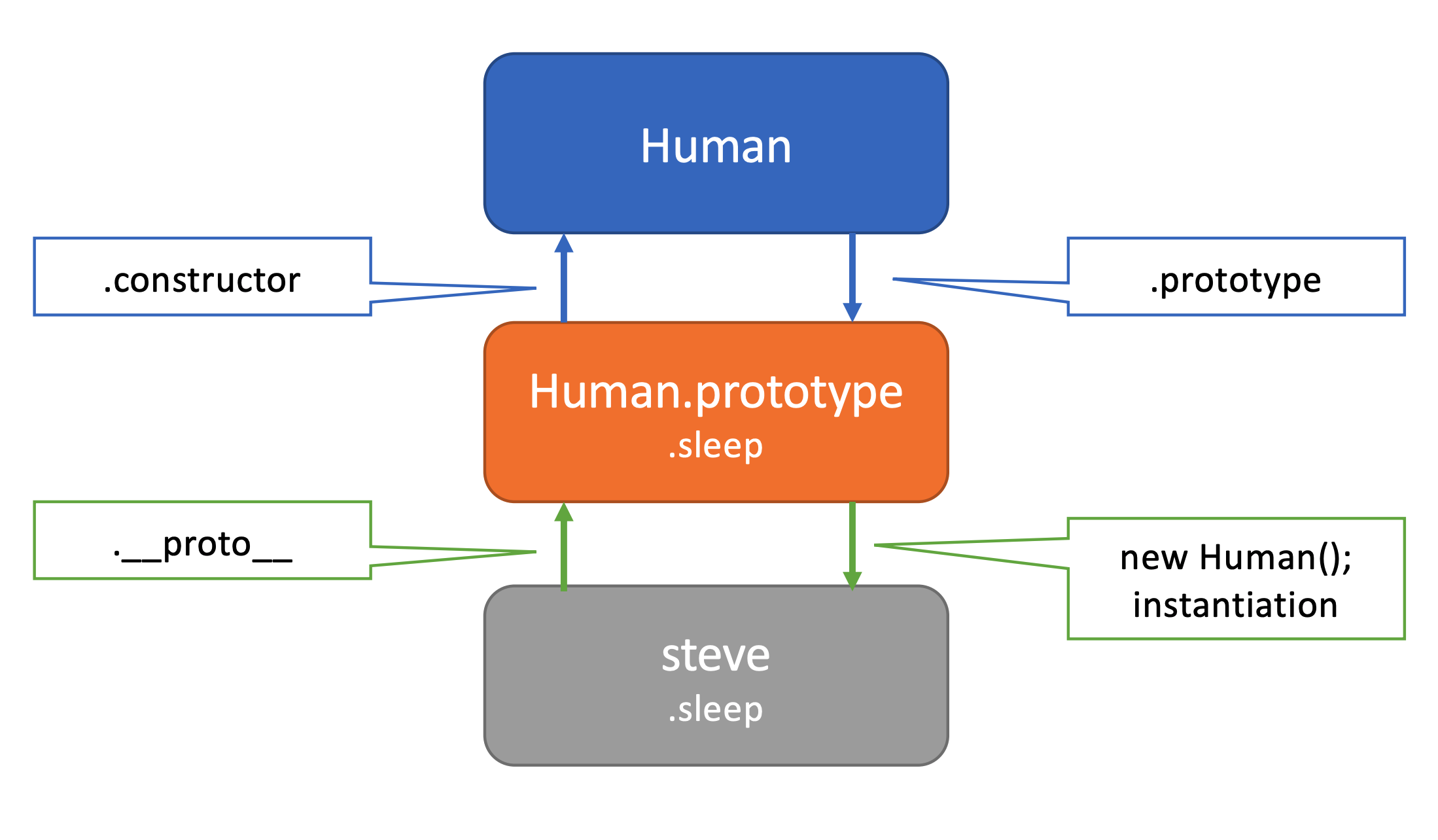
→ 클래스 Human과 인스턴스 steve, 프로토타입의 관계
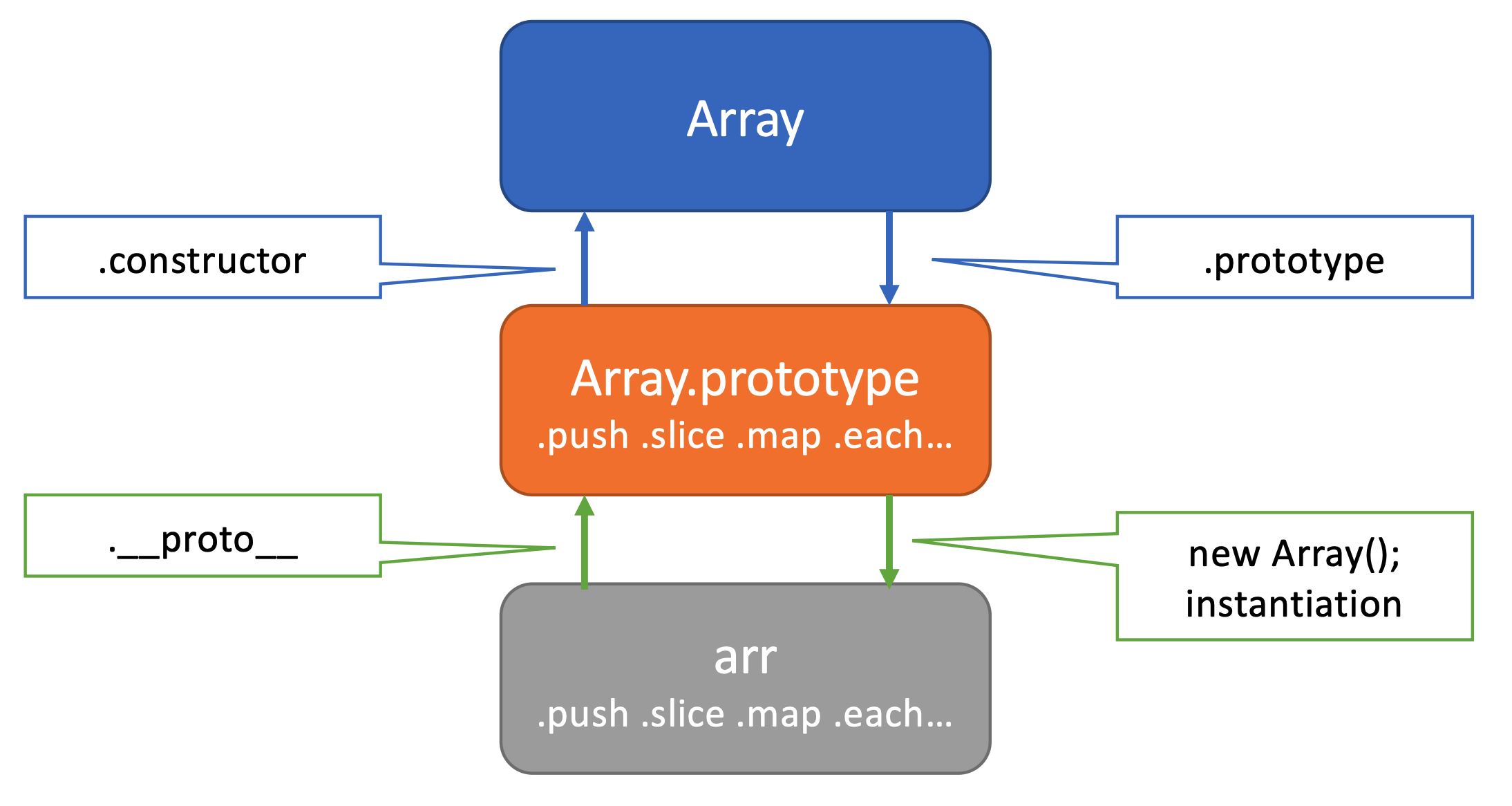
Array(배열) 클래스와 인스턴스, 그리고 프로토타입의 관계
배열 역시 원리가 동일
배열은 Array 클래스의 인스턴스이며, 프로토타입에는 다양한 메서드가 존재
프로토타입 체인
상속을 javascript에서 구현할때 프로토타입 체인을 사용한다.
클래스 Human의 메서드와 속성을 객체로 구현하면
let kimcoding = new Human('김코딩', 30);
// 속성
kimcoding.age;
kimcoding.gender;
// 메서드
kimcoding.eat();
kimcoding.sleep();클래스 Student 는 Human의 기본적인 메서드를 상속 받을 수 있다.
학생이기에 추가적인 특징 필요
let parkhacker = new Student('박해커', 22);
// 속성
parkhacker.grade;
parkhacker.age;
// 메서드
parkhacker.learn();
parkhacker.eat();age ,gender 속성 존재. Student는 Human 의 특징을 그대로 물려받는다.
부모 클래스(Human): 속성과 메서드를 물려주는 클래스
자식 클래스(Student): 속성과 메서드를 물려받는 클래스
→ 상속 과정
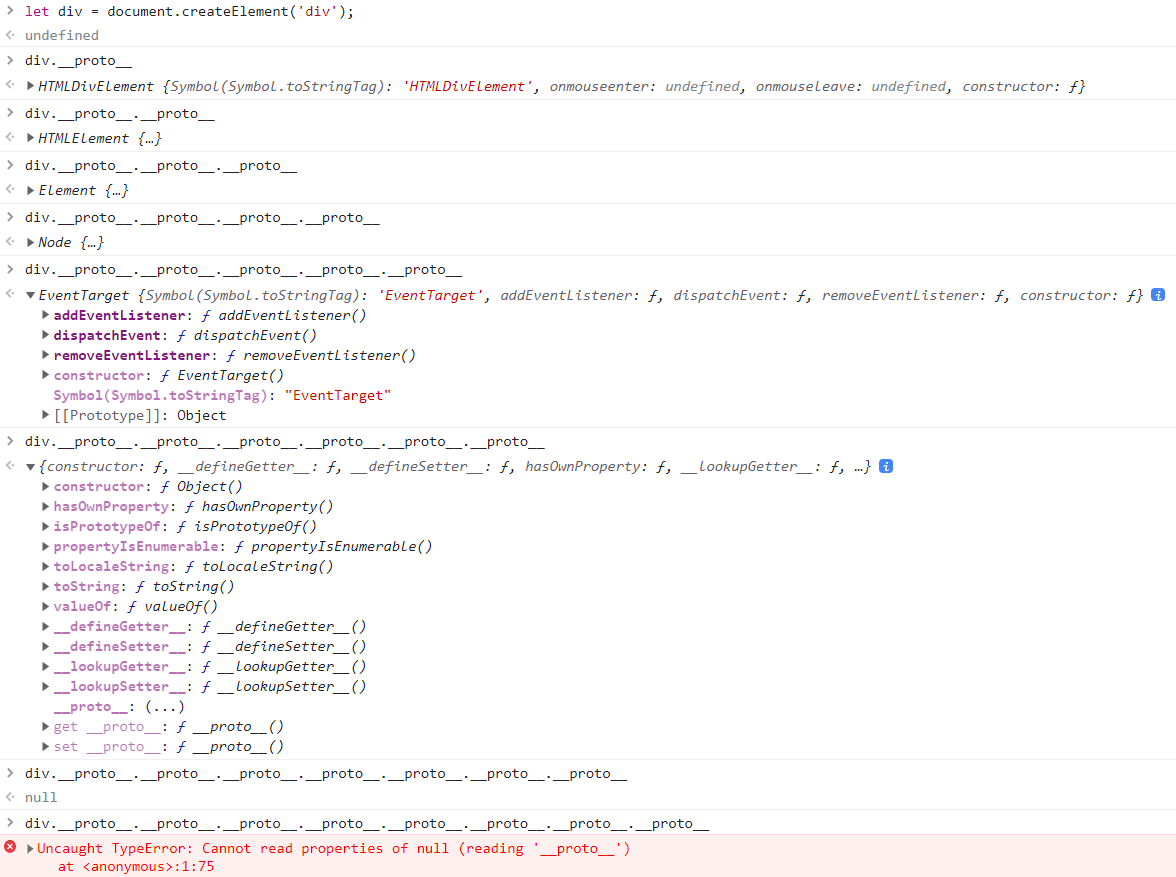
DOM과 프로토타입
DOM 엘리먼트는 innerHTML과 같은 속성, 또는 append()와 같은 메서드가 있다.
각각의 엘리먼트가 해당 메서드나 속성이 있다 → Element라는 공통의 부모를 가지고 있다.
EventTarget의 부모는 모든 클래스의 조상인 Object
인스턴스의 __proto__ 를 이용하면 확실하게 확인 가능
__proto__ 를 이용하면 부모클래스의 프로토타입, 혹은 ‘부모의 부모 클래스’의 프로토타입 탐색 가능