1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2819
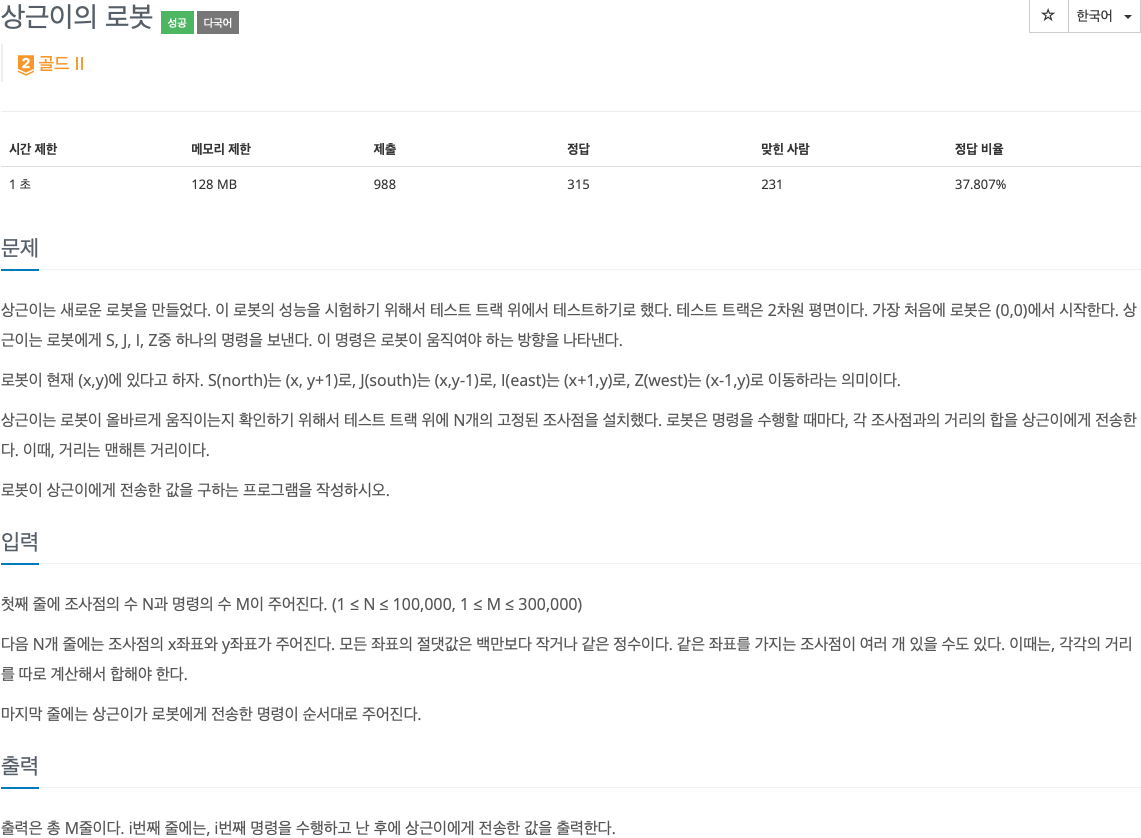
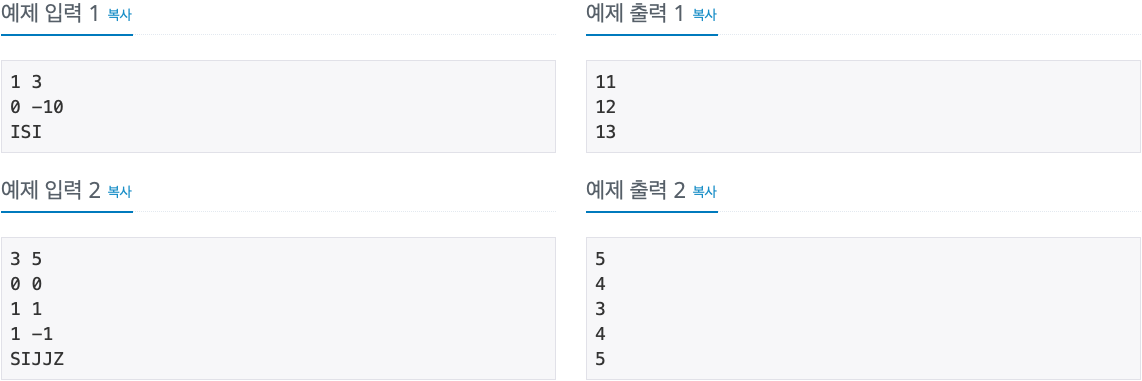
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static final int BASE = 1_000_000;
static int investigationPointCount;
static int orderCount;
static int cx;
static int cy;
static int positiveXCount;
static int zeroXCount;
static int negativeXCount;
static int positiveYCount;
static int zeroYCount;
static int negativeYCount;
static long answer;
static char[] orders;
static int[] investigationPointX;
static int[] investigationPointY;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
investigationPointCount = scanner.nextInt();
orderCount = scanner.nextInt();
investigationPointX = new int[BASE * 2 + 1];
investigationPointY = new int[BASE * 2 + 1];
for (int idx = 0; idx < investigationPointCount; idx++) {
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int y = scanner.nextInt();
investigationPointX[BASE + x]++;
investigationPointY[BASE + y]++;
answer += (Math.abs(x) + Math.abs(y));
if (x > 0) {
positiveXCount++;
} else if (x < 0) {
negativeXCount++;
} else {
zeroXCount++;
}
if (y > 0) {
positiveYCount++;
} else if (y < 0) {
negativeYCount++;
} else {
zeroYCount++;
}
}
orders = scanner.nextLine().toCharArray();
}
/*
* 주어지는 좌표의 x좌표, y좌표가 -1,000,000 ~ 1,000,000 사이의 값이기 때문에 음수들을 배열로 표현하기 위하여 1,000,000을 더한 값을 좌표값으로 갖는다
* 우선 (0, 0) 위치에 있을 때 조사점들까지 거리의 합을 answer라는 변수에 구한다
* 그리고 x, y좌표에서 음수, 0, 양수의 개수를 각각 구한다
*
* 각 명령에 따라 로봇이 위치하는 x좌표 또는 y좌표를 움직이고 아래와 같은 작업을 진행한다
* 1) 움직이는 방향이 음의 방향인 경우(즉, J, Z 명령)
* - 조사점들까지의 거리의 합을 나타내는 answer 변수에 (양의 x/y 개수 + 0값인 x/y 개수 - 음의 x/y 개수)를 더해준다
* - 양의 x/y 개수, 0값인 x/y 개수, 음의 x/y 개수는 현재 로봇의 위치에 따라 상대적으로 음인지, 양인지 0인지를 나타내는 개수이기 때문에
* - 음의 방향으로 움직이면 양인 경우와 0인 경우는 맨해튼 거리가 증가할 것이고, 음인 경우는 맨해튼 거리가 감소할 것이다
* - 양의 x/y 개수에는 0값인 x/y 개수를 더해준다
* - 음의 방향으로 움직였으니 이전에 상대적으로 0값인 x/y값들이 양의 값으로 변경될 것이다
* - 0값인 x/y 개수는 현재 x/y좌표에 해당하는 조사점들의 개수로 변경한다
* - 음의 x/y 개수에는 현재 x/y 좌표에 해당하는 조사점들의 개수를 빼준다
* - 현재 x/y 좌표에 해당하는 조사점들은 이전에는 음의 x/y 좌표였다가 음의 방향으로 이동하면서 0값인 x/y 좌표가 되었으므로
* - 해당 개수들을 빼준다
* 2) 움직이는 방향이 양의 방향인 경우(즉, S, I 명령)
* - 조사점들까지의 거리의 합을 나타내는 answer 변수에 (음의 x/y 개수 + 0값인 x/y 개수 - 양의 x/y 개수)를 더해준다
* - 양의 x/y 개수, 0값인 x/y 개수, 음의 x/y 개수는 현재 로봇의 위치에 따라 상대적으로 음인지, 양인지 0인지를 나타내는 개수이기 때문에
* - 양의 방향으로 움직이면 음인 경우와 0인 경우는 맨해튼 거리가 증가할 것이고, 양인 경우는 맨해튼 거리가 감소할 것이다
* - 음의 x/y 개수에는 0값인 x/y 개수를 더해준다
* - 양의 방향으로 움직였으니 이전에 상대적으로 0값인 x/y값들이 음의 값으로 변경될 것이다
* - 0값인 x/y 개수는 현재 x/y좌표에 해당하는 조사점들의 개수로 변경한다
* - 양의 x/y 개수에는 현재 x/y 좌표에 해당하는 조사점들의 개수를 빼준다
* - 현재 x/y 좌표에 해당하는 조사점들은 이전에는 양의 x/y 좌표였다가 양의 방향으로 이동하면서 0값인 x/y 좌표가 되었으므로
* - 해당 개수들을 빼준다
*/
static void solution() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (char order : orders) {
if (order == 'S') {
cy++;
answer += (negativeYCount + zeroYCount - positiveYCount);
negativeYCount += zeroYCount;
zeroYCount = investigationPointY[cy + BASE];
positiveYCount -= investigationPointY[cy + BASE];
} else if (order == 'J') {
cy--;
answer += (positiveYCount + zeroYCount - negativeYCount);
positiveYCount += zeroYCount;
zeroYCount = investigationPointY[cy + BASE];
negativeYCount -= investigationPointY[cy + BASE];
} else if (order == 'I') {
cx++;
answer += (negativeXCount + zeroXCount - positiveXCount);
negativeXCount += zeroXCount;
zeroXCount = investigationPointX[cx + BASE];
positiveXCount -= investigationPointX[cx + BASE];
} else {
cx--;
answer += (positiveXCount + zeroXCount - negativeXCount);
positiveXCount += zeroXCount;
zeroXCount = investigationPointX[cx + BASE];
negativeXCount -= investigationPointX[cx + BASE];
}
result.append(answer).append('\n');
}
System.out.print(result);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
String nextLine() {
String str = "";
try {
str = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
}
}
