1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14289
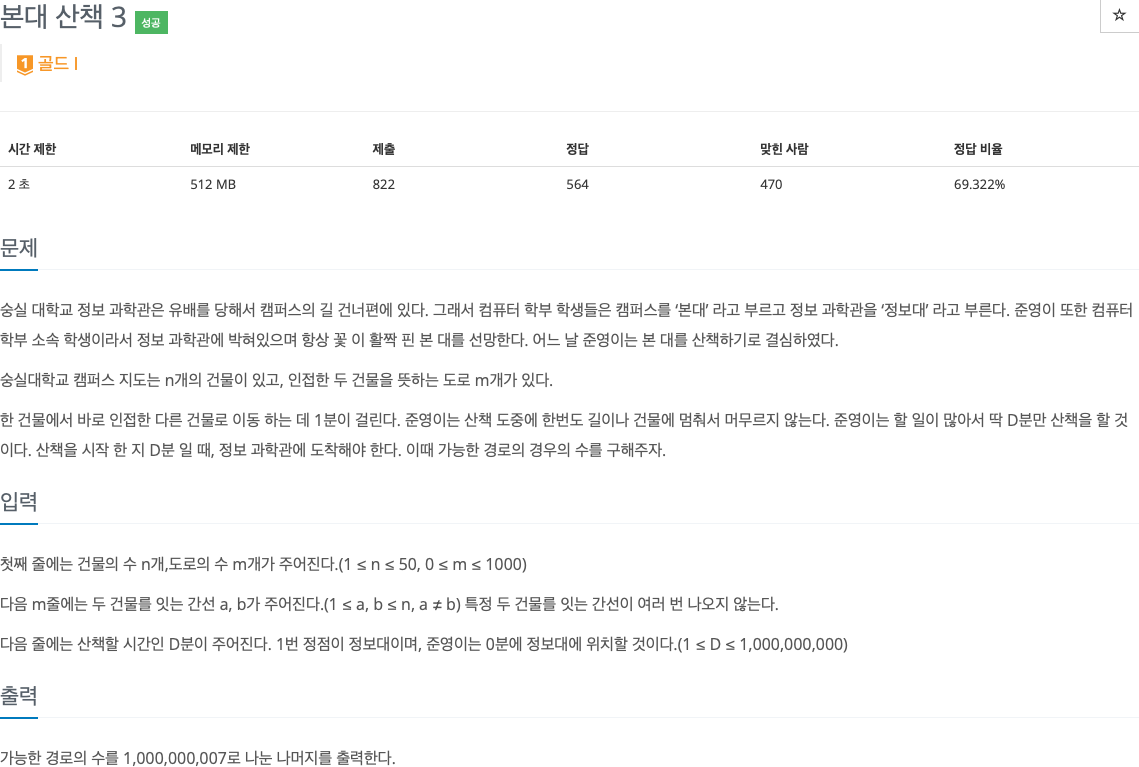
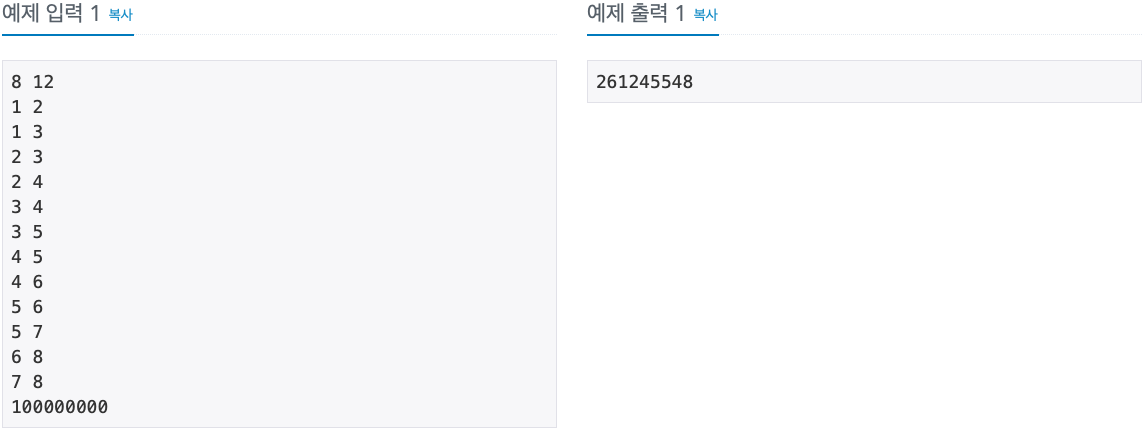
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static final int DIVISOR = 1_000_000_007;
static int n, m, D;
static long[][] moveNum;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
n = scanner.nextInt();
m = scanner.nextInt();
// moveNum[b1][b2] = b1번 건물에서 b2번 건물로 가는 경우의 수
moveNum = new long[n + 1][n + 1];
for(int road = 0; road < m; road++) {
int building1 = scanner.nextInt(), building2 = scanner.nextInt();
moveNum[building1][building2] = 1;
moveNum[building2][building1] = 1;
}
D = scanner.nextInt();
}
static void solution() {
// 분할 정복을 통해 moveNum을 곱해나가며 D분에 각 위치에서 다른 모든 위치로 이동할 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 구한다
// 이동할 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 나타내는 행렬을 곱해나가면서 D분일 때의 이동할 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 구한다
long[][] result = calculateMoveNum(D, moveNum);
// 구하고자 하는 정보과학관에서 정보과학관으로 돌아오는 경우의 수는 정보과학관이 1번이기 때문에
// result[1][1]이 정보과학관에서 정보과학관으로 돌아오는 경우의 수가 된다
System.out.println(result[1][1]);
}
static long[][] calculateMoveNum(int exponent, long[][] moveNum) {
// 만약 현재 시간이 1이라면 moveNum을 그대로 반환한다
if(exponent == 1) return moveNum;
// 재귀를 통해 (exponent / 2)분일 때의 이동할 수 있는 경우의 수를 구한다
long[][] temp = calculateMoveNum(exponent / 2, moveNum);
// 현재 우리가 구하고자 하는 것은 exponent분일 때의 이동할 수 있는 경우의 수이므로
// (exponent / 2)분일 때의 이동할 수 있는 경우의 수인 temp를 이용하여 temp * temp를 통해
// exponent분일 때의 이동할 수 있는 경우의 수를 구한다
long[][] result = multiplyMatrix(temp, temp);
// 만약 exponent가 홀수라면, temp * temp만 가지고는 exponent분일 때의 이동할 수 있는 경우의 수를 구할 수 없으니
// temp * temp를 한 행렬에 1분일 때의 경우의 수인 moveNum을 곱하여 exponent분일 때의 이동할 수 있는 경우의 수를 구한다
if(exponent % 2 == 1)
result = multiplyMatrix(result, moveNum);
return result;
}
static long[][] multiplyMatrix(long[][] mat1, long[][] mat2) {
long[][] result = new long[n + 1][n + 1];
for(int row = 0; row <= n; row++) {
for(int col = 0; col <= n; col++) {
for(int idx = 0; idx <= n; idx++) {
result[row][col] += (mat1[row][idx] * mat2[idx][col]);
result[row][col] %= DIVISOR;
}
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
