1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/12014
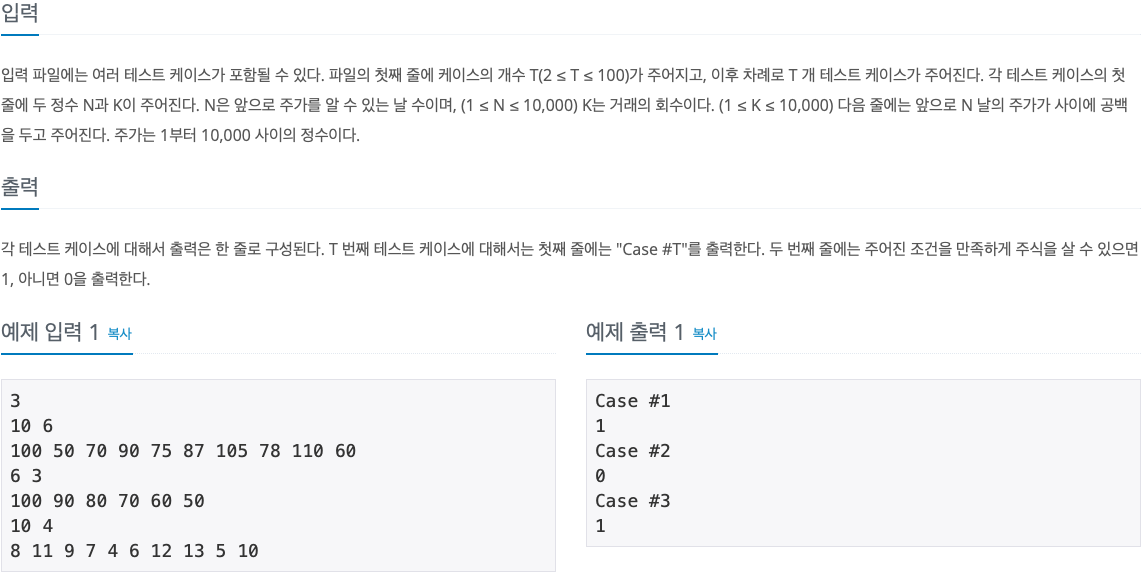
2. 문제

3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static Reader scanner = new Reader();
static int caseNum;
static int N;
static int K;
static int[] stockPrices;
static void input() {
N = scanner.nextInt();
K = scanner.nextInt();
stockPrices = new int[N];
for(int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++) {
stockPrices[idx] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
// K일 동안 직전에 주식을 샀을 때보다 가격이 올라갔을 때만 주식을 사기 위해서는 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열의 길이가 K보다 크거나 같으면 된다
// 그렇기 때문에 각 케이스에서 LIS의 길이를 구하여 해당 길이가 K보다 크거나 같다면 거래가 가능하므로 1을, K보다 작다면 거래가 불가능하므로 0을 출력하면 된다
// 이때 N보다 K가 클 경우, 알고있는 주식의 일수보다 거래해야하는 일수인 K가 더 크기 때문에 애초에 K일만큼 거래할 수 없으므로 0을 출력한다
static void solution() {
sb.append("Case #").append(caseNum++).append('\n');
if(N < K) {
sb.append(0).append('\n');
return;
}
List<Integer> lis = new ArrayList<>();
lis.add(0);
for(int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++) {
if(lis.get(lis.size() - 1) < stockPrices[idx]) {
lis.add(stockPrices[idx]);
} else {
int lisIdx = getLisIdx(stockPrices[idx], lis);
lis.set(lisIdx, stockPrices[idx]);
}
}
int lisSize = lis.size() - 1 == 0 ? 1 : lis.size() - 1;
if(K <= lisSize) {
sb.append(1).append('\n');
} else {
sb.append(0).append('\n');
}
}
static int getLisIdx(int target, List<Integer> lis) {
int left = 1;
int right = lis.size() - 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(lis.get(mid) < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return right;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
caseNum = 1;
int T = scanner.nextInt();
while(T-- > 0) {
input();
solution();
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
