1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11952
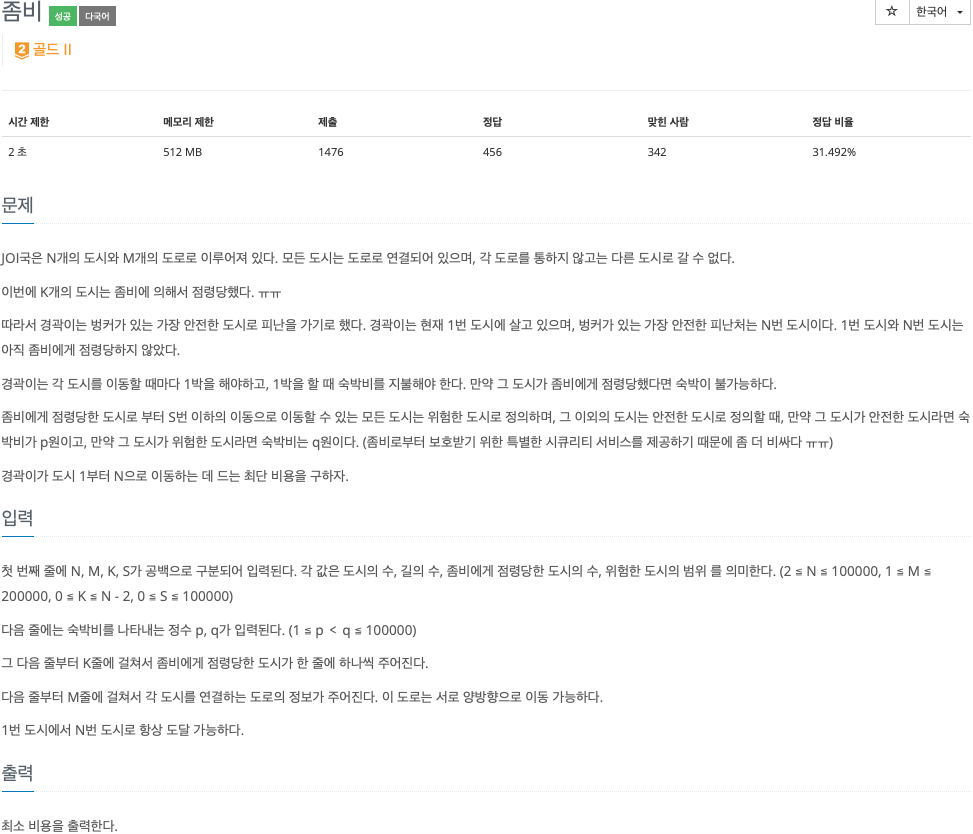
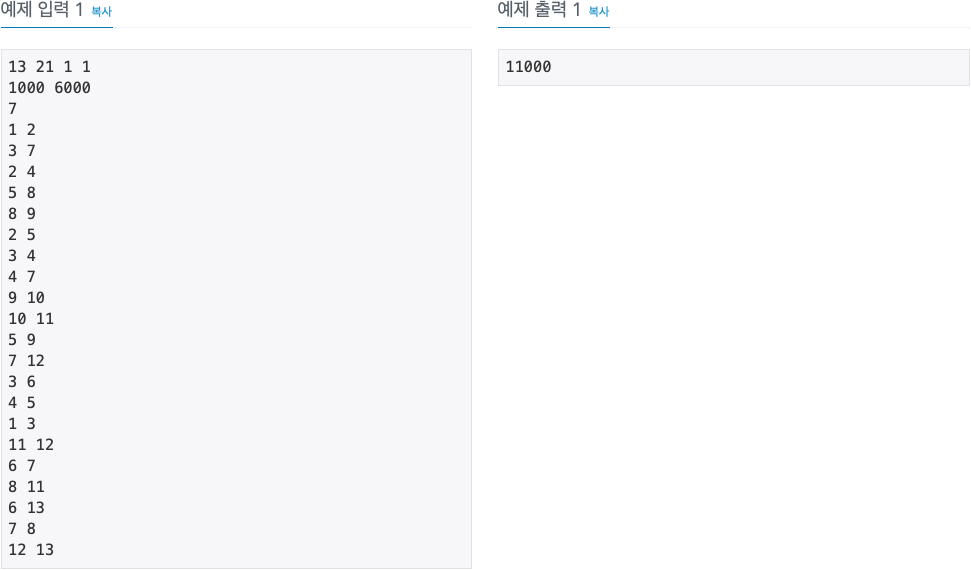
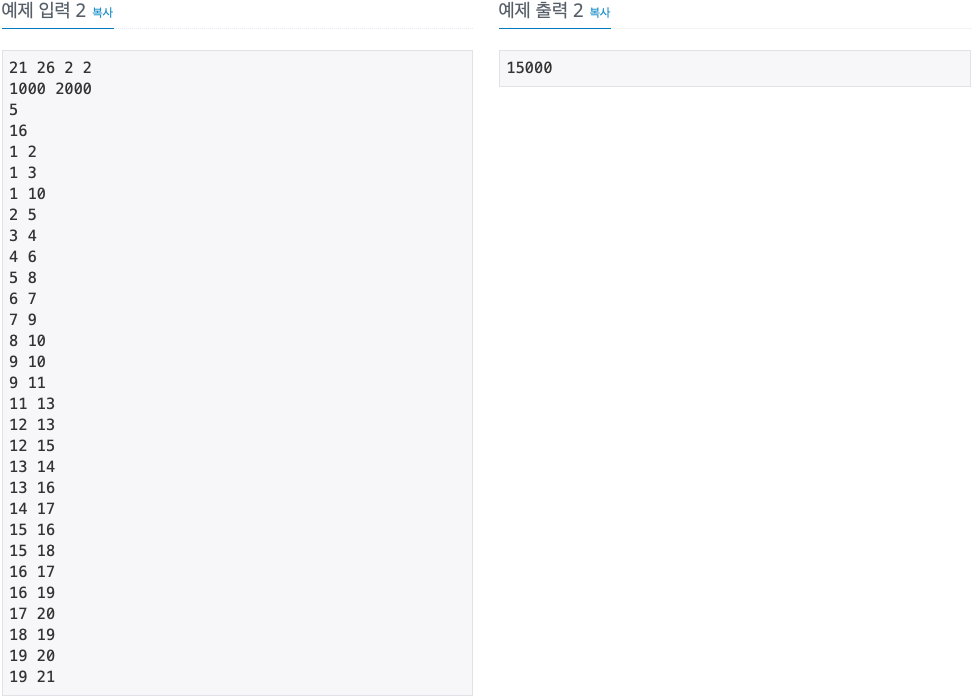
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int cityCount;
static int roadCount;
static int zombieCityCount;
static int dangerousCityRange;
static int safeCityPrice;
static int dangerousCityPrice;
static Set<Integer> zombieCities;
static Set<Integer> dangerousCities;
static Map<Integer, List<Integer>> roads;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
cityCount = scanner.nextInt();
roadCount = scanner.nextInt();
zombieCityCount = scanner.nextInt();
dangerousCityRange = scanner.nextInt();
safeCityPrice = scanner.nextInt();
dangerousCityPrice = scanner.nextInt();
zombieCities = new HashSet<>();
for (int zombieCity = 0; zombieCity < zombieCityCount; zombieCity++) {
zombieCities.add(scanner.nextInt());
}
roads = new HashMap<>();
for (int city = 1; city <= cityCount; city++) {
roads.put(city, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int road = 0; road < roadCount; road++) {
int city1 = scanner.nextInt();
int city2 = scanner.nextInt();
roads.get(city1).add(city2);
roads.get(city2).add(city1);
}
}
/*
* 위험한 도시와 안전한 도시의 숙박비가 다르기 때문에 우선 위험한 도시가 어디인지 찾아야 한다
* 그러므로 BFS를 통해 좀비에 의해 점령당한 도시들 각각에서 S(dangerousCityRange)번 이하의 이동으로 이동할 수 있는 모든 도시를 찾는다
* -> 이때 구한 모든 도시가 위험한 도시가 된다
* 이렇게 구한 위험한 도시와 좀비에 의해 점령당한 도시 각각을 Set에 저장한다
* - 이후에 최단 비용을 구할 때 위험한 도시에 속하는지, 좀비에 의해 점령당한 도시에 속하는지, 안전한 도시에 속하는지 판단하기 위해 Set에 저장한다
*
* 위험한 도시를 모두 구했으니 시작 도시인 1번 도시부터 도착 도시인 N(cityCount)번 도시까지의 최단 비용을 구한다
* 이는 다익스트라를 이용하여 구한다
* - 1번 도시와 N번 도시에서는 숙박할 필요가 없으므로 N번 도시에 대한 숙박 비용은 추가하지 않는다
*/
static void solution() {
findDangerousCities();
System.out.println(dijkstra(1));
}
static long dijkstra(int startCity) {
Queue<Road> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
long[] prices = new long[cityCount + 1];
Arrays.fill(prices, Long.MAX_VALUE);
queue.offer(new Road(startCity, 0, 0));
prices[startCity] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Road cur = queue.poll();
if (prices[cur.cityNumber] < cur.price) {
continue;
}
for (int next : roads.get(cur.cityNumber)) {
if (zombieCities.contains(next)) {
continue;
}
int nextCity = next;
long nextPrice = cur.price;
if (nextCity != cityCount) {
if (dangerousCities.contains(next)) {
nextPrice += dangerousCityPrice;
} else {
nextPrice += safeCityPrice;
}
}
if (prices[nextCity] > nextPrice) {
prices[nextCity] = nextPrice;
if (nextCity != cityCount) {
queue.offer(new Road(nextCity, cur.moveCount + 1, nextPrice));
}
}
}
}
return prices[cityCount];
}
static void findDangerousCities() {
Queue<Road> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[cityCount + 1];
dangerousCities = new HashSet<>();
for (int zombieCity : zombieCities) {
queue.offer(new Road(zombieCity, 0, 0));
visited[zombieCity] = true;
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Road cur = queue.poll();
for (int nextCity : roads.get(cur.cityNumber)) {
if (!visited[nextCity] && cur.moveCount + 1 <= dangerousCityRange) {
visited[nextCity] = true;
dangerousCities.add(nextCity);
queue.offer(new Road(nextCity, cur.moveCount + 1, 0));
}
}
}
}
static class Road implements Comparable<Road> {
int cityNumber;
int moveCount;
long price;
public Road(int cityNumber, int moveCount, long price) {
this.cityNumber = cityNumber;
this.moveCount = moveCount;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Road o) {
if (price < o.price) {
return -1;
} else if (price > o.price) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
