🖇️ Matplotlib
파이썬의 대표 시각화 도구
plt로 많이 네이밍하여 사용
Jupyter Notebook 유저의 경우 matplotlib의 결과가 out session에 나타나는 것이 유리하므로 %matplotlib line 옵션을 사용
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
from matplotlib import rc
rc("font", family="Malgun Gothic")
get_ipython().run_line_magic("matplotlib", "inline")
# black 권고: 아마 정식 코드로 호출해서 사용하라는 의미
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 3, 5, -1, 3])
## x축 , y축
plt.show()⇊

─ 삼각함수 그리기
- numpy의 sin함수 가져오기
- np.arange(a,b,s): a부터 b까지의 s의 간격
- np.sin(value)
- 그래프의 결과가 중요한 경우 그래프를 그리는 코드를 def()로 작성
- 나중에 별도의 셀에서 그림만 나타낼 수있기 때문
import numpy as np
t = np.arange(0, 12, 0.01)
y = np.win(t)def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))#배경 사이즈 설정( 가로축 크기, 세로축 크기)
plt.plot(t, np.sin(t), label="sin")
plt.plot(t, np.cos(t), label="cos")
plt.grid() #격자무늬
plt.legend() #범례.legend(loc="upper right") 위치를 바꾸고 싶다면 legend()안에 loc=''입력
plt.xlabel("time")
plt.ylabel('Amplitude') #진폭
plt.title("Example of sinewave")
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊
t = np.arange(0, 5, 0.5)
def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.plot(t, t, "r--") ##r--: 빨간 점선
plt.plot(t, t ** 2, "bs") #bs=blue squared
plt.plot(t, t ** 3,"g^") ##g^ : green으로 위로 뾰족한 삼각형
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊
t =[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
y = [1, 4, 5, 8, 9, 5, 3]
#다양한 스타일 지정 가능
def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(
t,
y,
color="green",
linestyle="dashed",
marker="o",
markerfacecolor="blue",
markersize=12)
plt.xlim([-0.5, 6.5]) #X축 범위
plt.ylim([0.5, 9.5]) #y축 범위
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊

t = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
y = np.array([9, 8, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 4, 3, 4])
#scatter는 점을 뿌리듯이 그림
def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.scatter(t, y)
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊

colormap = t
#colormap 적용 가능
def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.scatter(t, y, s=50, c=colormap, marker=">")
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊

─Pandas에서 plot 그리기
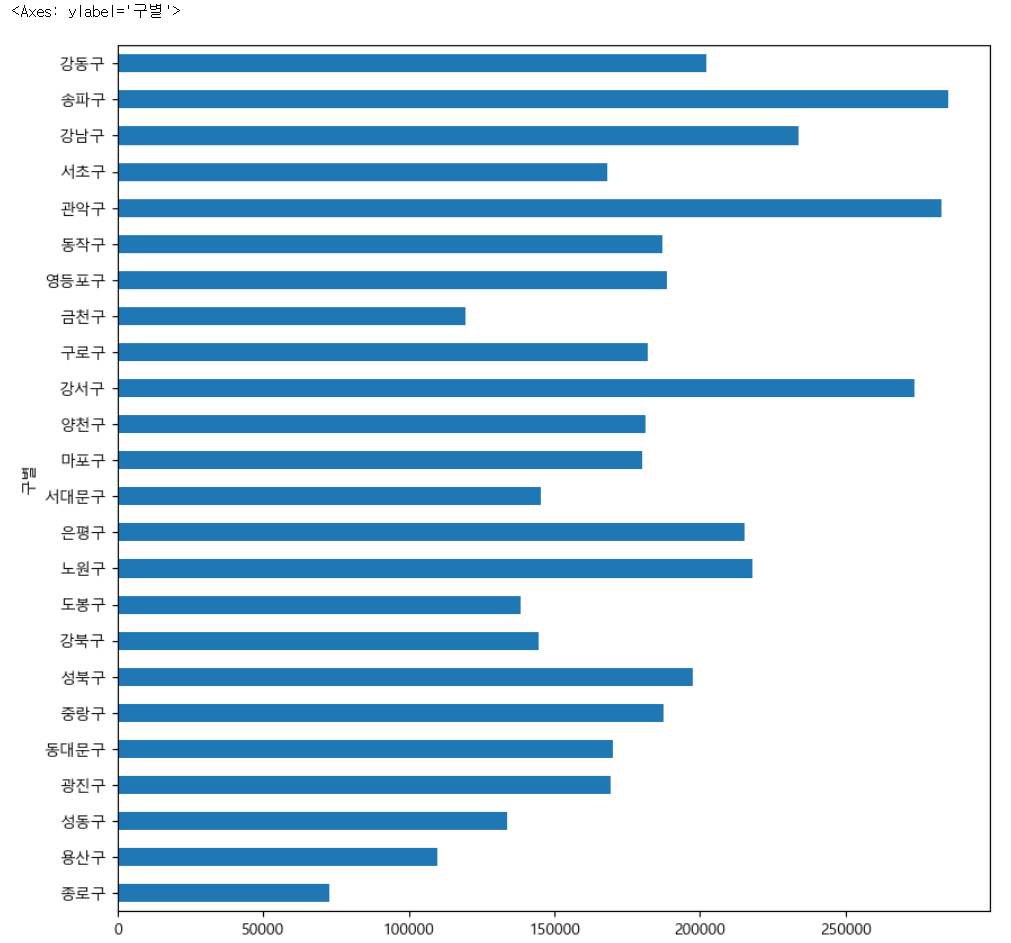
data_result["인구수"].plot(kind="bar", figsize=(10, 10))⇊

data_result["인구수"].plot(kind="barh", figsize=(10, 10)) #h=horizon 수평선⇊
🖇️ 데이터 시각화
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
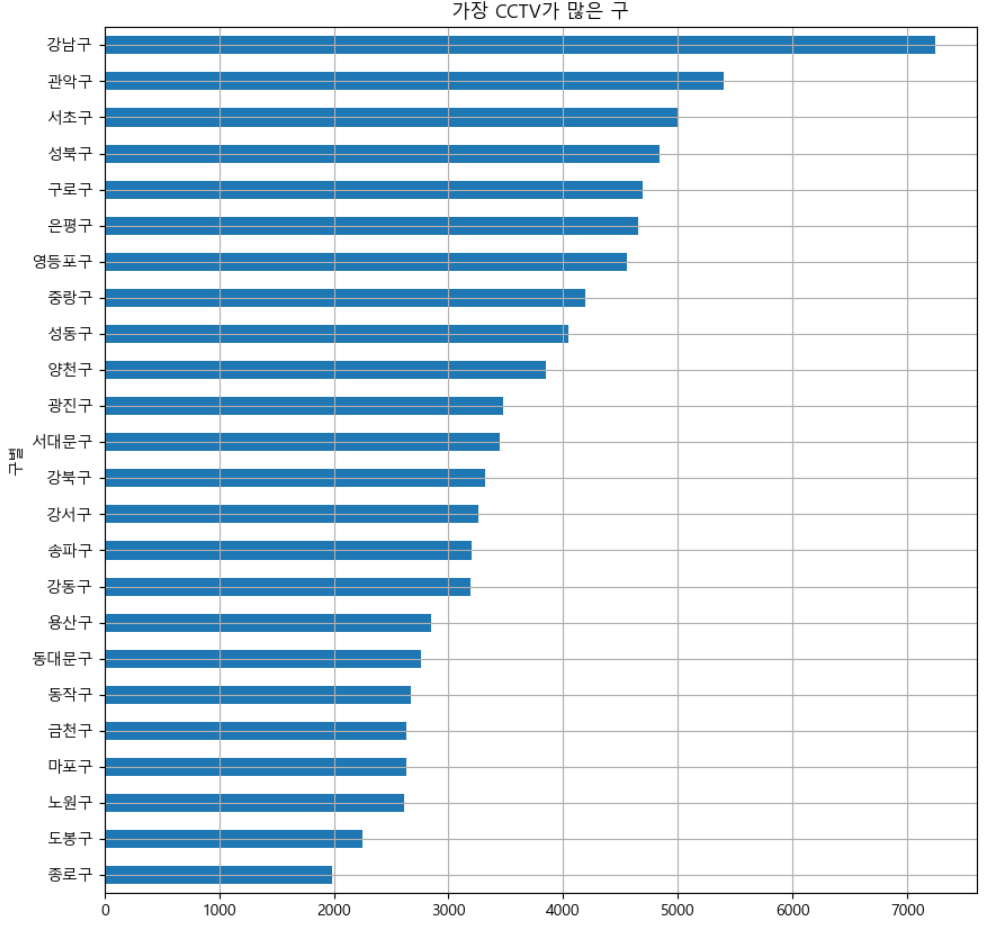
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False #마이너스 부호 때문에 한글이 깨질 수 가 있어 주는 설정- CCTV가 많은 구 순으로 시각화
def drawGraph():
data_result["총계"].sort_values_().plot(
kind="barh",
grid=True,
title="가장 CCTV가 많은 구",
figsize=(10, 10)
)drawGraph()⇊
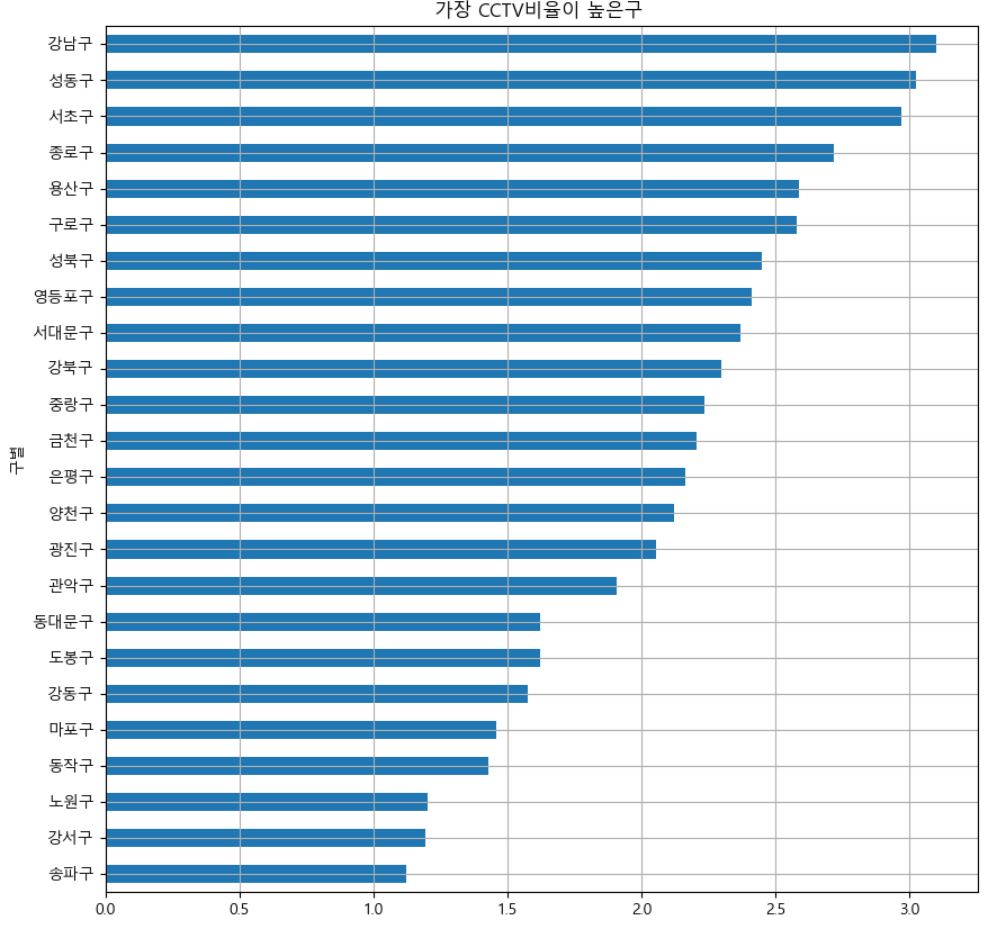
- CCTV 비율이 인구대비 가장 높은 구 순으로 시각화
def drawGraph():
data_result["CCTV비율"].sort_values().plot(
kind="barh",
grid=True,
title="가장 CCTV비율이 높은구 ",
figsize=(10, 10));drawGraph()⇊
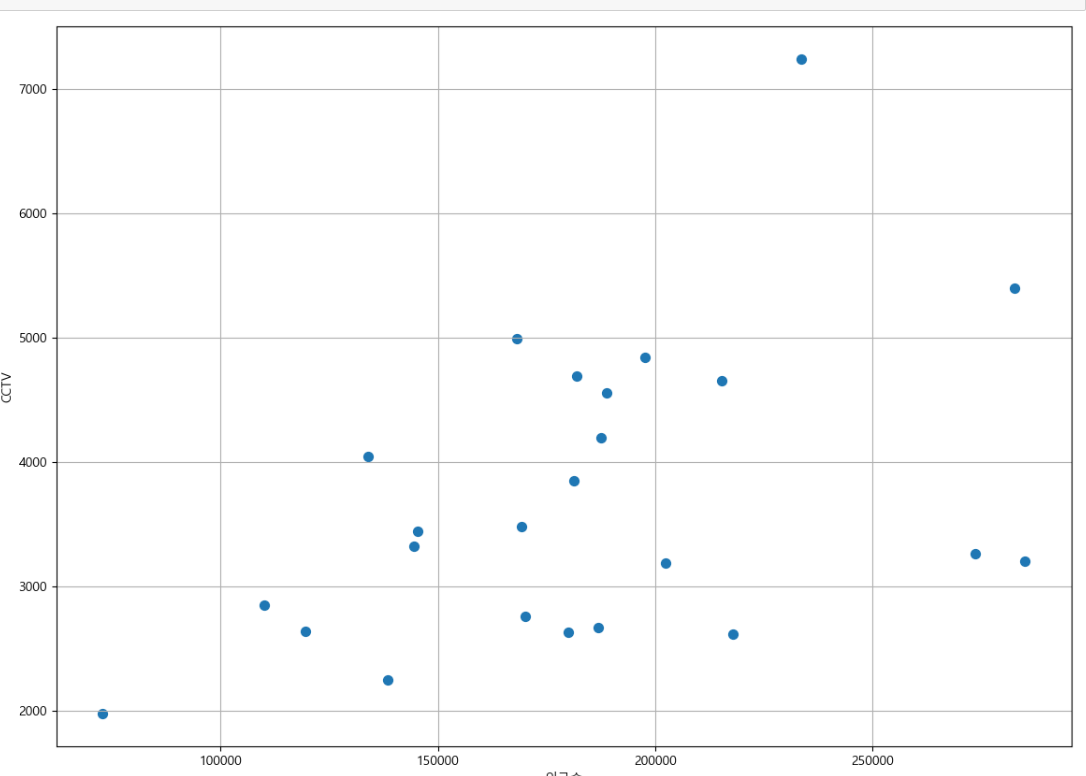
─ 데이터 경향 시각화
def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
plt.scatter(data_result["인구수"], data_result["총계"], s=50)
plt.xlabel("인구수")
plt.ylabel("CCTV")
plt.grid()
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊
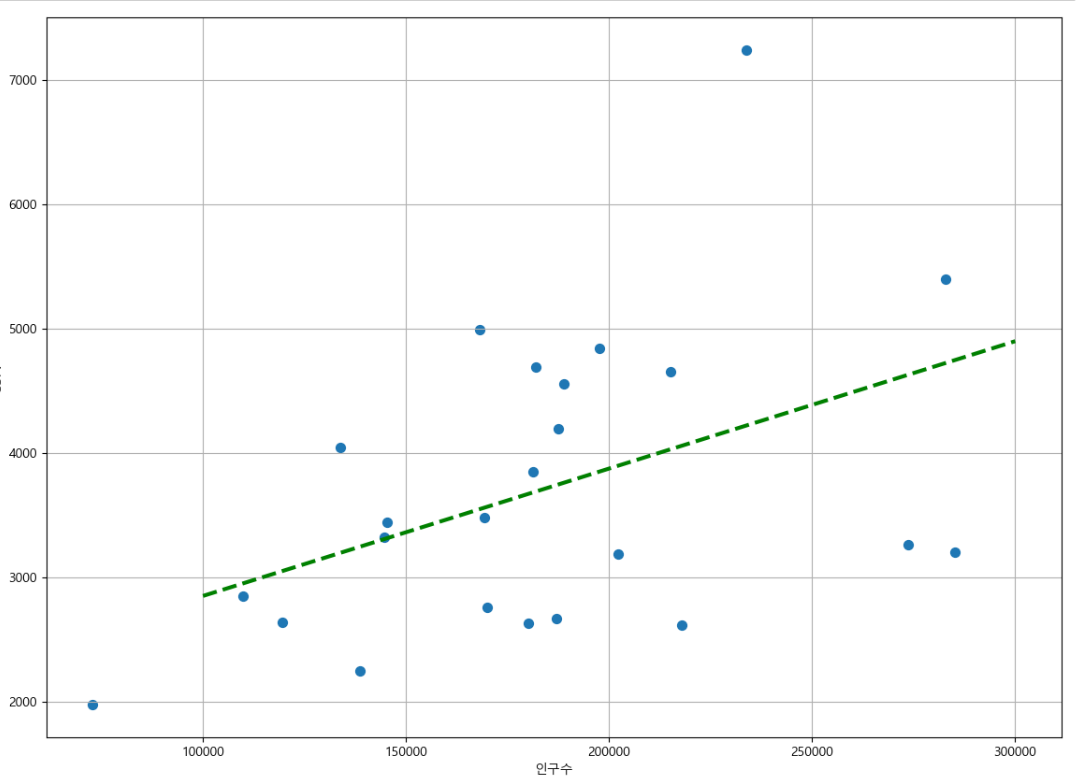
─ 선형회귀 Linear Regression
트렌드 파악 feat.Numpy
-Numpy를 이용한 1차 직선 만들기
-
numpy가 제공하는 간단한 함수를 이용하여 1차직선을 만들어 그래프 비교
- np.polyfit : 직선을 구성하기 위한 계수 계산 (y절편과 기울기 알려줌)
- np.poly1d : polyfit으로 찾은 계수로 python에서 사용할 함수로 변형
import numpy as np fpl = np.polyfit(data_result["인구수"], data_result["총계"], 1) fpl⇊
array([1.02437500e-02, 1.82564016e+03])
-polyfit에서 찾은 계수를 넣어 함수 완성
f1 = np.poly1d(fpl)ex) 인구 40000인 구에서 서울시 전체 경향에 맞는 적당한 CCTV의 수
f1(40000)⇊
2235.390158658218- np.linspace(a,b,n)
a부터 b까지 n개의 등간격 데이터 생성
-경향선을 그리기위해 x데이터 생성
fx = np.linspace(100000, 300000, 100)def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
plt.scatter(data_result["인구수"], data_result["총계"], s=50)
plt.plot(fx, f1(fx), ls="--", lw=3, color="g") ##lw=선의 굵기
plt.xlabel("인구수")
plt.ylabel("CCTV")
plt.grid()
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊
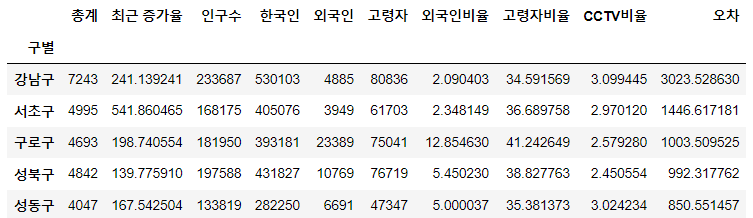
─ 경향과의 오차
data_result['오차'] = data_result['총계'] - f1(data_result['인구수'])
- 경향을 f1함수에 해당 인구 입력
- 현재값: data_result["총계"]
fp1 = np.polyfit(data_result['인구수'], data_result['총계'], 1)
f1 = np.poly1d(fp1)
fx = np.linspace(100000, 300000, 100)
data_result['오차'] = data_result['총계'] - f1(data_result['인구수'])
#경향과 비교하여 데이터의 오차가 너무 나는 데이터를 계산
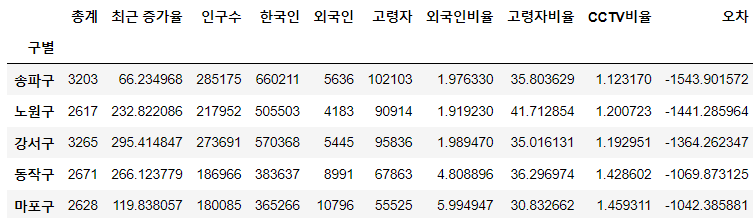
df_sort_f = data_result.sort_values(by='오차', ascending=False)
df_sort_t = data_result.sort_values(by='오차', ascending=True)-
경향 대비 CCTV를 많이 가진 구
df_sort_f.head()
-
경향 대비 CCTV를 적게 가진 구
df_sort_t.head()
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
#colormap을 사용자 정의로 세팅
color_step = ['#e74c3c', '#2ecc71', '#95a5a6', '#2ecc71', '#3498db', '#3498db']
my_cmap = ListedColormap(color_step)- s:마커의 크기, c: color 세팅에 방금 계산한 경향과의 오차 적용, cmap:사용자 정의맵
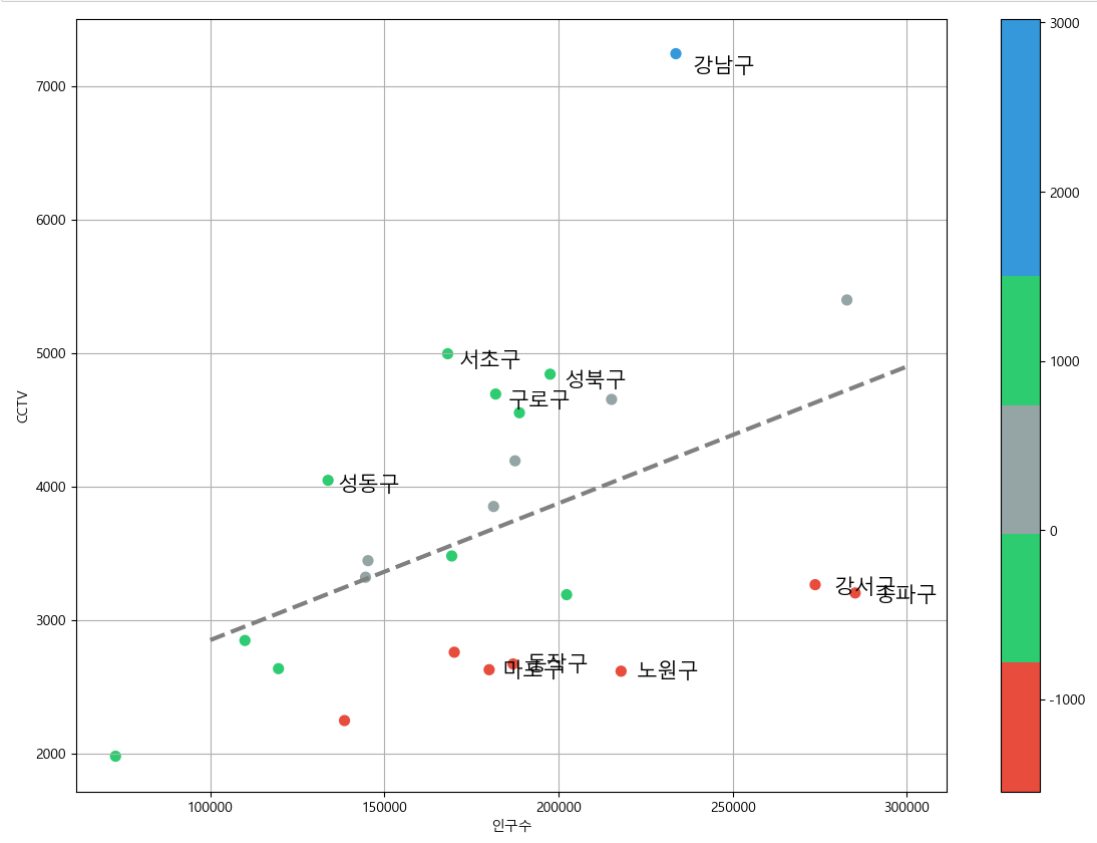
def drawGraph():
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
plt.scatter(data_result["인구수"], data_result["총계"], c=data_result['오차'], s=50, cmap=my_cmap)
plt.plot(fx, f1(fx), ls="--", lw=3, color="grey")
for n in range(5):
plt.text(
df_sort_f['인구수'][n] * 1.02,
df_sort_f['총계'][n] * 0.98,
df_sort_f.index[n],
fontsize=15)
plt.text(
df_sort_t['인구수'][n] * 1.02,
df_sort_t['총계'][n] * 0.98,
df_sort_t.index[n],
fontsize=15) ##오차가 큰 데이터 아래위로 5개씩만 마커 옆에 이름 표시
plt.xlabel('인구수')
plt.ylabel('CCTV')
plt.colorbar()
plt.grid()
plt.show()drawGraph()⇊
data_result.to_csv("..\\data\\01.CCTV_result.csv", sep=",", encoding="utf-8")-경로에 csv 파일 생성
