1. ISA(Instruction Set Architecture)
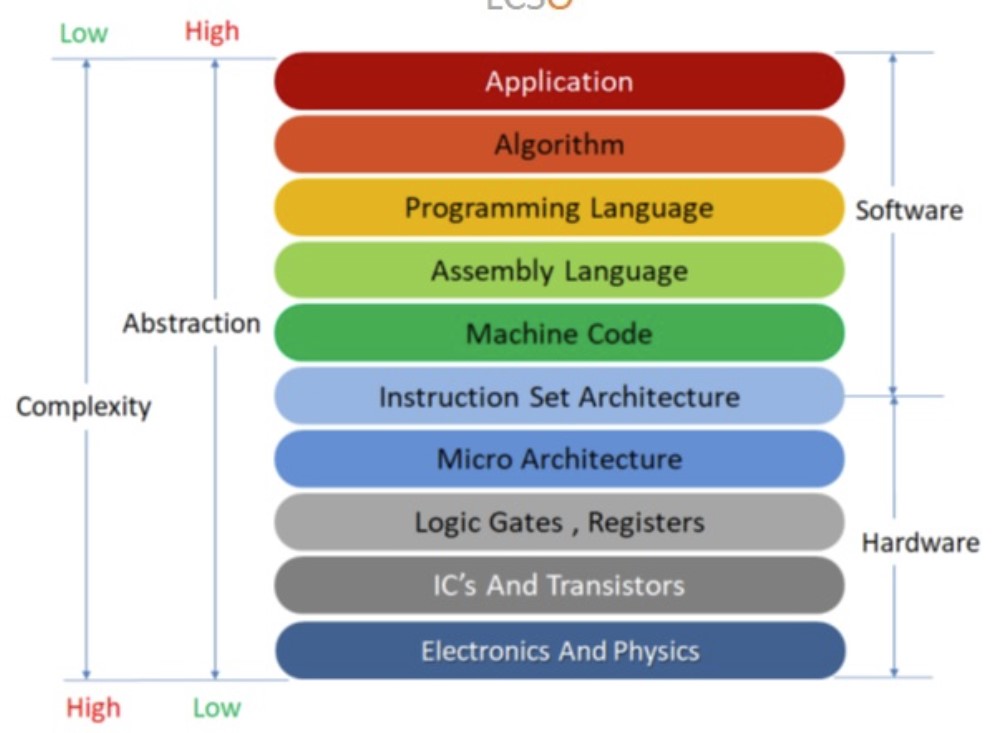
- ISA is a language that computer can understand and also interface between H/W and S/W
- HLL -> Comiler -> Low Level Language -> ISA -> H/W
- Low Level Language(S/W)에서 H/W에게 명령을 내릴 때의 Interface
- ISA를 통해 번역된 기계어를 CPU가 해석하고 행동한다.
- Microarchitecture : Implementation of ISA
- 정리
- Computer는 Register, Memory 2개의 state를 갖고있다.
- Computer의 state를 바꾸는 operation들의 집합을 ISA라고 정의할 수 있다.
2. CISC / RISC
-
CPU를 설계하는 방식
-
CISC
- Intel 사의 CPU에서 사용하는 방식으로 명령어들의 길이가 가변적이고 복잡하며 많은 종류가 있다.
- Program 당 들어가는 명령어의 갯수는 적다.
- CPU가 Memory랑 소통하는 방식이다.
- 복잡한 H/W 구조 <-> 간단한 S/W 구조(Hardware centric)
- Compile is easy
- Backward Compatability가 좋음
- 새로운 Condition 발생시에 instruction 을 그저 추가하기만 하면 됨
- 호환성이 좋아 PC환경에서 주로 사용된다.
-
RISC
- ARM 사의 CPU에서 사용하는 방식으로 명령어들의 길이가 고정적이고 간단하며 CISC 에 비해서 적은 명령어 수를 가진다.
- Program 당 들어가는 명령어의 갯수는 많다.
- CPU가 Register랑 소통하는 방식이다. (Memory also through PC)
- 간단한 H/W 구조 <-> 복잡한 S/W 구조(Software centric)
- Compile is more complex
| RISC | CISC | |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle per Instruction | Single Cycle | Several Cycles |
| Instructions per program | Larger | Smaller |
| Emphasize for performance | efficiency in CPI | efficiency in IC |
| Required memory | Heavy use | Efficient use |
| Implementation complexity | Low->Cheap | High->Expensive |
| # of registers | Larger | Smaller |
| Instruction | smaller number / simple / fixed instructions length(~200 instructions) | larger number / complex / variable instructions (>1,000 instructions) |
| Pipelining | Good | Bad |
| Power comsumption | Low->Embedded | High->Desktop |
- Question
-
Why RISC can have more registers than CISC?
- Simple Instructions -> Implementation complexity low -> more spare physical room for registers in CPU
-
Why CISC tried to reduce the number of instructions per program?
- memory was small and expensive
-
Which is more adequate for embedded system?
- RISC because it has simple implementation complexity; therefore, has less power comsumption
-
Which is easier to expand or add a new operation?
- CISC because it is good for backward compatibility
3. ISA Classification
1. Storing Operand
- Operand can be stored in the stack, accumulator, register, or memory
2. The number of Operands
- add, A,B,C => 3 operands
- add, A,B => 2 operands
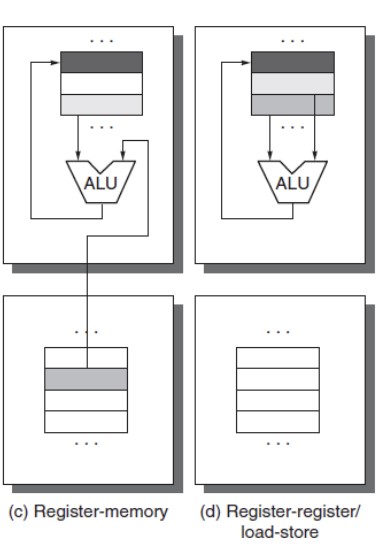
- Register-memory : CISC 방식
- Pros : can access memory (Data) without seperate instruction's load
- Cons : Instruction의 길이가 가변적이다. (동등하지 않다)
- Register-register : RISC 방식
- Pros : Instruction 의 길이가 fixed, simple하다.
- Cons : IC 의 갯수가 많다.
3. Addressing Mode
-
Byte = 8 bit
- How to convert among hexa, oct, binary, and decimal
-
Unit of Data
- KB = 10^3, MB = 10^6, GB = 10^9, TB = 10^12
-
Word
- Processor 가 메모리부터 데이터를 가지고와서 한번에 처리할 수 있는 고정된 단위
- Size of Register = Word
- 메모리부터 데이터를 가지고와서 임시저장장치인 register 에 저장되므로 register 사이즈보다 클 수 없다.
- Largest possible address size
- word = 32bit (4byte), double word = 64bit (8byte)
- word 는 메모리 주소가 4씩증가, double word 는 8씩 증가
-
Endian
- Little Endian : LSB is stored at lowest memory address
- Big Endian : MSB is stored at lowest memory address
- ex) if 5 -> 0000...0101
- Little Endian

- Big Endian

- Little Endian
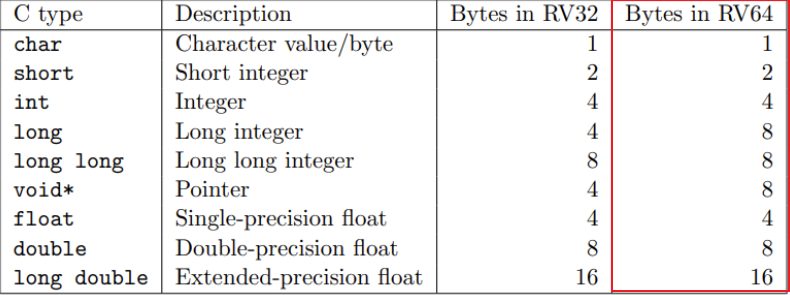
- Type and Size of Operands
- RISC-V 형태의 타입과 크기로 읽어볼 것!
- Type of Operations
- Arithmetic and Logic : add, subtract, multiply, divide, etc
- Data transfer : load, store
- Control : branch, jump
