1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1450
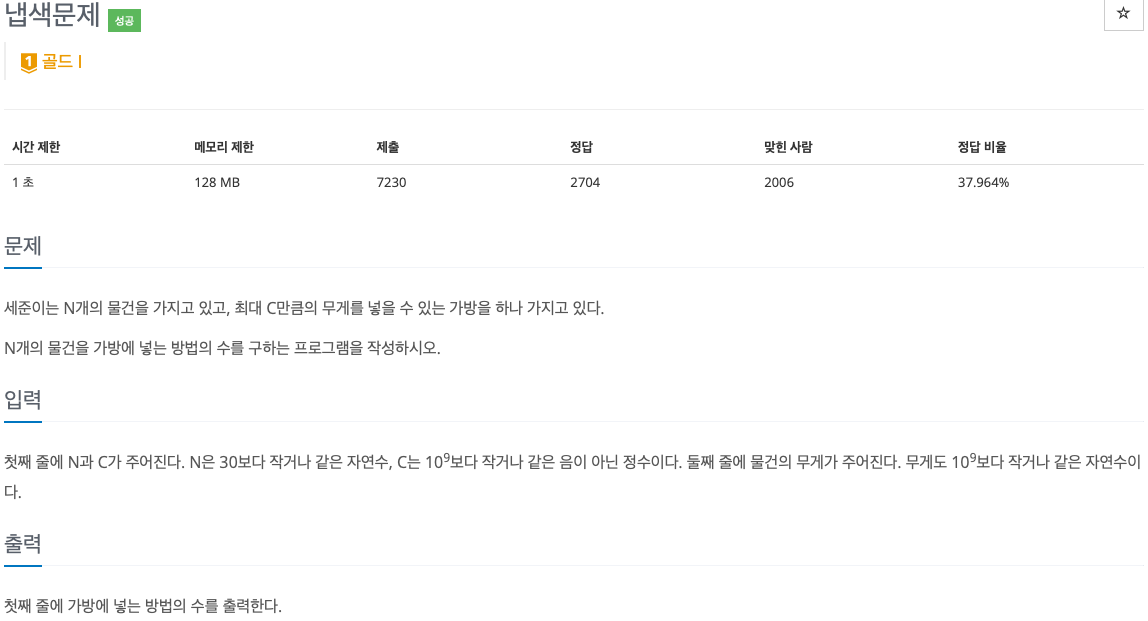
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int N, C;
static int[] weights;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
N = scanner.nextInt();
C = scanner.nextInt();
weights = new int[N];
for(int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++)
weights[idx] = scanner.nextInt();
}
static void solution() {
// 전체 물건의 개수가 최대 30개 -> 완전탐색을 수행하려면 2^30번(약 10억)의 연산이 필요함(불가능)
// 그러나 반만 줄이면 2^15(약 32000)번의 연산 -> 이는 가능
// 그러므로 반을 잘라서 각각에 대해 완전탐색을 진행하여 C 이하의 합들을 각각 구함
List<Integer> left = new ArrayList<>(), right = new ArrayList<>();
// 반으로 나누어 왼쪽 무게들과 오른쪽 무게들에 대해 각각 C 이하의 합들을 구함
backtracking(0, N / 2, 0, left);
backtracking(N / 2 + 1, N - 1, 0, right);
// 투포인터 진행을 위해 합들에 대해 오름차순 정렬을 진행
Collections.sort(left);
Collections.sort(right);
// 투포인터를 통해 전체 경우의 수를 구함
System.out.println(twoPointer(left, right));
}
static int twoPointer(List<Integer> left, List<Integer> right) {
int answer = 0, rightIdx = right.size() - 1;
// 왼쪽 무게들에서 구한 합들을 순회하면서
// - 오른쪽 무게들에서 구한 합과 합쳤을 때 가능한 경우의 수들을 각 합에 대해 구하여 누적
for(int leftIdx = 0; leftIdx < left.size(); leftIdx++) {
// 현재 순회하고 있는 왼쪽 무게들에서 구한 합을 leftSum이라고 한다면
// leftSum과 더했을 때 C 이하가 되는 오른쪽 무게들에서의 합의 최댓값을 구함
while(rightIdx >= 0 && left.get(leftIdx) + right.get(rightIdx) > C)
rightIdx--;
// 가능한 오른쪽 무게들에서의 합의 개수에 leftSum을 추가하지 않는 경우까지 포함하여 경우의 수를 누적
answer += rightIdx + 1;
}
return answer;
}
static void backtracking(int start, int end, int sum, List<Integer> list) {
// 합이 C가 넘으면 문제의 조건에 맞지 않으므로 다음 경우 확인
if(sum > C) return;
// 시작 인덱스가 끝 인덱스를 넘었다면 전체 인덱스를 모두 확인하였고 합이 C 이하이므로
// list에 해당 합을 넣어주고 다음 경우 확인
if(start > end) {
list.add(sum);
return;
}
// 현재 무게를 더한 경우와 더하지 않은 경우 각각에 대해 탐색 진행
backtracking(start + 1, end, sum, list);
backtracking(start + 1, end, sum + weights[start], list);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
