1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14908
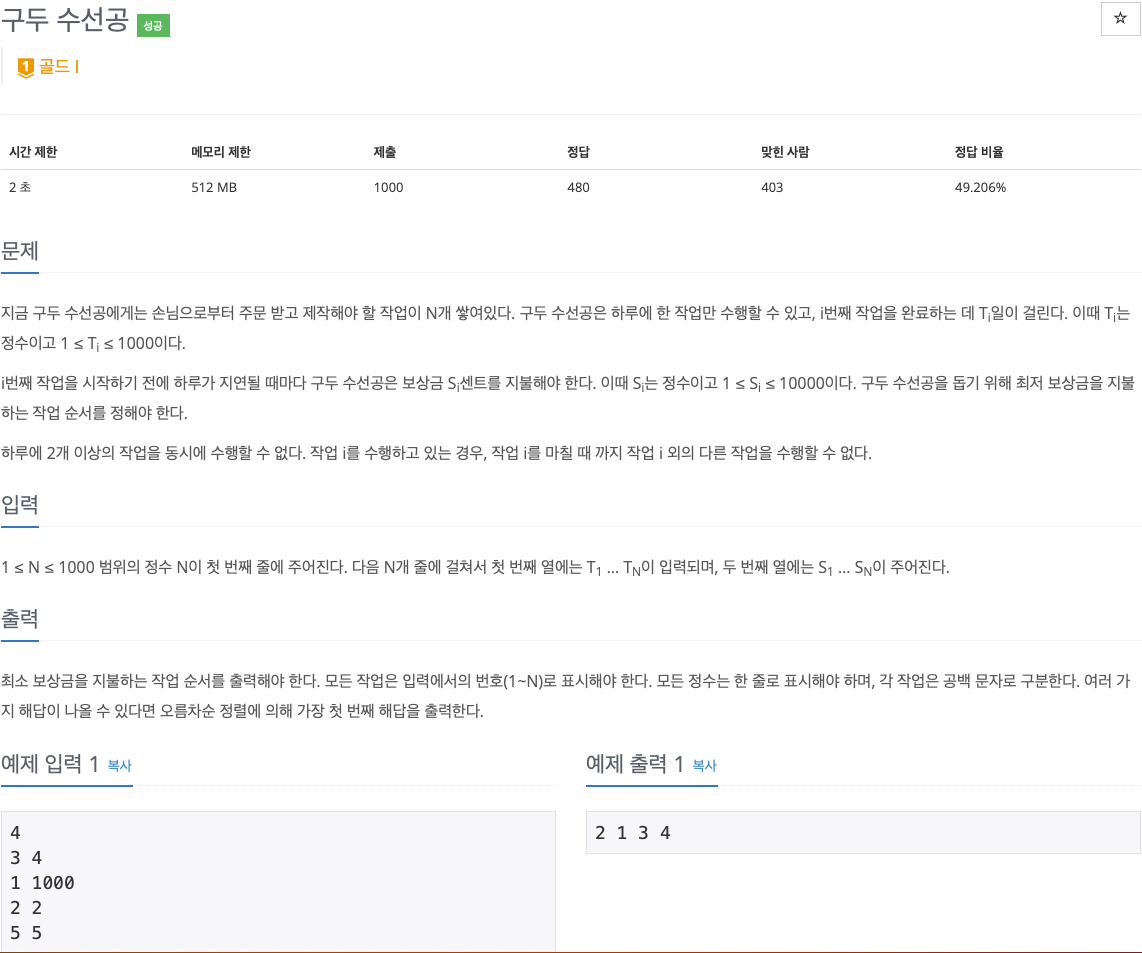
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
// 두 작업에 대해서 어떤 작업이 먼저 수행되어야 하는지를 생각해보자
// - 작업1이 T1, S1라는 값을 갖고, 작업2가 T2, S2라는 값을 갖을 때,
// - 작업1, 작업2 순서대로 작업이 진행되려면 다음을 만족해야 한다
// - T1 * S2 < T2 * S1
// - 위 수식을 정리하면 다음과 같다
// - T1 / S1 < T2 / S2
// - 즉, 작업들을 T / S 순으로 오름차순으로 정렬하면 된다!
// - 모든 작업들을 T / S 순으로 오름차순으로 정렬한 후에 그 순서대로 작업을 진행한다!
static int N;
static PriorityQueue<Task> tasks;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
N = scanner.nextInt();
tasks = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int idx = 1; idx <= N; idx++) {
int workingPeriod = scanner.nextInt();
int delayCost = scanner.nextInt();
tasks.offer(new Task(idx, workingPeriod, delayCost));
}
}
static void solution() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++) {
sb.append(tasks.poll().index).append(' ');
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
static class Task implements Comparable<Task> {
int index;
int workingPeriod;
int delayCost;
public Task(int index, int workingPeriod, int delayCost) {
this.index = index;
this.workingPeriod = workingPeriod;
this.delayCost = delayCost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Task t) {
double firstTaskCost = (double) workingPeriod / delayCost;
double secondTaskCost = (double) t.workingPeriod / t.delayCost;
if(firstTaskCost == secondTaskCost) {
return index - t.index;
}
return Double.compare(firstTaskCost, secondTaskCost);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
