1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/21761
2. 문제
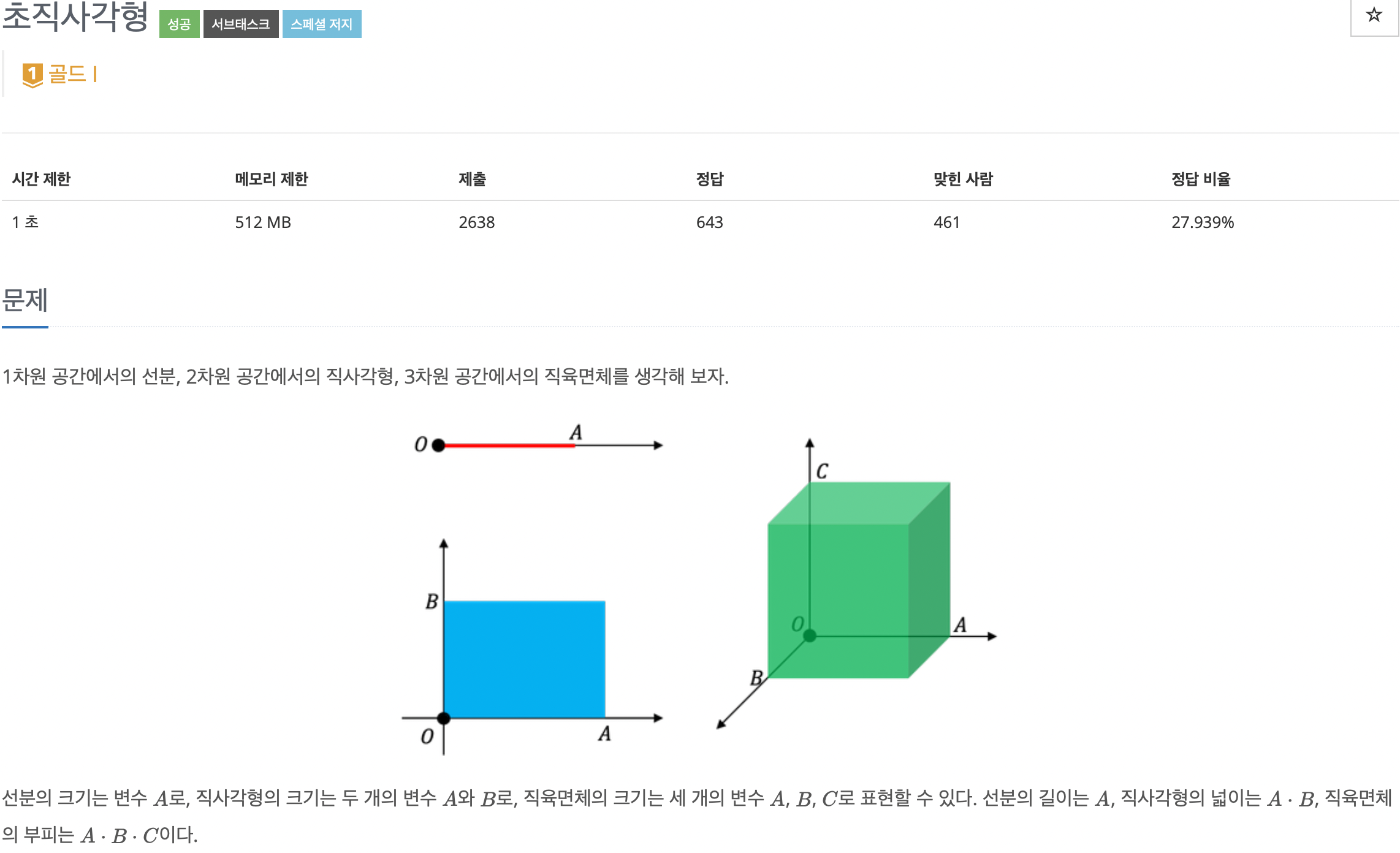


3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static final int SIZE = 4;
static int N, K;
static long[] lengths; // 네 개의 변수(순서대로 A, B, C, D)
static PriorityQueue<Integer>[] cards; // 각 변수에 맞는 카드의 증가값(순서대로 A, B, C, D)
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
N = scanner.nextInt();
K = scanner.nextInt();
lengths = new long[SIZE];
cards = new PriorityQueue[SIZE];
for(int idx = 0; idx < SIZE; idx++) {
lengths[idx] = scanner.nextInt();
// 각 변수에 맞는 카드의 증가값을 저장하는데, 이때 증가값들은 내림차순으로 정렬된 상태로 만들 것이다
// 증가값은 기존 변수값에 덧셈을 진행하는 것인데, 덧셈은 교환 법칙이 성립한다 -> 그러므로 카드 사용 순서에 상관이 없다!
// 그렇다면 부피를 키우기 위해서는 큰 수를 늘릴수록 이득이 되기 때문에 큰 수부터 차례대로 사용한다
cards[idx] = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
}
// 각 변수에 맞는 카드의 증가값들을 저장한다
for(int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++) {
int cardNum = scanner.next().charAt(0) - 'A', sumAmount = scanner.nextInt();
cards[cardNum].offer(sumAmount);
}
}
static void solution() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// K개의 카드를 사용해야하므로 K번 반복문을 돌며 K개의 카드를 선택한다
for(int count = 0; count < K; count++) {
// 4개의 변수 중 어떤 변수에 해당하는 카드를 사용해야 하는지 선택해야 한다
// 각 변수에서 가장 큰 변화값에 대해 (변화값 / 변수값)을 통해 각 변화값의 비율을 구한다
// -> 위처럼 비율을 구하게 되면 변화값을 1을 기준으로 하는 값으로 변경할 수 있으니 동등한 비교가 가능하다
// -> 그러므로 모두 1을 기준으로 하는 값으로 변경한 후에 그중 가장 큰 값을 선택하여 최대값에 해당하는 변수의 카드를 사용한다
// max : 최대 비율값, maxIdx : 최대 비율값에 해당하는 카드의 변수값
double max = 0;
int maxIdx = 0;
for(int idx = 0; idx < SIZE; idx++) {
// 더이상 해당 변수에 맞는 카드가 존재하지 않는다면 변화값 또한 없으니 다음 변수로 넘어간다
if(cards[idx].isEmpty()) continue;
// 해당 변수의 최대 변화값에 대해 비율을 구한다
double ratio = cards[idx].peek() / (double)lengths[idx];
// 만약 계산한 비율이 최대 비율보다 크다면
// 최대 비율을 갱신하고 그에 따라 변수값도 갱신한다
if(ratio > max) {
max = ratio;
maxIdx = idx;
}
}
// 선택한 카드에 맞게 해당 변수에 해당 변화값만큼을 증가시켜주고 이를 출력한다
int sumAmount = cards[maxIdx].poll();
lengths[maxIdx] += sumAmount;
sb.append((char)(maxIdx + 'A')).append(' ').append(sumAmount).append('\n');
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
