문자함수
text1 <- '2023-08-09'
text2 <- '오늘 하루도 행복하게 살자'
text3 <- '내년에도 늘 행복하게 살자'paste, paste0
: 변수에 값들을 하나로 묶는 함수
paste(text1,text2,text3) # sep= ' ' 기본값
paste(text1,text2,text3,sep='/')
paste(text1,text2,text3,sep=',')
paste(text1,text2,text3,sep='')
paste0(text1,text2,text3) # 공백문자 없이 이어 붙이는 함수
paste(employees$LAST_NAME,'의 직업은 ',employees$JOB_ID,'입니다.',sep=' ')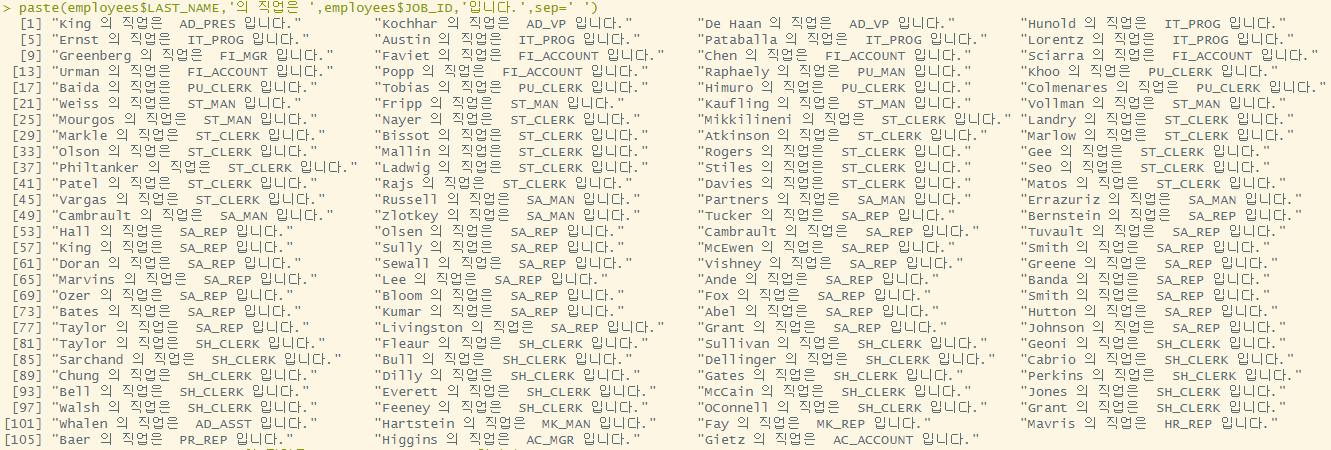
employees[!is.na(employees$COMMISSION_PCT),]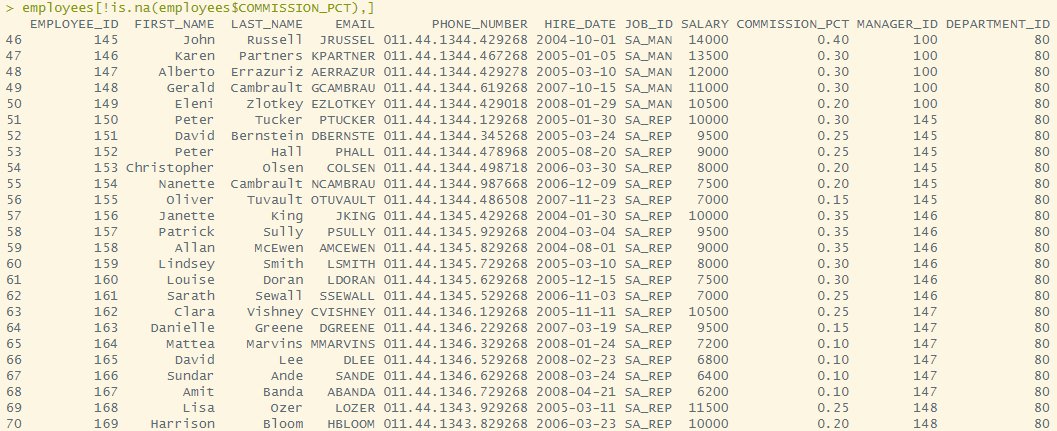
1. nchar
: 문자의 길이(수)를 리턴하는 함수
nchar('r developer')
nchar('r developer',type='chars') # type='chars' (기본값) 문자 수를 리턴
nchar('r developer',type='bytes') # type='bytes' 문자의 바이트값을 리턴
nchar('빅데이터',type='chars') # type='chars' (기본값) 문자 수를 리턴
nchar('빅데이터',type='bytes') # type='bytes' 문자 수를 리턴. 한 문자당 3byte를 차지(4*3=12)x <- c('R','Developer')
length(x) # 벡터의 갯수를 리턴
nchar(x) # 벡터 안의 각각의 글자 수를 리턴2. strsplit
: 부분문자로 분리하는 함수
strsplit('R Developer',split=' ') # 공백문자를 기준으로 분리
[[1]]
[1] "R" "Developer" # list 형식으로 리턴됨strsplit('R Developer',split=' ')[[1]][2]
unlist(strsplit('R Developer',split=' '))
strsplit('R,Developer',split=',')
strsplit('RDeveloper',split='') # split='' 한 글자씩 분리
strsplit('RDeveloper',split=character(0)) # split=character(0) 한 글자씩 분리x <- strsplit('R Developer',split=' ')
paste(x[[1]][1],x[[1]][2])
paste(x[[1]],collapse=' ')
paste(x[[1]],collapse=',') 벡터 안에 들어있는 각각의 단어들을 하나의 문장처럼 붙일 때 collapse라고 하는 옵션을 활용하는 것이 편하다!
y <- c('김밥','짜장면','냉면')
paste(y,collapse=',')
3. toupper
: 대문자로 변환하는 함수
toupper('r developer')4. tolower
: 소문자로 변환하는 함수
tolower('R DEVELOPER')※ package(라이브러리) 설치
install.packages("stringr") python과 달리 따로 cmd 창에서 패키지를 설치할 필요가 없다
package를 메모리에 로드
library(stringr) 현재 메모리에 로드된 package 확인
search()현재 메모리에 로드된 package unload
detach("package:stringr")
detach("package:stringr",unload=TRUE)package 삭제
remove.packages("stringr")기본 메소드가 아닌 특정 패키지로부터 가져온 메소드를 사용하는 경우 어떤 패키지로부터 왔는지 패키지 이름과 콜론(::)을 통해 출처를 밝혀주는 것이 좋다.
stringr::str_to_upper()
: 대문자 변환 함수
str_to_upper('r developer')
stringr::str_to_upper('r developer') stringr::str_to_lower()
: 소문자 변환 함수
str_to_lower('R DEVELOPER')
stringr::str_to_lower('R DEVELOPER') stringr::str_to_title()
: 단어별 첫글자 대문자 뒷글자 소문자 변환 함수
str_to_title('r dEVELOPER') # R Developer
stringr::str_to_title('r dEVELOPER') # R Developerstringr::str_to_sentence()
: 문장의 첫글자 대문자 뒷글자 소문자 변환 함수
str_to_sentence('r dEVELOPER') # R developer
stringr::str_to_sentence('r dEVELOPER') # R developer5. substr, substring
: 문자를 추출하는 함수
substr('R Developer',1,1)
substr('R Developer',1,5)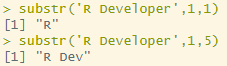
x <- 'R Developer'
nchar(x)
substr('R Developer',3,nchar(x))
substring('R Developer',3)
substr은 종료 지점까지 써줘야하는데 substring은 시작지점만 알면 종료지점을 몰라도 끝까지 리턴해준다.
substr(x,nchar(x),nchar(x)) # 제일 뒤에 한 글자 추출
substring(x,nchar(x))
substr(x,nchar(x)-1,nchar(x)) # 제일 뒤에 두 글자 추출
substring(x,nchar(x)-1)6. sub
: 첫번째 일치하는 문자만 바꾸는 함수
sub('R','PYTHON','R Programmer R Developer') 
'R'이라는 글자를 'PYTHON'으로 변경하는데 첫번째 'R'만 변경하겠다는 뜻이다.
7. gsub
: 일치하는 모든 문자를 바꾸는 함수
gsub('R','PYTHON','R Programmer R Developer')
숫자함수
1. round
: 지정한 자릿수를 기준으로 반올림하는 함수
145.926
-2-10 123 # 자릿수
round(45.926) # 46
round(45.926,0) # 46 / 기본값
round(45.926,1) # 45.9 / 소수 첫째자리까지 반올림
round(45.926,2) # 45.93 / 소수 둘째자리까지 반올림
round(45.926,-1) # 50 / 일의 자리까지 반올림
round(55.926,-2) # 100 / 백의 자리까지 반올림 2. signif
: 지정한 유효숫자만큼 자릿수를 만들어 반올림
45.926
12 345 # 자릿수
round(45.926,0) # 46
signif(45.926,1) # 50 / 첫번째 자릿수를 기준으로 두번째 자리부터 반올림
signif(45.926,2) # 46 / 두번째 자릿수를 기준으로 세번째 자리부터 반올림
signif(45.926,3) # 45.9 / 세번째 자릿수를 기준으로 네번째 자리부터 반올림
signif(155.926,1) # 200 / 첫번째 자릿수를 기준으로 두번째 자리부터 반올림
3. ceiling
: 숫자보다 크거나 같은 정수로 올림
ceiling(45.0) # 45
ceiling(45.1) # 464. trunc
: 소숫점을 버림 함수
trunc(45.926) # 45
trunc(45.926,2) # 45 / 자릿수를 지정해도 의미가 없다.5. floor
: 내림 함수
floor(45.926) # 45
floor(45.0) # 45
floor(-10.0) # -10
floor(-10.01) # -116. sqrt
: 제곱근
sqrt(16) # 47. abs
: 절대값
abs(-1) # 18. factorial
factorial(3) # 6(3*2*1)
factorial(4) # 24(4*3*2*1)
날짜함수
1. 현재날짜, 시간
Sys.Date() # 2023-08-09
Sys.time() # 2023-08-09 16:13:18 KST
Sys.timezone() # Asia/Seoul
date() # Wed Aug 9 16:13:54 2023
class("2023-08-09") # character
"2023-08-09" + 30 # "2023-08-09"은 문자이기 때문에 연산작업 시 오류 발생2. as.Date()
: 문자날짜를 날짜형으로 변환하는 함수
class(as.Date("2023-08-09")) # Date
class(as.Date("2023/08/09")) # Date
as.Date("2023-08-09",format='%Y-%m-%d') + 42 # 2023-09-20
as.Date("2023/08/09",format='%Y/%m/%d') + 42 # 2023-09-20
as.Date("20230809",format='%Y%m%d') + 42 # 2023-09-20
as.Date("2023.08.09",format='%Y.%m.%d') + 42 # 2023-09-20※ format
: 날짜모델요소
%Y : 년도4자리(세기포함)
%y : 년도2자리(세기불포함)
%m : 월
%d : 일
%B : 문자달(ex. August)
%b : 문자달 약어(ex. Aug)
%A : 요일
%a : 요일의 약어
%u : 숫자요일 1 ~ 7 : 월요일 1 ~ 일요일 7
%w : 숫자요일 0 ~ 6 : 일요일 0 ~ 토요일 6
%H : 시
%M : 분
%S : 초
%z : timezone 시간
%Z : timezone namex <- '2023년 8월 9일'
as.Date(x,format='%Y년 %m월 %d일') # 2023-08-09
class(as.Date(x,format='%Y년 %m월 %d일')) # Date
y <- '2023 august 9'
as.Date(y,format='%Y %B %d') # 오류 발생시간은 지역과 언어의 영향을 많이 받기 때문에 local 정보를 변경해야한다.
Sys.getlocale() # 현재 local 정보
Sys.setlocale(category='LC_ALL',locale='English.utf8') # local 변경
Sys.getlocale()
y <- '2023 august 9'
as.Date(y,format='%Y %B %d')
Sys.setlocale() # local 정보 기본값으로 초기화
Sys.getlocale()3. format 함수
: 날짜를 문자형으로 변환하는 함수, SQL의 to_char와 같은 개념.
Sys.Date() # 2023-08-09
format(Sys.Date(), '%Y%m%d') # 20230809
format(Sys.Date(), '%B') # 8월
format(Sys.Date(), '%b') # 8
format(Sys.Date(), '%A') # 수요일
format(Sys.Date(), '%a') # 수
Sys.setlocale(category='LC_ALL',locale='English.utf8')
format(Sys.Date(), '%B') # August
format(Sys.Date(), '%b') # Aug
format(Sys.Date(), '%A') # Wednesday
format(Sys.Date(), '%a') # Wed
Sys.setlocale()
format(Sys.Date(), '%u') # 월 1 ~ 일 7
format(Sys.Date(), '%w') # 일 0 ~ 토 6
format(Sys.time(), '%H') # 17
format(Sys.time(), '%M') # 00
format(Sys.time(), '%S') # 47
format(Sys.time(), '%z') # +0900
format(Sys.time(), '%Z') # KST4. weekdays
: 요일을 출력하는 함수
format(Sys.Date(),'%A') # 수요일
weekdays(Sys.Date()) # 수요일5. 날짜계산
Sys.Date() + 42
Sys.Date() - 10
as.integer(Sys.Date() - as.Date('2023-03-14'))
as.numeric(Sys.Date() - as.Date('2023-03-14'))6. difftime
: 두 날짜 간의 일 수를 리턴하는 함수
as.integer(difftime(Sys.Date(),as.Date('2023-03-14')))
as.numeric(difftime(Sys.Date(),as.Date('2023-03-14')))
years <- as.integer(Sys.Date() - as.Date(employees$HIRE_DATE)) / 365
employees[years >= 20,]※ lubridate
: 날짜 관련된 함수들이 포함되어있는 패키지
install.packages('lubridate')
library(lubridate)lubridate::today() # 2023-08-09
Sys.Date()
lubridate::now() # 2023-08-09 17:12:50 KST
Sys.time()날짜 -> 문자형으로 추출
class(format(Sys.Date(),'%Y')) # character날짜 -> 숫자형으로 추출
class(as.integer(format(Sys.Date(),'%Y'))) # integer
class(lubridate::year(Sys.Date())) # numeric년도 추출(수치형)
lubridate::year(Sys.Date())
lubridate::year(lubridate::today())
lubridate::year(lubridate::now())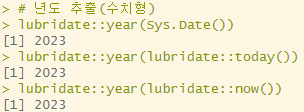
월 추출(수치형)
lubridate::month(now())
month(now())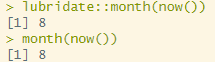
일 추출(수치형)
lubridate::day(now())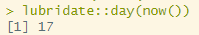
요일 추출
format(Sys.Date(),'%B')
format(Sys.Date(),'%b')
format(Sys.Date(),'%u') # 1(월) ~ 7(일)
format(Sys.Date(),'%w') # 0(일) ~ 6(토)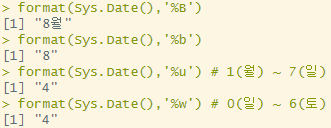
lubridate::wday(now(),week_start=7) # 1(일)~7(토)
lubridate::wday(now(),week_start=1) # 1(월)~7(일)
lubridate::wday(now(),week_start=1,label=T) # label=T 문자요일출력(factor 자료형)
lubridate::wday(now(),week_start=1,label=F) # label=F 기본값
paste0(as.vector(lubridate::wday(now(),week_start=1,label=T)),'요일')
format(Sys.Date(),'%A') 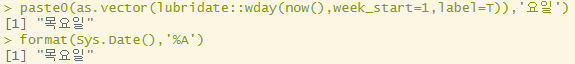
lubridate::years()
: 년수를 더하거나 뺄 때 사용하는 함수. SQL의 interval year to month와 같은 개념(to_yminterval('10-00'))
Sys.Date() + lubridate::years(1)
Sys.Date() + lubridate::years(10)
Sys.Date() + lubridate::years(-10)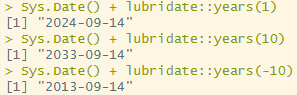
base::months()
: 월 수를 더하거나 뺄 때 사용하는 함수. SQL의 interval year to month와 같은 개념(to_yminterval('00-10'))
Sys.Date() + base::months(1)
Sys.Date() + base::months(10)
Sys.Date() - base::months(5)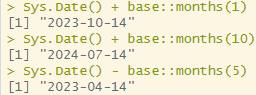
lubridate::days()
: 일 수를 더하거나 뺄 때 사용하는 함수. SQL의 interval day to second와 같은 개념(to_dsinterval('47'))
Sys.Date() + lubridate::days(47)
Sys.Date() - lubridate::days(47)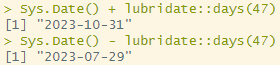
lubridate::hours()
: 시간을 더하거나 뺄 때 사용하는 함수
Sys.Date() + lubridate::hours(10) # Sys.Date()는 내부적으로 0시 0분. 10시간을 더하면 10:00시로 나옴.
Sys.time() + lubridate::hours(10)
Sys.time() - lubridate::hours(10)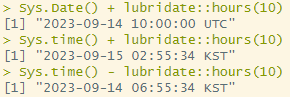
lubridate::minutes()
: 분을 더하거나 뺄 때 사용하는 함수
Sys.time() + lubridate::minutes(30)
Sys.time() - lubridate::minutes(30)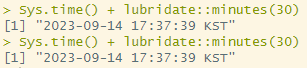
lubridate::seconds()
: 초를 더하거나 뺄 때 사용하는 함수.
Sys.time() + lubridate::seconds(300)
Sys.time() - lubridate::seconds(300)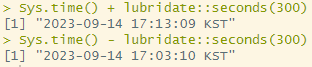
SQL의 interval day to second와 같은 개념(to_dsinterval('100 10:30:30'))
Sys.time() + lubridate::days(100)+lubridate::hours(10)+lubridate::minutes(30)+lubridate::seconds(30) 
lubridate::hms()
: 시분초를 더하거나 뺄 때 사용하는 함수
Sys.time() + lubridate::hours(10)+lubridate::minutes(30)+lubridate::seconds(30)
Sys.time() + lubridate::hms('10:30:30')
Sys.time() - lubridate::hms('10:30:30')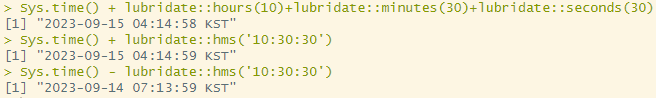
x <- lubridate::now()
lubridate::year(x) <- 1994 # 년도 수정
x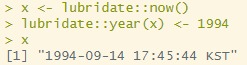
x <- Sys.time()
lubridate::year(x) <- 1994 # 년도 수정
lubridate::month(x) <- 10 # 월 수정
lubridate::day(x) <- 31 # 일 수정
lubridate::hour(x) <- 12 # 시간 수정
lubridate::minute(x) <- 41 # 분 수정
lubridate::second(x) <- 0 # 초 수정
x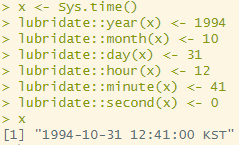
lubridate::quarter()
: 분기를 리턴하는 함수
lubridate::quarter(Sys.Date())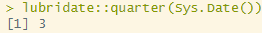
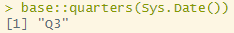
base::quarters()
: 분기를 리턴하는 함수
base::quarters(Sys.Date())