1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2136
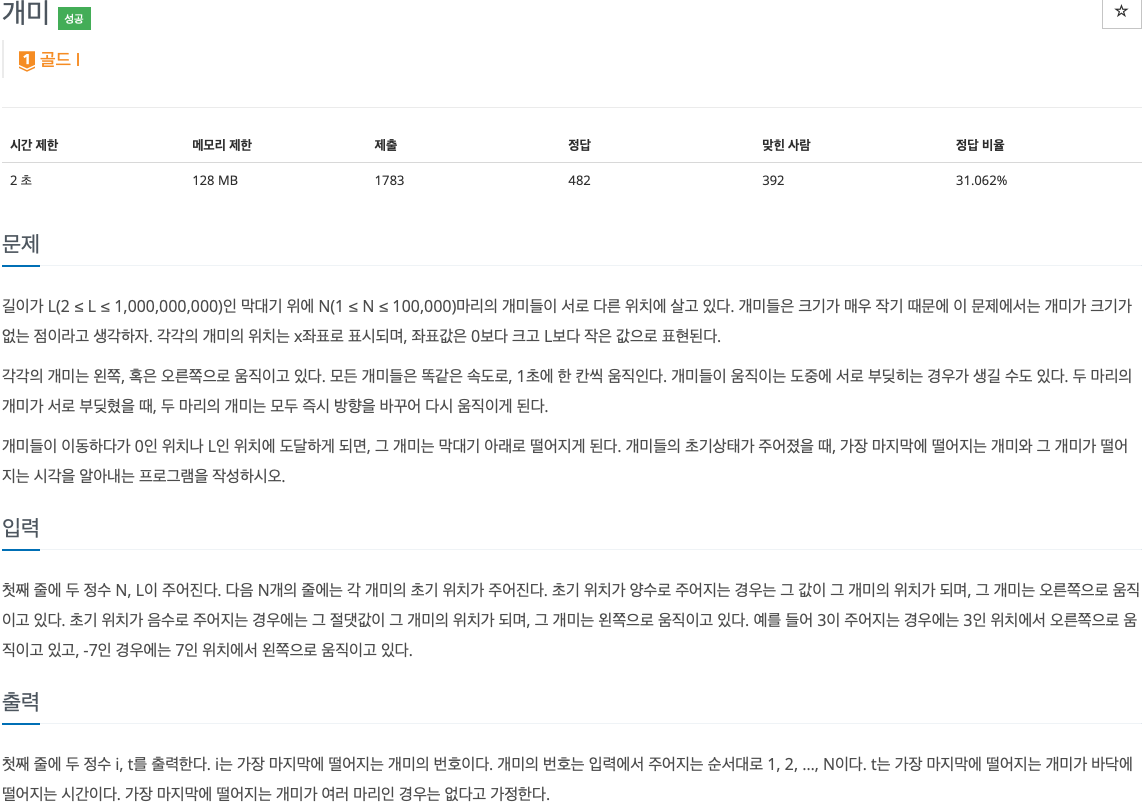
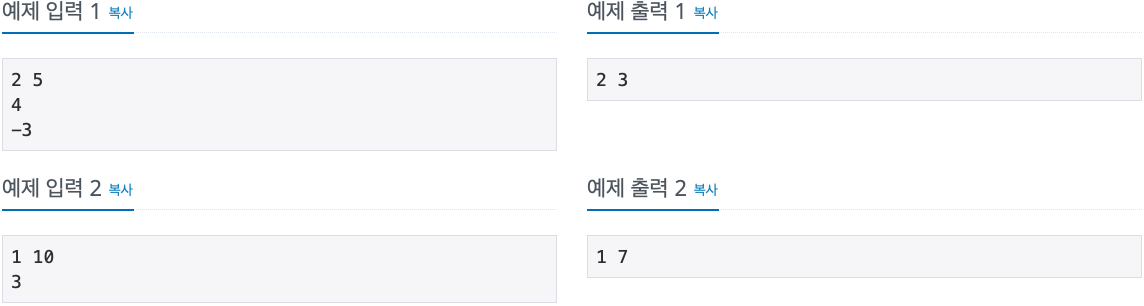
2. 문제
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int antNum;
static int length;
static int[] ants;
static int leftAnt;
static int rightAnt;
static int leftNum;
static Ant[] antInfo;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
antNum = scanner.nextInt();
length = scanner.nextInt();
ants = new int[antNum + 1];
leftAnt = rightAnt = leftNum = 0;
antInfo = new Ant[antNum];
for(int idx = 1; idx <= antNum; idx++) {
ants[idx] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
static void solution() {
/*
개미끼리 부딪히면 가던 방향을 바꿔서 반대 방향으로 간다
예를 들어 3번 개미가 오른쪽으로 진행하고, 4번 개미가 왼쪽으로 진행하는 상황에 8이라는 위치에서 부딪히면
3번은 다음에 7로, 4번은 9로 이동하게 된다
그런데 만약 4번이 그대로 진행했다면 7로 가게 될 것이고, 3번이 그대로 진행했다면 9로 가게 될 것이다
즉, 부딪힌 이후에는 3번이 가는 길을 4번이 가게 되는 것이고 4번이 가는 길을 3번이 가게 되는 것이다
또한 개미들은 만나자마자 방향을 바꾸기 때문에 오른쪽에 있던 개미가 왼쪽에 있는 개미를 건너뛸 수 없다
왼쪽에 있는 개미 역시 오른쪽에 있는 개미를 건너뛸 수 없다
그러므로 왼쪽으로 가는 개미들 중 0에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 개미가 0에서 떨어지는 시간을 구하고
오른쪽으로 가는 개미들 중 length에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 개미가 length에서 떨어지는 시간을 구한다
두 시간 중 더 긴 시간을 구하여
오른쪽으로 가는 개미가 더 늦게 떨어진다면 (왼쪽으로 가는 개미의 수 + 1)번째 개미가 가장 늦게 떨어질 것이고
왼쪽으로 가는 개미가 더 늦게 떨어진다면 왼쪽으로 가는 개미 중 가장 마지막 개미가 가장 늦게 떨어질 것이다
이러한 방법으로 가장 늦게 떨어지는 개미와 그 시간을 구한다
*/
// 개미들 중에서 오른쪽으로 가는 개미 중 가장 length에서 먼 개미와
// 왼쪽으로 가는 개미 중 가장 0에서 먼 개미를 구하고
// 왼쪽으로 가는 개미의 수를 구한다
// 그리고 antInfo에 해당 개미의 번호 및 현재 개미가 위치하고 있는 위치를 넣는다
for(int idx = 1; idx <= antNum; idx++) {
if(ants[idx] > 0) {
rightAnt = Math.max(rightAnt, length - ants[idx]);
} else if(ants[idx] < 0) {
leftNum++;
leftAnt = Math.max(Math.abs(ants[idx]), leftAnt);
}
antInfo[idx - 1] = new Ant(idx, Math.abs(ants[idx]));
}
// 개미의 위치를 기준으로 오름차순으로 정렬한다
Arrays.sort(antInfo);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 오른쪽으로 가는 개미가 더 늦게 떨어진다면
if(leftAnt < rightAnt) {
// (왼쪽으로 가는 개미의 수 + 1)번째 개미를 찾아서 그 개미의 번호와 시간을 출력한다
sb.append(antInfo[leftNum].antNumber).append(' ').append(rightAnt);
}
// 왼쪽으로 가는 개미가 더 늦게 떨어진다면
else {
// 왼쪽으로 가는 개미의 수번째 개미를 찾아서 그 개미의 번호와 시간을 출력한다
sb.append(antInfo[leftNum - 1].antNumber).append(' ').append(leftAnt);
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
static class Ant implements Comparable<Ant> {
int antNumber;
int position;
public Ant(int antNumber, int position) {
this.antNumber = antNumber;
this.position = position;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Ant ant) {
return position - ant.position;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}애드 혹 알고리즘
- 해당 문제를 풀기 위해 잘 알려진 정교한 알고리즘을 적용하지 않고 해결할 수 있는 유형의 문제
- 해당 문제를 해결하기 위해 직접 해당 문제만을 위한 아이디어를 찾아서 문제를 해결한다.

