1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1398
2. 문제
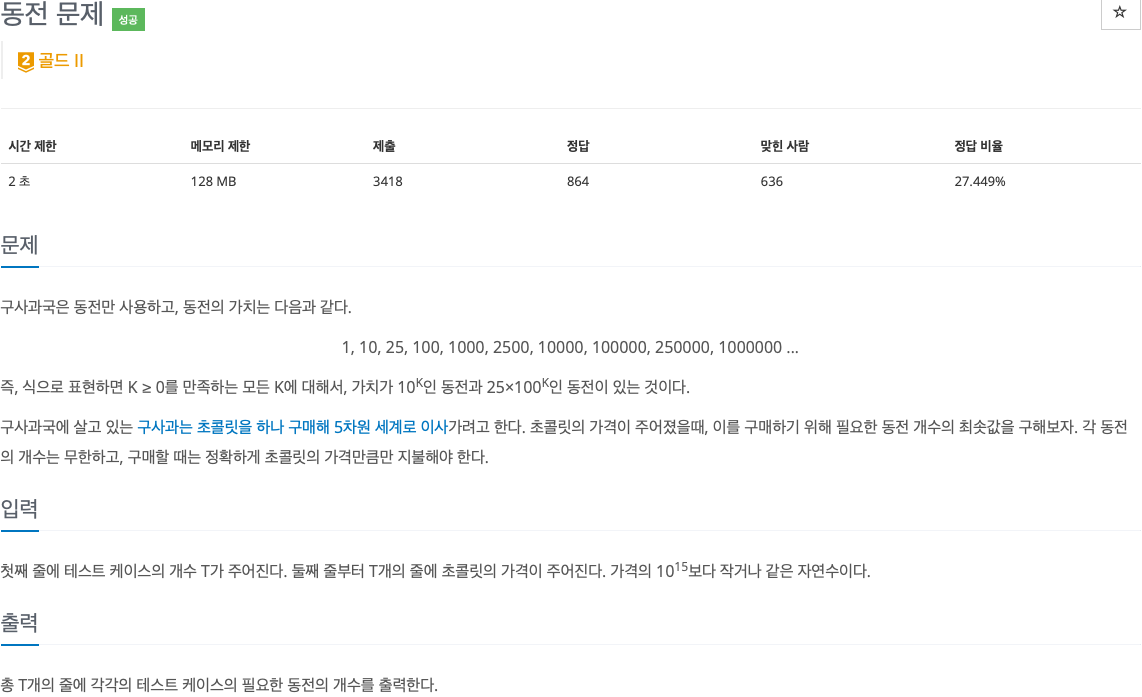
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static final int[] coin = new int[] {1, 10, 25};
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static Reader scanner = new Reader();
static long cost;
static int[] dp;
static void input() {
cost = scanner.nextLong();
}
static void solution() {
int coinCnt = 0; // 필요한 동전의 최소 개수
// 가격이 0이 되기 전까지 100 단위로 나눠 그 가격에서 필요한 동전의 최소 개수를 구하고 이를 누적한다
while(cost > 0) {
int remain100 = Math.toIntExact(cost % 100);
coinCnt += dp[remain100];
cost = cost / 100;
}
sb.append(coinCnt).append('\n');
}
static void init() {
// 동전의 가치들 -> 1, 10, 25, 100, 1000, 2500, 10000, 100000, 250000, ...
// 이를 3개씩 끊어보면 각 자리가 100배씩 증가하는 것을 볼 수 있다
// -> 100 단위마다 필요한 최소 동전의 개수가 독립적이다!
// 그러므로 우선 100까지 필요한 동전의 최소 개수를 구한다
dp = new int[100];
for(int cost = 1; cost < dp.length; cost++) {
dp[cost] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int idx = 0; idx < coin.length; idx++) {
if(cost - coin[idx] >= 0)
dp[cost] = Math.min(dp[cost], dp[cost - coin[idx]] + 1);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
init();
int T = scanner.nextInt();
while(T-- > 0) {
input();
solution();
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
}
